15+ Expository Writing Examples
Expository writing is a fundamental skill that plays a pivotal role in education, professional communication, and everyday life. It’s the art of conveying information, explaining ideas, and providing a clear understanding of a particular topic or subject. Whether you’re a student working on an academic paper, a professional crafting a report, or someone keen on enhancing their writing skills, understanding the principles of expository writing is essential. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into what expository writing is, break down the steps to write an effective expository piece, address common questions, and help you master this crucial skill.
What is Expository Writing?
Expository writing is a form of writing that aims to explain, describe, or inform the reader about a specific topic. It presents facts, data, and logical explanations without the writer’s personal opinions. Common types include essays, articles, and reports. Effective expository writing is clear, concise, and well-organized, helping readers understand complex information easily.
To excel in expository writing, it’s essential to master elements like context, theme, tone, text structure, and citations, which collectively enhance the overall quality and credibility of your work.
Expository Writing Format
Understanding the structure of expository writing is crucial for creating clear and informative content. Here is a detailed format to follow:
1. Introduction
- Hook: Start with an interesting fact, quote, or question to grab the reader’s attention.
- Background Information: Provide necessary context or background about the topic.
- Thesis Statement: Clearly state the main idea or purpose of the essay.
2. Body Paragraphs
Each body paragraph should focus on a single point that supports the thesis. Follow this structure:
- Topic Sentence: Introduce the main idea of the paragraph.
- Supporting Details: Provide facts, examples, statistics, and explanations to elaborate on the topic sentence.
- Transitions: Use transition words and phrases to maintain coherence and flow between paragraphs.
3. Conclusion
- Restate Thesis: Reiterate the main idea or purpose of the essay.
- Summary of Main Points: Summarize the key points discussed in the body paragraphs.
- Final Thought: End with a final thought, prediction, or call to action to leave a lasting impression on the reader.
Expository Writing Examples for High School
Expository writing in high school helps students develop the ability to explain, inform, or describe a topic clearly and logically. Here are some examples tailored for high school students:
1. Descriptive Essay
Title: The Life of a High School Student
Introduction
High school life is a unique experience that combines academic challenges with social development. Each student’s day is filled with various activities that shape their journey towards adulthood.
Body Paragraph 1: Academic Life
A typical day for a high school student starts early in the morning. Students attend classes in subjects such as mathematics, science, English, and history. Each subject presents its own challenges and requires dedication and effort. Teachers provide lessons, assign homework, and conduct assessments to gauge students’ understanding. The academic workload can be demanding, but it is essential for college preparation and future success.
Body Paragraph 2: Extracurricular Activities
Beyond academics, high school students engage in extracurricular activities. These activities range from sports teams, such as soccer and basketball, to arts programs, including drama and band. Extracurriculars allow students to explore their interests, develop new skills, and build lasting friendships. Participating in these activities also helps students manage their time effectively and learn the importance of teamwork and discipline.
Body Paragraph 3: Social Life
High school is also a time for social growth. Students interact with peers during lunch breaks, study sessions, and school events. Friendships formed during high school can be lifelong, providing support and camaraderie. Social events like dances, football games, and clubs offer opportunities for students to relax and enjoy their high school experience.
Conclusion
The life of a high school student is a balancing act between academics, extracurricular activities, and social interactions. These experiences prepare students for the challenges of adulthood and contribute to their personal growth and development.
2. Process Essay
Title: How to Prepare for College Applications
Introduction
The college application process can be daunting, but with careful planning and organization, students can navigate it successfully. This guide provides step-by-step instructions to help students prepare for their college applications.
Body Paragraph 1: Researching Colleges
The first step in the college application process is researching potential colleges. Students should consider factors such as location, size, programs offered, and campus culture. Visiting college websites, attending college fairs, and talking to current students or alumni can provide valuable insights. Creating a list of target, reach, and safety schools will help students manage their applications effectively.
Body Paragraph 2: Gathering Application Materials
Once students have identified their preferred colleges, the next step is to gather application materials. This typically includes transcripts, standardized test scores (such as the SAT or ACT), letters of recommendation, and a personal statement. Students should request transcripts and recommendation letters well in advance to ensure they meet application deadlines. Writing a compelling personal statement requires reflection and careful editing to highlight strengths and aspirations.
