90+ Correlative Conjunctions Examples
In the realm of language and literature, there exists a multitude of tools that can transform simple sentences into captivating works of art. One such tool, often overlooked but highly influential, is the clever use of correlative conjunctions. These linguistic marvels have the power to connect ideas, emphasize relationships, and create a harmonious flow within a sentence. Unlock the secrets of correlative conjunctions and take your writing to new heights as we embark on this enlightening journey together.
What Is a Correlative Conjunction?
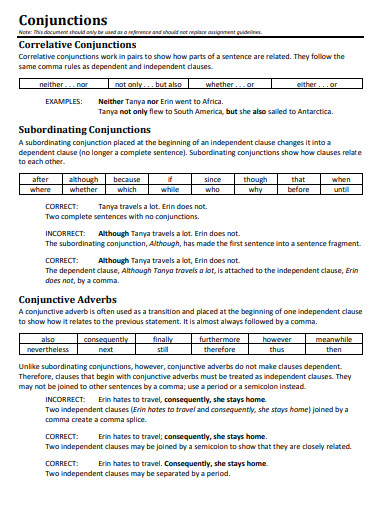
Correlative conjunctions are pairs of words that work together to link related elements within a sentence. Common pairs include “either…or,” “neither…nor,” “both…and,” and “not only…but also.” These conjunctions help create parallel structure, emphasizing the relationship between the connected elements and ensuring clarity and balance in writing.
Correlative Conjunctions Rules
1. Parallel Structure
When using correlative conjunctions, ensure that the elements they connect are grammatically parallel. This means that the same parts of speech or structures should follow each part of the conjunction pair.
Example:
- Correct: “She is not only smart but also hardworking.”
- Incorrect: “She is not only smart but also works hard.”
2. Subject-Verb Agreement
The subject and verb must agree in number, even when correlative conjunctions connect subjects.
Example:
- Correct: “Either the teacher or the students are responsible for the project.”
- Incorrect: “Either the teacher or the students is responsible for the project.”
3. Consistency
Ensure that both elements being connected by correlative conjunctions are consistent in meaning and structure to avoid confusion.
Example:
- Correct: “He is interested not only in football but also in basketball.”
- Incorrect: “He is interested not only in football but also basketball.”
4. Avoiding Double Negatives
When using “neither…nor,” avoid adding another negative in the sentence, as this can create a double negative.
Example:
- Correct: “She can neither dance nor sing.”
- Incorrect: “She can’t neither dance nor sing.”
5. Proper Pairing
Always use correlative conjunctions in pairs to maintain the relationship between the connected elements.
Example:
- Correct: “He likes both pizza and pasta.”
- Incorrect: “He likes both pizza.”
6. Clarity and Simplicity
Use correlative conjunctions to enhance clarity and simplicity in your writing. Avoid overcomplicating sentences by ensuring the connected elements are clear and straightforward.
Example:
- Correct: “She wants to travel either to Paris or to Rome.”
- Incorrect: “She wants to travel either to Paris or she would like to go to Rome.”
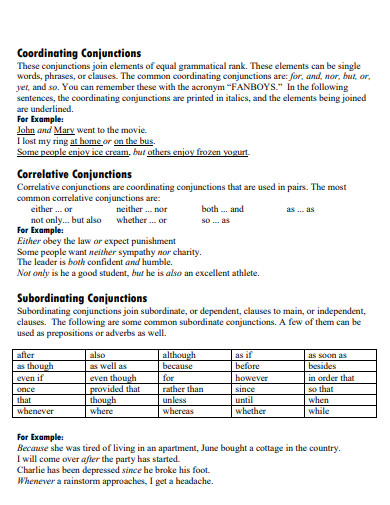
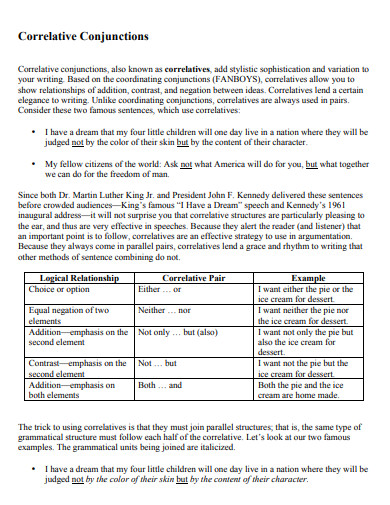
Correlative Conjunctions List
Correlative conjunctions are pairs of conjunctions that work together to connect equal parts of a sentence. Here is a list of common correlative conjunctions:
1. Either…or
- Used to present two alternatives or choices.
