130+ Adjective Phrase Examples
Unlock the full potential of your writing with our comprehensive guide on Adjective Phrase Examples, How to Use, and Tips. This article is your one-stop resource for mastering the art of using adjective phrases effectively. Whether you’re a student, a writer, or someone simply interested in English grammar, this guide offers actionable insights to elevate your linguistic skills.
What is the Adjective Phrase? – Definition
An adjective phrase is a group of words that collectively function as an adjective in a sentence. Simply put, it adds description or clarification to a noun or pronoun, enhancing the overall meaning of the sentence.
How to Identify Adjective Phrases
Adjective phrases are groups of words that describe or modify a noun or pronoun in a sentence, adding detail or clarification. These phrases consist of an adjective (the head) along with any modifiers or complements. Here’s how to identify them:
Look for the Head Adjective
- Start with the Adjective: Identify the adjective serving as the head of the phrase. This is the word that directly modifies the noun or pronoun.
Check for Modifiers
- Modifiers and Complements: Look for any words that modify the head adjective or complete its meaning. These can be adverbs, prepositional phrases, or other adjectives.
Identify the Noun or Pronoun Modified
- Target of Modification: Determine which noun or pronoun the adjective phrase is modifying. This helps confirm that the phrase functions adjectivally.
Prepositional Phrases as Adjective Phrases
- Prepositional Clues: Many adjective phrases are introduced by prepositions. If a prepositional phrase acts to describe a noun, it’s functioning as an adjective phrase.
Use Replacement Test
- Substitution Test: Try replacing the phrase with a single adjective. If the sentence still makes sense, you’ve likely identified an adjective phrase.
Examples
- Sentence: The dog with brown spots loves to play.
- Adjective Phrase: with brown spots
- Modified Noun: dog
- Sentence: She is known for her exceptionally quick thinking.
- Adjective Phrase: exceptionally quick
- Modified Noun: thinking
- Sentence: The car in the driveway belongs to my neighbor.
- Adjective Phrase: in the driveway
- Modified Noun: car
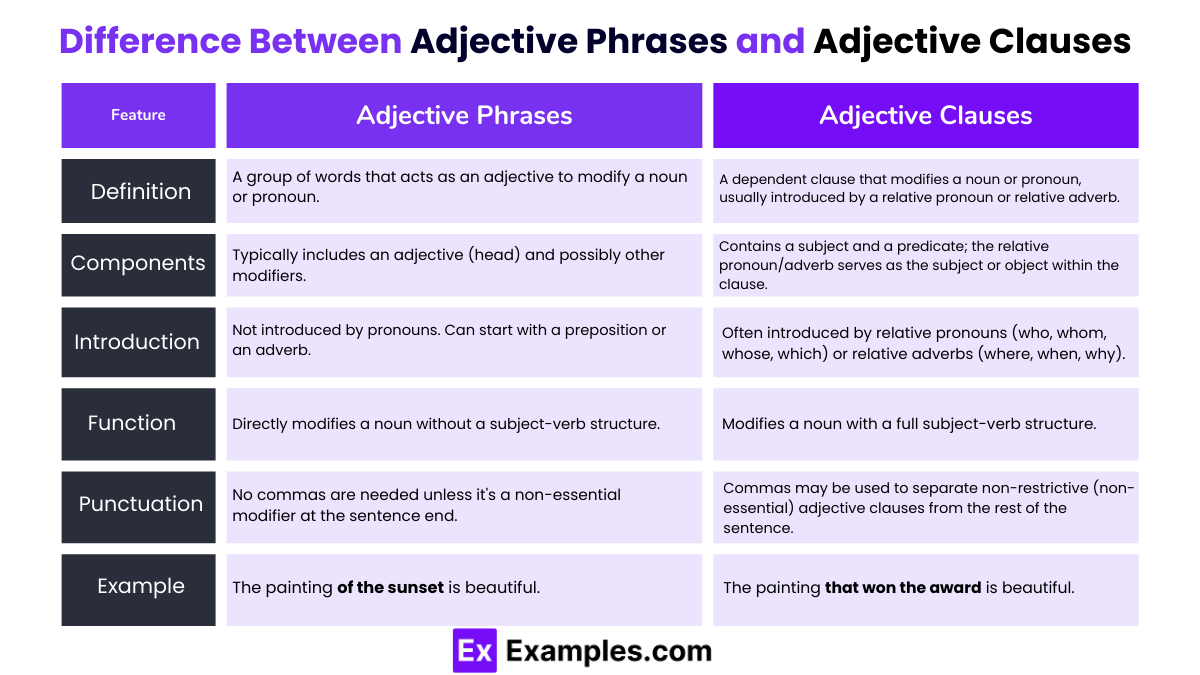
Difference Between Adjective Phrases and Adjective Clauses
