Former vs Latter – Examples, Differences, Usage
Understanding the correct usage of “former” and “latter” is crucial for clear and effective communication. These terms serve as linguistic signposts, guiding readers through the specifics of a two-part sequence withi9n a sentence. “Former” points us to the first mentioned item, while “latter” directs attention to the second or final item. Their application is not just a matter of choice but of precision, as they help to avoid ambiguity and enhance the clarity of written discourse.
Navigating the use of “former” and “latter” can seem daunting, especially for those encountering these terms for the first time or those unsure of their exact meanings. However, the rules governing their use are surprisingly straightforward, provided one remembers that they are only applicable in contexts involving two items. This article aims to demystify these terms by delving deeper into their meanings, differences, and correct applications, bolstered by practical examples. By mastering the distinctions between “former” and “latter,” readers can elevate their writing, ensuring it is not only grammatically correct but also rich in precision and clarity.
Former and Latter – Meanings
In English, “former” and “latter” are terms often used to refer to time or sequence, but they have distinct meanings and are used in different contexts.
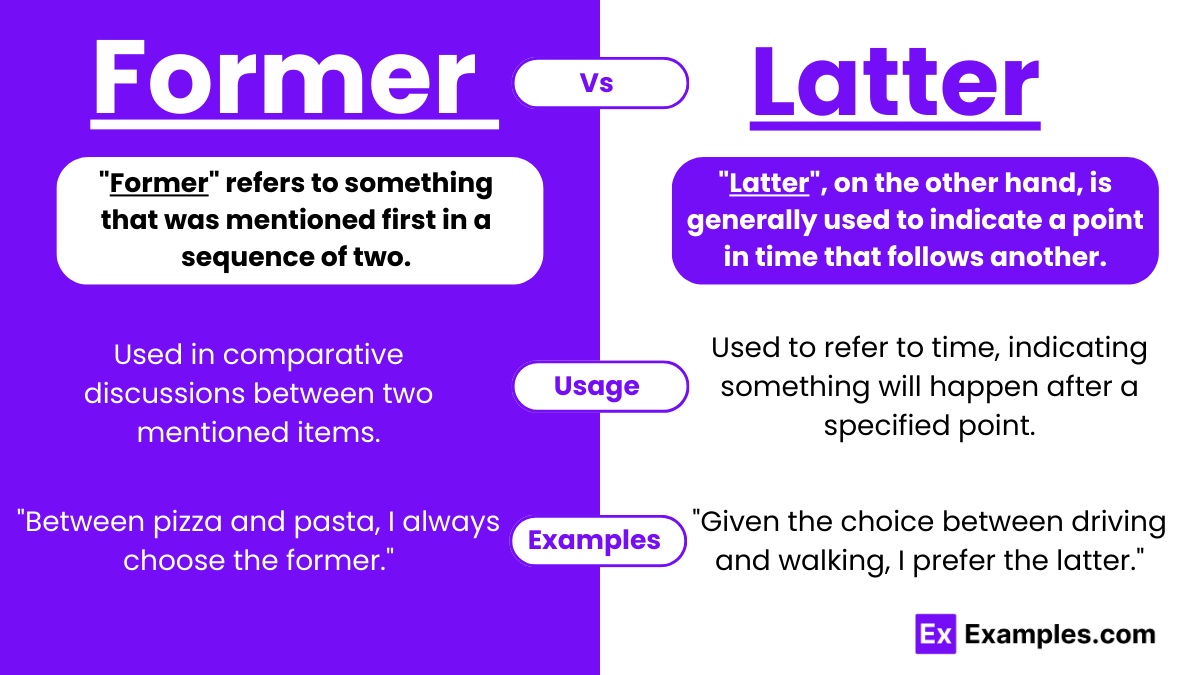
- Former refers to something that was mentioned first in a sequence of two. It is used to denote the first of two items, people, or situations mentioned in a discussion or text. For example, in the sentence “Alice prefers coffee, while Bob likes tea; the former is more of a morning person,” “former” clearly points to Alice and her preference for coffee, indicating she was mentioned first.
- Latter, on the other hand, is generally used to indicate a point in time that follows another. Unlike “former,” which is used to reference the first of two mentioned items, “latter” does not specifically compare two items but rather suggests a subsequent time or event. For instance, saying “I will do my homework latter” implies that the action (doing homework) will occur at a future time, following the current moment or after another event.
It’s crucial to note that “latter” does not serve the same comparative function between two elements as “former.” Instead, it’s used to refer to temporal sequences without directly comparing two specific items. Understanding the differences between these terms is key to using them correctly and effectively in written and spoken English, ensuring clear communication of time and sequence.
