19+ Intercultural Competency Examples
Intercultural Competency is a crucial skill in Intercultural Communication, enabling individuals to interact effectively and respectfully with people from diverse cultural backgrounds. This competency encompasses a range of abilities, including cultural awareness, sensitivity, adaptability, and empathy. It’s essential for navigating the complexities of today’s globalized world, whether in business, education, or social interactions. Developing intercultural competency enhances personal and professional relationships and fosters a deeper understanding and appreciation of cultural diversity.
What is Intercultural Competency?

Intercultural Competency refers to the capability to understand, communicate with, and effectively interact with people across cultures. It involves awareness of one’s own cultural worldview, knowledge of other cultural practices and worldviews, respectful attitude towards cultural differences, and cross-cultural skills. This competency is vital in today’s interconnected world, aiding in overcoming potential cultural barriers and fostering successful Intercultural Communication.
What is the Best Example of Intercultural Competency?

A prime example of Intercultural Competency can be observed in multicultural team management where leaders effectively navigate and reconcile diverse cultural perspectives to achieve common goals. This involves recognizing each team member’s cultural background, adapting communication styles to ensure inclusivity, and resolving conflicts by understanding different cultural viewpoints. Such competency not only enhances team dynamics but also contributes to a more productive and harmonious work environment.
20 Examples of Intercultural Competency

