200+ Action Verb Examples
Action verbs are a powerful tool for making your article writing more dynamic and engaging. Whether you’re writing an article, book, or even a simple sentence, action verbs can help you convey a sense of motion and energy that will captivate your readers. In this article, we’ll explore what action verbs are, how to use them effectively, and answer some common questions about their use in formal writing.
What is an Action Verb?
An action verb is a verb that expresses physical or mental action. It’s part of the sentence that tells you what the simple subject is doing, and it can be either transitive (requiring a direct object) or intransitive (not requiring a direct object). Examples of action verbs include “run,” “swim,” “think,” and “write.”
Types of Action Verbs
Action verbs, also known as dynamic verbs, describe actions, processes, or activities. They are essential for conveying clear, dynamic, and specific actions in sentences. Here are the different types of action verbs with examples:
1. Physical Action Verbs
These verbs describe physical activities that can be seen or heard.
- Examples: run, jump, swim, throw, kick, climb
- Sentences:
- She ran to the store.
- They swim every morning.
2. Mental Action Verbs
These verbs describe cognitive activities, thoughts, or mental processes.
- Examples: think, believe, understand, imagine, remember, consider
- Sentences:
- He believes in hard work.
- She understands the problem well.
3. Transitive Verbs
These verbs require an object to complete their meaning.
- Examples: read (a book), drive (a car), eat (an apple), buy (a gift), write (a letter)
- Sentences:
- She wrote a letter.
- He bought a new car.
4. Intransitive Verbs
These verbs do not require an object to complete their meaning.
- Examples: sleep, arrive, go, sit, walk, cry
- Sentences:
- She slept peacefully.
- He cried all night.
5. Regular Action Verbs
These verbs follow a standard pattern when conjugated (adding -ed or -d for past tense).
- Examples: play, work, talk, move, call
- Sentences:
- They played soccer yesterday.
- She worked late.
6. Irregular Action Verbs
These verbs do not follow a standard conjugation pattern.
- Examples: go (went), see (saw), eat (ate), have (had), take (took)
- Sentences:
- He went to the park.
- She saw the movie last night.
7. Phrasal Verbs
These verbs are combinations of a verb and one or more particles (prepositions or adverbs) that create a new meaning.
- Examples: look after, give up, break down, take off, run into
- Sentences:
- She looked after the children.
- He gave up smoking.
8. Stative Verbs
While typically describing states or conditions rather than actions, they sometimes overlap
with action verbs when describing a state resulting from an action.
- Examples: own, love, know, belong, need
- Sentences:
- She owns a car.
- They need help.
9. Auxiliary (Helping) Verbs
These verbs are used alongside main verbs to form tenses, moods, and voices.
- Examples: be, have, do (when used with another verb)
- Sentences:
- She is running.
- They have finished their homework.
10. Modal Verbs
These verbs express necessity, possibility, permission, or ability.
- Examples: can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would
- Sentences:
- She can swim.
- He might come to the party.