Body Paragraph 3: Completing Applications
After gathering all necessary materials, students can begin completing their applications. This involves filling out forms, uploading documents, and paying application fees. Many colleges use the Common Application, which allows students to apply to multiple schools with one application. It’s crucial to proofread each application carefully to avoid any errors or omissions. Students should also keep track of deadlines and submit applications on time.
Conclusion
Preparing for college applications requires thorough research, careful organization, and timely submission of materials. By following these steps, students can increase their chances of gaining admission to their desired colleges and take a significant step toward their future careers.
3. Comparison and Contrast Essay
Title: Public School vs. Private School
Introduction
Choosing between public and private schools is a significant decision for many families. Each type of school offers unique advantages and challenges. Understanding the differences can help parents and students make an informed choice.
Body Paragraph 1: Cost
One of the primary differences between public and private schools is cost. Public schools are funded by the government and offer free education to students. In contrast, private schools charge tuition fees, which can be a financial burden for some families. However, private schools often offer scholarships and financial aid to help offset the cost.
Body Paragraph 2: Class Size
Class size is another critical difference. Public schools typically have larger class sizes due to limited funding and resources. This can affect the level of individual attention each student receives. Private schools, on the other hand, usually have smaller class sizes, allowing for more personalized instruction and support.
Body Paragraph 3: Curriculum and Resources
Curriculum and resources vary significantly between public and private schools. Public schools must adhere to state guidelines and standardized testing, which can limit curriculum flexibility. Private schools have more freedom to design their programs and may offer specialized courses or advanced placement options. Additionally, private schools often have better facilities and more extracurricular opportunities due to higher funding.
Conclusion
Both public and private schools have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Public schools offer free education and a diverse environment, while private schools provide smaller class sizes and specialized programs. Families must weigh these factors based on their individual needs and priorities to make the best decision for their child’s education.
4. Cause and Effect Essay
Title: The Effects of Social Media on Teenagers
Introduction
Social media has become an integral part of teenagers’ lives, influencing various aspects of their development. While it offers several benefits, it also has significant negative effects on teenagers’ mental and physical health.
Body Paragraph 1: Mental Health
One of the most significant effects of social media on teenagers is its impact on mental health. Excessive use of social media platforms can lead to anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. The constant comparison with others’ seemingly perfect lives can create feelings of inadequacy and loneliness. Cyberbullying is another critical issue, where negative comments and harassment can severely affect a teenager’s emotional well-being.
Body Paragraph 2: Academic Performance
Social media can also impact teenagers’ academic performance. The distraction of notifications and the urge to stay connected can lead to decreased focus and productivity. Many teenagers spend hours on social media, reducing the time available for studying and completing assignments. This can result in lower grades and a lack of interest in academic pursuits.
Body Paragraph 3: Physical Health
The physical health of teenagers can also be affected by social media use. Prolonged screen time can lead to eye strain, headaches, and disrupted sleep patterns. Lack of physical activity due to time spent online can contribute to obesity and other health issues. Encouraging teenagers to balance their social media use with physical activities and proper rest is essential for maintaining their overall health.
Conclusion
While social media provides a platform for communication and self-expression, its negative effects on teenagers’ mental, academic, and physical health cannot be ignored. Parents and educators must guide teenagers in using social media responsibly and help them develop healthy habits to mitigate these adverse effects.
5. Problem and Solution Essay
Title: Addressing School Bullying
Introduction
School bullying is a pervasive problem that affects students’ well-being and academic performance. Finding effective solutions to combat bullying is essential for creating a safe and supportive learning environment.
Body Paragraph 1: Identifying the Problem
Bullying can take many forms, including physical aggression, verbal harassment, and cyberbullying. It can lead to severe consequences for victims, such as anxiety, depression, and decreased academic performance. Recognizing the signs of bullying and understanding its impact is the first step in addressing the issue.
