19+ Language Barriers to Communication Examples
In the realm of effective communication, Language barriers stand as significant obstacles, often hindering the flow of information and understanding. This comprehensive guide delves into the various facets of these barriers, exploring their impact and offering practical solutions. From workplaces to personal interactions, understanding and addressing Language barriers to Communication is crucial for fostering clearer, more productive dialogues.
What are Language Barriers to Communication?

Language barriers to Communication refer to the challenges and misunderstandings that arise when individuals or groups do not share a common language or have varying levels of proficiency. These barriers can lead to misinterpretation, confusion, and even conflict. Understanding these barriers is key to improving interactions in diverse settings, from global business to multicultural communities.
What is the Best Example of Language Barriers to Communication?

A prime example of Language barriers to Communication is a business meeting between people from different countries where each participant speaks a different native language. The lack of a common linguistic ground can result in miscommunications, missed nuances, and potential misunderstandings, highlighting the need for effective translation or interpretation services in such scenarios.
20 Examples of Language Barriers to Communication

Language barriers in communication can manifest in various forms, significantly impacting the effectiveness of interactions. This guide presents 20 unique and distinct examples, each accompanied by a brief explanation and sample sentences, demonstrating how these barriers occur and can be navigated in real-world scenarios. Understanding these examples is crucial for identifying and addressing Language barriers to Communication to ensure clear and effective exchanges.
- Misinterpretation of Accents: Different accents can lead to misunderstandings.
Example: “Can you repeat that, please? I’m not familiar with your accent.” - Technical Jargon in a Business Meeting: Specialized language can alienate non-experts.
Example: “Let’s use simpler terms to ensure everyone understands the financial concepts.” - Grammar Misunderstandings in Emails: Incorrect grammar can change the message’s meaning.
Example: “Could you clarify what you meant in your last email?” - Difficulty in Understanding Fast Speech: Rapid speech can be hard to follow.
Example: “Please speak more slowly; I’m having trouble keeping up.” - Using Slang in a Multicultural Classroom: Slang can confuse non-native speakers.
Example: “I’ll explain the slang terms so everyone can follow the lecture.” - Cultural Misinterpretations in Marketing: Cultural nuances can lead to misinterpretation.
Example: “This phrase might not resonate the same way in a different culture.” - Language Differences in International Conferences: Language barriers can hinder global understanding.
Example: “Let’s provide translation services for all attendees.” - Miscommunication in Healthcare Settings: Medical terms can be confusing.
Example: “Let me explain your diagnosis in simpler terms.” - Language Barrier in Customer Service: Misunderstandings can lead to customer dissatisfaction.
Example: “Could you explain your concern again? I want to make sure I understand.” - Different Interpretations of Legal Language: Legal jargon can be misinterpreted.
Example: “I’ll break down the legal terms into simpler language for clarity.” - Language Barrier in Online Education: Lack of face-to-face interaction can exacerbate misunderstandings.
Example: “Please let me know if any part of the lesson was unclear.” - Translation Errors in Manuals: Poor translations can lead to incorrect usage.
Example: “This manual’s translation is confusing; let’s find a more accurate version.” - Misunderstanding of Colloquial Phrases: Colloquialisms can be confusing to non-natives.
Example: “This colloquial phrase means…” - Communication Issues in Multilingual Teams: Multiple languages can lead to fragmentation.
Example: “Let’s summarize key points in everyone’s language for clarity.” - Ineffective Communication Due to Low Language Proficiency: Limited language skills can hinder expression.
Example: “Let’s use visual aids to help bridge the language gap.” - Cultural Assumptions in Business Negotiations: Cultural misunderstandings can impact negotiations.
Example: “In my culture, this gesture means…” - Use of Idioms in International Diplomacy: Idioms can be misinterpreted.