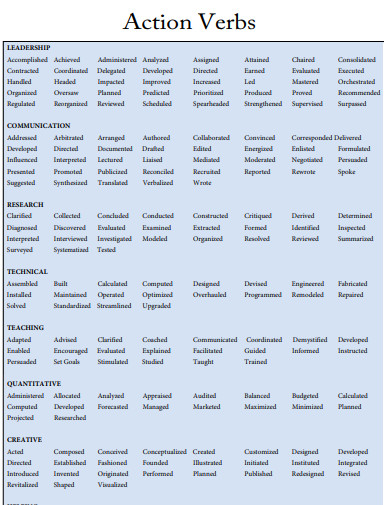
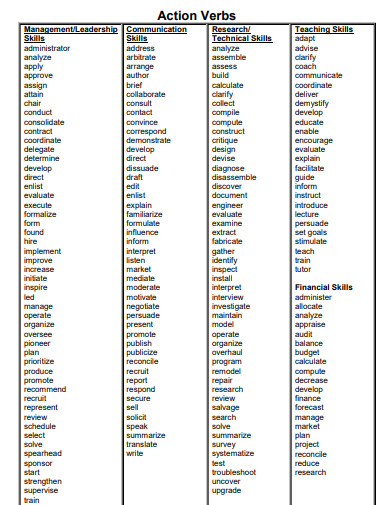
List of Action Verbs
| General Action Verbs | Leadership and Management | Research and Analysis | Creative Roles | Technical Roles | Communication Roles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Achieved | Administered | Analyzed | Acted | Assembled | Addressed |
| Administered | Chaired | Assessed | Composed | Built | Advertised |
| Analyzed | Coordinated | Clarified | Conceptualized | Calculated | Authored |
| Arranged | Directed | Collected | Created | Computed | Communicated |
| Assembled | Executed | Compared | Designed | Designed | Conveyed |
| Assessed | Facilitated | Conducted | Developed | Developed | Convinced |
| Built | Guided | Critiqued | Directed | Engineered | Corresponded |
| Calculated | Headed | Detected | Fashioned | Fabricated | Drafted |
| Collaborated | Led | Determined | Formulated | Installed | Edited |
| Conducted | Managed | Diagnosed | Illustrated | Maintained | Explained |
| Created | Mentored | Evaluated | Imagined | Operated | Informed |
| Delegated | Operated | Examined | Invented | Programmed | Marketed |
| Designed | Organized | Experimented | Modeled | Repaired | Persuaded |
| Developed | Oversaw | Explored | Painted | Solved | Presented |
| Directed | Planned | Identified | Performed | Tested | Promoted |
| Eliminated | Prioritized | Inspected | Photographed | Troubleshot | Publicized |
| Enhanced | Produced | Interpreted | Planned | Updated | Reported |
| Evaluated | Reviewed | Investigated | Revised | Upgraded | Spoke |
Action Verb Examples:

Action Verb Examples Sentences
General Action Verbs
- Achieved: She achieved her sales targets for the third consecutive quarter.
- Administered: He administered the company’s employee benefits program.
- Analyzed: They analyzed the market trends to forecast next year’s growth.
- Arranged: She arranged the meeting with the board of directors.
- Assembled: The team assembled the prototype in less than a week.
- Assessed: The teacher assessed the students’ progress with weekly quizzes.
- Built: He built a strong network of professional contacts.
- Calculated: She calculated the budget for the upcoming project.
- Collaborated: They collaborated with the marketing team to launch the new product.
- Conducted: He conducted the training session for new employees.
Leadership and Management
- Administered: She administered the company’s new policy changes.
- Chaired: He chaired the annual general meeting.
- Coordinated: They coordinated the international conference with over 500 attendees.
- Directed: She directed the team through the complex project.
- Executed: He executed the strategic plan successfully.
- Facilitated: They facilitated the workshop on leadership skills.
- Guided: She guided the new hires through their orientation process.
- Headed: He headed the research and development department.
- Led: They led the company through a significant transformation.
- Managed: She managed a team of 15 engineers.
Research and Analysis
- Analyzed: He analyzed the survey data to draw meaningful conclusions.
- Assessed: She assessed the risk factors associated with the project.
- Clarified: They clarified the research objectives with the stakeholders.
- Collected: He collected data from various sources for his thesis.
- Compared: She compared the results from different experiments.
- Conducted: They conducted a comprehensive study on climate change.
- Critiqued: He critiqued the methodology used in the research paper.
- Detected: She detected a significant error in the calculations.
- Determined: They determined the root cause of the problem.
- Diagnosed: He diagnosed the issues in the software system.
Creative Roles
- Acted: She acted in the lead role of the school play.
- Composed: He composed a beautiful piece of music for the film.
- Conceptualized: They conceptualized the new advertising campaign.
- Created: She created an innovative design for the product.
- Designed: He designed the layout for the new website.
- Developed: They developed a new app that simplifies online shopping.
- Directed: She directed the short film that won several awards.
- Fashioned: He fashioned a sculpture out of recycled materials.
- Formulated: They formulated a new theory in quantum physics.
- Illustrated: She illustrated the children’s book beautifully.
Technical Roles
- Assembled: He assembled the new computer from scratch.
- Built: She built a robot that can navigate through mazes.
- Calculated: They calculated the necessary parameters for the bridge construction.
- Computed: He computed the final scores for the competition.
- Designed: She designed a new circuit board for the device.
