30+ Hyphen Examples
Hyphens, often overlooked yet remarkably versatile, serve as linguistic bridges, connecting words, phrases, and concepts. With their subtle presence, they clarify compound adjectives, such as “well-known,” and denote joint authorship in multi-author citations. In a digital age rife with jargon and rapid communication, hyphens maintain clarity, distinguishing “re-cover” from “recover.” Their absence can alter meanings, emphasizing the significance of their judicious use. Understanding hyphens is not merely a matter of grammar; it’s a testament to precision in language.
What is a Hyphen?
A hyphen is a punctuation mark used to join words or parts of words together. It clarifies compound adjectives, like “well-known,” and denotes joint authorship in citations. Its absence can alter meanings significantly. Hyphens maintain clarity in language, distinguishing “re-cover” from “recover.” Understanding their judicious use is crucial for precision in communication.
Function of Hyphen
The function of a hyphen is multifaceted and serves various linguistic purposes:
- Joining Words: Hyphens are used to connect words or parts of words to create compound words or phrases, such as “mother-in-law” or “well-being.”
- Clarifying Compound Adjectives: Hyphens clarify the relationship between words in compound adjectives, ensuring clarity in meaning. For example, “high-speed train” clarifies that “high” modifies “speed” and not “train.”
- Denoting Joint Authorship: In citations or attributions involving multiple authors, hyphens indicate joint authorship, such as “Smith-Jones study.”
- Separating Syllables: Hyphens are used to divide words at the end of lines in typesetting to maintain proper spacing and readability.
- Expressing Word Formation: Hyphens can denote word formation, particularly in prefixes and suffixes, such as “pre-approval” or “re-evaluate.”
- Avoiding Ambiguity: Hyphens help avoid ambiguity and misinterpretation in language, distinguishing between words like “re-cover” (to cover again) and “recover” (to regain).
Importance of Hyphen
The importance of hyphens lies in their ability to enhance clarity, precision, and readability in language usage. Here’s why hyphens are significant:
- Clarity and Precision: Hyphens clarify the relationship between words in compound terms or phrases, preventing ambiguity and ensuring precise communication. For instance, “small-business owner” clarifies that “small” pertains to the business’s size, not the owner’s stature.
- Readability and Understanding: By joining words or parts of words, hyphens aid in readability by breaking down complex terms into easily digestible units. This facilitates comprehension, especially in technical or specialized context.
- Grammar and Syntax: Hyphens play a vital role in adhering to grammatical conventions and syntactical rules, particularly in compound adjectives, prefixes, and word formation. They help maintain grammatical correctness and coherence in writing.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): In digital content creation, hyphens can impact SEO by influencing keyword placement and readability. Proper use of hyphens in compound keywords or phrases can improve search engine visibility and ranking.
- Typesetting and Formatting: In publishing and design, hyphens are essential for typesetting and formatting, especially in justified text where they help maintain consistent spacing and line breaks.
- Professionalism and Clarity: Correct usage of hyphens reflects professionalism and attention to detail in writing. It enhances the overall quality of communication and contributes to a positive impression on readers or audiences.
When to Use a Hyphen?
Knowing when to use a hyphen is crucial for clear and precise writing. Here are some common scenarios:
- Compound Words: Use a hyphen to connect two or more words that function together as a single idea before a noun, such as “well-being” or “high-quality.”
- Compound Adjectives: Hyphenate compound adjectives that come before a noun to clarify their relationship, like “long-term solution” or “high-speed train.”
- Prefixes: Hyphenate prefixes before proper nouns or capitalized words, such as “pre-World War II” or “anti-American.”
- Numbers and Fractions: Hyphenate spelled-out fractions and compound numbers from twenty-one to ninety-nine, like “three-quarters” or “fifty-five.”
- Joining Words: Hyphens can join prefixes to words to avoid confusion or awkward combinations, such as “ex-husband” or “pro-choice.”
