100+ Adjective Examples
Discover the transformative power of adjectives in our comprehensive guide designed to elevate your language skills. Learn the definition, meaning, and diverse types of adjectives that can enrich your conversations and writing. Gain valuable insights through unique sentence usage examples and get hands-on tips on how to use adjectives effectively. Don’t miss this all-in-one guide that serves as your roadmap to mastering adjectives and enhancing your communication prowess.
What is an Adjective? – Definition
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or a pronoun. Simply put, it gives more information about what someone or something is like.
The primary function of an adjective is to offer additional details about the noun or pronoun it is describing. It can tell you what kind, how many, or which one. Adjectives usually precede the noun they modify, but they can also come after a linking verb like “is” or “seems.”
What is the Best Example of an Adjective?
The best example to understand an adjective is the word “happy” in the sentence, “She is happy.” Here, “happy” is the adjective that modifies the pronoun “She,” giving more information about her emotional state. The adjective “happy” provides a clearer picture of what she is like, adding depth and context to the sentence.
List of Adjectives
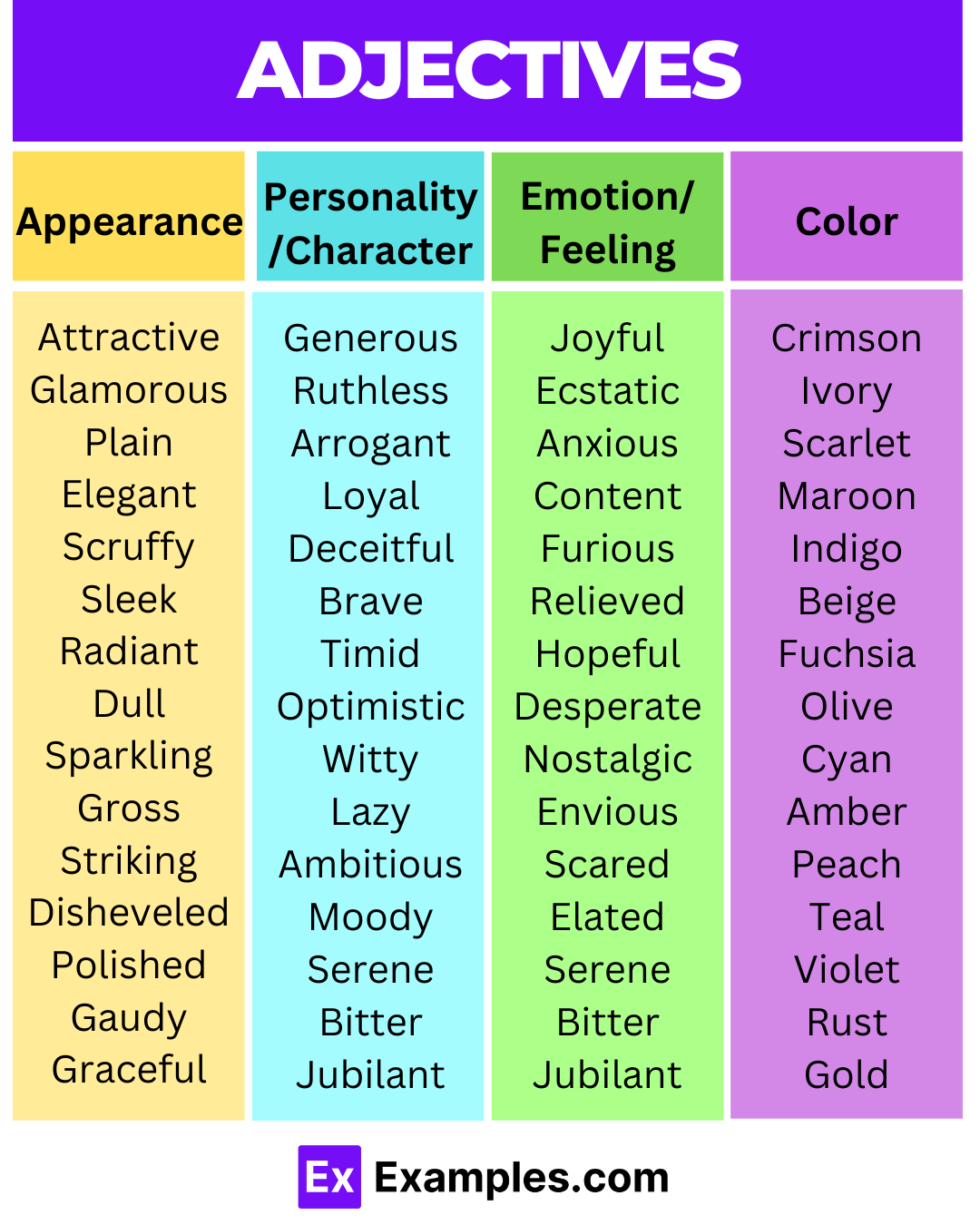
100 Adjective Examples

Adjectives play a crucial role in enhancing your language by adding spice and specificity to your sentences. They serve as descriptive words that modify nouns and pronouns, providing a richer, fuller understanding of a subject. Whether you’re a writer looking to engage your readers or a student keen on vocabulary improvement, our comprehensive list of 100 unique, distinct, and best examples of adjectives is your go-to resource.
- Beautiful: The beautiful sunset amazed everyone.
- Quick: He was quick to finish the task.
- Careful: Be careful while crossing the road.
- Polite: He is a polite young man.
- Tiny: She found a tiny pebble.
- Loud: The loud music disturbed the neighbors.
- Happy: Sarah felt happy today.
- Lonely: The lonely tree stood in the field.
- Bright: The bright star shone in the sky.
- Greedy: The greedy child ate all the cookies.
- Anxious: He was anxious about the exam results.
- Clever: She solved the puzzle with a clever trick.
- Wise: The wise owl observed from the tree.
- Curious: The curious cat ventured into the garden.
- Smooth: The smooth surface was easy to clean.
- Spacious: They moved into a spacious apartment.
