50+ Antonym Examples
An Antonym is a term that signifies the opposite of another word. For instance, “hot” is the antonym of “cold,” while “happy” contrasts with “sad.” Understanding antonyms enriches vocabulary by highlighting contrasts, thereby deepening language comprehension.
What is an Antonym?
An antonym is a word that has the opposite meaning of another word. For example, “hot” is an antonym of “cold,” and “happy” is an antonym of “sad.” Antonyms are important in vocabulary because they provide contrast and help to expand our understanding of language.
List of Antonyms
Here’s a list of antonyms:
- Absent – Present
- Big – Small
- Cold – Hot
- Day – Night
- Empty – Full
- Fast – Slow
- Good – Bad
- Happy – Sad
- In – Out
- Join – Separate
- Kind – Mean
- Light – Dark
- More – Less
- Near – Far
- Old – New
- Positive – Negative
- Question – Answer
- Right – Left
- Start – Finish
- Tall – Short
- Up – Down
- Visible – Invisible
- Win – Lose
- Expand – Contract
- Yes – No
- Zero – Nonexistent
Importance of Antonyms
Antonyms play a crucial role in vocabulary development for several reasons:
1.Contrast and Clarity: Antonyms provide contrast, helping to clarify meanings by showing opposite concepts. Understanding antonyms enhances comprehension and communication by offering clear distinctions between words with opposing meanings.
2.Nuanced Expression: Antonyms allow for nuanced expression, enabling speakers and writers to convey subtleties in meaning. By using antonyms, individuals can express shades of emotion, degrees of intensity, and variations in context more precisely.
3.Vocabulary Expansion: Learning antonyms expands vocabulary by introducing new words and concepts. By understanding the opposite of a word, individuals gain insight into related terms and broaden their lexical knowledge, enriching their language proficiency.
4.Critical Thinking: Recognizing antonyms fosters critical thinking skills by prompting individuals to analyze relationships between words and concepts. It encourages deeper reflection on language use and enhances linguistic awareness, leading to more effective communication.
5.Writing and Speaking Skills: Antonyms enhance writing and speaking skills by offering alternatives and enhancing language variety. They enable individuals to choose words that best convey their intended meaning and create engaging, dynamic expression.
6.Contextual Understanding: Antonyms aid in understanding context by providing clues about word meanings within sentences, paragraphs, or texts. Recognizing antonyms helps readers decipher unfamiliar words and comprehend texts more effectively.
Difference between synonyms and antonyms
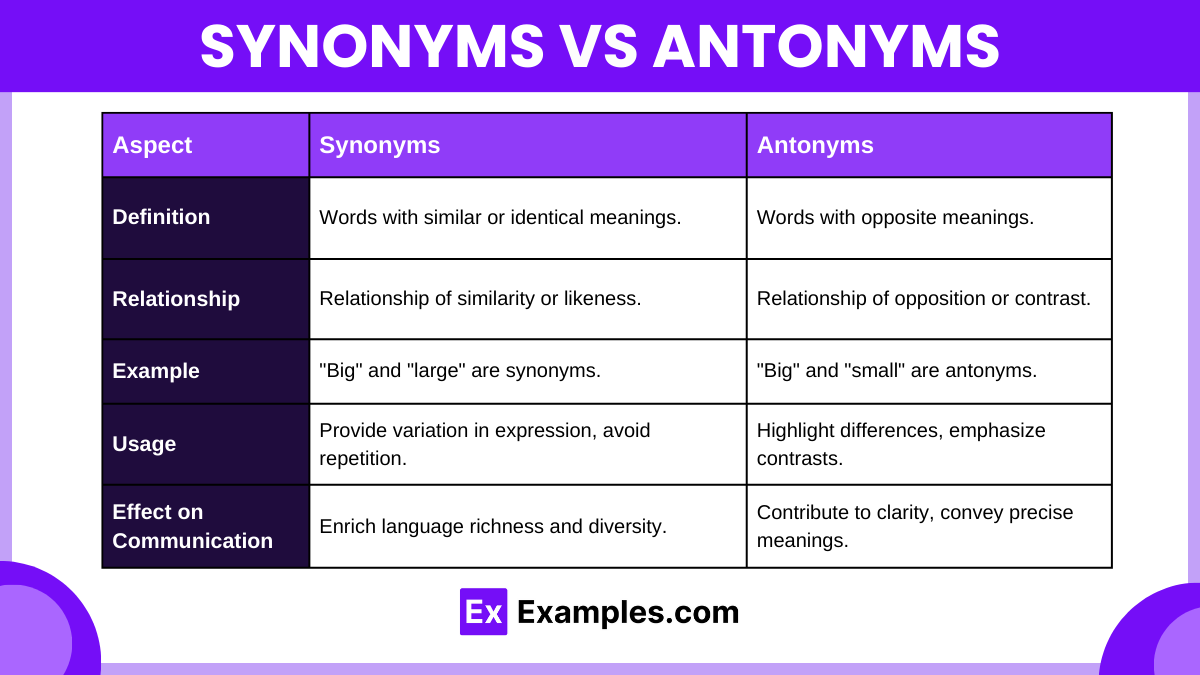
| Aspect | Synonyms | Antonyms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Words with similar or identical meanings. | Words with opposite meanings. |
| Relationship | Relationship of similarity or likeness. | Relationship of opposition or contrast. |
| Example | “Big” and “large” are synonyms. | “Big” and “small” are antonyms. |
| Usage | Provide variation in expression, avoid repetition. | Highlight differences, emphasize contrasts. |
| Effect on Communication | Enrich language richness and diversity. | Contribute to clarity, convey precise meanings. |
- Meaning:
- Synonyms: Synonyms are words that have similar or identical meanings. They represent different ways of expressing the same concept or idea.