- Developed: They developed software that enhances cybersecurity.
- Engineered: He engineered a solution to the persistent issue.
- Fabricated: She fabricated the metal parts needed for the machine.
- Installed: They installed the new operating system on all computers.
- Maintained: He maintained the company’s network infrastructure.
Communication Roles
- Addressed: She addressed the audience with confidence.
- Advertised: He advertised the new product on various social media platforms.
- Authored: They authored a best-selling novel.
- Communicated: She communicated the changes effectively to the team.
- Conveyed: He conveyed the importance of the new policy.
- Convinced: They convinced the board to approve the project.
- Corresponded: She corresponded with clients through email.
- Drafted: He drafted the proposal for the new initiative.
- Edited: They edited the manuscript for clarity and coherence.
- Explained: She explained the complex process in simple terms.
Action Verb Examples for Resume
- Achieved: Achieved a 25% increase in sales revenue within six months.
- Administered: Administered the company’s payroll system, ensuring timely payments to over 200 employees.
- Analyzed: Analyzed customer feedback data to improve product features and user satisfaction.
- Arranged: Arranged and coordinated international travel for executives, optimizing schedules and reducing costs.
- Assembled: Assembled a high-performing sales team that exceeded quarterly targets consistently.
- Assessed: Assessed financial reports to identify cost-saving opportunities, reducing expenses by 15%.
- Built: Built a robust customer relationship management system that increased client retention by 20%.
- Calculated: Calculated project costs and managed budgets, ensuring projects were completed within financial constraints.
- Collaborated: Collaborated with cross-functional teams to develop and launch new product lines.
- Conducted: Conducted market research to inform strategic business decisions and drive growth.
- Created: Created engaging content for social media campaigns, increasing followers by 50%.
- Designed: Designed a new user interface that improved website navigation and user experience.
- Developed: Developed a comprehensive training program that enhanced employee skills and productivity.
- Directed: Directed a successful marketing campaign that boosted brand awareness by 40%.
- Facilitated: Facilitated weekly team meetings to ensure project alignment and clear communication.
- Implemented: Implemented a new inventory management system that reduced stock discrepancies by 30%.
- Led: Led a team of 15 in the successful execution of a major software development project.
- Managed: Managed a portfolio of key accounts, increasing client satisfaction and retention rates.
- Monitored: Monitored network performance and implemented solutions to improve system reliability.
- Organized: Organized corporate events, improving client engagement and strengthening business relationships.
Action Verb Examples for Kids
- Jumped: The frog jumped over the log.
- Painted: Sarah painted a beautiful picture of a sunset.
- Ran: The dog ran fast to catch the ball.
- Built: Tim built a tall tower with his blocks.
- Sang: Lucy sang her favorite song at the school concert.
- Drew: Sam drew a funny cartoon on his notebook.
- Baked: Mom and I baked cookies for the school fair.
- Played: The children played soccer in the park.
- Wrote: Emma wrote a letter to her grandma.
- Cleaned: Jake cleaned his room before dinner.
- Helped: Mia helped her friend with homework.
- Read: Max read a story about dinosaurs.
- Ate: They ate ice cream after lunch.
- Danced: Lily danced gracefully at the recital.
- Found: Ben found a shiny pebble on the beach.
- Watched: They watched a movie together.
- Listened: The class listened to the teacher’s instructions.
- Jumped: The kids jumped on the trampoline.
- Cooked: Dad cooked spaghetti for dinner.
- Rode: Ethan rode his bike around the neighborhood.
Action Verb Examples for Objectives
General Career Objectives
- Achieve
- Objective: To achieve significant milestones in project management by enhancing team productivity and delivering projects on time.
- Administer
- Objective: To administer efficient office operations and streamline administrative processes to boost overall productivity.
- Analyze
- Objective: To analyze market trends and consumer behavior to develop effective marketing strategies.
- Build
- Objective: To build strong relationships with clients to ensure customer satisfaction and repeat business.
- Collaborate
- Objective: To collaborate with cross-functional teams to drive innovative solutions and achieve organizational goals.
Leadership and Management Objectives
- Lead
- Objective: To lead a dynamic team towards achieving organizational objectives and fostering a collaborative work environment.