Body Paragraph 2: Implementing Anti-Bullying Programs
Schools can implement comprehensive anti-bullying programs to prevent and address bullying. These programs should include clear policies, staff training, and student education on recognizing and responding to bullying. Encouraging students to report bullying incidents and providing support for victims are crucial components of these programs.
Body Paragraph 3: Promoting a Positive School Culture
Creating a positive school culture is essential for preventing bullying. Schools should promote inclusivity, respect, and kindness through various initiatives, such as peer mentoring, community service projects, and extracurricular activities. Encouraging open communication between students, teachers, and parents can also help build a supportive environment where bullying is less likely to occur.
Conclusion
Addressing school bullying requires a multi-faceted approach that includes identifying the problem, implementing anti-bullying programs, and promoting a positive school culture. By taking these steps, schools can create a safer and more supportive environment for all students.
Expository Writing Examples for kids
Expository writing helps kids explain, describe, or inform others about a topic in a clear and straightforward manner. Here are some examples tailored for younger students:
1. Descriptive Essay
Title: My Favorite Animal
Introduction
My favorite animal is the elephant. Elephants are fascinating creatures known for their large size and unique features.
Body Paragraph 1: Physical Characteristics
Elephants are the largest land animals. They have big ears, a long trunk, and thick, grey skin. Their tusks are made of ivory and can be very long.
Body Paragraph 2: Habitat
Elephants live in various habitats, including savannas, forests, and grasslands. They are mainly found in Africa and Asia.
Body Paragraph 3: Diet
Elephants are herbivores, which means they eat plants. They enjoy eating leaves, fruits, and bark. An adult elephant can eat up to 300 pounds of food in a day!
Conclusion
Elephants are amazing animals with their impressive size, interesting habitats, and unique diet. This is why they are my favorite animal.
2. Process Essay
Title: How to Make a Peanut Butter and Jelly Sandwich
Introduction
Making a peanut butter and jelly sandwich is simple and fun. Here’s how you can make one.
Body Paragraph 1: Gather Ingredients
First, you need to gather all the ingredients. You will need bread, peanut butter, jelly, and a butter knife.
Body Paragraph 2: Spread Peanut Butter
Next, take two slices of bread. Use the butter knife to spread peanut butter on one side of one slice of bread.
Body Paragraph 3: Spread Jelly
Then, spread jelly on one side of the other slice of bread. You can use the same knife, but clean it first, or use a different one.
Body Paragraph 4: Combine and Enjoy
Finally, put the two slices of bread together with the peanut butter and jelly sides facing each other. Your sandwich is ready to eat. Enjoy!
Conclusion
Making a peanut butter and jelly sandwich is easy if you follow these steps. It’s a delicious and quick snack.
3. Comparison and Contrast Essay
Title: Dogs vs. Cats
Introduction
Dogs and cats are both popular pets, but they are very different in many ways.
Body Paragraph 1: Personality
Dogs are usually very friendly and love to play. They are loyal and often protect their owners. Cats, on the other hand, are more independent. They like to be alone sometimes and can be very curious.
Body Paragraph 2: Care
Taking care of a dog often requires more time. Dogs need to be walked, played with, and groomed regularly. Cats are easier to care for. They use a litter box and clean themselves.
Body Paragraph 3: Communication
Dogs communicate by barking, wagging their tails, and showing their emotions openly. Cats communicate through meowing, purring, and using their body language, which can be more subtle.
Conclusion
Both dogs and cats make wonderful pets, but they have different needs and personalities. Whether you prefer a playful dog or an independent cat depends on your lifestyle and what kind of pet you want.
4. Cause and Effect Essay
Title: Why We Need to Save Water
Introduction
Saving water is important for many reasons. Here’s why we should all try to use less water.
Body Paragraph 1: Limited Resource
Water is a limited resource. There is only so much fresh water available on Earth, and we need to make sure there is enough for everyone.
Body Paragraph 2: Environment
Using too much water can harm the environment. It can dry up rivers and lakes, affecting plants and animals that live there.
Body Paragraph 3: Future Generations
If we save water now, we will have enough for the future. It’s important to think about the generations to come and make sure they have the water they need.