Summary
“Former” and “latter” serve distinct purposes related to sequence and time. “Former” is employed to reference the first of two items or subjects mentioned, helping to specify or clarify when two things are discussed, such as in contrasting preferences or characteristics. On the other hand, “latter” indicates a subsequent time or event, not directly comparing two distinct items but rather suggesting progression or future action. While “former” is used in a comparative context between two mentioned elements, “latter” focuses on the timing of actions or events, making it crucial to understand and apply these terms correctly to ensure clear and precise communication.
Difference Between Former and Latter
| Aspect | Former | Latter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Refers to the first of two items, people, or situations mentioned. | Indicates a subsequent time or event, not directly comparing two items but suggesting progression. |
| Usage Context | Used in comparative discussions between two mentioned items. | Used to refer to time, indicating something will happen after a specified point. |
| Example | In “John likes apples, and Mary likes oranges; the former prefers fruit,” “former” refers to John. | “I will visit the store latter” means the visit will happen at a future time, after now. |
| Function | Specifies or clarifies in a comparison of two. | Indicates progression or future action without direct comparison. |
| Relation | Always relates to two specifically mentioned subjects or objects. | Relates to the timing of events or actions, not limited to comparisons. |
How to remember the difference between former and latter
To easily remember the difference between “former” and “latter,” think of “former” as referring to the “first” item mentioned out of two, with both starting with the letter “F.” On the other hand, “latter” relates to the “latter” or last item mentioned, with “latter” and “latter” sharing the starting letter “L.” This simple association with their starting letters — “F” for “former” (first) and “L” for “latter” (latter) — can help you quickly recall which is which when distinguishing between two things in a sentence.
When to use Former vs Latter
When to Use “Former”
- Comparing Two Things: Use “former” when you need to refer back to the first of two items, concepts, or individuals mentioned in a sentence or discussion. It specifically points to the initial option or subject in a pair.
- Clarifying Preferences or Choices: When distinguishing between two options or preferences, “former” is used to indicate the option that was listed or mentioned first. It helps clarify which of the two is being discussed or preferred.
- Highlighting a Sequence: In texts where two items are introduced sequentially, “former” refers back to the first item. This is useful in academic or analytical writing where clarity between two subjects is crucial.
When to Use “Latter”
- Indicating Time: Use “latter” when referring to a point in time that follows the present moment or the context currently being discussed. It is not used for comparing two things but for discussing the timing of events or actions.
- Describing Sequential Actions or Events: “Latter” is appropriate when outlining steps, actions, or events that will happen subsequent to the current focus. It suggests progression or the next phase without directly comparing two distinct entities.
- Future Reference: In planning or discussing future events, tasks, or intentions, “latter” is used to denote that something is intended to occur after a specified point, without being compared to another specific item or event.
Examples of Former vs Later
Former Examples
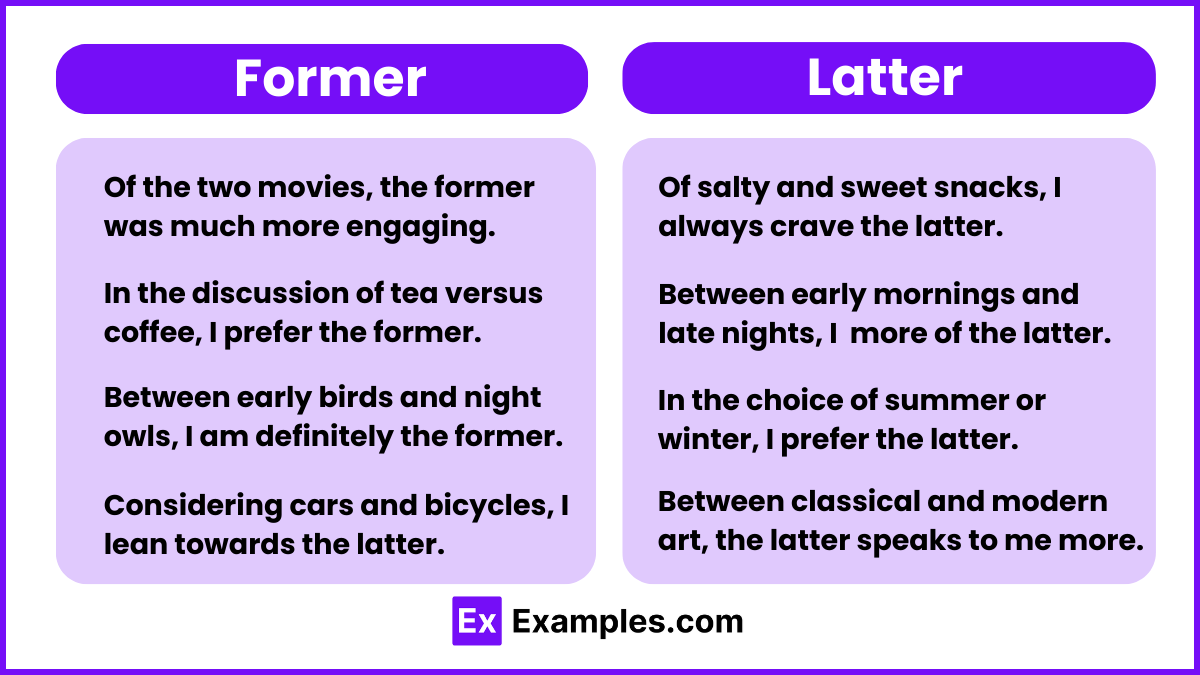
- In a Comparison: “Sarah loves to read fiction, whereas Kim prefers non-fiction. The former spends her weekends at the library.”