- Example: “You can either come with us or stay home.”
2. Neither…nor
- Used to negate two alternatives or choices.
- Example: “She likes neither tea nor coffee.”
3. Both…and
- Used to join two positive elements.
- Example: “He is both intelligent and hardworking.”
4. Not only…but also
- Used to emphasize that both elements are true or important.
- Example: “She is not only a great singer but also a talented dancer.”
5. Whether…or
- Used to express doubt or choice between alternatives.
- Example: “He didn’t know whether to laugh or cry.”
6. Such…that
- Used to show cause and effect.
- Example: “It was such a hot day that we decided to go swimming.”
7. No sooner…than
- Used to indicate that one event quickly follows another.
- Example: “No sooner had we arrived than it started to rain.”
8. As…as
- Used to compare the equality of two elements.
- Example: “She is as tall as her brother.”
9. So…that
- Used to show cause and effect.
- Example: “He was so tired that he fell asleep immediately.”
10. Just as…so
- Used to indicate that one thing is similar to another.
- Example: “Just as the sun rises in the east, so does it set in the west.”
11. Scarcely…when
- Used to indicate that one event quickly follows another.
- Example: “Scarcely had I finished my meal when the phone rang.”
12. The more…the more
- Used to show increasing or decreasing parallelism.
- Example: “The more you practice, the more you improve.”
Examples of Correlative Conjunctions:
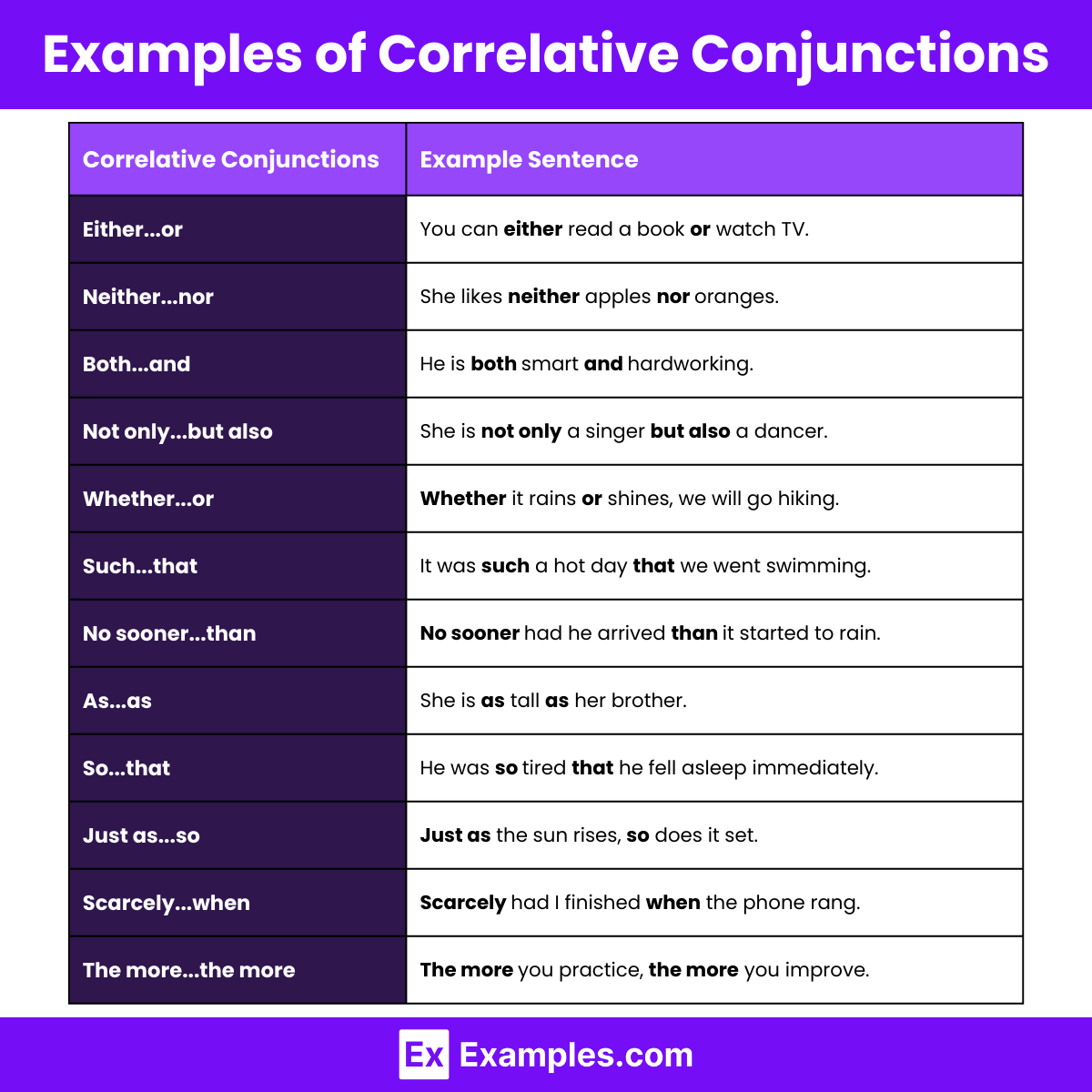
Correlative Conjunctions Examples Sentences
Here are examples of sentences using correlative conjunctions:
1. Either…or
- You can either come with us or stay home.
- Either she will call or she will email.
- He wants to either study law or become a doctor.
- Either you apologize or face the consequences.
2. Neither…nor
- She likes neither tea nor coffee.
- Neither John nor Mary was at the party.
- The movie was neither interesting nor entertaining.
- I have neither the time nor the patience for this.
3. Both…and
- He is both intelligent and hardworking.
- She enjoys both reading and writing.
- They visited both Paris and London.
- The project was both challenging and rewarding.
4. Not only…but also
