29+ Formal Communication Skills Examples
Unlock the full potential of effective communication with our Comprehensive Guide on Formal Communication Skills. In this detailed exploration, discover key examples illustrating the nuances of formal communication in various contexts. From workplace scenarios to real-life interactions, grasp the essence of impeccable communication. Elevate your skills with insights into verbal and nonverbal cues, assertive communication, and more. Dive into the world of Formal Communication Skills and empower yourself with impactful communication examples. Communication Examples await your exploration in this enriching guide
What is Formal Communication Skills?
Formal Communication Skills encompass the structured and official ways individuals convey information in various settings. In straightforward terms, it involves the ability to communicate in a professional, planned, and intentional manner. Whether in the workplace or daily life, understanding the essence of formal communication skills is crucial for effective interaction. Let’s delve into the clear definition of this skill set and its practical applications.

What is the best Example of Formal Communication Skills?
One standout example of Formal Communication Skills is the articulate delivery of a business presentation. Imagine a scenario where a team leader presents project updates during a formal meeting. The use of planned language, clear visuals, and adherence to a structured format exemplifies formal communication. This ensures that information is conveyed with precision, fostering a professional and organized atmosphere. Explore the intricacies of this exemplary situation, showcasing how Formal Communication Skills enhance clarity and effectiveness in various professional settings
30 Formal Communication Skills Examples
Explore a diverse array of Formal Communication Skills Examples to elevate your proficiency in professional interactions. From workplace scenarios to real-life situations, grasp the nuances of effective communication. Enhance your skills with these practical examples, each contributing to a comprehensive understanding of formal communication.

- Business Meetings: Navigate discussions with finesse, ensuring all participants contribute meaningfully.
- Email Etiquette: Craft clear and concise emails, fostering efficient communication in the digital realm.
- Client Presentations: Convey complex ideas persuasively, leaving a lasting impression on clients.
- Team Briefings: Deliver project updates succinctly, maintaining team focus and motivation.
- Job Interviews: Showcase your qualifications confidently, leaving a favorable impression on potential employers.
- Formal Reports: Present data coherently, enabling informed decision-making within the organization.
- Policy Communication: Clearly articulate company policies, ensuring a uniform understanding among employees.
- Legal Correspondence: Draft precise legal documents, minimizing ambiguity and potential disputes.
- Educational Lectures: Engage students effectively, facilitating a conducive learning environment.
- Conference Calls: Navigate virtual meetings seamlessly, fostering collaboration across geographical boundaries.
- Customer Service Interactions: Address customer queries professionally, ensuring satisfaction and loyalty.
- Performance Reviews: Deliver constructive feedback, promoting professional growth among team members.
- Board Presentations: Convey strategic plans convincingly to board members, gaining support for initiatives.
- Official Memos: Communicate important announcements formally, ensuring a consistent flow of information.
- Project Proposals: Present project ideas persuasively, securing approval and support.
- Job Descriptions: Draft comprehensive job descriptions, attracting qualified candidates to the organization.
- Company Policies: Communicate changes in policies clearly, avoiding confusion among employees.
- Training Workshops: Facilitate training sessions effectively, ensuring participants grasp key concepts.
- Press Releases: Draft impactful press releases, shaping public perception positively.
- Collaboration Agreements: Negotiate and finalize collaborations with clarity, avoiding misunderstandings.
- Financial Reports: Present financial data accurately, aiding stakeholders in decision-making.
- Strategic Planning Sessions: Communicate strategic goals, aligning the team towards a common vision.
- Client Proposals: Craft compelling proposals, showcasing the value of your products or services.
- Crisis Communication: Address crises with transparency, maintaining trust among stakeholders.
- Product Launch Presentations: Unveil new products with flair, capturing the audience’s attention.
- Academic Papers: Present research findings cohesively, contributing to the academic community.
- Regulatory Compliance Communication: Communicate regulatory changes clearly, ensuring adherence.
- Project Status Updates: Keep stakeholders informed about project progress, highlighting achievements and addressing challenges.
- Employee Handbook: Clearly communicate company policies and expectations through a comprehensive employee handbook.
- Government Communications: Convey government initiatives clearly, fostering public understanding and cooperation.
Formal Communication Skills Examples in the Workplace
Explore exemplary instances of formal communication skills within the workplace. These real-world examples demonstrate the application of structured and professional communication, fostering effective collaboration and productivity in organizational settings.
- Meeting Agendas: Prepare clear meeting agendas to guide discussions and maintain focus on key topics.