| Feature | Adjective Phrases | Adjective Clauses |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A group of words that acts as an adjective to modify a noun or pronoun. | A dependent clause that modifies a noun or pronoun, usually introduced by a relative pronoun or relative adverb. |
| Components | Typically includes an adjective (head) and possibly other modifiers. | Contains a subject and a predicate; the relative pronoun/adverb serves as the subject or object within the clause. |
| Introduction | Not introduced by pronouns. Can start with a preposition or an adverb. | Often introduced by relative pronouns (who, whom, whose, which) or relative adverbs (where, when, why). |
| Example | The painting of the sunset is beautiful. | The painting that won the award is beautiful. |
| Function | Directly modifies a noun without a subject-verb structure. | Modifies a noun with a full subject-verb structure. |
| Punctuation | No commas are needed unless it’s a non-essential modifier at the sentence end. | Commas may be used to separate non-restrictive (non-essential) adjective clauses from the rest of the sentence. |
| Interchangeability | Cannot stand alone as a sentence; lacks a subject and predicate. | Cannot stand alone as a complete sentence but contains a subject and predicate. |
10+ Interactive Examples of Adjective Phrases
- The house on the hill overlooks the valley.
- Adjective Phrase: on the hill
- Modified Noun: house
- She gave us a basket filled with fresh fruit.
- Adjective Phrase: with fresh fruit
- Modified Noun: basket
- The cat with striped fur slept in the sun.
- Adjective Phrase: with striped fur
- Modified Noun: cat
- He bought a car known for its durability.
- Adjective Phrase: known for its durability
- Modified Noun: car
- The book on the top shelf is my favorite.
- Adjective Phrase: on the top shelf
- Modified Noun: book
- They walked through the garden blooming with roses.
- Adjective Phrase: blooming with roses
- Modified Noun: garden
- She has a voice soothing and calm, perfect for storytelling.
- Adjective Phrase: soothing and calm
- Modified Noun: voice
- The painting worth a thousand words captivated everyone.
- Adjective Phrase: worth a thousand words
- Modified Noun: painting
- We took a path covered in fallen leaves.
- Adjective Phrase: covered in fallen leaves
- Modified Noun: path
- The letter sealed with wax held mysterious news.