Conclusion
Saving water helps protect our planet and ensures that we have enough for the future. We should all try to use water wisely.
5. Problem and Solution Essay
Title: How to Reduce Plastic Waste
Introduction
Plastic waste is a big problem for our environment. Here are some ways we can help reduce it.
Body Paragraph 1: Reuse and Recycle
One way to reduce plastic waste is to reuse and recycle plastic items. Instead of throwing them away, we can find new uses for them or make sure they are recycled properly.
Body Paragraph 2: Use Less Plastic
Another way to reduce plastic waste is to use less plastic. We can use cloth bags instead of plastic ones, drink from reusable bottles, and avoid buying products with lots of plastic packaging.
Body Paragraph 3: Educate Others
Teaching others about the importance of reducing plastic waste can also help. If more people understand the problem, they will be more likely to take action.
Conclusion
Reducing plastic waste is important for keeping our environment clean and safe. By reusing, recycling, using less plastic, and educating others, we can make a big difference.
Expository Writing Examples for College
Expository writing at the college level involves detailed exploration, explanation, and analysis of complex topics. Here are some comprehensive examples tailored for college students:
1. Descriptive Essay
Title: The Impact of Climate Change on Coastal Ecosystems
Introduction
Climate change is significantly affecting coastal ecosystems around the world. These changes are impacting biodiversity, sea levels, and human communities.
Body Paragraph 1: Rising Sea Levels
One of the most visible effects of climate change on coastal ecosystems is rising sea levels. As global temperatures increase, polar ice melts and seawater expands. This results in higher sea levels that threaten coastal habitats, such as mangroves and salt marshes, leading to habitat loss and increased erosion.
Body Paragraph 2: Ocean Acidification
Increased carbon dioxide emissions not only contribute to global warming but also result in ocean acidification. This process alters the chemical composition of seawater, making it more acidic. Ocean acidification adversely affects marine life, particularly organisms with calcium carbonate shells or skeletons, such as corals and shellfish.
Body Paragraph 3: Biodiversity Loss
Climate change disrupts the delicate balance of coastal ecosystems, leading to biodiversity loss. Species that cannot adapt quickly to changing conditions face extinction. For example, coral reefs, which are home to a vast array of marine life, are bleaching and dying at alarming rates due to higher water temperatures.
Conclusion
Climate change poses a serious threat to coastal ecosystems, impacting sea levels, ocean chemistry, and biodiversity. Protecting these vital areas requires immediate and sustained efforts to reduce carbon emissions and implement conservation strategies.
2. Process Essay
Title: How to Conduct a Literature Review for a Research Paper
Introduction
A literature review is a crucial part of any research paper. It provides a comprehensive overview of existing research on a topic. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to conduct an effective literature review.
Body Paragraph 1: Define Your Research Question
The first step in conducting a literature review is to clearly define your research question or thesis. This will guide your search for relevant literature. Ensure your question is specific and manageable.
Body Paragraph 2: Search for Relevant Literature
Next, use academic databases like PubMed, JSTOR, and Google Scholar to find scholarly articles, books, and other sources related to your topic. Use keywords and Boolean operators to refine your search. Keep track of the sources you find, noting their relevance and quality.
Body Paragraph 3: Evaluate and Analyze Sources
Once you have a collection of sources, evaluate their credibility, relevance, and contribution to the field. Look for patterns, gaps, and conflicts in the literature. Summarize and synthesize the information to provide a clear picture of the current state of research on your topic.
Body Paragraph 4: Organize Your Review
Organize your literature review logically. You can structure it thematically, chronologically, or methodologically. Each section should address a different aspect of your research question, highlighting key findings and significant studies.
Conclusion
Conducting a literature review involves defining a research question, searching for relevant literature, evaluating and analyzing sources, and organizing the review. By following these steps, you can create a comprehensive and insightful literature review that supports your research paper.
3. Comparison and Contrast Essay
Title: Traditional vs. Online Education
Introduction
The debate between traditional and online education has gained prominence in recent years. Both modes of education offer distinct advantages and challenges.