- She is not only a great singer but also a talented dancer.
- He not only completed the task but also did it ahead of time.
- The book is not only informative but also entertaining.
- We visited not only the museum but also the art gallery.
5. Whether…or
- He didn’t know whether to laugh or cry.
- Whether you agree or disagree, we need to make a decision.
- She couldn’t decide whether to stay or leave.
- Whether it rains or shines, we will go hiking.
6. Such…that
- It was such a hot day that we decided to go swimming.
- She had such a good time that she didn’t want to leave.
- The lecture was such a bore that he fell asleep.
- He spoke such fluent French that everyone was impressed.
7. No sooner…than
- No sooner had we arrived than it started to rain.
- No sooner did he finish his speech than the audience applauded.
- No sooner was she seated than the meeting began.
- No sooner had the game begun than it started to rain.
8. As…as
- She is as tall as her brother.
- He can run as fast as a cheetah.
- The cake was as delicious as it looked.
- Her dress is as beautiful as the sunrise.
9. So…that
- He was so tired that he fell asleep immediately.
- She was so happy that she couldn’t stop smiling.
- The food was so spicy that it made me cry.
- The movie was so boring that we left early.
10. Just as…so
- Just as the sun rises in the east, so does it set in the west.
- Just as you sow, so shall you reap.
- Just as we plan carefully, so should we execute flawlessly.
- Just as she prepares thoroughly, so does she perform well.
11. Scarcely…when
- Scarcely had I finished my meal when the phone rang.
- Scarcely had she entered the room when she was asked to leave.
- Scarcely had he left when it started to rain.
- Scarcely had the movie started when the power went out.
12. The more…the more
- The more you practice, the more you improve.
- The more he talks, the more annoyed I get.
- The more we learn, the more we realize how little we know.
- The more she exercised, the more fit she became.
Correlative Conjunctions Examples Using “Whether…or”
- Whether you join us or not, the meeting will proceed as scheduled.
- She couldn’t decide whether to stay or to leave the party early.
- Whether he wins or loses, he always maintains a positive attitude.