- Adjective Phrase: sealed with wax
- Modified Noun: letter
Adjective Phrases vs. Solo Adjectives
| Feature | Adjective Phrases | Solo Adjectives |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A group of words that includes an adjective (the head) and modifies a noun or pronoun. | A single word that modifies a noun or pronoun by describing or specifying its qualities or states. |
| Components | Consists of a head adjective and may include other modifiers, such as adverbs, prepositional phrases, or additional adjectives. | Only the adjective itself, without additional modifiers. |
| Function | Adds detailed description or clarification to a noun, often including where, when, how, or to what extent something is. | Provides a straightforward description or classification of a noun, typically relating to size, color, shape, material, or quality. |
| Examples | – The book on the bottom shelf is mine. – The flowers blooming in the garden are beautiful. | – The red book is mine. – The beautiful flowers are blooming. |
| Punctuation | Adjective phrases do not require special punctuation unless they are nonrestrictive phrases, in which case they may be set off by commas. | Solo adjectives directly precede the noun they modify and do not need additional punctuation. |
| Flexibility in Sentence | Can provide extensive detail and context by modifying the noun in more specific ways. | Offers a direct, succinct modification to the noun with limited detail. |
| Interchangeability and Order | The order within an adjective phrase is fixed based on grammatical rules and meaning. | When multiple solo adjectives modify the same noun, their order follows specific conventions (e.g., opinion, size, age, shape, color, origin, material, purpose). |
100+ Adjective Phrase Examples

Grasping the concept of adjective phrases is easier when you have concrete examples. This section gives you a thorough compilation of 100 distinctive examples of adjective phrases. These examples can serve as invaluable references for linguists, writers, students, or anyone who wishes to master the English language. In each sentence, the adjective phrase is highlighted in bold for easy identification.
- The dog with a wagging tail is friendly.
- The coffee that is piping hot is too much for me.
- The boy wearing a red shirt is my brother.
- She is the girl with curly hair.
- The tree laden with apples is old.
- The painting from the Renaissance era is priceless.
- The car with a sleek design is expensive.
- The cake topped with whipped cream looks delicious.
- The story that you told me was interesting.
- The city known for its cultural heritage is Paris.
- The girl armed with confidence gave the speech.
- The house on the hilltop has a great view.
- The program full of bugs needs fixing.
- The shoes made of leather are durable.
- The mountain covered in snow is majestic.
- The book written by J.K. Rowling is popular.
- The actor famous for his roles in comedies is coming to town.
- The laptop equipped with high-end components is powerful.
- The kids playing in the park are loud.
- The film directed by Steven Spielberg was a hit.
- The town beside the river is peaceful.
- The dish flavored with exotic spices is mouth-watering.
- The watch gifted by my grandfather is precious to me.
- The stadium filled with fans was electric.
- The lesson filled with practical examples was informative.
- The company renowned for its customer service is successful.
- The beach with golden sand is perfect for vacation.
- The airplane flying at high altitude is barely visible.
- The house decorated for Christmas looks beautiful.
- The notebook covered in doodles is mine.
- The baby asleep in the crib is adorable.
- The speech filled with factual data was convincing.
- The restaurant known for its vegan options is booked solid.
- The couple madly in love couldn’t be separated.
- The cellphone with a cracked screen needs repair.
- The teacher well-versed in ancient history is giving a lecture.
- The student eager to learn excelled in class.
- The bird with colorful feathers is a parrot.
- The movie based on true events is inspiring.
- The road leading to the forest is treacherous.
- The cafe near the art gallery is quaint.
- The play written by Shakespeare is a classic.
- The cat with green eyes is mysterious.
- The garden filled with flowers smells heavenly.
- The car that won the race is fast.
- The hotel overlooking the ocean is luxurious.
- The guy in a leather jacket looks cool.
- The dessert sprinkled with cinnamon was delicious.
- The decision made in haste was regrettable.
- The kids running around are energetic.
- The woman dressed in black is a spy.
- The building constructed in the 1800s is historic.
- The sky clear of clouds is beautiful.
- The river teeming with fish is an angler’s dream.
- The poem full of metaphors is thought-provoking.
- The food spiced with saffron was gourmet.
- The room painted in blue feels calming.
- The office located downtown is convenient.
- The artist known for abstract paintings is innovative.
- The school accredited by the state is reputable.
- The dog that barks loudly is annoying.
- The book filled with adventure stories is captivating.
- The restaurant serving Italian cuisine is expensive.
- The play dealing with social issues is thought-provoking.
- The team undefeated this season is confident.
- The coffee brewed to perfection smells amazing.