Body Paragraph 1: Learning Environment
Traditional education provides a structured learning environment with face-to-face interaction between students and teachers. This setting fosters immediate feedback and engagement. In contrast, online education offers flexibility, allowing students to learn at their own pace and schedule, but it can lack direct interaction.
Body Paragraph 2: Accessibility and Flexibility
Online education is highly accessible and flexible, making it ideal for students with other commitments such as work or family. It allows learners to access course materials from anywhere with an internet connection. Traditional education, however, requires physical presence, which can be a limitation for those with busy schedules or geographic constraints.
Body Paragraph 3: Cost and Resources
Online education is often more affordable than traditional education due to lower tuition fees and the absence of commuting and housing costs. However, traditional education provides access to campus resources such as libraries, laboratories, and extracurricular activities, which can enhance the learning experience.
Body Paragraph 4: Social Interaction
Traditional education promotes social interaction and networking opportunities, which are vital for personal and professional growth. Students engage in group work, discussions, and campus events. Online education, while offering forums and virtual meetings, may not provide the same level of social engagement.
Conclusion
Both traditional and online education have their own strengths and weaknesses. The choice between them depends on individual needs and preferences, including the desired learning environment, accessibility, cost, and opportunities for social interaction.
4. Cause and Effect Essay
Title: The Effects of Social Media on Academic Performance
Introduction
Social media has become an integral part of students’ lives, profoundly impacting their academic performance. Understanding these effects can help in developing strategies to balance social media use and academic responsibilities.
Body Paragraph 1: Distraction and Time Management
One of the primary effects of social media on academic performance is distraction. Students often spend significant amounts of time on social platforms, which can detract from their study time and focus. Poor time management due to excessive social media use leads to procrastination and rushed assignments, resulting in lower academic performance.
Body Paragraph 2: Stress and Mental Health
Social media can also affect students’ mental health, contributing to stress and anxiety. Constant exposure to curated, idealized images and posts can lead to feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem. This mental strain can negatively impact students’ ability to concentrate and perform academically.
Body Paragraph 3: Social Connections and Support
On the positive side, social media facilitates social connections and support networks. Students can collaborate on projects, share resources, and seek help from peers and educators. This collaborative aspect can enhance learning experiences and academic outcomes.
Body Paragraph 4: Access to Information and Learning Resources
Social media provides access to a vast array of information and learning resources. Educational pages, groups, and influencers offer valuable content that can supplement classroom learning. However, the reliability of information on social media can vary, and students need to develop critical thinking skills to discern credible sources.
Conclusion
Social media has both positive and negative effects on academic performance. While it offers opportunities for social support and access to educational resources, it also poses challenges related to distraction and mental health. Balancing social media use and academic responsibilities is crucial for students to achieve optimal academic outcomes.
5. Problem and Solution Essay
Title: Addressing the Problem of Food Insecurity on College Campuses
Introduction
Food insecurity is a growing problem on college campuses, affecting students’ health and academic performance. Developing effective solutions to address this issue is crucial for student well-being and success.
Body Paragraph 1: Understanding Food Insecurity
Food insecurity refers to the lack of reliable access to sufficient, nutritious food. Many college students experience food insecurity due to financial constraints, high tuition costs, and limited access to affordable food options. This issue can lead to poor nutrition, stress, and hindered academic performance.
Body Paragraph 2: Campus Food Pantries
One effective solution is the establishment of campus food pantries. These pantries provide free food and essential items to students in need. Colleges can partner with local food banks and community organizations to stock these pantries. Promoting awareness of these resources ensures that students know where to seek help.
Body Paragraph 3: Meal Plan Scholarships
Another solution is offering meal plan scholarships to students facing financial difficulties. These scholarships can cover the cost of campus meal plans, ensuring that students have access to regular, nutritious meals. Universities can fund these scholarships through alumni donations, grants, and fundraising events.
Body Paragraph 4: Financial Education Programs
Implementing financial education programs can also help address food insecurity. Teaching students about budgeting, managing expenses, and accessing financial aid can empower them to make informed decisions and reduce the risk of food insecurity. Workshops and online resources can provide valuable guidance and support.