- Brave: The brave soldier fought valiantly.
- Charming: The charming actor won many hearts.
- Nervous: She felt nervous before the interview.
- Warm: The warm blanket felt good in winter.
- Fluffy: The fluffy pillow was very comfortable.
- Witty: His witty remarks always make everyone laugh.
- Creative: She came up with a creative solution.
- Busy: The busy bee collected nectar.
- Generous: The generous man donated to charity.
- Lazy: The lazy dog lay in the sun all day.
- Grateful: I am grateful for your help.
- Slim: She is in slim shape due to regular exercise.
- Handsome: The handsome prince wooed the princess.
- Silly: The silly joke made everyone giggle.
- Messy: His room is always messy.
- Quiet: She is quiet but very intelligent.
- Huge: The huge elephant walked slowly.
- Mysterious: The mysterious castle had many secrets.
- Cozy: The cozy cabin was perfect for the weekend.
- Fresh: The fresh flowers smelled wonderful.
- Angry: The angry customer complained to the manager.
- Healthy: She leads a healthy lifestyle.
- Tall: The tall skyscraper dominated the skyline.
- Innocent: The innocent child looked bewildered.
- Gloomy: The room felt gloomy without light.
- Elegant: She wore an elegant gown to the event.
- Lively: The lively party went on until midnight.
- Proud: The proud father cheered for his son.
- Shy: The shy girl didn’t talk much.
- Adventurous: The adventurous hiker scaled the mountain.
- Soft: The soft towel felt nice against my skin.
- Wealthy: The wealthy businessman invested in stocks.
- Tasty: The tasty meal satisfied my hunger.
- Glamorous: She looked glamorous at the awards ceremony.
- Rusty: The rusty gate creaked as it opened.
- Wet: The wet ground made it difficult to walk.
- Delicious: The delicious cake was a hit at the party.
- Fragile: Handle the fragile vase carefully.
- Noisy: The noisy crowd cheered for the team.
- Organized: Her organized desk made it easy to find things.
- Vivid: The artist used vivid colors in his painting.
- Young: The young sapling needs extra care.
- Crafty: The crafty fox escaped the trap.
- Old: The old book smelled of history.
- Tough: The tough material is perfect for outdoor use.
- Chilly: It’s a chilly evening, so wear a jacket.
- Faithful: The faithful dog protected its owner.
- Determined: He was determined to finish the marathon.
- Awkward: The awkward moment made everyone cringe.
- Humorous: His humorous talk was the highlight of the event.
- Grumpy: The grumpy old man yelled at the kids.
- Unique: She has a unique style of writing.
- Dull: The dull knife needs sharpening.
- Sincere: His sincere apology was accepted.
- Clean: The clean room was a pleasant surprise.
- Gritty: The gritty surface provides better grip.
- Dreamy: The dreamy landscape looked like a painting.
- Nasty: The nasty weather ruined our picnic.
- Wrinkled: The wrinkled shirt needs ironing.
- Talented: The talented musician played beautifully.
- Zesty: The zesty sauce added flavor to the dish.
- Enthusiastic: The enthusiastic fans supported their team.
- Scenic: The scenic route was a joy to drive on.
- Hopeful: She was hopeful about her job interview.
- Eager: He was eager to learn new skills.
- Jealous: The jealous coworker spread rumors.
- Romantic: The romantic dinner was a success.
- Skeptical: He was skeptical about the new proposal.
- Modern: The modern architecture caught my eye.
- Radiant: Her radiant smile lit up the room.
- Graceful: The graceful dancer moved effortlessly.
- Empty: The empty box was discarded.
- Keen: She has a keen eye for detail.
- Confident: The confident speaker captivated the audience.
- Clumsy: The clumsy waiter dropped a plate.
- Classic: The classic novel stood the test of time.
- Peaceful: The peaceful garden was perfect for relaxation.
- Transparent: The transparent fabric was light and airy.
- Excited: The excited children opened their gifts.
- Sharp: The sharp blade cut easily through the material.
- Reliable: The reliable car never broke down.
- Rough: The rough terrain made hiking challenging.
- Lazy: The lazy river flowed gently.
- Innovative: The innovative gadget made life easier.
Adjective Clause Examples
Adjective clauses are dependent clauses that act as adjectives in a sentence. They describe a noun and are introduced by relative pronouns like “who,” “which,” or “that.” Below are unique and distinct examples to help you understand the concept better.
- Charming: The woman, who is charming, caught everyone’s attention at the party.
- Sunny: The beach that is sunny all year round is my favorite.
- Fascinated: The child, who is fascinated by dinosaurs, loves visiting museums.
- Endangered: The animal which is endangered should be protected.
- Opulent: The restaurant, which is opulent, is known for its luxurious experience.
Predicate Adjective Examples
Predicate adjectives are adjectives that follow a linking verb and provide more information about the subject of the sentence. Explore the distinct and best examples below to enhance your understanding.
- Sleepy: The dog is sleepy.
- Nervous: She became nervous before her speech.
- Cheerful: The kids are cheerful during the holidays.
- Cautious: The driver was cautious in the rain.
- Healthy: The salad is healthy.
Adjective Examples in Sentences
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns and pronouns. They make sentences with adjectives more dynamic and interesting. Here are unique examples showcasing adjectives in sentences.
- Windy: The windy weather disrupted the outdoor event.
- Mysterious: She had a mysterious aura that intrigued people.
- Spacious: The spacious room could accommodate many guests.
- Puzzled: His puzzled expression made me rethink my words.
- Thirsty: The thirsty traveler drank from the stream.
Adjective Phrase Examples
Adjective phrases are groups of words that function as an adjective in a sentence. They can add flair and specific details to your writing. Find out more with these distinct examples.
- Quick as a fox: The dog, quick as a fox, caught the frisbee.
- Cold as ice: Her stare was cold as ice.
- Red as a rose: Her lips were red as a rose.
- Strong as an ox: He is strong as an ox.
- Bright as the sun: Her eyes are bright as the sun.