- The hill covered in snow looks picturesque.
- The meal served with a side of salad was filling.
- The software designed for graphic editing is user-friendly.
- The movie packed with action scenes was exhilarating.
- The woman wearing a red dress is the host for the evening.
- The cake layered with cream and strawberries was delicious.
- The child holding a balloon looks happy.
- The program focused on mental health is informative.
- The car equipped with the latest features is a good buy.
- The room painted in pastel shades is calming.
- The building constructed in 1900 is a historical landmark.
- The soup made from organic vegetables is healthy.
- The company known for innovation is Apple.
- The lake filled with crystal clear water is mesmerizing.
- The conference aimed at young entrepreneurs is inspiring.
- The leader respected by all was wise and fair.
- The film nominated for several awards is a must-watch.
- The boy skilled in mathematics won the competition.
- The dish infused with exotic spices was mouth-watering.
- The project backed by the government is promising.
- The holiday celebrated around the world is New Year’s Day.
- The park filled with colorful flowers is beautiful.
- The gym equipped with modern machines is popular.
- The artist inspired by nature creates stunning pieces.
- The city known for its nightlife is Las Vegas.
- The garden home to various bird species is a nature lover’s paradise.
- The teacher appreciated by everyone is retiring this year.
- The vacation planned for the summer got postponed.
- The shopping mall having more than 200 stores is gigantic.
- The football player recruited from college is talented.
- The painting valued at a million dollars is priceless.
- The book on the top shelf is my favorite mystery novel.
- She wore a necklace made of pure gold to the event.
- The painting in the museum’s main hall caught everyone’s attention.
What are Adjective Phrase Structure Rules?
Adjective phrase structure rules govern how an adjective phrase is formed within a sentence. Typically, an adjective phrase consists of an adjective serving as the headword, sometimes followed or preceded by modifiers or complementing phrases. These could be adverbs, prepositional phrases, or even other adjectives.
For example, in the sentence “The pie is incredibly delicious,” “incredibly delicious” is the adjective phrase. Here, “delicious” is the headword and “incredibly” is the modifier.
How do you form an adjective phrase?
Forming an adjective phrase isn’t as complex as it might seem. Start with the adjective that describes the noun you are focusing on. From there, you can add modifiers to make your description more detailed.
- Choose the Headword: Identify the main adjective you wish to use.
- Example: Happy
- Add Modifiers: These can be adverbs or other adjectives that give more context to the headword.
- Example: Extremely happy
- Add Complements: Some adjectives need additional information to complete their meaning, often following prepositions like ‘of,’ ‘in,’ or ‘with.’
- Example: Happy with his performance
- Verify Syntax: Ensure that your adjective phrase fits grammatically within the sentence.
What do you call an adjective phrase?
An adjective phrase is often simply referred to as an “AdjP” in syntactic analysis. In everyday language, it is commonly called a “descriptive phrase” or “qualifying phrase.” Its main role is to provide more information about a noun or pronoun, making the sentence more detailed and interesting. An adjective phrase can serve as a subject complement, an object complement, or even as a predicative expression. Understanding what to call it depends on how deeply you are delving into the syntactic or functional analysis of a sentence.
Mastering the use of adjective phrases can add depth and clarity to your writing, enabling you to communicate more precisely.
Adjective Phrase Exercises for Kids
Engaging in adjective phrase exercises can be a fun and educational way for kids to improve their language skills. These exercises can include fill-in-the-blanks, matching games, and sentence construction activities. For instance:
- Fill-in-the-Blanks: Provide sentences with missing adjective phrases and ask the child to complete them.
- Example: The dog is ___ (add an adjective phrase like “very playful”).
- Matching Game: List various nouns and adjective phrases separately and let the kids match them.
- Example: Match “cake” with “delicious and moist.”
- Sentence Construction: Ask the kids to construct their own sentences using a given adjective phrase.