- Policy Updates: Announce changes in company policies through official channels, ensuring a uniform understanding among employees.
- Project Proposals: Present project proposals formally, outlining objectives, timelines, and anticipated outcomes.
- Performance Appraisals: Conduct formal performance appraisals, providing constructive feedback to facilitate professional growth.
- Official Emails: Craft formal emails for internal communication, conveying information clearly and professionally.
- Company Newsletters: Disseminate important company updates through formal newsletters, enhancing internal communication.
- Training Programs: Organize formal training sessions to impart new skills and knowledge to employees.
- Employee Recognition Programs: Communicate employee achievements formally, fostering a positive work environment.
- Team Briefings: Conduct regular formal briefings to update teams on project progress and organizational goals.
- Employee Handbook: Clearly communicate company policies and expectations through a comprehensive employee handbook.
Formal Communication Skills Examples in Business
Delve into the world of formal communication skills within the realm of business. These examples showcase how structured and intentional communication contributes to successful business interactions, negotiations, and collaborations.
- Client Proposals: Draft persuasive proposals to showcase products or services, emphasizing value and benefits.
- Negotiation Meetings: Navigate business negotiations formally, ensuring clarity and mutual understanding.
- Executive Reports: Prepare formal reports for executives, presenting data and insights for strategic decision-making.
- Strategic Planning Sessions: Communicate strategic goals and initiatives, aligning the team toward common objectives.
- Financial Presentations: Present financial data formally, aiding stakeholders in investment and decision-making.
- Board Meetings: Conduct formal board meetings to discuss organizational strategies and governance matters.
- Collaboration Agreements: Negotiate and finalize collaborations formally, defining roles and expectations.
- Product Launch Presentations: Unveil new products formally, capturing the audience’s attention and interest.
- Stakeholder Updates: Keep stakeholders informed through formal updates on project progress and milestones.
- Investor Relations Communications: Communicate effectively with investors through formal reports and updates.
Formal Communication Skills Examples in Real Life
Discover how formal communication skills manifest in everyday life situations. From personal interactions to community involvement, these real-life examples demonstrate the significance of clear and intentional communication beyond professional settings.
- Family Meetings: Conduct formal family meetings to discuss important matters and make collective decisions.
- Community Presentations: Deliver formal presentations in community events, fostering understanding and collaboration.
- School Parent-Teacher Conferences: Communicate formally with parents, discussing students’ progress and development.
- Public Speeches: Deliver formal speeches on relevant topics, capturing the audience’s attention and conveying a clear message.
- Volunteer Organization Updates: Communicate formally within volunteer organizations, ensuring alignment with goals and initiatives.
- Municipal Council Meetings: Participate in formal council meetings to discuss community issues and solutions.
- Neighborhood Watch Announcements: Disseminate important information formally within a neighborhood, promoting safety and awareness.
- Social Club Events: Organize and communicate details of social club events formally, ensuring member participation.
- Charity Fundraising Campaigns: Coordinate and promote charity campaigns formally, reaching a broader audience.
- Community Workshops: Conduct formal workshops to educate and empower community members on various subjects
What are the Basic Elements of Formal Communication?
Formal communication is structured, intentional, and follows established channels within an organization. To grasp its essence, understanding the fundamental elements is crucial.
- Hierarchy and Structure: Recognize the role of organizational hierarchy in formal communication. Information flows through established levels, ensuring a structured and organized process.
- Official Channels: Formal communication relies on official channels like emails, memos, and official meetings. These channels maintain a professional tone and facilitate clear information transmission.
- Rules and Procedures: Formal communication adheres to predetermined rules and procedures. This ensures consistency and clarity in conveying messages.
- Documentation: In formal communication, documentation is key. Written records, reports, and official documents play a pivotal role in maintaining transparency and accountability.
- Professional Language: The language used in formal communication is professional, avoiding informal or colloquial expressions. This promotes clarity and a serious tone.
- Planned and Deliberate: Unlike informal communication, formal communication is planned and deliberate. Messages are carefully crafted to convey specific information accurately.
- Feedback Channels: Formal communication allows for structured feedback channels, enabling a two-way flow of information. This ensures that messages are understood and acted upon appropriately.
Understanding these basic elements provides a solid foundation for navigating the intricacies of formal communication within any organizational context.
How to Improve Formal Communication Skills?
Enhancing formal communication skills is essential for professional success. Here’s a comprehensive guide to refining and mastering this crucial skill set.
- Active Listening: Cultivate active listening skills to understand information thoroughly. Respond thoughtfully to demonstrate comprehension.