Examples of an Absolute Adjective is
Absolute adjectives are adjectives that stand alone and don’t require comparison. They are usually not graded and present an ultimate condition. Explore this concept with a unique example.
- Dead: The battery in my phone is dead.
- Unique: This artwork is unique; there’s nothing else like it.
- Perfect: Your performance was perfect.
- Infinite: The universe is often considered infinite.
- Whole: I spent the whole day working on this project.
Coordinate Adjective Examples
Coordinate adjectives independently modify the same noun and are often separated by commas. Below are unique examples to help you grasp the concept:
- The artist painted a vivid, mesmerizing mural.
- She wore a bold, colorful scarf.
- The mysterious, haunting melody stuck in my mind.
- The tall, lanky man walked into the room.
- The meal was delicious, satisfying to everyone present.
Proper Adjective Examples
Proper adjectives are capitalized and typically derived from proper nouns. Check out these distinct examples:
- They bought French wine for the party.
- The American football game was exhilarating.
- She read a Shakespearean sonnet in class.
- The Japanese art exhibit was stunning.
- They adopted a Siamese cat from the shelter.
Predicative Adjective Examples
Predicative adjectives appear after a linking verb and provide more information about the subject. Here are five exclusive examples:
- The coffee was bitter.
- The child is talented.
- The sky turned darker.
- The project was successful.
- The novel was intriguing.
Attributive Adjective Examples
Attributive adjectives come directly before the noun they modify. Below are unique examples:
- The silent night was beautiful.
- She bought a tiny plant for her desk.
- The scary movie made everyone jump.
- He read a short poem to the audience.
- The crispy fries were gone in seconds.
Appositive Adjective
An appositive adjective renames or elaborates on a noun in the sentence. Here are unique examples to clarify this type:
- The book, informative and well-written, sold out quickly.
- The house, ancient and mysterious, stood alone at the end of the street.
- The chef, talented and creative, won the competition.
- The actor, charismatic and convincing, received a standing ovation.
- The painting, vibrant and surreal, drew a lot of attention.
Comparative Adjective Examples
Comparative adjectives compare two things and often end in “-er” or use “more” or “less.” Here are unique examples:
- Her coffee is stronger than mine.
- The second book was more interesting than the first one.
- His jokes are less funny than hers.
- The mountain is higher than the hill.
- The exam was easier than I expected.
Compound Adjective Examples
Compound adjectives consist of more than one word to describe a noun. Explore these distinct examples:
- He gave a well-reasoned argument.
- The ten-year-old girl won the spelling bee.
- They live in a high-rise building.
- The movie was action-packed.
- I bought a brand-new laptop.
Superlative Adjective Examples
Superlative adjectives compare more than two things and usually end in “-est” or use “most” or “least.” Check out these unique examples:
- She is the smartest person in the class.
- That was the most exciting game of the year.
- This is the least interesting book I’ve read.
- He is the fastest runner on the team.
- This is the smallest room in the house.
Example of an Adjective Words
Adjectives can take many forms and be placed in various parts of a sentence. Here are diverse adjective words examples:
- The quick fox jumps over the lazy dog.
- She is a brilliant student.
- It was a sunny day.
- The happy couple danced all night.
- His answer was incorrect.
Participial Adjective
Participial adjectives act like adjectives but are formed from verbs. Explore these unique examples:
- The bored students stared out the window.
- The broken vase lay on the floor.
- I was amazed by the performance.
- The sleeping baby looked peaceful.
- Her written report earned an A+.
Adjective Noun Examples
Adjective-noun combinations are the backbone of descriptive language. Here are some distinctive examples:
- The cold wind cut through my coat.
- She has a sharp intellect.
- He bought a new car.
- We saw a beautiful sunset.
- The smart student aced the test.
Adjective Descriptive Examples
Descriptive adjectives add detail and richness to sentences. Examine these unique examples:
- Her melodic voice filled the room.
- He wore a tattered shirt.
- The cake had a creamy texture.
- They own a spacious apartment.
- She gave a rousing speech.
Demonstrative Adjective Examples
Demonstrative adjectives point out particular nouns. Here are some illustrative examples:
- This book is mine.
- Those people are friendly.
- She prefers these apples.
- That cat is adorable.
- We will attend those events.
Possessive Adjective Examples
Possessive adjectives indicate ownership. Take a look at these unique examples:
- My dog is friendly.
- Her idea was brilliant.
- Our house is on the next street.
- Their garden is beautiful.
- His painting won the first prize.
Examples of Adjective of Quality
Adjectives of quality describe the subject’s characteristics. Here are some unique examples:
- She has beautiful eyes.
- The delicious pizza was gone in seconds.
- He is a kind man.
- The room is spacious.
- The flower has a sweet smell.
Predicate Adjective Examples
Predicate adjectives follow linking verbs to describe the subject. Take note of these exclusive examples:
- The movie was thrilling.
- The test was easy.
- The journey seems long.
- The song was melodic.
- The workshop was informative.
Adjective Prepositional Phrase Examples
An adjective prepositional phrase serves the function of an adjective in a sentence. Here are some unique examples:
- The girl with blue eyes is my sister.
- The cake in the glass container is chocolate flavored.
- The cat on the roof is stray.
- The books under the table are old.
- The picture above the fireplace is antique.
Hyphenated Adjective Examples
Hyphenated adjectives often come before a noun and describe it more accurately. Here are unique examples:
- The well-known author is giving a speech.
- She is a quick-thinking individual.
- We had a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity.
- They took a cross-country trip.
- The recipe is mouth-watering.
Article Adjective Examples
Article adjectives include ‘a,’ ‘an,’ and ‘the.’ They are used to define a noun. Here are some examples:
- The sun is bright.
- She has an orange.
- We are taking a vacation.
- There is the answer.
- He has a great idea.
Examples of Adjective Prepositional Phrases
These prepositional phrases function as adjectives. Here are some unique examples:
- The cake with sprinkles is delicious.
- The girl in the red dress is my cousin.