In this sentence, “former” refers to Sarah and her preference for fiction. - In a Sequence: “Between tea and coffee, the former is my favorite morning beverage.”
Here, “former” indicates tea, as it was mentioned first. - Clarifying Position: “Of the two cars, the sedan and the SUV, the former is more fuel-efficient.”
“Former” points to the sedan because it was listed first. - Preference Clarification: “In the debate between staying in and going out, Joe prefers the former, enjoying quiet nights at home.” Here, “former” specifically identifies staying in as Joe’s preferred choice.
- Historical Interest: “Between studying the Roman Empire and the Medieval period, the former fascinates Henry more.”
“Former” indicates Henry’s greater interest in the Roman Empire.
Later Examples
- Referring to Time: “I have a meeting now, but I’ll join you for lunch later.”
“Later” indicates a time after the current moment, with no comparison to another event. - In Progression: “She plans to study for her exams now and go out with friends later.”
This use of “later” suggests a subsequent action or event. - Future Plans: “We discussed the budget earlier; we’ll tackle the marketing plan later.”
Here, “later” refers to a future point when the marketing plan will be discussed. - Day Planning: “We’ll have a team meeting in the morning and review the reports later in the day.”
“Later” indicates the reports will be reviewed at a subsequent time after the meeting. - Sequential Learning: “Start with the basics of programming and tackle more complex concepts later.”
In this context, “later” suggests a progression in learning difficulty.
Former and latter as adjectives
In English, the adjectives “former” and “latter” are used to refer to the first and second of two things or people mentioned, respectively. When you discuss two subjects and need to reference them later, “former” points back to the first mentioned, while “latter” refers to the second. This distinction helps clarify which subject is being talked about without needing to repeat their names or descriptions.
Examples
- In the debate between coffee and tea, the former is preferred for its energizing effect, while the latter is chosen for its variety of flavors.
- Here, “former” refers to coffee, and “latter” to tea.
- Between cats and dogs, the former are known for their independence, whereas the latter are celebrated for their loyalty.
- In this case, “former” points to cats, and “latter” to dogs.
- Of the novels “Pride and Prejudice” and “Wuthering Heights,” the former explores themes of manners and marriage, while the latter delves into passionate but doomed love.
- “Former” is used for “Pride and Prejudice,” and “latter” for “Wuthering Heights.”
Former and latter as noun phrases
When used as noun phrases, “former” and “latter” act similarly to their adjective forms but take on the role of nouns in sentences. They still refer to the first and second of two things or people mentioned, respectively, but do so by standing in as placeholders for those subjects. This usage simplifies sentences and avoids repetition, keeping communication clear and concise.
Examples
- Of jazz and blues, the former originated in the late 19th to early 20th century, while the latter has roots in the deep South of the United States.
- Here, “the former” stands in place of “jazz,” and “the latter” refers to “blues.”
- Between studying and working, the former offers an opportunity to expand knowledge, whereas the latter provides practical experience.
- In this example, “the former” is used for “studying,” and “the latter” refers to “working.”
- Regarding morning workouts and evening exercises, the former can energize your day ahead, while the latter helps to relieve the day’s stress.
- “The former” replaces “morning workouts,” and “the latter” signifies “evening exercises.”
FAQs
What is the rule for former and latter?
The rule is straightforward: “former” refers to the first of two things mentioned, and “latter” refers to the second. This distinction aids clarity in discussions involving two subjects.
How do you use the latter phrase?
“The latter” is used to refer back to the second of two topics or items mentioned previously in a conversation or text, avoiding repetition.
Why is it called the former and the latter?
“Former” and “latter” come from Old English, serving to distinguish the first and second of two mentioned items, respectively, in a clear and concise manner.
When people say latter?
People say “latter” when referring to the second of two items or subjects mentioned in a discussion, indicating a specific preference or detail about it.
Why do people say latter instead of later?
“Latter” is used instead of “later” to specifically refer to the second of two items mentioned earlier, not to denote something occurring after a certain time.