- Clarity and Conciseness: Practice delivering messages with clarity and conciseness. Avoid unnecessary details and communicate the core message directly.
- Body Language: In formal communication, body language matters. Maintain appropriate posture, make eye contact, and use gestures judiciously to convey confidence and engagement.
- Adapt to the Audience: Tailor your communication style to suit your audience. Consider their expectations, knowledge, and preferences to convey messages effectively.
- Structured Messaging: Organize your thoughts before communicating. Use a structured format, ensuring a logical flow of information in written and verbal communication.
- Professional Writing Skills: Hone your writing skills for formal documentation. Ensure grammatical accuracy, clarity, and adherence to the professional tone.
- Politeness and Respect: Practice politeness and respect in all communications. Use formal salutations and be mindful of cultural nuances to build positive relationships.
- Feedback Solicitation: Actively seek feedback on your communication style. Identify areas for improvement and continuously refine your skills based on constructive input.
- Role-Playing Exercises: Engage in role-playing exercises to simulate real communication scenarios. This helps build confidence and sharpens your ability to respond effectively.
- Continuous Learning: Stay updated on communication trends and best practices. Embrace a mindset of continuous learning to adapt to evolving communication challenges.
What is Difference Between Formal and Informal Communication Skills?
Formal and informal communication skills represent distinct approaches to conveying information in various settings. Differentiating between these two styles is crucial for effective interactions. Here’s a comprehensive guide presented in a table format to illuminate the variances:
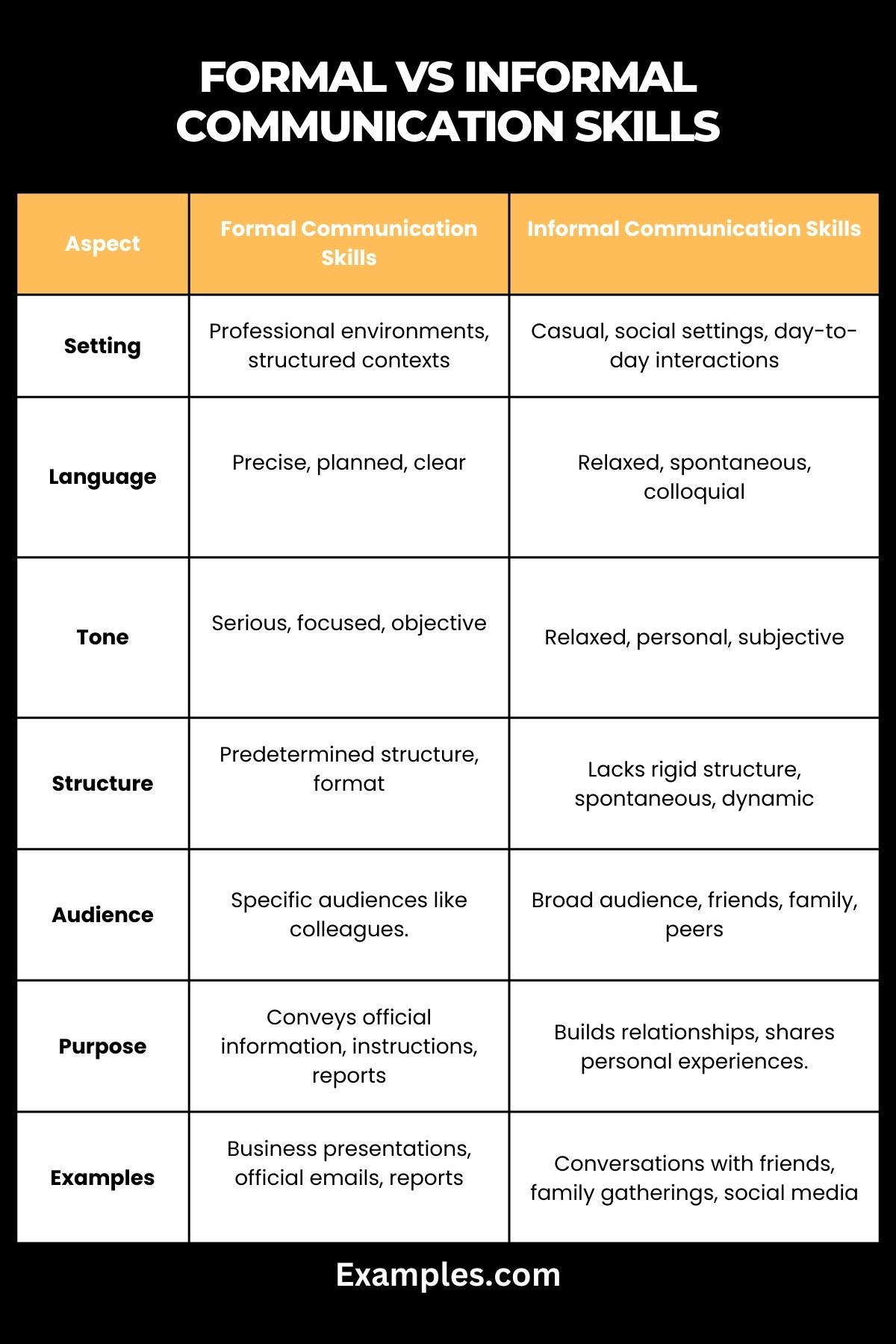
| Aspect | Formal Communication Skills | Informal Communication Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Setting | Typically in professional environments structured contexts. | Commonly in casual, social settings, and day-to-day interactions. |
| Language | Utilizes precise, planned, and clear language. | Involves relaxed, spontaneous, and colloquial language. |
| Tone | Tends to be serious, focused, and objective. | Reflects a more relaxed, personal, and subjective tone. |
| Structure | Follows a predetermined structure and format. | Lacks a rigid structure, often spontaneous and dynamic. |
| Audience | Targets specific audiences such as colleagues, clients, or superiors. | Involves a broad audience, including friends, family, and peers. |
| Purpose | Conveys official information, instructions, or reports. | Aims for building relationships, sharing personal experiences, and casual discussions. |
| Examples | Business presentations, official emails, and reports. | Conversations with friends, family gatherings, and social media interactions. |
Mastering Formal Communication Skills is a transformative journey. By adhering to structured approaches in various settings, individuals can enhance workplace efficiency, build professional relationships, and convey ideas with precision. This guide has illuminated the nuances, providing actionable tips for effective communication. Elevate your skills, embrace clarity, and make a lasting impact through the power of formal communication.