- The car with the black tint is new.
- The team under the experienced coach is winning.
- The house across the street is for sale.
Examples of Adjectives Describing a Person
Adjectives can also describe the qualities or features of people. Here are some unique adjective examples to describe a person:
- She is an intelligent woman.
- He is a compassionate person.
- The teacher is very patient.
- The athlete is incredibly fit.
- He is a witty comedian.
Adjectives Modify Nouns
Adjectives serve the important role of modifying nouns, providing more detail or clarity. They can describe the color, size, shape, and many other characteristics of a noun. For instance, in the phrase “a beautiful sunset,” the word beautiful is an adjective that modifies the noun “sunset.”
What are the Degrees of Adjectives?
Degrees of adjectives refer to the intensity or comparison level of the adjective in use. There are three primary degrees:
- Positive Degree: This is the simplest form of an adjective and offers a base level of quality. For example, “He is tall.”
- Comparative Degree: This degree compares two or more entities. For example, “She is taller than him.”
- Superlative Degree: This degree compares more than two entities and indicates the highest quality. For example, “He is the tallest person in the room.”
| Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
|---|---|---|
| quick | quicker | quickest |
| sharp | sharper | sharpest |
| kind | kinder | kindest |
| tall | taller | tallest |
| fast | faster | fastest |
| smart | smarter | smartest |
| strong | stronger | strongest |
| light | lighter | lightest |
| dark | darker | darkest |
| happy | happier | happiest |
What are the Different Types of Adjectives?
Various types of adjectives serve different roles in sentences. Below are some common types:
- Descriptive Adjectives: These adjectives describe the qualities or states of being of nouns. Examples include “happy,” “sad,” and “bright.”
- Quantitative Adjectives: These adjectives describe the quantity of something. Examples are “some,” “many,” and “few.”
- Demonstrative Adjectives: These adjectives point out particular nouns. Examples are “this,” “that,” “these,” and “those.”
- Possessive Adjectives: These adjectives indicate ownership or possession. Examples include “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” and “their.”
- Interrogative Adjectives: These adjectives are used in questions. Examples are “which,” “what,” and “whose.”
- Indefinite Adjectives: These adjectives do not point out any particular noun, but they indicate a type or group. Examples include “any,” “several,” and “few.”
Uses of Adjectives
- Describing Nouns: Adjectives modify nouns by giving more information about their qualities, quantities, or states. This helps create a vivid picture in the reader’s or listener’s mind.
Examples: “a red apple,” “a loud noise.” - Specifying Quantity: Adjectives can indicate the amount or number of a noun, either exactly or approximately.
Examples: “several books,” “one hundred apples.” - Identifying or Classifying: They can help categorize or identify particular nouns, making it clear which one is being referred to.
Examples: “the outer layer,” “an electronic device.” - Comparing Nouns: Through comparative and superlative forms, adjectives compare one noun to another or to a group, respectively. This use highlights differences or similarities between objects, people, or ideas.
Examples: “She is the tallest in her class,” “This is a better option.” - Expressing a Relationship: Certain adjectives express a relationship or pertinence to something else, often ending in suffixes like “-ic,” “-al,” “-ian,” etc.
Examples: “economic policy,” “biological studies.” - Indicating Possession: Possessive adjectives show ownership or possession. Examples are “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” “their.”
- Defining Quality or Characteristic: They define a specific characteristic or quality of a noun, adding depth to descriptions.
Examples: “a melancholy tune,” “a spicy flavor.”
When Nouns are Adjectives and Adjectives are Nouns
In some instances, words can function as both nouns and adjectives, depending on their placement and role within a sentence.
- Nouns as Adjectives: When a noun is used to describe another noun, it acts as an adjective. In the phrase “chicken soup,” “chicken” is technically a noun, but here it serves as an adjective to describe the kind of soup.
- Adjectives as Nouns: An adjective can also function as a noun when it stands in for a group of people or things that share a particular attribute. For example, in the sentence “The rich should contribute more to society,” “rich” is an adjective by nature but acts as a noun to represent people who are wealthy.
Understanding how nouns and adjectives can switch roles in different contexts can help you become more versatile in constructing varied and meaningful sentences.
How to Use Adjectives – Step by Step Guide
Using adjectives effectively can elevate your writing and speech, making them more descriptive and engaging. Follow this step-by-step guide to ensure you’re using adjectives appropriately.
Step 1: Identify the Noun
Before you can use an adjective, you need to identify the noun or pronoun you wish to describe. Ask yourself what the main subject of your sentence is.
Step 2: Determine the Quality to Describe
Consider what aspect or characteristic you want to highlight about the noun. Is it the color, size, shape, or some other quality? Knowing what you want to convey helps you choose the appropriate adjective.
Step 3: Choose the Right Adjective
Once you know what quality you want to describe, select an adjective that most accurately represents it. Use dictionaries or thesauruses to find synonyms if you need alternatives.
Step 4: Adjective Placement
In English, adjectives are generally placed before the noun they describe. For example, “The tall man entered the room.” Alternatively, adjectives can be used in a predicate construction, coming after the verb, as in “The cake is delicious.”
Step 5: Using Multiple Adjectives
When you want to use more than one adjective, the order generally goes: quantity, quality, size, age, shape, color, origin, material, and purpose. For example, “She wore a beautiful long red dress.”
Step 6: Use Comparative and Superlative Forms Wisely
When comparing two or more things, use comparative adjectives like “taller,” “smaller,” etc., and for showcasing the extremity, use superlative forms like “tallest,” “smallest.”
Step 7: Be Mindful of Adjective Overuse
While adjectives can add a lot to a sentence, overuse can lead to verbosity. Be concise and only use adjectives when they serve a specific purpose in enhancing your narrative.
How do you use two adjectives in a sentence?
Using two adjectives in a sentence can offer a more nuanced description of a noun, making your communication more effective and engaging. However, there’s an order to placing adjectives in a sentence to make it sound natural to native English speakers. Typically, the order of adjectives is: quantity, quality, size, age, shape, color, origin, material, and purpose.