- Develop
- Objective: To develop strategic plans that enhance business growth and operational efficiency.
- Direct
- Objective: To direct company initiatives and ensure alignment with long-term business goals.
- Mentor
- Objective: To mentor junior staff and cultivate their professional growth and development.
- Implement
- Objective: To implement effective management practices that drive team performance and productivity.
Research and Analysis Objectives
- Research
- Objective: To research emerging technologies and trends to provide insights that drive innovation.
- Evaluate
- Objective: To evaluate existing processes and recommend improvements based on thorough analysis.
- Investigate
- Objective: To investigate market conditions and provide actionable intelligence to support business decisions.
- Interpret
- Objective: To interpret complex data sets and present findings in a clear, concise manner.
- Assess
- Objective: To assess project risks and develop mitigation strategies to ensure successful project outcomes.
Creative Objectives
- Create
- Objective: To create compelling visual content that enhances brand identity and engagement.
- Design
- Objective: To design innovative products that meet customer needs and exceed market expectations.
- Develop
- Objective: To develop unique marketing campaigns that drive brand awareness and sales growth.
- Illustrate
- Objective: To illustrate concepts and ideas through captivating graphics and visuals.
- Compose
- Objective: To compose engaging copy for various media platforms to captivate target audiences.
Technical Objectives
- Engineer
- Objective: To engineer robust and scalable software solutions that address client requirements.
- Program
- Objective: To program and maintain high-performance applications to improve user experience.
- Optimize
- Objective: To optimize network infrastructure to ensure reliability and efficiency.
- Integrate
- Objective: To integrate cutting-edge technologies into existing systems to enhance functionality.
- Troubleshoot
- Objective: To troubleshoot technical issues promptly and implement effective solutions to minimize downtime.
Past tense Action Verb Examples
General Action Verbs
- Achieved
- Achieved a 20% increase in sales within the first quarter.
- Administered
- Administered employee benefit programs for a company with 200+ employees.
- Analyzed
- Analyzed market trends to forecast sales growth for the next fiscal year.
- Arranged
- Arranged corporate events, enhancing client relationships.
- Assembled
- Assembled a high-performing team that met all project deadlines.
- Assessed
- Assessed the financial health of the company, leading to a 15% cost reduction.
- Built
- Built a strong network of professional contacts.
- Calculated
- Calculated monthly budgets, ensuring accurate financial planning.
- Collaborated
- Collaborated with cross-functional teams to improve product quality.
- Conducted
- Conducted training sessions for new hires, resulting in improved productivity.
Leadership and Management
- Administered
- Administered the implementation of a new software system company-wide.
- Chaired
- Chaired bi-weekly meetings to align team efforts with company goals.
- Coordinated
- Coordinated international project teams, ensuring seamless communication.
- Directed
- Directed the launch of a new product line, generating $1M in revenue.
- Executed
- Executed strategic initiatives that boosted company growth by 25%.
- Facilitated
- Facilitated workshops on leadership development for senior managers.
- Guided
- Guided a team through a major rebranding effort.
- Headed
- Headed the research and development department, leading to five new patents.
- Led
- Led a team of 20 in delivering projects ahead of schedule.
- Managed
- Managed a budget of $500,000, ensuring efficient use of resources.
Research and Analysis
- Analyzed
- Analyzed customer feedback to improve product features.
- Assessed
- Assessed project risks and developed mitigation strategies.
- Clarified
- Clarified research objectives to align with stakeholder expectations.
- Collected
- Collected data from 500+ survey respondents to support market research.
- Compared
- Compared historical sales data to identify growth opportunities.
- Conducted
- Conducted thorough research on industry trends and competitor analysis.
- Critiqued
- Critiqued internal processes to identify areas for improvement.
- Detected
- Detected inefficiencies in the workflow and recommended solutions.
- Determined
- Determined the root causes of performance issues through data analysis.
- Diagnosed
- Diagnosed technical problems and provided effective solutions.
Creative Roles
- Acted
- Acted as the creative lead for marketing campaigns, boosting brand visibility.
- Composed
- Composed engaging content for social media platforms, increasing followers.
- Conceptualized
- Conceptualized innovative design ideas for new product packaging.
- Created
- Created compelling visual content for digital advertising.