Conclusion
Food insecurity on college campuses is a serious issue that requires multifaceted solutions. Establishing campus food pantries, offering meal plan scholarships, and providing financial education programs are effective strategies to support students and ensure their well-being and academic success.
More Expository Writing Samples & Examples in PDF
1. Expository Writing Example

regworldlit.files.wordpress.com
2. Expository Writing Handout Example
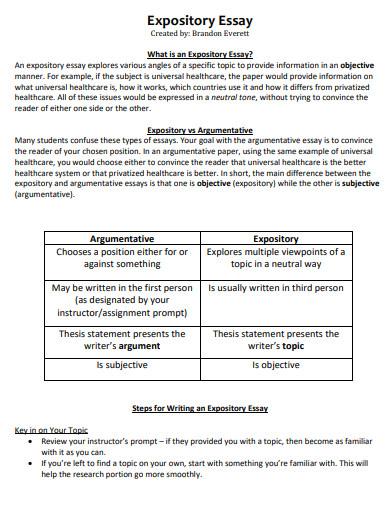
csueastbay.edu
3. Characteristics of Expository Writing Example

nova.edu
4. Expository Essay Writing Example

assets.cambridge.org
5. Expository Project Writing Example

cdaschools.org
6. Strategies for Expository Writing Example

scholarworks.lib.csusb.edu
7. High School Expository Writing Example
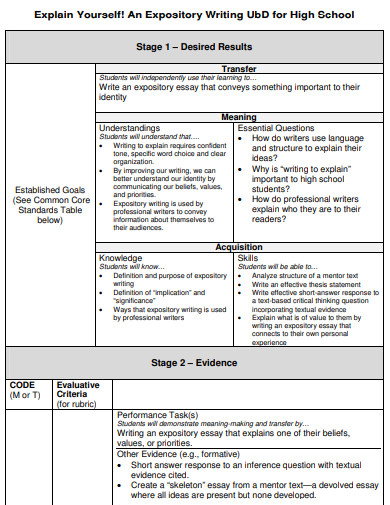
digitalcommons.trinity.edu
8. Expository Rubic Writing Example
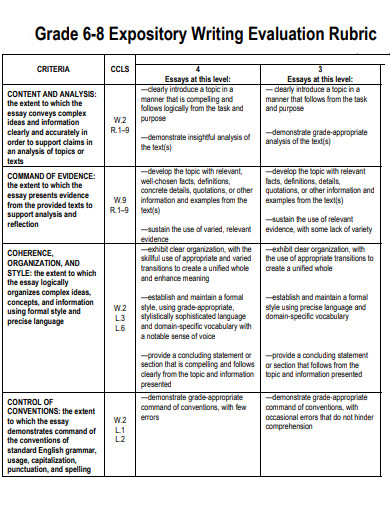
rcsdk12.org
Types of Expository Writing
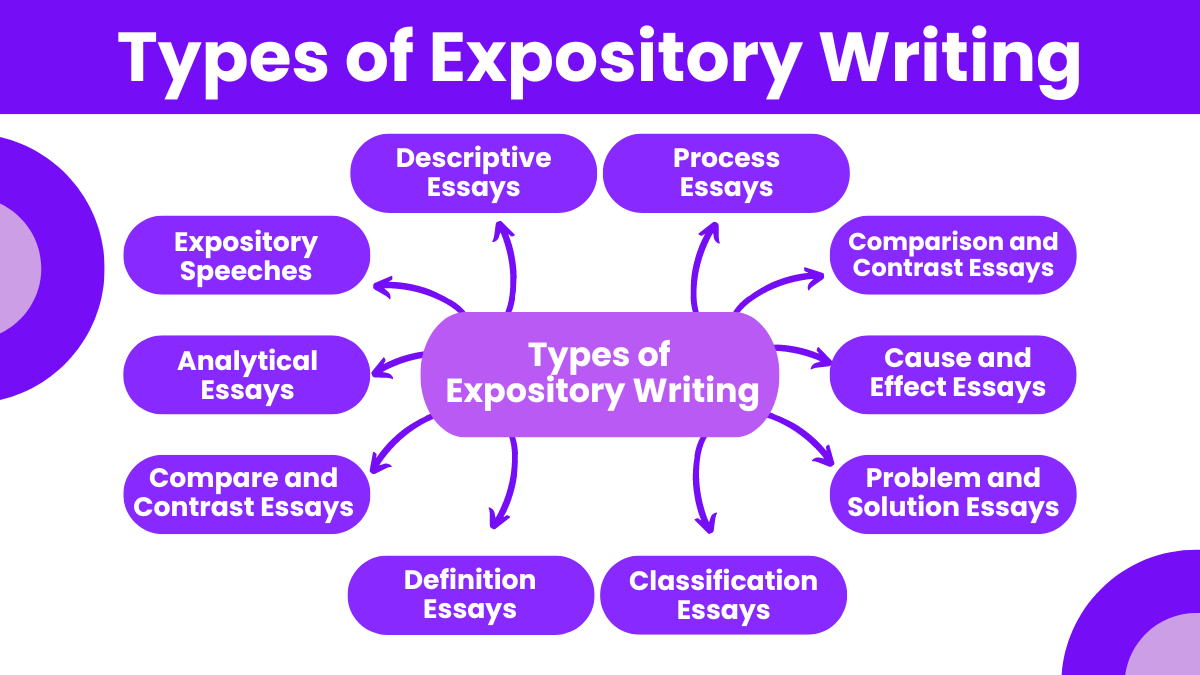
Expository writing aims to inform, explain, or describe a subject to the reader. Here are the primary types of expository writing:
1. Descriptive Essays
Descriptive essays provide detailed descriptions of a subject, painting a clear picture for the reader. They often use sensory details to help the reader visualize the topic.
Example: Describing the features and atmosphere of a bustling city market.
2. Process Essays
Process essays, also known as “how-to” essays, give step-by-step instructions on how to complete a task or process.
Example: How to create a successful study schedule for college exams.
3. Comparison and Contrast Essays
Comparison and contrast essays analyze the similarities and differences between two or more subjects.
Example: Comparing online learning to traditional classroom learning.
4. Cause and Effect Essays
Cause and effect essays explore the reasons why something happens (cause) and the results of it happening (effect).
Example: The causes and effects of global warming.
5. Problem and Solution Essays
Problem and solution essays identify a problem and propose one or more solutions.