- Example: Use “amazingly fast” in a sentence.
These exercises not only make learning fun but also provide a practical understanding of how adjective phrases work.
How to Use Adjective Phrases? – Step by Step Guide
Adjective phrases can add depth, detail, and clarity to your sentences. They not only make your writing more engaging but also elevate its quality. Here’s a step-by-step guide to using adjective phrases effectively:
- Identify the Target Noun: Know the noun you want to describe.
- Example: Car
- Select the Adjective: Choose the adjective that best describes the noun.
- Example: Expensive
- Expand the Adjective: Turn your chosen adjective into an adjective phrase by adding other words to it.
- Example: Expensive to maintain
- Placement: Place the adjective phrase either before the noun as a pre-modifier or after a linking verb.
- Pre-modifier Example: An expensive to maintain car
- Post-modifier Example: The car is expensive to maintain
- Check for Clarity: Read the sentence to ensure it is clear and the adjective phrase is enhancing, not complicating, the noun’s meaning.
- Revise: Make any necessary changes for clarity or conciseness.
By carefully implementing these steps, you can master the art of using adjective phrases to make your sentences richer and more detailed.
Tips for Using Adjective Phrase
When using adjective phrases, there are some things you need to consider for effective implementation. Here are some tips:
- Be Concise: While adjective phrases add detail, too many words can make them cumbersome. Stick to what is necessary for clarity and impact.
- Order of Words: The sequence of words in an adjective phrase matters. Make sure the order is logical and easy to understand.
- Maintain Parallel Structure: When using multiple adjective phrases, try to maintain a parallel structure for ease of reading.
- Avoid Ambiguity: Make sure that it’s clear which noun the adjective phrase is modifying, especially in complex sentences with multiple nouns.
- Use Punctuation Wisely: In some cases, especially with longer adjective phrases, you may need to use commas or other punctuation marks for clarity.
- Check for Redundancies: Sometimes, the adjective phrase might repeat information already present in the sentence. Eliminate such redundancies to make your writing crisp.
- Be Consistent: Keep a consistent style and tone when incorporating adjective phrases into your writing.
These tips and the step-by-step guide above will ensure that you use adjective phrases in a manner that enhances your writing style and effectively communicates your message.
FAQs
How Do You Identify an Adjective in a Phrase?
To identify an adjective in a phrase, look for a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives in phrases give more information about an object’s qualities, such as its color, size, shape, or condition. The key adjective often comes before the noun it modifies and can be part of a longer phrase that provides additional detail.
What is an Example of an Adjective Phrase Head?
An example of an adjective phrase head is the word “beautiful” in the phrase “beautifully decorated cake.” Here, “beautiful” is the head adjective that describes the cake, and the phrase provides additional detail about the cake’s appearance.
What is an Adjective for Kids?
An adjective for kids is a describing word that tells us more about a noun. It can describe color, size, shape, or how many. For example, in “big red ball,” “big” and “red” are adjectives that tell us about the ball’s size and color.
How Do You Put Adjective Phrases in the Sentence?
Adjective phrases are placed directly before or after the noun they modify. When placed before, they usually describe qualities or attributes. When after, they often start with a preposition or a verb. For example, “The cat with white paws slept peacefully” places the adjective phrase after the noun.
What Are the Rules of Adjective Phrase?
The rules of adjective phrase include:
- An adjective phrase must modify a noun or pronoun.
- It can be placed before or after the noun it modifies.
- If the phrase is before the noun, it usually directly describes it. If it’s after, it might begin with a preposition or an infinitive.
- The head of an adjective phrase is an adjective.
What is an Adjective Phrase or an Adverb Phrase?
An adjective phrase modifies a noun or pronoun by describing it, while an adverb phrase modifies verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs by answering how, when, where, or to what extent. For example, “The dog with a loud bark” uses an adjective phrase, and “He runs incredibly fast” uses an adverb phrase.