Example 1:
In the sentence “She wore a beautiful, long dress,” both “beautiful” (quality) and “long” (size) are adjectives describing the noun “dress.”
Example 2:
He read a short, interesting article. Here, “short” (size) and “interesting” (quality) are the adjectives describing the noun “article.”
Adjectives Vs Adverbs
| Feature | Adjectives | Adverbs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Words that describe or modify nouns and pronouns. | Words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. |
| Purpose | To specify size, color, shape, type, and other qualities of nouns. | To indicate manner, time, frequency, degree, and place of actions. |
| Question Answered | “What kind?”, “Which one?”, “How many?” | “How?”, “When?”, “Where?”, “To what extent?” |
| Position | Usually placed before the noun they modify or after linking verbs. | Often placed after the verb they modify or at the beginning/end of a sentence. |
| Examples | – A quiet room.
– An interesting book. – The red apple. |
– He runs quickly.
– She sings beautifully. – It happened yesterday. |
Tips for Using Adjectives
Maintain Adjective Order
Stick to the conventional order of adjectives for natural-sounding sentences. Disordering the adjectives can make the sentence sound awkward.
Use Commas or ‘And’ Between Coordinate Adjectives
If you can place an “and” between the two adjectives, or swap them without changing the meaning, they are coordinate adjectives and should be separated by a comma. For example, “She is smart, funny” or “She is smart and funny.”
Omit Commas for Cumulative Adjectives
If the adjectives build upon each other, and you can’t logically place an “and” between them, omit the comma. For instance, “She wore a reddish brown coat,” not “reddish, brown coat.”
Be Mindful of Overuse
While adjectives can make your sentence more descriptive, overusing them can lead to verbose and confusing sentences. Use them sparingly for maximum effect.
Check for Redundancy
Sometimes, the noun you’re describing already includes the quality you’re attributing to it. In such cases, the adjective becomes redundant. For example, instead of saying “round circle,” just say “circle.”
Choose Stronger Adjectives
Instead of piling up adjectives, try to find a single, more powerful adjective that can effectively describe the noun. For instance, instead of saying “very big,” you might say “enormous.”
By keeping these tips in mind, you can effectively utilize adjectives to make your writing more descriptive, engaging, and grammatically accurate.
100+ Adjective Examples

Discover the transformative power of adjectives in our comprehensive guide designed to elevate your language skills. Learn the definition, meaning, and diverse types of adjectives that can enrich your conversations and writing. Gain valuable insights through unique sentence usage examples and get hands-on tips on how to use adjectives effectively. Don’t miss this all-in-one guide that serves as your roadmap to mastering adjectives and enhancing your communication prowess.
What is an Adjective? – Definition
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or a pronoun. Simply put, it gives more information about what someone or something is like.
The primary function of an adjective is to offer additional details about the noun or pronoun it is describing. It can tell you what kind, how many, or which one. Adjectives usually precede the noun they modify, but they can also come after a linking verb like “is” or “seems.”
What is the Best Example of an Adjective?
The best example to understand an adjective is the word “happy” in the sentence, “She is happy.” Here, “happy” is the adjective that modifies the pronoun “She,” giving more information about her emotional state. The adjective “happy” provides a clearer picture of what she is like, adding depth and context to the sentence.
List of Adjectives

100 Adjective Examples

Adjectives play a crucial role in enhancing your language by adding spice and specificity to your sentences. They serve as descriptive words that modify nouns and pronouns, providing a richer, fuller understanding of a subject. Whether you’re a writer looking to engage your readers or a student keen on vocabulary improvement, our comprehensive list of 100 unique, distinct, and best examples of adjectives is your go-to resource.
Beautiful: The beautiful sunset amazed everyone.
Quick: He was quick to finish the task.
Careful: Be careful while crossing the road.
Polite: He is a polite young man.
Tiny: She found a tiny pebble.
Loud: The loud music disturbed the neighbors.
Happy: Sarah felt happy today.
Lonely: The lonely tree stood in the field.
Bright: The bright star shone in the sky.
Greedy: The greedy child ate all the cookies.
Anxious: He was anxious about the exam results.
Clever: She solved the puzzle with a clever trick.
Wise: The wise owl observed from the tree.
Curious: The curious cat ventured into the garden.
Smooth: The smooth surface was easy to clean.
Spacious: They moved into a spacious apartment.
Brave: The brave soldier fought valiantly.
Charming: The charming actor won many hearts.
Nervous: She felt nervous before the interview.
Warm: The warm blanket felt good in winter.
Fluffy: The fluffy pillow was very comfortable.
Witty: His witty remarks always make everyone laugh.
Creative: She came up with a creative solution.
Busy: The busy bee collected nectar.
Generous: The generous man donated to charity.
Lazy: The lazy dog lay in the sun all day.
Grateful: I am grateful for your help.
Slim: She is in slim shape due to regular exercise.
Handsome: The handsome prince wooed the princess.
Silly: The silly joke made everyone giggle.
Messy: His room is always messy.
Quiet: She is quiet but very intelligent.
Huge: The huge elephant walked slowly.
Mysterious: The mysterious castle had many secrets.
Cozy: The cozy cabin was perfect for the weekend.
Fresh: The fresh flowers smelled wonderful.
Angry: The angry customer complained to the manager.
Healthy: She leads a healthy lifestyle.
Tall: The tall skyscraper dominated the skyline.
Innocent: The innocent child looked bewildered.
Gloomy: The room felt gloomy without light.
Elegant: She wore an elegant gown to the event.
Lively: The lively party went on until midnight.
Proud: The proud father cheered for his son.
Shy: The shy girl didn’t talk much.
Adventurous: The adventurous hiker scaled the mountain.
Soft: The soft towel felt nice against my skin.
Wealthy: The wealthy businessman invested in stocks.
Tasty: The tasty meal satisfied my hunger.
Glamorous: She looked glamorous at the awards ceremony.
Rusty: The rusty gate creaked as it opened.