29+ Formal Communication Skills Examples

Unlock the full potential of effective communication with our Comprehensive Guide on Formal Communication Skills. In this detailed exploration, discover key examples illustrating the nuances of formal communication in various contexts. From workplace scenarios to real-life interactions, grasp the essence of impeccable communication. Elevate your skills with insights into verbal and nonverbal cues, assertive communication, and more. Dive into the world of Formal Communication Skills and empower yourself with impactful communication examples. Communication Examples await your exploration in this enriching guide
What is Formal Communication Skills?
Formal Communication Skills encompass the structured and official ways individuals convey information in various settings. In straightforward terms, it involves the ability to communicate in a professional, planned, and intentional manner. Whether in the workplace or daily life, understanding the essence of formal communication skills is crucial for effective interaction. Let’s delve into the clear definition of this skill set and its practical applications.

What is the best Example of Formal Communication Skills?
One standout example of Formal Communication Skills is the articulate delivery of a business presentation. Imagine a scenario where a team leader presents project updates during a formal meeting. The use of planned language, clear visuals, and adherence to a structured format exemplifies formal communication. This ensures that information is conveyed with precision, fostering a professional and organized atmosphere. Explore the intricacies of this exemplary situation, showcasing how Formal Communication Skills enhance clarity and effectiveness in various professional settings
30 Formal Communication Skills Examples
Explore a diverse array of Formal Communication Skills Examples to elevate your proficiency in professional interactions. From workplace scenarios to real-life situations, grasp the nuances of effective communication. Enhance your skills with these practical examples, each contributing to a comprehensive understanding of formal communication.

Business Meetings: Navigate discussions with finesse, ensuring all participants contribute meaningfully.
Email Etiquette: Craft clear and concise emails, fostering efficient communication in the digital realm.
Client Presentations: Convey complex ideas persuasively, leaving a lasting impression on clients.
Team Briefings: Deliver project updates succinctly, maintaining team focus and motivation.
Job Interviews: Showcase your qualifications confidently, leaving a favorable impression on potential employers.
Formal Reports: Present data coherently, enabling informed decision-making within the organization.
Policy Communication: Clearly articulate company policies, ensuring a uniform understanding among employees.
Legal Correspondence: Draft precise legal documents, minimizing ambiguity and potential disputes.
Educational Lectures: Engage students effectively, facilitating a conducive learning environment.
Conference Calls: Navigate virtual meetings seamlessly, fostering collaboration across geographical boundaries.