Intercultural competency is essential in today’s globalized world. It involves understanding, respecting, and effectively communicating with people from diverse cultures. This skill set is increasingly valuable, both in personal and professional contexts. By embracing intercultural communication, individuals and organizations can foster more inclusive and productive environments. Here are 20 examples showcasing intercultural competency, each accompanied by a brief explanation and sample communication sentences.
1. Active Listening in Diverse Settings: Showing genuine interest in the perspectives of colleagues from various cultures.
Example: “I really want to understand your viewpoint. Can you tell me more about your cultural practices?”
2. Adapting Communication Styles: Altering one’s communication approach to suit the cultural context.
Example: “I’ve noticed that directness varies across cultures. How would you prefer to receive feedback?”
3. Cultural Sensitivity in Marketing Campaigns: Creating advertising that respects and appeals to multiple cultures.
Example: “Let’s ensure our campaign imagery reflects diverse cultural backgrounds.”
4. Inclusive Decision Making: Incorporating diverse viewpoints in organizational decisions.
Example: “I think it’s important we consider how this decision affects our teams globally.”
5. Language Flexibility: Using clear, simple language or switching languages if needed.
Example: “Would it be easier for you if I provided this information in Spanish?”
6. Empathetic Conflict Resolution: Addressing misunderstandings with a focus on cultural empathy.
Example: “I understand this might be a cultural misunderstanding. Let’s work together to resolve it.”
7. Celebrating Cultural Festivals: Acknowledging and participating in the cultural festivals of colleagues.
Example: “Happy Diwali! I’d love to learn more about this festival.”
8. Constructive Feedback Across Cultures: Providing feedback that is culturally sensitive.
Example: “I want to give feedback in a way that’s respectful of your cultural norms. How should I approach this?”
9. Global Team Collaboration: Facilitating effective collaboration in culturally diverse teams.
Example: “Let’s discuss how we can leverage our diverse backgrounds to enhance our project.”
10. Cultural Adaptability in Relocation: Adapting quickly to a new cultural environment when relocating.
Example: “I’m researching local customs to better integrate into my new community.”
11. Intercultural Negotiation Skills: Negotiating deals while respecting cultural differences.
Example: “I understand the importance of relationship-building in your culture before we proceed with negotiations.”
12. Respect for Cultural Time Perceptions: Being mindful of different cultural perceptions of time.
Example: “I realize punctuality can have different meanings in various cultures. What’s your perspective?”
13. Cultural Awareness Training: Participating in or conducting cultural sensitivity training.
Example: “This training helped me understand the nuances of intercultural communication.”
14. Addressing Stereotypes: Actively challenging and avoiding cultural stereotypes.
Example: “I know it’s a common stereotype, but let’s not make assumptions about their culture.”
15. Intercultural Mentoring: Mentoring someone from a different cultural background.
Example: “As your mentor, I’m here to help you navigate the cultural aspects of our workplace.”
16. Diverse Hiring Practices: Implementing hiring practices that value cultural diversity.
Example: “We’re looking for candidates who can bring a diverse cultural perspective to our team.”
17. Cross-Cultural Customer Service: Providing customer service that considers cultural nuances.
Example: “I understand your concern. Let me explain this in a way that might be more aligned with your cultural expectations.”
18. Cultural Immersion Experiences: Engaging in experiences to deeply understand different cultures.
Example: “Living in Japan for a month really opened my eyes to different ways of working and living.”
19. Reflecting on Personal Biases: Regularly reflecting on and challenging one’s own cultural biases.
Example: “I’m constantly trying to be aware of my biases and how they affect my interactions.”
20. Embracing Diverse Cultural Perspectives: Actively seeking out and valuing diverse cultural viewpoints.
Example: “Your perspective is unique and valuable. Can you share more about your cultural background?”
These examples underscore the importance of intercultural competency in fostering effective and respectful communication across diverse cultural landscapes
Types of Intercultural Competency
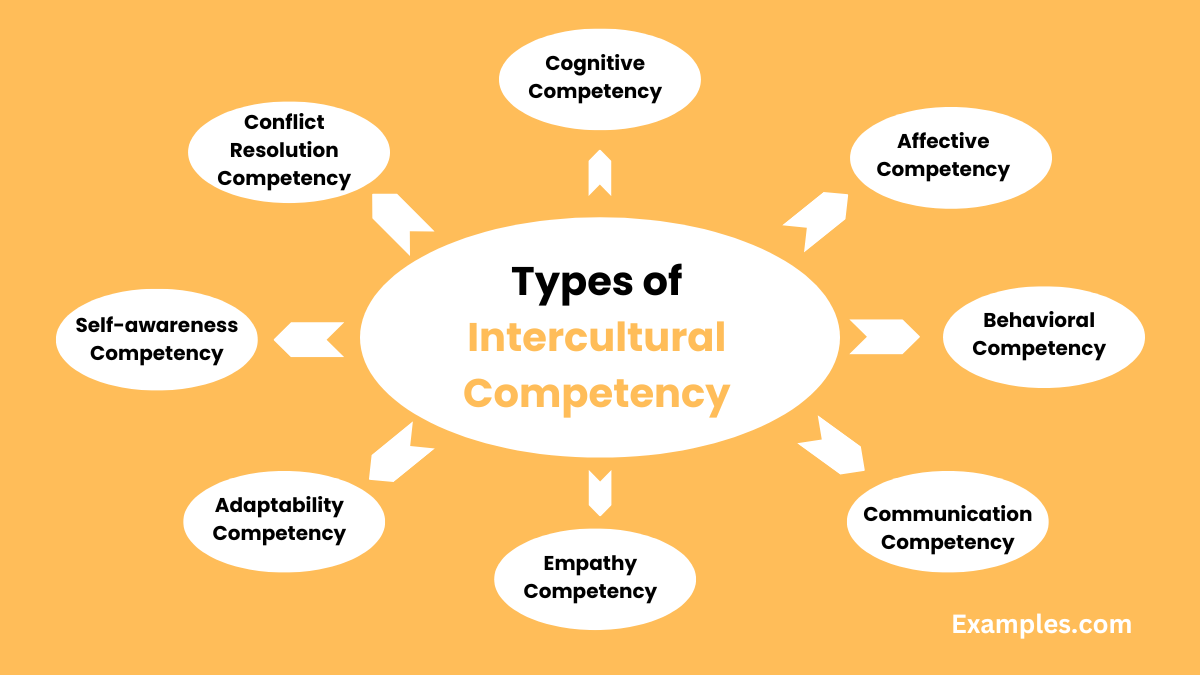
Intercultural Competency in the realm of Intercultural Communication can be categorized into several types, each addressing different aspects of cultural interactions.
- Cognitive Competency: Involves knowledge and understanding of different cultures and worldviews.
- Affective Competency: Relates to attitudes, emotions, and values towards cultural differences.
- Behavioral Competency: Encompasses skills and behaviors for effective intercultural interactions.
- Communication Competency: Focuses on language skills and non-verbal communication understanding.
- Empathy Competency: The ability to empathize with individuals from diverse backgrounds.
- Adaptability Competency: Flexibility in adapting to new cultural environments.
- Self-awareness Competency: Recognizing one’s own cultural biases and perspectives.
- Conflict Resolution Competency: Skills in resolving misunderstandings and conflicts in a culturally sensitive manner.
Each type plays a crucial role in enhancing Intercultural Communication and fostering meaningful cross-cultural interactions.
Components of Intercultural Competency
Intercultural Competency consists of several key components that contribute to effective and respectful Intercultural Communication.
- Cultural Awareness: Understanding one’s own culture and recognizing its influence on perceptions.
- Cultural Knowledge: Acquiring knowledge about different cultural practices and norms.
- Communication Skills: Developing skills to convey and interpret messages across cultures.
- Empathy: Ability to see situations from others’ cultural perspectives.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Showing respect and consideration for different cultural practices.
- Adaptability: Flexibility in adjusting behaviors and attitudes in diverse settings.
- Open-mindedness: Being open to new cultural experiences and ideas.
- Tolerance for Ambiguity: Comfort with cultural uncertainties and complexities.
These components are essential for developing Intercultural Competency and navigating the complexities of diverse cultural landscapes.
Importance of Intercultural Competency
Intercultural Competency is increasingly crucial in today’s globalized world, particularly in the context of Intercultural Communication.
- Enhances Global Business Relations: Facilitates successful international business negotiations and partnerships.
- Improves Cross-Cultural Understanding: Promotes deeper understanding and appreciation of diverse cultures.
- Supports Effective Communication: Reduces misunderstandings and improves communication effectiveness.
- Fosters Inclusive Environments: Essential for creating inclusive workplaces and social spaces.
- Enhances Personal and Professional Growth: Broadens personal perspectives and professional opportunities.
- Reduces Cultural Conflicts: Helps in navigating and resolving cultural misunderstandings.
- Strengthens Global Networks: Aids in building robust and diverse professional networks.
- Promotes Global Citizenship: Encourages responsible and informed interactions in a global context.
The importance of developing Intercultural Competency cannot be overstated, as it is key to thriving in an interconnected and culturally diverse world.
Intercultural Competency is vital for effective Intercultural Communication in our increasingly interconnected world. This guide has explored the types, components, and importance of developing such competencies, emphasizing their role in fostering successful cross-cultural interactions. Whether in personal growth, professional development, or global business relations, Intercultural Competency is a fundamental skill set that enhances understanding, respect, and collaboration across diverse cultural landscapes.
19+ Intercultural Competency Examples