Example: “This idiom is a metaphor for…” - Language Misunderstandings in Tourist Interactions: Tourists and locals often face language barriers.
Example: “Can you show me on the map? I don’t understand the directions.” - Language Constraints in Scientific Research Collaboration: Scientific terms can vary internationally.
Example: “Let’s define our scientific terms to avoid confusion.” - Non-verbal Miscommunication Across Cultures: Non-verbal cues can have different meanings.
Example: “In my culture, this gesture is seen as respectful.”
Addressing these examples of Language barriers to Communication through clear, patient, and empathetic dialogue is key to improving mutual understanding and collaboration.
Types of Language Barriers to Communication
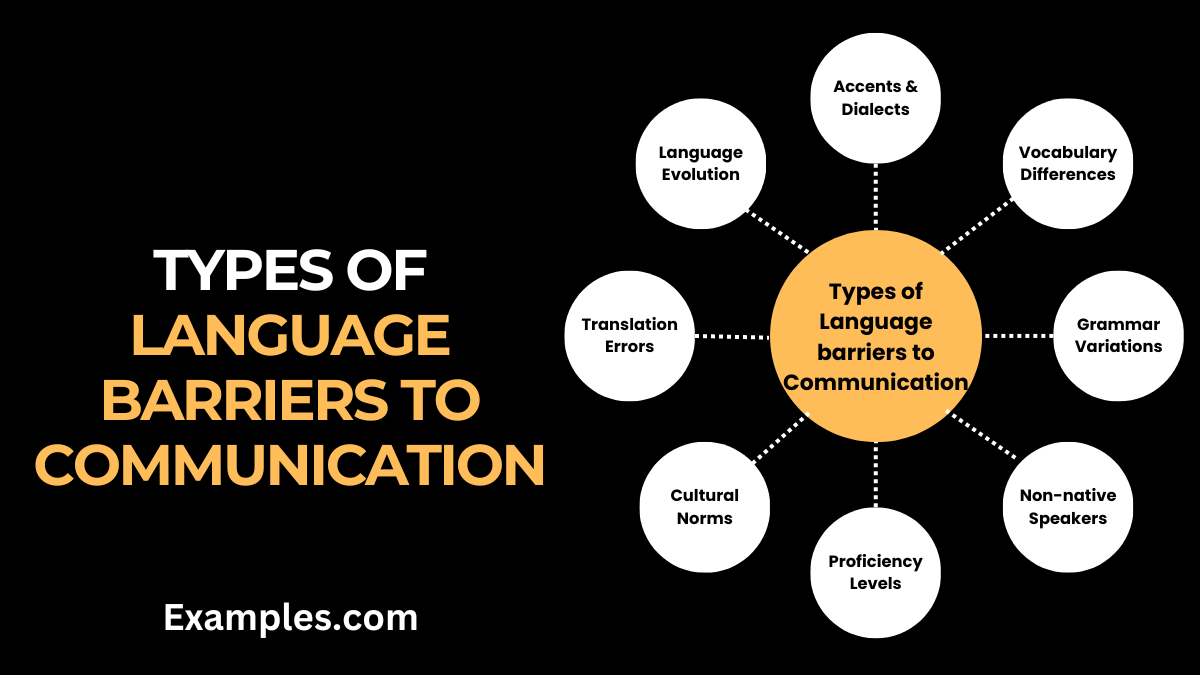
Language barriers in communication are diverse and can impact interactions significantly. This section explores the various types of these barriers, offering insights into their nature and effects.
- Accents and Dialects: Different accents or dialects can lead to misunderstandings, even among speakers of the same language.
- Vocabulary Differences: Specific jargon or technical language can create barriers in understanding.
- Grammar and Syntax Variations: Discrepancies in grammar and syntax between languages can lead to confusion.
- Non-native Speakers: Challenges faced by non-native speakers in comprehending or expressing ideas clearly.
- Language Proficiency Levels: Varied proficiency levels among communicators can hinder effective exchange.
- Cultural Language Norms: Cultural differences in communication styles and norms can create barriers.
- Translation and Interpretation Errors: Misinterpretations or inaccuracies in translation.
- Language Evolution and Slang: The evolution of language and use of slang can alienate certain groups.
How to Overcome Language Barriers to Communication
Overcoming language barriers requires strategic approaches and an understanding of the complexities involved. Here are some effective strategies:
- Use Clear and Simple Language: Avoid jargon and complex vocabulary for clarity.
- Employ Translation Services: Utilize professional translation and interpretation services.
- Cultural Sensitivity Training: Educate individuals about different cultural communication norms.
- Language Learning: Encourage learning basic phrases or languages of others.
- Visual Aids: Use visual communication tools to support understanding.
- Active Listening: Practice active listening to ensure comprehension.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implement feedback loops to confirm understanding.
- Patience and Empathy: Show patience and empathy towards non-native speakers.
Tips to Improve Language Barriers to Communication
Improving communication across language barriers is crucial for effective interaction. Here are some practical tips:
- Regular Language Practice: Regular practice can enhance language proficiency.
- Cultural Exchange Programs: Participate in cultural exchanges to understand different communication styles.
- Technology Use: Leverage language translation apps and tools.
- Body Language and Non-Verbal Cues: Utilize body language effectively to aid communication.
- Professional Development Workshops: Attend workshops focusing on cross-cultural communication.
- Peer-to-Peer Learning: Engage in language exchange with peers.
- Clarity in Speech and Writing: Be clear and concise in both verbal and written communication.
- Encourage Open Dialogue: Create an environment where language barriers can be openly discussed and addressed.
Understanding and addressing Language barriers to Communication is essential in our increasingly interconnected world. By recognizing the various types of barriers, employing strategies to overcome them, and following tips to improve communication, we can foster more inclusive and effective interactions across diverse linguistic landscapes. This guide offers a comprehensive approach to navigating and enhancing communication in the presence of language barriers.
19+ Language Barriers to Communication Examples
In the realm of effective communication, Language barriers stand as significant obstacles, often hindering the flow of information and understanding. This comprehensive guide delves into the various facets of these barriers, exploring their impact and offering practical solutions. From workplaces to personal interactions, understanding and addressing Language barriers to Communication is crucial for fostering clearer, more productive dialogues.
What are Language Barriers to Communication?

