Interpersonal Communication vs Intrapersonal Communication
Embark on a journey into the realms of Interpersonal Communication vs Intrapersonal Communication with our comprehensive guide. Gain insights into the intricacies of human interaction and self-reflection through illuminating examples. Explore the fascinating world of communication instances, unraveling the interconnected web of relationships and internal dialogues that shape our daily lives. This guide provides a holistic perspective on effective communication, offering valuable insights into both interpersonal and intrapersonal dynamics.
Difference between Interpersonal Communication and Intrapersonal Communication?
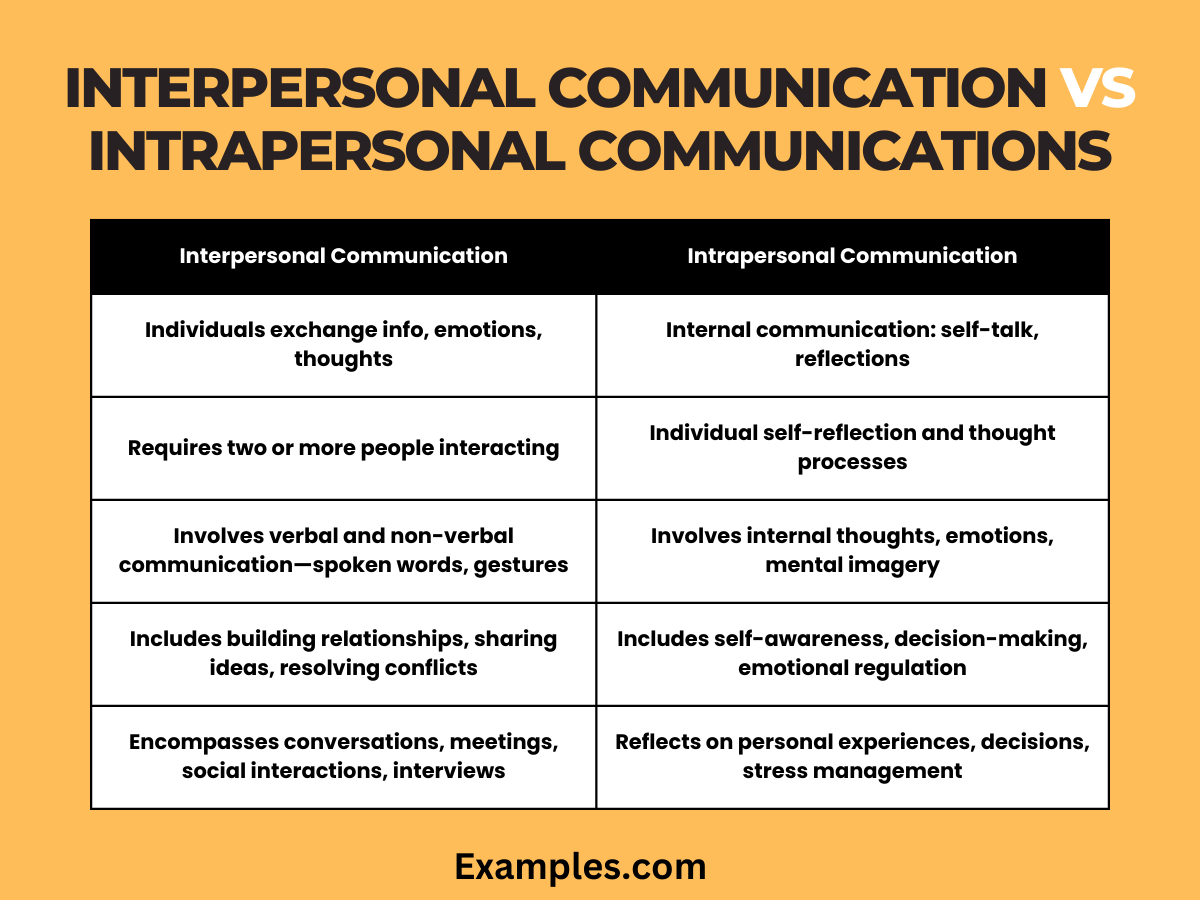
Communication is a multifaceted concept, and two crucial dimensions are Interpersonal and Intrapersonal Communication. Let’s break down the distinctions between these two forms in a comprehensive table:
| Criteria | Interpersonal Communication | Intrapersonal Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Communication between individuals, involving exchange of information, emotions, and thoughts. | Communication that occurs within an individual’s own mind, involving self-talk and internal dialogues. |
| Participants | Involves at least two people interacting with each other. | Involves a single individual engaging in self-reflection and internal thought processes. |
| Channels | Verbal and non-verbal communication, including spoken words, gestures, and body language. | Internal thoughts, emotions, and mental imagery. |
| Purpose | Building relationships, sharing ideas, resolving conflicts, and expressing emotions. | Self-awareness, decision-making, problem-solving, and emotional regulation. |
| Examples | Conversations, meetings, social interactions, and interviews. | Reflecting on personal experiences, decision-making processes, and managing stress. |
| Feedback | Immediate, as it involves real-time interaction and responses. | Internal, often based on personal reflection and introspection. |
| Impact on Others | Directly influences the perceptions and emotions of the other person involved. | Indirectly influences interpersonal interactions by shaping one’s behavior and responses. |
| Skills Emphasized | Listening, empathy, verbal and non-verbal expression, and conflict resolution. | Self-awareness, critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and decision-making. |
| Context | Social and external environments play a significant role in shaping communication. | Primarily influenced by internal thoughts, emotions, and personal experiences. |
| Examples in Daily Life | Casual conversations, team meetings, social gatherings, and romantic relationships. | Reflecting on personal goals, analyzing experiences, and managing one’s emotional well-being. |
Understanding these distinctions provides a foundation for navigating the diverse landscape of communication, contributing to more effective interpersonal connections and enhanced self-awareness.