- Designed
- Designed user-friendly interfaces for mobile applications.
- Developed
- Developed a new branding strategy that enhanced company image.
- Directed
- Directed a successful marketing video that received over 1M views.
- Fashioned
- Fashioned unique product displays for trade shows.
- Formulated
- Formulated creative solutions to improve user experience.
- Illustrated
- Illustrated storyboards for advertising campaigns.
Technical Roles
- Assembled
- Assembled and tested computer hardware components.
- Built
- Built and maintained company website, improving user engagement.
- Calculated
- Calculated technical specifications for engineering projects.
- Computed
- Computed complex algorithms to optimize software performance.
- Designed
- Designed electrical circuits for new electronic devices.
- Developed
- Developed a software tool that automated repetitive tasks.
- Engineered
- Engineered solutions to complex technical problems.
- Fabricated
- Fabricated mechanical parts using precision tools.
- Installed
- Installed and configured network systems for improved connectivity.
- Maintained
- Maintained IT infrastructure, ensuring minimal downtime.
Communication Roles
- Addressed
- Addressed customer inquiries with timely and accurate information.
- Advertised
- Advertised new services through targeted email campaigns.
- Authored
- Authored technical manuals for user guidance.
- Communicated
- Communicated project updates to stakeholders regularly.
- Conveyed
- Conveyed complex technical information to non-technical audiences.
- Convinced
- Convinced clients to adopt new solutions through effective presentations.
- Corresponded
- Corresponded with international clients to manage project expectations.
- Drafted
- Drafted press releases that garnered media attention.
- Edited
- Edited and proofread marketing materials for accuracy and clarity.
- Explained
- Explained product features and benefits to potential customers.
Action Verb Present tense Examples
General Action Verbs
- Achieve
- Achieve significant sales targets through strategic planning and execution.
- Administer
- Administer employee benefit programs to enhance workforce satisfaction.
- Analyze
- Analyze market trends to provide actionable business insights.
- Arrange
- Arrange meetings and events to foster collaboration and productivity.
- Assemble
- Assemble project teams to drive successful outcomes.
- Assess
- Assess financial reports to identify cost-saving opportunities.
- Build
- Build strong relationships with clients to ensure long-term partnerships.
- Calculate
- Calculate budgets to ensure accurate financial planning.
- Collaborate
- Collaborate with cross-functional teams to develop innovative solutions.
- Conduct
- Conduct training sessions to improve employee skills and knowledge.
Leadership and Management
- Lead
- Lead a dynamic team to achieve organizational objectives.
- Develop
- Develop strategic plans that drive business growth.
- Direct
- Direct company initiatives to align with long-term goals.
- Mentor
- Mentor junior staff to foster professional development.
- Implement
- Implement management practices that enhance team performance.
- Coordinate
- Coordinate projects to ensure timely and efficient completion.
- Facilitate
- Facilitate meetings to ensure clear communication among team members.
- Guide
- Guide teams through complex projects to successful completion.
- Oversee
- Oversee daily operations to ensure efficiency and effectiveness.
- Plan
- Plan resource allocation to maximize productivity.
Research and Analysis
- Research
- Research emerging trends to stay ahead in the industry.
- Evaluate
- Evaluate data to determine business opportunities and risks.
- Investigate
- Investigate market conditions to inform strategic decisions.
- Interpret
- Interpret data to provide clear and actionable insights.
- Assess
- Assess project risks and develop mitigation strategies.
- Analyze
- Analyze customer feedback to enhance product development.
- Collect
- Collect data to support comprehensive research studies.
- Compare
- Compare historical data to identify patterns and trends.
- Examine
- Examine processes to identify areas for improvement.
- Determine
- Determine root causes of issues through detailed analysis.
Creative Roles
- Create
- Create compelling content that engages audiences.
- Design
- Design innovative solutions that meet customer needs.
- Develop
- Develop marketing campaigns that drive brand awareness.
- Illustrate
- Illustrate complex ideas through clear and engaging visuals.
- Compose
- Compose original music that captivates listeners.
- Conceptualize
- Conceptualize creative concepts for advertising projects.
- Craft
- Craft stories that resonate with target audiences.