Wet: The wet ground made it difficult to walk.
Delicious: The delicious cake was a hit at the party.
Fragile: Handle the fragile vase carefully.
Noisy: The noisy crowd cheered for the team.
Organized: Her organized desk made it easy to find things.
Vivid: The artist used vivid colors in his painting.
Young: The young sapling needs extra care.
Crafty: The crafty fox escaped the trap.
Old: The old book smelled of history.
Tough: The tough material is perfect for outdoor use.
Chilly: It’s a chilly evening, so wear a jacket.
Faithful: The faithful dog protected its owner.
Determined: He was determined to finish the marathon.
Awkward: The awkward moment made everyone cringe.
Humorous: His humorous talk was the highlight of the event.
Grumpy: The grumpy old man yelled at the kids.
Unique: She has a unique style of writing.
Dull: The dull knife needs sharpening.
Sincere: His sincere apology was accepted.
Clean: The clean room was a pleasant surprise.
Gritty: The gritty surface provides better grip.
Dreamy: The dreamy landscape looked like a painting.
Nasty: The nasty weather ruined our picnic.
Wrinkled: The wrinkled shirt needs ironing.
Talented: The talented musician played beautifully.
Zesty: The zesty sauce added flavor to the dish.
Enthusiastic: The enthusiastic fans supported their team.
Scenic: The scenic route was a joy to drive on.
Hopeful: She was hopeful about her job interview.
Eager: He was eager to learn new skills.
Jealous: The jealous coworker spread rumors.
Romantic: The romantic dinner was a success.
Skeptical: He was skeptical about the new proposal.
Modern: The modern architecture caught my eye.
Radiant: Her radiant smile lit up the room.
Graceful: The graceful dancer moved effortlessly.
Empty: The empty box was discarded.
Keen: She has a keen eye for detail.
Confident: The confident speaker captivated the audience.
Clumsy: The clumsy waiter dropped a plate.
Classic: The classic novel stood the test of time.
Peaceful: The peaceful garden was perfect for relaxation.
Transparent: The transparent fabric was light and airy.
Excited: The excited children opened their gifts.
Sharp: The sharp blade cut easily through the material.
Reliable: The reliable car never broke down.
Rough: The rough terrain made hiking challenging.
Lazy: The lazy river flowed gently.
Innovative: The innovative gadget made life easier.
Adjective Clause Examples
Adjective clauses are dependent clauses that act as adjectives in a sentence. They describe a noun and are introduced by relative pronouns like “who,” “which,” or “that.” Below are unique and distinct examples to help you understand the concept better.
Charming: The woman, who is charming, caught everyone’s attention at the party.
Sunny: The beach that is sunny all year round is my favorite.
Fascinated: The child, who is fascinated by dinosaurs, loves visiting museums.
Endangered: The animal which is endangered should be protected.
Opulent: The restaurant, which is opulent, is known for its luxurious experience.
Predicate Adjective Examples
Predicate adjectives are adjectives that follow a linking verb and provide more information about the subject of the sentence. Explore the distinct and best examples below to enhance your understanding.
Sleepy: The dog is sleepy.
Nervous: She became nervous before her speech.
Cheerful: The kids are cheerful during the holidays.
Cautious: The driver was cautious in the rain.
Healthy: The salad is healthy.
Adjective Examples in Sentences
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns and pronouns. They make sentences with adjectives more dynamic and interesting. Here are unique examples showcasing adjectives in sentences.
Windy: The windy weather disrupted the outdoor event.
Mysterious: She had a mysterious aura that intrigued people.
Spacious: The spacious room could accommodate many guests.
Puzzled: His puzzled expression made me rethink my words.
Thirsty: The thirsty traveler drank from the stream.
Adjective Phrase Examples
Adjective phrases are groups of words that function as an adjective in a sentence. They can add flair and specific details to your writing. Find out more with these distinct examples.
Quick as a fox: The dog, quick as a fox, caught the frisbee.
Cold as ice: Her stare was cold as ice.
Red as a rose: Her lips were red as a rose.
Strong as an ox: He is strong as an ox.
Bright as the sun: Her eyes are bright as the sun.
Examples of an Absolute Adjective is
Absolute adjectives are adjectives that stand alone and don’t require comparison. They are usually not graded and present an ultimate condition. Explore this concept with a unique example.
Dead: The battery in my phone is dead.
Unique: This artwork is unique; there’s nothing else like it.
Perfect: Your performance was perfect.
Infinite: The universe is often considered infinite.
Whole: I spent the whole day working on this project.
Coordinate Adjective Examples
Coordinate adjectives independently modify the same noun and are often separated by commas. Below are unique examples to help you grasp the concept:
The artist painted a vivid, mesmerizing mural.
She wore a bold, colorful scarf.
The mysterious, haunting melody stuck in my mind.
The tall, lanky man walked into the room.
The meal was delicious, satisfying to everyone present.
Proper Adjective Examples
Proper adjectives are capitalized and typically derived from proper nouns. Check out these distinct examples:
They bought French wine for the party.
The American football game was exhilarating.
She read a Shakespearean sonnet in class.
The Japanese art exhibit was stunning.
They adopted a Siamese cat from the shelter.
Predicative Adjective Examples
Predicative adjectives appear after a linking verb and provide more information about the subject. Here are five exclusive examples:
The coffee was bitter.
The child is talented.
The sky turned darker.
The project was successful.
The novel was intriguing.
Attributive Adjective Examples
Attributive adjectives come directly before the noun they modify. Below are unique examples:
The silent night was beautiful.
She bought a tiny plant for her desk.
The scary movie made everyone jump.
He read a short poem to the audience.
The crispy fries were gone in seconds.
Appositive Adjective
An appositive adjective renames or elaborates on a noun in the sentence. Here are unique examples to clarify this type:
The book, informative and well-written, sold out quickly.
The house, ancient and mysterious, stood alone at the end of the street.
The chef, talented and creative, won the competition.
The actor, charismatic and convincing, received a standing ovation.