Language barriers to Communication refer to the challenges and misunderstandings that arise when individuals or groups do not share a common language or have varying levels of proficiency. These barriers can lead to misinterpretation, confusion, and even conflict. Understanding these barriers is key to improving interactions in diverse settings, from global business to multicultural communities.
What is the Best Example of Language Barriers to Communication?

A prime example of Language barriers to Communication is a business meeting between people from different countries where each participant speaks a different native language. The lack of a common linguistic ground can result in miscommunications, missed nuances, and potential misunderstandings, highlighting the need for effective translation or interpretation services in such scenarios.
20 Examples of Language Barriers to Communication

Language barriers in communication can manifest in various forms, significantly impacting the effectiveness of interactions. This guide presents 20 unique and distinct examples, each accompanied by a brief explanation and sample sentences, demonstrating how these barriers occur and can be navigated in real-world scenarios. Understanding these examples is crucial for identifying and addressing Language barriers to Communication to ensure clear and effective exchanges.
Misinterpretation of Accents: Different accents can lead to misunderstandings.
Example: “Can you repeat that, please? I’m not familiar with your accent.”Technical Jargon in a Business Meeting: Specialized language can alienate non-experts.
Example: “Let’s use simpler terms to ensure everyone understands the financial concepts.”Grammar Misunderstandings in Emails: Incorrect grammar can change the message’s meaning.
Example: “Could you clarify what you meant in your last email?”Difficulty in Understanding Fast Speech: Rapid speech can be hard to follow.
Example: “Please speak more slowly; I’m having trouble keeping up.”Using Slang in a Multicultural Classroom: Slang can confuse non-native speakers.
Example: “I’ll explain the slang terms so everyone can follow the lecture.”Cultural Misinterpretations in Marketing: Cultural nuances can lead to misinterpretation.
Example: “This phrase might not resonate the same way in a different culture.”Language Differences in International Conferences: Language barriers can hinder global understanding.
Example: “Let’s provide translation services for all attendees.”Miscommunication in Healthcare Settings: Medical terms can be confusing.
Example: “Let me explain your diagnosis in simpler terms.”Language Barrier in Customer Service: Misunderstandings can lead to customer dissatisfaction.
Example: “Could you explain your concern again? I want to make sure I understand.”Different Interpretations of Legal Language: Legal jargon can be misinterpreted.
Example: “I’ll break down the legal terms into simpler language for clarity.”Language Barrier in Online Education: Lack of face-to-face interaction can exacerbate misunderstandings.
Example: “Please let me know if any part of the lesson was unclear.”Translation Errors in Manuals: Poor translations can lead to incorrect usage.
Example: “This manual’s translation is confusing; let’s find a more accurate version.”Misunderstanding of Colloquial Phrases: Colloquialisms can be confusing to non-natives.
Example: “This colloquial phrase means…”Communication Issues in Multilingual Teams: Multiple languages can lead to fragmentation.
Example: “Let’s summarize key points in everyone’s language for clarity.”Ineffective Communication Due to Low Language Proficiency: Limited language skills can hinder expression.
Example: “Let’s use visual aids to help bridge the language gap.”Cultural Assumptions in Business Negotiations: Cultural misunderstandings can impact negotiations.
Example: “In my culture, this gesture means…”Use of Idioms in International Diplomacy: Idioms can be misinterpreted.
Example: “This idiom is a metaphor for…”Language Misunderstandings in Tourist Interactions: Tourists and locals often face language barriers.
Example: “Can you show me on the map? I don’t understand the directions.”Language Constraints in Scientific Research Collaboration: Scientific terms can vary internationally.
Example: “Let’s define our scientific terms to avoid confusion.”Non-verbal Miscommunication Across Cultures: Non-verbal cues can have different meanings.
Example: “In my culture, this gesture is seen as respectful.”
Addressing these examples of Language barriers to Communication through clear, patient, and empathetic dialogue is key to improving mutual understanding and collaboration.
Types of Language Barriers to Communication