Customer Service Interactions: Address customer queries professionally, ensuring satisfaction and loyalty.
Performance Reviews: Deliver constructive feedback, promoting professional growth among team members.
Board Presentations: Convey strategic plans convincingly to board members, gaining support for initiatives.
Official Memos: Communicate important announcements formally, ensuring a consistent flow of information.
Project Proposals: Present project ideas persuasively, securing approval and support.
Job Descriptions: Draft comprehensive job descriptions, attracting qualified candidates to the organization.
Company Policies: Communicate changes in policies clearly, avoiding confusion among employees.
Training Workshops: Facilitate training sessions effectively, ensuring participants grasp key concepts.
Press Releases: Draft impactful press releases, shaping public perception positively.
Collaboration Agreements: Negotiate and finalize collaborations with clarity, avoiding misunderstandings.
Financial Reports: Present financial data accurately, aiding stakeholders in decision-making.
Strategic Planning Sessions: Communicate strategic goals, aligning the team towards a common vision.
Client Proposals: Craft compelling proposals, showcasing the value of your products or services.
Crisis Communication: Address crises with transparency, maintaining trust among stakeholders.
Product Launch Presentations: Unveil new products with flair, capturing the audience’s attention.
Academic Papers: Present research findings cohesively, contributing to the academic community.
Regulatory Compliance Communication: Communicate regulatory changes clearly, ensuring adherence.
Project Status Updates: Keep stakeholders informed about project progress, highlighting achievements and addressing challenges.
Employee Handbook: Clearly communicate company policies and expectations through a comprehensive employee handbook.
Government Communications: Convey government initiatives clearly, fostering public understanding and cooperation.
Formal Communication Skills Examples in the Workplace
Explore exemplary instances of formal communication skills within the workplace. These real-world examples demonstrate the application of structured and professional communication, fostering effective collaboration and productivity in organizational settings.
Meeting Agendas: Prepare clear meeting agendas to guide discussions and maintain focus on key topics.
Policy Updates: Announce changes in company policies through official channels, ensuring a uniform understanding among employees.
Project Proposals: Present project proposals formally, outlining objectives, timelines, and anticipated outcomes.
Performance Appraisals: Conduct formal performance appraisals, providing constructive feedback to facilitate professional growth.
Official Emails: Craft formal emails for internal communication, conveying information clearly and professionally.
Company Newsletters: Disseminate important company updates through formal newsletters, enhancing internal communication.
Training Programs: Organize formal training sessions to impart new skills and knowledge to employees.
Employee Recognition Programs: Communicate employee achievements formally, fostering a positive work environment.
Team Briefings: Conduct regular formal briefings to update teams on project progress and organizational goals.
Employee Handbook: Clearly communicate company policies and expectations through a comprehensive employee handbook.
Formal Communication Skills Examples in Business
Delve into the world of formal communication skills within the realm of business. These examples showcase how structured and intentional communication contributes to successful business interactions, negotiations, and collaborations.
Client Proposals: Draft persuasive proposals to showcase products or services, emphasizing value and benefits.
Negotiation Meetings: Navigate business negotiations formally, ensuring clarity and mutual understanding.
Executive Reports: Prepare formal reports for executives, presenting data and insights for strategic decision-making.
Strategic Planning Sessions: Communicate strategic goals and initiatives, aligning the team toward common objectives.
Financial Presentations: Present financial data formally, aiding stakeholders in investment and decision-making.
Board Meetings: Conduct formal board meetings to discuss organizational strategies and governance matters.
Collaboration Agreements: Negotiate and finalize collaborations formally, defining roles and expectations.
Product Launch Presentations: Unveil new products formally, capturing the audience’s attention and interest.
Stakeholder Updates: Keep stakeholders informed through formal updates on project progress and milestones.
Investor Relations Communications: Communicate effectively with investors through formal reports and updates.
Formal Communication Skills Examples in Real Life
Discover how formal communication skills manifest in everyday life situations. From personal interactions to community involvement, these real-life examples demonstrate the significance of clear and intentional communication beyond professional settings.
Family Meetings: Conduct formal family meetings to discuss important matters and make collective decisions.
Community Presentations: Deliver formal presentations in community events, fostering understanding and collaboration.
School Parent-Teacher Conferences: Communicate formally with parents, discussing students’ progress and development.
Public Speeches: Deliver formal speeches on relevant topics, capturing the audience’s attention and conveying a clear message.
Volunteer Organization Updates: Communicate formally within volunteer organizations, ensuring alignment with goals and initiatives.