The painting, vibrant and surreal, drew a lot of attention.
Comparative Adjective Examples
Comparative adjectives compare two things and often end in “-er” or use “more” or “less.” Here are unique examples:
Her coffee is stronger than mine.
The second book was more interesting than the first one.
His jokes are less funny than hers.
The mountain is higher than the hill.
The exam was easier than I expected.
Compound Adjective Examples
Compound adjectives consist of more than one word to describe a noun. Explore these distinct examples:
He gave a well-reasoned argument.
The ten-year-old girl won the spelling bee.
They live in a high-rise building.
The movie was action-packed.
I bought a brand-new laptop.
Superlative Adjective Examples
Superlative adjectives compare more than two things and usually end in “-est” or use “most” or “least.” Check out these unique examples:
She is the smartest person in the class.
That was the most exciting game of the year.
This is the least interesting book I’ve read.
He is the fastest runner on the team.
This is the smallest room in the house.
Example of an Adjective Words
Adjectives can take many forms and be placed in various parts of a sentence. Here are diverse adjective words examples:
The quick fox jumps over the lazy dog.
She is a brilliant student.
It was a sunny day.
The happy couple danced all night.
His answer was incorrect.
Participial Adjective
Participial adjectives act like adjectives but are formed from verbs. Explore these unique examples:
The bored students stared out the window.
The broken vase lay on the floor.
I was amazed by the performance.
The sleeping baby looked peaceful.
Her written report earned an A+.
Adjective Noun Examples
Adjective-noun combinations are the backbone of descriptive language. Here are some distinctive examples:
The cold wind cut through my coat.
She has a sharp intellect.
He bought a new car.
We saw a beautiful sunset.
The smart student aced the test.
Adjective Descriptive Examples
Descriptive adjectives add detail and richness to sentences. Examine these unique examples:
Her melodic voice filled the room.
He wore a tattered shirt.
The cake had a creamy texture.
They own a spacious apartment.
She gave a rousing speech.
Demonstrative Adjective Examples
Demonstrative adjectives point out particular nouns. Here are some illustrative examples:
This book is mine.
Those people are friendly.
She prefers these apples.
That cat is adorable.
We will attend those events.
Possessive Adjective Examples
Possessive adjectives indicate ownership. Take a look at these unique examples:
My dog is friendly.
Her idea was brilliant.
Our house is on the next street.
Their garden is beautiful.
His painting won the first prize.
Examples of Adjective of Quality
Adjectives of quality describe the subject’s characteristics. Here are some unique examples:
She has beautiful eyes.
The delicious pizza was gone in seconds.
He is a kind man.
The room is spacious.
The flower has a sweet smell.
Predicate Adjective Examples
Predicate adjectives follow linking verbs to describe the subject. Take note of these exclusive examples:
The movie was thrilling.
The test was easy.
The journey seems long.
The song was melodic.
The workshop was informative.
Adjective Prepositional Phrase Examples
An adjective prepositional phrase serves the function of an adjective in a sentence. Here are some unique examples:
The girl with blue eyes is my sister.
The cake in the glass container is chocolate flavored.
The cat on the roof is stray.
The books under the table are old.
The picture above the fireplace is antique.
Hyphenated Adjective Examples
Hyphenated adjectives often come before a noun and describe it more accurately. Here are unique examples:
The well-known author is giving a speech.
She is a quick-thinking individual.
We had a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity.
They took a cross-country trip.
The recipe is mouth-watering.
Article Adjective Examples
Article adjectives include ‘a,’ ‘an,’ and ‘the.’ They are used to define a noun. Here are some examples:
The sun is bright.
She has an orange.
We are taking a vacation.
There is the answer.
He has a great idea.
Examples of Adjective Prepositional Phrases
These prepositional phrases function as adjectives. Here are some unique examples:
The cake with sprinkles is delicious.
The girl in the red dress is my cousin.
The car with the black tint is new.
The team under the experienced coach is winning.
The house across the street is for sale.
Examples of Adjectives Describing a Person
Adjectives can also describe the qualities or features of people. Here are some unique adjective examples to describe a person:
She is an intelligent woman.
He is a compassionate person.
The teacher is very patient.
The athlete is incredibly fit.
He is a witty comedian.
Adjectives Modify Nouns
Adjectives serve the important role of modifying nouns, providing more detail or clarity. They can describe the color, size, shape, and many other characteristics of a noun. For instance, in the phrase “a beautiful sunset,” the word beautiful is an adjective that modifies the noun “sunset.”
What are the Degrees of Adjectives?
Degrees of adjectives refer to the intensity or comparison level of the adjective in use. There are three primary degrees:
Positive Degree: This is the simplest form of an adjective and offers a base level of quality. For example, “He is tall.”
Comparative Degree: This degree compares two or more entities. For example, “She is taller than him.”
Superlative Degree: This degree compares more than two entities and indicates the highest quality. For example, “He is the tallest person in the room.”
Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
|---|---|---|
quick | quicker | quickest |
sharp | sharper | sharpest |
kind | kinder | kindest |
tall | taller | tallest |
fast | faster | fastest |
smart | smarter | smartest |
strong | stronger | strongest |
light | lighter | lightest |
dark | darker | darkest |
happy | happier | happiest |
What are the Different Types of Adjectives?
Various types of adjectives serve different roles in sentences. Below are some common types:
Descriptive Adjectives: These adjectives describe the qualities or states of being of nouns. Examples include “happy,” “sad,” and “bright.”
Quantitative Adjectives: These adjectives describe the quantity of something. Examples are “some,” “many,” and “few.”
Demonstrative Adjectives: These adjectives point out particular nouns. Examples are “this,” “that,” “these,” and “those.”
Possessive Adjectives: These adjectives indicate ownership or possession. Examples include “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” and “their.”
Interrogative Adjectives: These adjectives are used in questions. Examples are “which,” “what,” and “whose.”
Indefinite Adjectives: These adjectives do not point out any particular noun, but they indicate a type or group. Examples include “any,” “several,” and “few.”