- Whether it rains or shines, the festival will be held outdoors.
- You need to tell me whether you can come or if you need to reschedule.
- Whether we travel by car or by train, we need to leave early.
- They haven’t decided whether to buy a house or rent an apartment.
- Whether you believe it or not, it’s the truth.
- Whether we succeed or fail, we will have learned something valuable.
- Whether she likes it or not, she has to follow the rules.
Correlative Conjunctions Examples Using “Neither…nor”
- She likes neither tea nor coffee.
- Neither John nor Mary was at the party.
- The movie was neither interesting nor entertaining.
- I have neither the time nor the patience for this.
- Neither the manager nor the employees understood the new policy.
- He is neither rich nor famous.
- Neither the cat nor the dog was allowed in the house.
- They found neither the key nor the map.
- She is neither happy nor satisfied with her job.
- The solution is neither practical nor cost-effective.
Correlative Conjunctions Examples Using “Either…or”
- You can either come with us or stay home.
- Either she will call or she will email.
- He wants to either study law or become a doctor.
- Either you apologize or face the consequences.
- We can either go to the beach or visit the museum.
- Either he forgot or he ignored the instructions.
- You should either finish your homework or go to bed early.
- Either the manager or the assistant will attend the meeting.
- She needs to either change her attitude or leave the team.
- Either take the offer or look for another job.
Correlative Conjunctions Examples Using “Both…and”
- He is both intelligent and hardworking.
- She enjoys both reading and writing.
- They visited both Paris and London.
- The project was both challenging and rewarding.
- Both the teacher and the students were excited about the trip.
- The recipe is both simple and delicious.
- She speaks both English and Spanish fluently.
- Both the movie and the book were fantastic.
- He has both experience and enthusiasm for the job.
- Both the weather and the scenery were perfect for hiking.
More Correlative Conjunctions Templates & Examples:
1. Correlative Conjunctions Example
2. Correlative Conjunctions Template
3. Sample Correlative Conjunctions
4. Simple Correlative Conjunctions
5. Using Correlative Conjunctions
6. Correlative Conjunctions Definitions And Examples
7. Correlative Conjunctions Format
8. Basic Correlative Conjunctions
9. The Correlative Conjunctions
10. Correlative Conjunctions Worksheet
Functions of Correlative Conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions are pairs of conjunctions that work together to link related elements in a sentence, ensuring parallel structure and clarity. Here are the main functions of correlative conjunctions:
1. Connecting Two Equal Elements
Correlative conjunctions link two elements of equal grammatical importance, whether they are words, phrases, or clauses.
Example: “She is both smart and diligent.”
2. Providing Alternatives
They present two or more alternatives or choices, allowing the writer to show options clearly.
Example: “You can either come with us or stay home.”
3. Emphasizing Negation
Correlative conjunctions can be used to emphasize negation of both elements in a pair.
Example: “He likes neither apples nor oranges.”
4. Creating Parallel Structure
They ensure parallelism in sentences by making sure the connected elements are grammatically similar, enhancing readability and coherence.
Example: “She wants to not only visit Paris but also explore London.”
5. Showing Cause and Effect
Some correlative conjunctions are used to illustrate a cause-and-effect relationship between two elements.
Example: “It was such a hot day that we decided to go swimming.”
6. Indicating Comparisons
They can be used to make comparisons between two elements, often highlighting similarity or difference.
Example: “He is as tall as his brother.”
7. Adding Emphasis
Correlative conjunctions can add emphasis to both parts of the sentence, making the elements stand out more clearly.
Example: “She is not only a good teacher but also a great mentor.”
8. Expressing Condition
They can indicate conditions that depend on each other or present contrasting situations.
Example: “Whether you agree or not, we need to proceed.”
9. Illustrating Sequence
They help in showing sequences or immediate succession of events.
Example: “No sooner had he finished his meal than he left the table.”
10. Highlighting Intensity or Degree
Some correlative conjunctions express the intensity or degree of an action or quality.
Example: “The more he practiced, the better he became.”
What does a Correlative Conjunction do?