10 Examples of Interpersonal Communication
Explore the essence of interpersonal communication with these 10 compelling examples, showcasing the richness of human interaction. From verbal exchanges to subtle non-verbal cues, these instances encapsulate the diversity of interpersonal connections. Enhance your understanding of effective communication through these real-world scenarios, each illustrating the power of interpersonal dynamics.
- Expressing Empathy: In a challenging situation, a friend expresses genuine concern, saying, “I understand how you feel; I’m here for you.”
- Active Listening: During a conversation, someone engages in active listening by nodding, maintaining eye contact, and responding thoughtfully to the speaker.
- Conflict Resolution: In a team meeting, coworkers address a disagreement diplomatically, finding a compromise that benefits everyone.
- Constructive Feedback: A manager provides constructive feedback to an employee, highlighting strengths and suggesting areas for improvement.
- Non-Verbal Affirmation: In a relationship, partners exchange affectionate glances and smiles, conveying love and connection without words.
- Effective Questioning: During an interview, the interviewer asks open-ended questions to elicit detailed responses from the candidate.
- Cultural Sensitivity: In a diverse group, individuals demonstrate cultural sensitivity by respecting and appreciating each other’s traditions and perspectives.
- Negotiation Skills: In a business negotiation, parties skillfully navigate differences, reaching a mutually beneficial agreement.
- Expressing Gratitude: A colleague shows appreciation by saying, “Thank you for your hard work; it made a significant impact on the project.”
- Team Collaboration: In a collaborative project, team members communicate seamlessly, leveraging each other’s strengths for a successful outcome.
10 Examples of Intrapersonal Communication
Delve into the realm of intrapersonal communication with these 10 illuminating examples, illustrating the art of self-reflection and internal dialogue. From decision-making processes to managing emotions, these instances highlight the significance of effective intrapersonal communication in personal growth and well-being. Explore the internal conversations that shape thoughts, actions, and individual experiences, contributing to enhanced self-awareness and empowerment.
- Positive Self-Affirmation: Facing a challenge, an individual boosts confidence through positive self-talk, saying, “I can overcome this; I am resilient.”
- Goal Setting: Intrapersonal communication drives goal-setting, as someone internally plans steps towards personal or professional achievements.
- Critical Self-Reflection: After a presentation, a professional engages in critical self-reflection, assessing strengths and areas for improvement.
- Managing Stress: Amidst stress, an individual practices intrapersonal communication by calming internal thoughts through deep breathing and positive affirmations.
- Decision-Making Process: Facing a career choice, someone navigates the decision-making process by weighing pros and cons in internal deliberations.
- Creative Visualization: An artist uses intrapersonal communication to visualize and plan artistic creations before translating them into reality.
- Emotional Regulation: In response to a challenging situation, an individual regulates emotions through internal dialogue, fostering emotional resilience.
- Self-Motivation: Confronting a task, someone internally motivates themselves with thoughts like, “I can do this; the effort is worthwhile.”
- Mindfulness Practices: Engaging in mindfulness, an individual communicates with themselves, focusing on the present moment and fostering mental clarity.
- Personal Growth Reflection: Periodically, an individual reflects on personal growth, acknowledging achievements and setting new milestones for continuous improvement.
Comparison between Interpersonal Communication and Intrapersonal Communication
Embark on a nuanced exploration of the distinctions between Interpersonal Communication and Intrapersonal Communication through this comprehensive point-by-point guide:
1. Nature of Interaction:
- Interpersonal Communication: Involves direct interaction between two or more individuals, fostering personal connections.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Focuses on self-talk and internal dialogue, involving communication within an individual’s own mind.
2. Participants and Dynamics:
- Interpersonal Communication: Engages multiple participants, allowing for the exchange of thoughts, emotions, and information in a shared space.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Involves a solitary participant, emphasizing self-reflection, internal processing, and individual cognitive processes.
3. Emphasis on Relationships:
- Interpersonal Communication: Emphasizes building and maintaining relationships, considering the feelings, perspectives, and interactions between individuals.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Focuses on self-awareness, personal reflection, and understanding one’s own thoughts, emotions, and motivations.