Uses of Adjectives
Describing Nouns: Adjectives modify nouns by giving more information about their qualities, quantities, or states. This helps create a vivid picture in the reader’s or listener’s mind.
Examples: “a red apple,” “a loud noise.”Specifying Quantity: Adjectives can indicate the amount or number of a noun, either exactly or approximately.
Examples: “several books,” “one hundred apples.”Identifying or Classifying: They can help categorize or identify particular nouns, making it clear which one is being referred to.
Examples: “the outer layer,” “an electronic device.”Comparing Nouns: Through comparative and superlative forms, adjectives compare one noun to another or to a group, respectively. This use highlights differences or similarities between objects, people, or ideas.
Examples: “She is the tallest in her class,” “This is a better option.”Expressing a Relationship: Certain adjectives express a relationship or pertinence to something else, often ending in suffixes like “-ic,” “-al,” “-ian,” etc.
Examples: “economic policy,” “biological studies.”Indicating Possession: Possessive adjectives show ownership or possession. Examples are “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” “their.”
Defining Quality or Characteristic: They define a specific characteristic or quality of a noun, adding depth to descriptions.
Examples: “a melancholy tune,” “a spicy flavor.”
When Nouns are Adjectives and Adjectives are Nouns
In some instances, words can function as both nouns and adjectives, depending on their placement and role within a sentence.
Nouns as Adjectives: When a noun is used to describe another noun, it acts as an adjective. In the phrase “chicken soup,” “chicken” is technically a noun, but here it serves as an adjective to describe the kind of soup.
Adjectives as Nouns: An adjective can also function as a noun when it stands in for a group of people or things that share a particular attribute. For example, in the sentence “The rich should contribute more to society,” “rich” is an adjective by nature but acts as a noun to represent people who are wealthy.
Understanding how nouns and adjectives can switch roles in different contexts can help you become more versatile in constructing varied and meaningful sentences.
How to Use Adjectives – Step by Step Guide
Using adjectives effectively can elevate your writing and speech, making them more descriptive and engaging. Follow this step-by-step guide to ensure you’re using adjectives appropriately.
Step 1: Identify the Noun
Before you can use an adjective, you need to identify the noun or pronoun you wish to describe. Ask yourself what the main subject of your sentence is.
Step 2: Determine the Quality to Describe
Consider what aspect or characteristic you want to highlight about the noun. Is it the color, size, shape, or some other quality? Knowing what you want to convey helps you choose the appropriate adjective.
Step 3: Choose the Right Adjective
Once you know what quality you want to describe, select an adjective that most accurately represents it. Use dictionaries or thesauruses to find synonyms if you need alternatives.
Step 4: Adjective Placement
In English, adjectives are generally placed before the noun they describe. For example, “The tall man entered the room.” Alternatively, adjectives can be used in a predicate construction, coming after the verb, as in “The cake is delicious.”
Step 5: Using Multiple Adjectives
When you want to use more than one adjective, the order generally goes: quantity, quality, size, age, shape, color, origin, material, and purpose. For example, “She wore a beautiful long red dress.”
Step 6: Use Comparative and Superlative Forms Wisely
When comparing two or more things, use comparative adjectives like “taller,” “smaller,” etc., and for showcasing the extremity, use superlative forms like “tallest,” “smallest.”
Step 7: Be Mindful of Adjective Overuse
While adjectives can add a lot to a sentence, overuse can lead to verbosity. Be concise and only use adjectives when they serve a specific purpose in enhancing your narrative.
How do you use two adjectives in a sentence?
Using two adjectives in a sentence can offer a more nuanced description of a noun, making your communication more effective and engaging. However, there’s an order to placing adjectives in a sentence to make it sound natural to native English speakers. Typically, the order of adjectives is: quantity, quality, size, age, shape, color, origin, material, and purpose.
Example 1:
In the sentence “She wore a beautiful, long dress,” both “beautiful” (quality) and “long” (size) are adjectives describing the noun “dress.”
Example 2:
He read a short, interesting article. Here, “short” (size) and “interesting” (quality) are the adjectives describing the noun “article.”
Adjectives Vs Adverbs
Feature | Adjectives | Adverbs |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Words that describe or modify nouns and pronouns. | Words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. |
Purpose | To specify size, color, shape, type, and other qualities of nouns. | To indicate manner, time, frequency, degree, and place of actions. |
Question Answered | “What kind?”, “Which one?”, “How many?” | “How?”, “When?”, “Where?”, “To what extent?” |
Position | Usually placed before the noun they modify or after linking verbs. | Often placed after the verb they modify or at the beginning/end of a sentence. |
Examples | – A quiet room. – An interesting book. – The red apple. | – He runs quickly. – She sings beautifully. – It happened yesterday. |
Tips for Using Adjectives
Maintain Adjective Order
Stick to the conventional order of adjectives for natural-sounding sentences. Disordering the adjectives can make the sentence sound awkward.
Use Commas or ‘And’ Between Coordinate Adjectives
If you can place an “and” between the two adjectives, or swap them without changing the meaning, they are coordinate adjectives and should be separated by a comma. For example, “She is smart, funny” or “She is smart and funny.”
Omit Commas for Cumulative Adjectives
If the adjectives build upon each other, and you can’t logically place an “and” between them, omit the comma. For instance, “She wore a reddish brown coat,” not “reddish, brown coat.”
Be Mindful of Overuse
While adjectives can make your sentence more descriptive, overusing them can lead to verbose and confusing sentences. Use them sparingly for maximum effect.
Check for Redundancy
Sometimes, the noun you’re describing already includes the quality you’re attributing to it. In such cases, the adjective becomes redundant. For example, instead of saying “round circle,” just say “circle.”
Choose Stronger Adjectives
Instead of piling up adjectives, try to find a single, more powerful adjective that can effectively describe the noun. For instance, instead of saying “very big,” you might say “enormous.”
By keeping these tips in mind, you can effectively utilize adjectives to make your writing more descriptive, engaging, and grammatically accurate.