Example: Addressing the issue of cyberbullying in schools and proposing effective prevention strategies.
6. Classification Essays
Classification essays break down a broad subject into categories or groups and explain each one.
Example: Classifying different genres of music and describing their characteristics.
7. Definition Essays
Definition essays explain the meaning of a term or concept, often providing a detailed analysis and examples.
Example: Defining what constitutes a healthy lifestyle.
8. Compare and Contrast Essays
Compare and contrast essays examine the similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example: Comparing the economic systems of capitalism and socialism.
9. Analytical Essays
Analytical essays break down a complex topic into its components and examine them in detail.
Example: Analyzing the themes and motifs in Shakespeare’s “Macbeth.”
10. Expository Speeches
While not written essays, expository speeches follow similar principles, aiming to inform or explain a topic to an audience.
Example: A speech explaining the benefits of renewable energy sources.
Purpose of Expository Writing
Expository writing serves to explain, inform, and describe. Its primary goal is to convey information clearly and logically, ensuring the reader understands the subject without confusion. Here are the key purposes of expository writing:
1. To Inform
Expository writing provides factual information about a topic. It aims to educate the reader by presenting data, statistics, and factual details in an organized manner.
Example: Informing readers about the life cycle of a butterfly.
2. To Explain
This type of writing breaks down complex concepts into simpler parts, making them easier to understand. It clarifies ideas and processes.
Example: Explaining how photosynthesis works in plants.
3. To Describe
Expository writing paints a vivid picture of a subject by detailing its characteristics, features, and attributes. It helps the reader visualize the topic.
Example: Describing the architectural features of the Eiffel Tower.
4. To Analyze
It involves examining a topic in detail, exploring various aspects and their relationships. This helps in understanding the deeper meaning or function of the subject.