- Perform
- Perform artistic pieces that entertain and inspire.
- Produce
- Produce high-quality content for various media platforms.
- Sketch
- Sketch initial designs for product development.
Technical Roles
- Assemble
- Assemble hardware components to build efficient systems.
- Build
- Build software applications that solve user problems.
- Calculate
- Calculate technical specifications for engineering projects.
- Develop
- Develop algorithms to improve software performance.
- Engineer
- Engineer solutions to complex technical challenges.
- Fabricate
- Fabricate parts using advanced manufacturing techniques.
- Install
- Install and configure systems to ensure optimal performance.
- Maintain
- Maintain IT infrastructure to ensure continuous operation.
- Optimize
- Optimize network performance for maximum efficiency.
- Troubleshoot
- Troubleshoot technical issues to provide prompt solutions.
Communication Roles
- Address
- Address customer inquiries with clarity and precision.
- Advertise
- Advertise products through targeted marketing strategies.
- Author
- Author articles that inform and engage readers.
- Communicate
- Communicate project updates to stakeholders effectively.
- Convey
- Convey complex information in an easy-to-understand manner.
- Convince
- Convince potential clients to adopt our solutions.
- Correspond
- Correspond with clients to manage their expectations.
- Draft
- Draft press releases that attract media attention.
- Edit
- Edit content to ensure accuracy and coherence.
- Explain
- Explain product features to help customers make informed decisions.
More About Action Verb:
1. Action Verb
2. Action Verbs List
3. List of Action Verbs for Resumes
4. Actions Verbs A to Z
5. Action Verb List for Resumes & Cover Letters
6. Action Verbs Example
7. Sample Action Verbs
8. Glossary of Action Verb
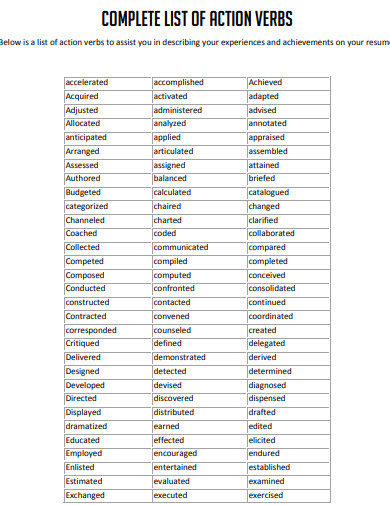
9. Complete List of Action Verb
10. Formal Action Verb
Action Verb Rules
Action verbs are essential in writing as they convey specific actions and make sentences more dynamic and clear. Here are some key rules and guidelines for using action verbs effectively:
1. Use Active Voice
Use action verbs in the active voice to make sentences more direct and vigorous.
- Example: “She completed the project on time.” (Active) vs. “The project was completed by her on time.” (Passive)
2. Be Specific
Choose specific action verbs that clearly describe the action.
- Example: “He analyzed the data” is more specific than “He looked at the data.”
3. Use Present Tense for Current Roles
When describing current duties, use present tense action verbs.
- Example: “Manage a team of 10” (current role)
4. Use Past Tense for Previous Roles
When describing past duties or accomplishments, use past tense action verbs.
- Example: “Managed a team of 10” (previous role)
5. Avoid Repetition
Use a variety of action verbs to avoid repetition and make your writing more engaging.
- Example: Instead of repeatedly using “managed,” vary with “led,” “supervised,” “coordinated,” etc.
6. Match the Verb to the Context
Ensure the action verb matches the context and accurately describes the action.
- Example: “Engineered a solution” is suitable for technical contexts, while “Facilitated a discussion” is suitable for a leadership context.
7. Use Strong Verbs
Opt for strong, impactful verbs to convey confidence and competence.
- Example: “Implemented a new system” is stronger than “Put in a new system.”
8. Highlight Achievements
Use action verbs to highlight achievements and contributions.
- Example: “Increased sales by 20%” or “Developed a new marketing strategy.”
9. Be Concise
Use action verbs to keep sentences concise and to the point.
- Example: “Led a successful project” is more concise than “Was in charge of leading a successful project.”
10. Use Parallel Structure
When listing multiple actions, use parallel structure to improve readability.
- Example: “Designed, developed, and implemented the new system.”