Municipal Council Meetings: Participate in formal council meetings to discuss community issues and solutions.
Neighborhood Watch Announcements: Disseminate important information formally within a neighborhood, promoting safety and awareness.
Social Club Events: Organize and communicate details of social club events formally, ensuring member participation.
Charity Fundraising Campaigns: Coordinate and promote charity campaigns formally, reaching a broader audience.
Community Workshops: Conduct formal workshops to educate and empower community members on various subjects
What are the Basic Elements of Formal Communication?
Formal communication is structured, intentional, and follows established channels within an organization. To grasp its essence, understanding the fundamental elements is crucial.
Hierarchy and Structure: Recognize the role of organizational hierarchy in formal communication. Information flows through established levels, ensuring a structured and organized process.
Official Channels: Formal communication relies on official channels like emails, memos, and official meetings. These channels maintain a professional tone and facilitate clear information transmission.
Rules and Procedures: Formal communication adheres to predetermined rules and procedures. This ensures consistency and clarity in conveying messages.
Documentation: In formal communication, documentation is key. Written records, reports, and official documents play a pivotal role in maintaining transparency and accountability.
Professional Language: The language used in formal communication is professional, avoiding informal or colloquial expressions. This promotes clarity and a serious tone.
Planned and Deliberate: Unlike informal communication, formal communication is planned and deliberate. Messages are carefully crafted to convey specific information accurately.
Feedback Channels: Formal communication allows for structured feedback channels, enabling a two-way flow of information. This ensures that messages are understood and acted upon appropriately.
Understanding these basic elements provides a solid foundation for navigating the intricacies of formal communication within any organizational context.
How to Improve Formal Communication Skills?
Enhancing formal communication skills is essential for professional success. Here’s a comprehensive guide to refining and mastering this crucial skill set.
Active Listening: Cultivate active listening skills to understand information thoroughly. Respond thoughtfully to demonstrate comprehension.
Clarity and Conciseness: Practice delivering messages with clarity and conciseness. Avoid unnecessary details and communicate the core message directly.
Body Language: In formal communication, body language matters. Maintain appropriate posture, make eye contact, and use gestures judiciously to convey confidence and engagement.
Adapt to the Audience: Tailor your communication style to suit your audience. Consider their expectations, knowledge, and preferences to convey messages effectively.
Structured Messaging: Organize your thoughts before communicating. Use a structured format, ensuring a logical flow of information in written and verbal communication.
Professional Writing Skills: Hone your writing skills for formal documentation. Ensure grammatical accuracy, clarity, and adherence to the professional tone.
Politeness and Respect: Practice politeness and respect in all communications. Use formal salutations and be mindful of cultural nuances to build positive relationships.
Feedback Solicitation: Actively seek feedback on your communication style. Identify areas for improvement and continuously refine your skills based on constructive input.
Role-Playing Exercises: Engage in role-playing exercises to simulate real communication scenarios. This helps build confidence and sharpens your ability to respond effectively.
Continuous Learning: Stay updated on communication trends and best practices. Embrace a mindset of continuous learning to adapt to evolving communication challenges.
What is Difference Between Formal and Informal Communication Skills?
Formal and informal communication skills represent distinct approaches to conveying information in various settings. Differentiating between these two styles is crucial for effective interactions. Here’s a comprehensive guide presented in a table format to illuminate the variances:

Aspect | Formal Communication Skills | Informal Communication Skills |
|---|---|---|
Setting | Typically in professional environments structured contexts. | Commonly in casual, social settings, and day-to-day interactions. |
Language | Utilizes precise, planned, and clear language. | Involves relaxed, spontaneous, and colloquial language. |
Tone | Tends to be serious, focused, and objective. | Reflects a more relaxed, personal, and subjective tone. |
Structure | Follows a predetermined structure and format. | Lacks a rigid structure, often spontaneous and dynamic. |
Audience | Targets specific audiences such as colleagues, clients, or superiors. | Involves a broad audience, including friends, family, and peers. |
Purpose | Conveys official information, instructions, or reports. | Aims for building relationships, sharing personal experiences, and casual discussions. |
Examples | Business presentations, official emails, and reports. | Conversations with friends, family gatherings, and social media interactions. |
Mastering Formal Communication Skills is a transformative journey. By adhering to structured approaches in various settings, individuals can enhance workplace efficiency, build professional relationships, and convey ideas with precision. This guide has illuminated the nuances, providing actionable tips for effective communication. Elevate your skills, embrace clarity, and make a lasting impact through the power of formal communication.