4. Communication Channels:
- Interpersonal Communication: Utilizes various channels such as face-to-face interactions, calls, and personalized messages.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Primarily occurs through internal dialogue, thoughts, and reflective processes within an individual’s mind.
5. Objectives and Purpose:
- Interpersonal Communication: Primarily focused on building relationships, sharing emotions, resolving conflicts, and fostering connections.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Aims to enhance self-awareness, clarify thoughts, manage emotions, and engage in internal problem-solving and decision-making.
6. Feedback Dynamics:
- Interpersonal Communication: Involves immediate and personalized feedback, allowing for real-time adjustments based on verbal and non-verbal cues.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Feedback is internal and reflective, involving self-assessment, introspection, and personal insights without immediate external cues.
7. Role of Non-Verbal Cues:
- Interpersonal Communication: Non-verbal cues like body language and facial expressions play a significant role in conveying emotions and messages.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Relies more on internal non-verbal cues, such as mental imagery, self-expression, and the interpretation of one’s own emotional responses.
8. Context and Adaptability:
- Interpersonal Communication: Highly influenced by the relational context, considering the history and dynamics between individuals.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Context is self-contained, adapting to the individual’s unique internal experiences, thoughts, and emotions.
9. Daily Life Scenarios:
- Interpersonal Communication: Encompasses everyday conversations with friends, family, and colleagues, emphasizing personal bonds and shared experiences.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Occurs in moments of self-reflection, decision-making, problem-solving, and emotional processing during individual experiences.
10. Impact on Social Dynamics:
- Interpersonal Communication: Integral to social dynamics, shaping the quality of personal relationships and connections.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Influences personal well-being, self-development, and individual decision-making, contributing to overall mental and emotional health.
By unraveling the dimensions of interpersonal and intrapersonal communication, individuals gain insights into how they engage with others and themselves, fostering meaningful connections and personal growth.
Relationship between Interpersonal Communication and Intrapersonal Communication
Embark on a comprehensive exploration of the intricate relationship between Interpersonal Communication and Intrapersonal Communication through this detailed point-by-point guide:
1. Focused Participants:
- Interpersonal Communication: Involves direct interaction between two or more individuals, fostering personal connections and shared experiences.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Centrally involves a solitary participant, emphasizing internal dialogue and self-reflection within an individual’s mind.
2. Dynamic Interactions:
- Interpersonal Communication: Engages participants in dynamic exchanges, allowing for the flow of thoughts, emotions, and information in real-time.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Encourages internal dialogue, self-reflection, and the processing of thoughts and emotions in a more contemplative and individualized manner.
3. Relationship Emphasis:
- Interpersonal Communication: Places emphasis on building and maintaining relationships, considering the nuances of human connection and shared understanding.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Shifts the focus inward, promoting self-awareness, personal growth, and a deeper understanding of one’s own thoughts and emotions.
4. Channels of Communication:
- Interpersonal Communication: Utilizes various channels such as face-to-face interactions, calls, and personalized messages for expressive communication.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Primarily relies on internal channels, involving thoughts, self-talk, mental imagery, and the processing of emotions within the individual’s mind.
5. Objectives and Intent:
- Interpersonal Communication: Primarily geared towards building connections, sharing emotions, resolving conflicts, and fostering mutual understanding.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Aims to enhance self-awareness, clarify personal thoughts, manage emotions, and engage in internal problem-solving and decision-making.
6. Feedback Dynamics:
- Interpersonal Communication: Incorporates immediate and personalized feedback, allowing for real-time adjustments based on verbal and non-verbal cues.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Feedback is internal and reflective, involving self-assessment, introspection, and personal insights without external cues.
7. Non-Verbal Expression:
- Interpersonal Communication: Relies on non-verbal cues like body language and facial expressions to convey emotions and messages.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Engages internal non-verbal cues, such as mental imagery, self-expression, and the interpretation of one’s own emotional responses.
8. Adaptability to Context:
- Interpersonal Communication: Highly influenced by the relational context, considering the unique history and dynamics between individuals.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Adapts to the individual’s internal context, encompassing personal experiences, beliefs, and emotional responses.
9. Daily Life Scenarios:
- Interpersonal Communication: Encompasses everyday conversations with friends, family, and colleagues, shaping personal relationships and shared moments.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Manifests during moments of self-reflection, decision-making, and emotional processing, contributing to personal growth and well-being.
10. Impact on Dynamics:
- Interpersonal Communication: Integral to social dynamics, influencing the quality of personal relationships and connections within a broader social context.
- Intrapersonal Communication: Influences personal dynamics, contributing to individual well-being, self-development, and informed decision-making.
By navigating the realms of both interpersonal and intrapersonal communication, individuals can cultivate meaningful connections with others while also fostering a deeper understanding of themselves, promoting holistic well-being and personal growth.