11. Tailor Verbs to the Job Description
Use action verbs that align with the job description and industry standards.
- Example: For a marketing role, use verbs like “promoted,” “advertised,” and “marketed.”
12. Quantify When Possible
If possible, pair action verbs with quantifiable results to show impact.
- Example: “Increased efficiency by 30%” instead of just “Increased efficiency.”
Action Verbs vs. Stative Verbs
| Aspect | Action Verbs | Stative Verbs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verbs that describe physical or mental actions | Verbs that describe a state of being, emotion, or condition |
| Examples | run, jump, write, build, analyze, manage | be, have, know, like, believe, understand |
| Usage in Sentences | – He runs every morning.<br>- She built a sandcastle. | – She knows the answer.<br>- I like chocolate. |
| Tense Forms | Typically used in all tenses to indicate actions | Usually used in present simple or past simple tense |
| Dynamic vs. Static | Indicates dynamic actions and changes | Indicates static conditions or states |
| Continuous Form | Can be used in continuous (progressive) forms | Generally not used in continuous forms |
| Focus | Focuses on what the subject is doing | Focuses on what the subject is or feels |
| Example in Continuous Form | – He is running right now.<br>- They are analyzing the data. | – She is knowing the answer. (incorrect)<br>- I am liking chocolate. (incorrect) |
| Use in Resumes | Used to highlight actions and achievements | Rarely used in resumes, as they do not convey action |
Action Verbs vs. Linking Verbs
| Aspect | Action Verbs | Linking Verbs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Describe physical or mental actions | Connect the subject to additional information (state or condition) |
| Examples | run, write, build, manage | be, seem, become, appear |
| Focus | What the subject is doing | What the subject is or seems |
| Usage in Sentences | – She runs daily. – He writes books. | – She is a teacher. – He seems tired. |
| Continuous Form | Can be used in continuous forms (e.g., running, writing) | Rarely used in continuous forms (e.g., being, seeming) |
| Function | Show action performed by the subject | Link the subject to a subject complement (predicate noun or adjective) |
| Use in Resumes | Highlight actions and achievements | Rarely used in resumes, as they don’t convey action or accomplishments |
How to use Actions Verbs
Action Verbs can be used in many ways for different types of writing. Here’s a step-by-step guide to using action verbs in your writing:
Step 1: Subject
Identify the subject of your sentence.
Step 2: Choose one that describes
Choose an action verb that accurately describes what the subject is doing.
Step 3: Direct object
If necessary, add a direct object after the verb to complete the sentence.
Step 4: subject-verb agreement
Check your subject-verb agreement to ensure that your verb matches the number of the subject.
Step 5: Action verbs
Use action verbs to make your writing more dynamic and engaging.
What are action verbs?
Action verbs describe physical or mental actions, showing what the subject is doing, such as run, jump, write, build, or analyze.
Why are action verbs important in resumes?
Action verbs highlight your accomplishments and responsibilities, making your resume more dynamic and engaging to potential employers.
Can action verbs be used in continuous tense?
Yes, action verbs can be used in continuous forms, such as running, writing, or building, to indicate ongoing actions.
How do action verbs differ from linking verbs?
Action verbs describe actions, while linking verbs connect the subject to additional information about its state or condition, like be, seem, or become.
What are some common action verbs for leadership roles?
Common action verbs for leadership roles include lead, manage, direct, coordinate, and supervise, which highlight managerial and guiding actions.
How can I use action verbs in job descriptions?
Use action verbs to clearly define the duties and responsibilities of a role, such as analyze data, manage projects, or develop strategies.
What are some action verbs for technical roles?
Action verbs for technical roles include build, develop, engineer, program, and troubleshoot, describing technical tasks and problem-solving abilities.
Can action verbs be used to describe past accomplishments?
Yes, use past tense action verbs, like managed, developed, or implemented, to describe past accomplishments and responsibilities in resumes or reports.
What is the difference between transitive and intransitive action verbs?
Transitive action verbs require a direct object (e.g., build a house), while intransitive action verbs do not (e.g., run).
How do action verbs enhance writing?
Action verbs make writing more vivid and precise, clearly showing what actions are being taken, making your content more engaging and easier to understand.