- Word Breaks: Hyphens are used at the end of lines in typesetting to indicate where a word is divided between syllables to maintain proper spacing and readability
Types of Hyphens
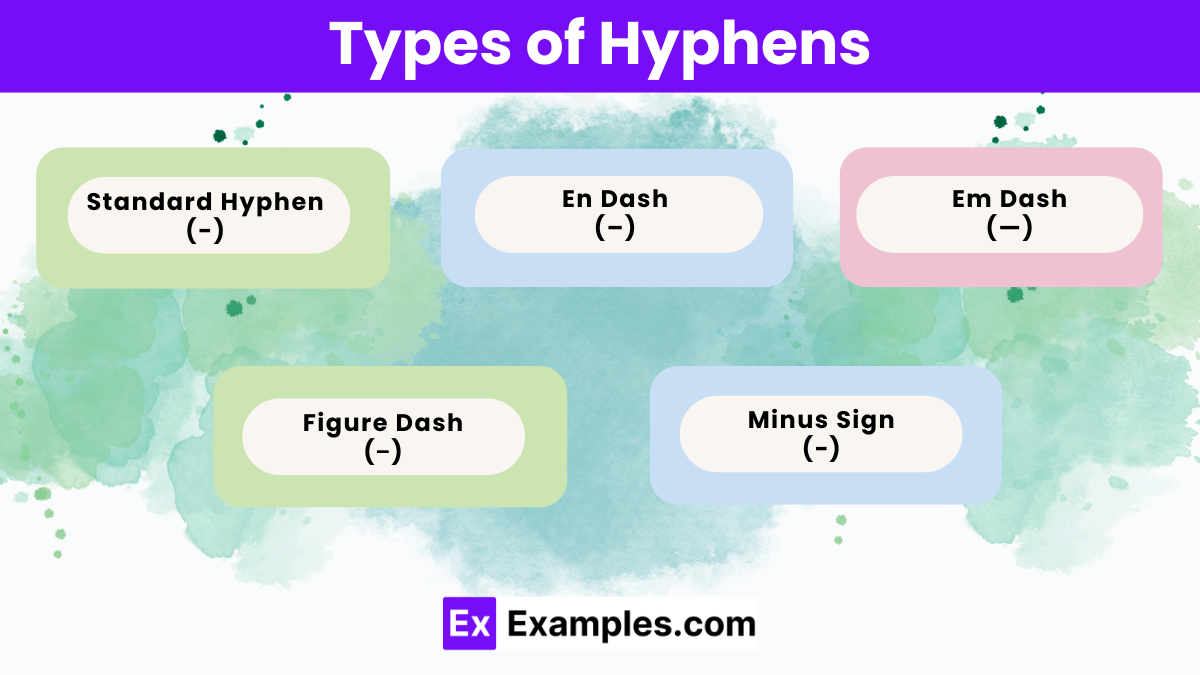
Hyphens come in various types, each serving specific purposes in writing and typography:
- Standard Hyphen (-): This is the most common type of hyphen, used to join words or parts of words in compound terms, such as “mother-in-law” or “self-confidence.”
- En Dash (–): Slightly longer than a hyphen, the en dash is used to indicate a range or connection between two elements, such as “pages 10–15” or “New York–London flight.”
- Em Dash (—): Longer than both the hyphen and en dash, the em dash is used to indicate a break in thought, an interruption, or an emphasis within a sentence—much like this example.
- Figure Dash (‒): This dash is used in numerical ranges, such as phone numbers or dates, where the en dash or hyphen might be unclear or ambiguous.
- Minus Sign (−): Often used in mathematical expressions or equations to indicate subtraction, the minus sign is similar in appearance to a hyphen but serves a different purpose.