Correlative conjunctions are pairs of conjunctions that work together to connect equal elements in a sentence, ensuring balance and clarity. Here are the main functions of correlative conjunctions:
1. Link Equal Elements
Correlative conjunctions connect two words, phrases, or clauses of equal grammatical value, maintaining parallel structure and ensuring that both elements are treated with equal importance.
Example: “She is both intelligent and hardworking.”
2. Provide Alternatives or Choices
They present options or choices, clearly indicating that one or the other (or sometimes both) is possible.
Example: “You can either join us or stay home.”
3. Emphasize Negation
Correlative conjunctions can stress the negation of two alternatives, indicating that neither of the connected elements is true or applicable.
Example: “He likes neither tea nor coffee.”
4. Ensure Parallelism
They enforce grammatical parallelism, ensuring that the structure of the sentence is balanced and easier to read and understand.
Example: “She wants to not only visit Paris but also explore London.”
5. Highlight Cause and Effect
Some correlative conjunctions demonstrate a cause-and-effect relationship between two connected elements.
Example: “It was such a hot day that we decided to go swimming.”
6. Make Comparisons
Correlative conjunctions can compare two elements, showing similarities or differences.
Example: “He is as tall as his brother.”
7. Add Emphasis
They add emphasis to the connected elements, making them stand out more prominently in the sentence.
Example: “She is not only a good teacher but also a great mentor.”
8. Express Conditions
They can express conditions that depend on each other or contrast with each other.
Example: “Whether you agree or not, we need to proceed.”
9. Illustrate Sequence
They show the immediate succession of events or actions.
Example: “No sooner had he finished his meal than he left the table.”
10. Indicate Intensity or Degree
Some correlative conjunctions express the intensity or degree of an action or quality.
Example: “The more he practiced, the better he became.”
How to Use Correlative Conjunctions
Using correlative conjunctions requires finesse and a keen understanding of their various applications. Let’s delve into a step-by-step guide that will enable you to master the art of incorporating these conjunctions seamlessly into your writing.
Step 1: Identify the Appropriate Correlative Conjunction Pair:
Before diving into the depths of a sentence, identify the correlative conjunction pair that best suits your intention. Each pair carries its unique nuance, and selecting the appropriate one ensures precision and clarity.
Step 2: Establish Parallel Structure:
Correlative conjunctions thrive on parallel structure, where elements on either side of the conjunction mirror each other in form and function. This symmetry enhances readability and brings harmony to your sentence.
Step 3: Maintain Balance and Consistency:
When using correlative conjunctions, maintain balance and consistency in your sentence structure. This ensures equal weightage to both ideas and avoids any unintended biases or imbalances.
What are correlative conjunctions?
Correlative conjunctions are pairs of conjunctions that work together to connect equal elements in a sentence, ensuring balance and parallel structure. Examples include “either…or” and “neither…nor.”
Why use correlative conjunctions?
They provide clarity, emphasize relationships between elements, and ensure grammatical parallelism, making sentences more coherent and easier to read.
Can you give examples of correlative conjunctions?
Yes, common pairs include “either…or,” “neither…nor,” “both…and,” “not only…but also,” “whether…or,” and “such…that.”
How do correlative conjunctions ensure parallel structure?
They link grammatically equal elements, ensuring that both parts of the conjunction pair follow the same structure, which enhances readability and clarity.
What is the difference between coordinating and correlative conjunctions?
Coordinating conjunctions connect individual words or clauses of equal importance, while correlative conjunctions come in pairs to link related elements within sentences.
Can correlative conjunctions be used in complex sentences?
Yes, correlative conjunctions can link clauses, phrases, or words within complex sentences, maintaining balance and parallel structure.
How do you use “either…or”?
“Either…or” presents alternatives or choices. Example: “You can either come with us or stay home.”
How do you use “neither…nor”?
“Neither…nor” negates two alternatives. Example: “He likes neither tea nor coffee.”
What is the function of “not only…but also”?
It emphasizes that both elements are true or important. Example: “She is not only a great singer but also a talented dancer.”
Why is parallelism important in correlative conjunctions?
Parallelism ensures that the elements linked by correlative conjunctions are grammatically similar, enhancing the clarity, balance, and flow of the sentence.