- Antonyms: Antonyms are words that have opposite meanings. They represent contrasting concepts or ideas.
- Relationship:
- Synonyms: Synonyms share a relationship of similarity or likeness. They can be substituted for each other in a sentence without significantly changing the meaning.
- Antonyms: Antonyms share a relationship of opposition or contrast. They represent opposing concepts or ideas that are different in meaning.
- Example:
- Synonyms: For example, “big” and “large” are synonyms because they both refer to something of considerable size.
- Antonyms: For example, “big” and “small” are antonyms because they represent opposite ends of the size spectrum.
- Usage:
- Synonyms: Synonyms are often used to avoid repetition in writing or to provide variation in expression. They contribute to language richness and diversity.
- Antonyms: Antonyms are used to highlight differences or contrasts between concepts. They are useful for emphasizing distinctions and clarifying meanings.
- Effect on Communication:
- Synonyms: Synonyms can enhance communication by providing alternative words with similar meanings, adding nuance and depth to language.
- Antonyms: Antonyms contribute to clarity in communication by contrasting ideas or concepts, helping to convey precise meanings and facilitating comprehension.
50 Antonyms
- Hot – Cold
- Fast – Slow
- High – Low
- Big – Small
- Happy – Sad
- Light – Dark
- Strong – Weak
- Loud – Quiet
- Brave – Cowardly
- Beautiful – Ugly
- Good – Bad
- Positive – Negative
- Rich – Poor
- Full – Empty
- Love – Hate
- Up – Down
- Day – Night
- Win – Lose
- True – False
- Easy – Difficult
- Young – Old
- Right – Wrong
- Clean – Dirty
- Inside – Outside
- Open – Closed
- Friend – Enemy
- Happy – Unhappy
- Brave – Fearful
- Healthy – Sick
- Forward – Backward
- Safe – Dangerous
- Hard – Soft
- Dry – Wet
- Innocent – Guilty
- Loud – Soft
- Shallow – Deep
- Straight – Crooked
- Start – Finish
- Narrow – Wide
- Success – Failure
- Fresh – Stale
- Far – Near
- Above – Below
- Buy – Sell
- Light – Heavy
- True – Fake
- Warm – Cool
- Empty – Full
- Give – Take
- Careful – Careless
Examples of Antonyms in a Sentences
- It was a scorching day, but the evening breeze brought a welcome relief, turning the air from hot to cold.
- She ran fast to catch the bus, but her brother preferred to walk slowly and enjoy the scenery.
- The price of the house was high, but the apartment next door was much more affordable, with a low monthly rent.
- The big elephant trumpeted loudly, while the small mouse scurried silently across the floor.
- Sarah felt happy when she received good news, but she couldn’t help feeling sad when she heard about the accident.
- As the sun set, the sky turned from light blue to dark purple, signaling the end of the day.
- His strong grip made it easy to carry the heavy boxes, while her weak arms struggled to lift even the smallest ones.
- The concert was so loud that she had to cover her ears, but the library was quiet, with only the sound of turning pages.
- Despite his fears, he summoned the courage to speak up, while his cowardly friend remained silent in the corner.
- The garden was filled with beautiful flowers of all colors, but the weeds growing nearby looked ugly and unkempt.
FAQs
What are types of antonyms?
The types of antonyms include gradable, complementary, relational, directional, and converse antonyms, each representing different relationships between words.
Are there any resources available for learning antonyms?
Yes, there are various online resources, including dictionaries, vocabulary-building websites, and educational materials specifically focused on antonyms.
How can I improve my understanding of antonyms?
Practice identifying antonyms in context, explore different types of antonyms, and use them actively in writing and speech to become more proficient in understanding and using them.