Hyphen vs. Dash
| Aspect | Hyphen (-) | Dash (–) |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Shorter, like a minus sign | Slightly longer |
| Usage | Joining words or indicating ranges (e.g., 18-25) | Indicating ranges or relationships (e.g., 10–15) |
| Examples | self-confidence, 18-25 | New York–London flight |
| Function | Used for compound words and numerical ranges | Used for indicating connections or relationships |
| Typical Usage | Text, compound terms | Tables, ranges, connections |
Hyphens with Prefixes
Hyphens with prefixes are used to ensure clarity and readability, especially when the prefix and the root word might cause confusion or ambiguity if left unhyphenated. Here’s a breakdown:
- Prefixes with Hyphens: Some prefixes are commonly hyphenated when combined with a root word to avoid confusion or to create a new meaning. Examples include:
- Non-: Non-alcoholic, non-native.
- Pre-: Pre-existing, pre-approval.
- Ex-: Ex-husband, ex-president.
- Exceptions: Not all prefixes require hyphens; it depends on whether their combination with the root word could cause confusion. For example:
- Un-: Unhappy, uncertain.
- Co-: Coexist, cooperate.
- Consistency: Maintaining consistency in hyphenation is important within a text or document. If a prefix is hyphenated in one word, it should typically be hyphenated in similar contexts throughout the text.
Examples of Hyphenated Compound Words
- Mother-in-law: Referring to the mother of one’s spouse.
- Well-being: Referring to a state of health and happiness.
- Self-confidence: Referring to belief in oneself and one’s abilities.
- Co-worker: Referring to a colleague or associate in the workplace.
- High-speed: Referring to something that moves or operates at a fast pace.
- Six-year-old: Referring to someone who is six years of age.
- Check-in: Referring to the process of registering upon arrival, often used in hotels or airports.
- Up-to-date: Referring to something that is current or modern.
- Mind-set: Referring to a person’s attitudes, beliefs, or outlook.
- Good-natured: Referring to someone who is friendly and amiable by disposition.
Examples of Hyphen in Sentence
- She drove her well–loved, vintage car down the winding, tree–lined road.
- The small–business owner was thrilled to receive positive feedback from customers.
- The family–friendly restaurant offers a variety of kid–friendly meals.
- He lived in a two–bedroom, apartment complex in the heart of the city.
- The eco–friendly company promotes sustainable practices in its manufacturing process.
- We enjoyed a once–in–a–lifetime opportunity to see the Northern Lights.
- Her quick–witted, humorous remarks always livened up the conversation.
- The state–of–the–art facility is equipped with the latest technology.
- She wore a well–fitting, tailor–made suit to the job interview.
- The open–minded, forward–thinking approach of the organization appealed to many.
Examples of Hyphen in Writing
- Poetry: “The moonlit sky cast a silver-blue hue over the tranquil, still waters.”
- Fiction: “The old, weather-beaten house stood at the end of the long, winding road.”
- Journalism: “The 20-year-old athlete broke the long-standing record with a last-minute, heart-stopping finish.”
- Technical Writing: “The user-friendly interface provides easy-to-navigate options for customization.”
- Business Communication: “The company offers a range of cost-effective, time-saving solutions for small businesses.”
- Academic Writing: “The peer-reviewed, scholarly article presents groundbreaking research in the field of neuroscience.”
- Creative Writing: “Her larger-than-life personality filled the room with warmth and laughter.”
- Marketing Copy: “Unlock the full potential of your business with our cutting-edge, industry-leading software.”
- Email Correspondence: “Please find attached the revised, updated version of the proposal.”
- Blogging: “The step-by-step guide offers practical, actionable advice for improving your productivity.”
Is a Hyphen and an Apostrophe the same thing?
No, a hyphen and an apostrophe are not the same. A hyphen is used to join words or parts of words, while an apostrophe is used to indicate possession or contraction in words.
Why is a Hyphen used between two Words?
A hyphen is used between two words to join them together into a compound word or to connect elements in a phrase, creating clarity, indicating a combined meaning, or modifying a noun.
Why do you put a Hyphen between Words?
A hyphen is placed between words to join them together into a compound word, clarify meaning, indicate a combined concept, or modify a following noun, improving readability and precision in written communication.