Language barriers in communication are diverse and can impact interactions significantly. This section explores the various types of these barriers, offering insights into their nature and effects.
Accents and Dialects: Different accents or dialects can lead to misunderstandings, even among speakers of the same language.
Vocabulary Differences: Specific jargon or technical language can create barriers in understanding.
Grammar and Syntax Variations: Discrepancies in grammar and syntax between languages can lead to confusion.
Non-native Speakers: Challenges faced by non-native speakers in comprehending or expressing ideas clearly.
Language Proficiency Levels: Varied proficiency levels among communicators can hinder effective exchange.
Cultural Language Norms: Cultural differences in communication styles and norms can create barriers.
Translation and Interpretation Errors: Misinterpretations or inaccuracies in translation.
Language Evolution and Slang: The evolution of language and use of slang can alienate certain groups.
How to Overcome Language Barriers to Communication
Overcoming language barriers requires strategic approaches and an understanding of the complexities involved. Here are some effective strategies:
Use Clear and Simple Language: Avoid jargon and complex vocabulary for clarity.
Employ Translation Services: Utilize professional translation and interpretation services.
Cultural Sensitivity Training: Educate individuals about different cultural communication norms.
Language Learning: Encourage learning basic phrases or languages of others.
Visual Aids: Use visual communication tools to support understanding.
Active Listening: Practice active listening to ensure comprehension.
Feedback Mechanisms: Implement feedback loops to confirm understanding.
Patience and Empathy: Show patience and empathy towards non-native speakers.
Tips to Improve Language Barriers to Communication
Improving communication across language barriers is crucial for effective interaction. Here are some practical tips:
Regular Language Practice: Regular practice can enhance language proficiency.
Cultural Exchange Programs: Participate in cultural exchanges to understand different communication styles.
Technology Use: Leverage language translation apps and tools.
Body Language and Non-Verbal Cues: Utilize body language effectively to aid communication.
Professional Development Workshops: Attend workshops focusing on cross-cultural communication.
Peer-to-Peer Learning: Engage in language exchange with peers.
Clarity in Speech and Writing: Be clear and concise in both verbal and written communication.
Encourage Open Dialogue: Create an environment where language barriers can be openly discussed and addressed.
Understanding and addressing Language barriers to Communication is essential in our increasingly interconnected world. By recognizing the various types of barriers, employing strategies to overcome them, and following tips to improve communication, we can foster more inclusive and effective interactions across diverse linguistic landscapes. This guide offers a comprehensive approach to navigating and enhancing communication in the presence of language barriers.