Example: Analyzing the impact of social media on teenagers.
5. To Compare and Contrast
Expository writing highlights the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. This helps readers understand the relative characteristics and qualities of each subject.
Example: Comparing renewable energy sources like solar and wind power.
6. To Instruct
Instructional expository writing provides step-by-step guidance on how to perform a task or process. It aims to ensure the reader can successfully follow the instructions.
Example: Providing a recipe for baking chocolate chip cookies.
7. To Classify
It categorizes a broad topic into smaller groups or types, explaining each category’s distinct characteristics. This helps in organizing information logically.
Example: Classifying different types of clouds and describing their features.
How to draft an Expository Writing
Drafting an expository writing piece involves several key steps to ensure clarity, coherence, and effectiveness. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you draft a successful expository essay or article:
1. Choose a Topic
Select a topic that interests you and can be explained or described clearly. Ensure it’s neither too broad nor too narrow.
2. Conduct Research
Gather information from reliable sources such as books, academic journals, reputable websites, and expert interviews. Take detailed notes and organize your findings.
3. Create an Outline
An outline helps you organize your thoughts and ensures a logical flow of information. Your outline should include:
- Introduction: Hook, background information, thesis statement.
- Body Paragraphs: Each paragraph should cover a single point that supports your thesis. Include topic sentences, supporting details, and transitions.
- Conclusion: Restate the thesis, summarize main points, and provide a final thought.
4. Write the Introduction
- Hook: Start with an engaging sentence to grab the reader’s attention.
- Background Information: Provide context or necessary background about the topic.
- Thesis Statement: Clearly state the main idea or purpose of your essay.
5. Develop Body Paragraphs
Each paragraph should focus on a single point. Use this structure:
- Topic Sentence: Introduce the main idea of the paragraph.
- Supporting Details: Provide facts, examples, statistics, and explanations to elaborate on the topic sentence.
- Transitions: Use transition words and phrases to maintain coherence and flow between paragraphs.
6. Write the Conclusion
- Restate Thesis: Reiterate the main idea or purpose of the essay.
- Summary of Main Points: Summarize the key points discussed in the body paragraphs.
- Final Thought: End with a final thought, prediction, or call to action to leave a lasting impression on the reader.
7. Revise and Edit
Review your draft to ensure clarity and coherence. Check for:
- Content Accuracy: Verify facts and information.
- Logical Flow: Ensure ideas are presented in a logical order.
- Clarity and Conciseness: Remove unnecessary words or jargon.
- Grammar and Spelling: Correct grammatical errors and typos.
8. Seek Feedback
Ask peers, teachers, or mentors to review your draft and provide feedback. Use their suggestions to improve your writing.
How is expository writing different from narrative writing?
Expository writing explains or informs about a topic, while narrative writing tells a story with a plot, characters, and a sequence of events.
What are the key elements of expository writing?
Key elements include a clear thesis statement, logical organization, evidence-based supporting details, and a conclusion that reinforces the main idea.
How do you choose a topic for an expository essay?
Choose a topic that interests you, is neither too broad nor too narrow, and has enough available information for research.
What are common types of expository writing?
Common types include descriptive essays, process essays, comparison and contrast essays, cause and effect essays, and problem and solution essays.
How do you structure an expository essay?
An expository essay typically follows a five-paragraph structure: introduction, three body paragraphs, and conclusion, with each section serving a specific purpose.
How do you write a strong thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement clearly states the main idea of the essay, is specific and concise, and sets the direction for the entire piece.
What is the role of transitions in expository writing?
Transitions help to maintain the flow of ideas, guiding the reader smoothly from one point to the next and ensuring logical coherence.
How do you ensure your expository writing is clear and concise?
Use straightforward language, avoid jargon, and focus on presenting information logically and succinctly, removing unnecessary words and details.
Why is evidence important in expository writing?
Evidence supports your claims, adds credibility, and helps to persuade the reader by providing concrete examples, statistics, and expert opinions.
How can you improve your expository writing skills?
Practice regularly, read a variety of expository texts, seek feedback from peers or teachers, and revise your work to enhance clarity and coherence.