Intercultural Competency is a crucial skill in Intercultural Communication, enabling individuals to interact effectively and respectfully with people from diverse cultural backgrounds. This competency encompasses a range of abilities, including cultural awareness, sensitivity, adaptability, and empathy. It’s essential for navigating the complexities of today’s globalized world, whether in business, education, or social interactions. Developing intercultural competency enhances personal and professional relationships and fosters a deeper understanding and appreciation of cultural diversity.
What is Intercultural Competency?

Intercultural Competency refers to the capability to understand, communicate with, and effectively interact with people across cultures. It involves awareness of one’s own cultural worldview, knowledge of other cultural practices and worldviews, respectful attitude towards cultural differences, and cross-cultural skills. This competency is vital in today’s interconnected world, aiding in overcoming potential cultural barriers and fostering successful Intercultural Communication.
What is the Best Example of Intercultural Competency?

A prime example of Intercultural Competency can be observed in multicultural team management where leaders effectively navigate and reconcile diverse cultural perspectives to achieve common goals. This involves recognizing each team member’s cultural background, adapting communication styles to ensure inclusivity, and resolving conflicts by understanding different cultural viewpoints. Such competency not only enhances team dynamics but also contributes to a more productive and harmonious work environment.
20 Examples of Intercultural Competency

Intercultural competency is essential in today’s globalized world. It involves understanding, respecting, and effectively communicating with people from diverse cultures. This skill set is increasingly valuable, both in personal and professional contexts. By embracing intercultural communication, individuals and organizations can foster more inclusive and productive environments. Here are 20 examples showcasing intercultural competency, each accompanied by a brief explanation and sample communication sentences.
1. Active Listening in Diverse Settings: Showing genuine interest in the perspectives of colleagues from various cultures.
Example: “I really want to understand your viewpoint. Can you tell me more about your cultural practices?”
2. Adapting Communication Styles: Altering one’s communication approach to suit the cultural context.
Example: “I’ve noticed that directness varies across cultures. How would you prefer to receive feedback?”
3. Cultural Sensitivity in Marketing Campaigns: Creating advertising that respects and appeals to multiple cultures.
Example: “Let’s ensure our campaign imagery reflects diverse cultural backgrounds.”
4. Inclusive Decision Making: Incorporating diverse viewpoints in organizational decisions.
Example: “I think it’s important we consider how this decision affects our teams globally.”
5. Language Flexibility: Using clear, simple language or switching languages if needed.
Example: “Would it be easier for you if I provided this information in Spanish?”
6. Empathetic Conflict Resolution: Addressing misunderstandings with a focus on cultural empathy.
Example: “I understand this might be a cultural misunderstanding. Let’s work together to resolve it.”
7. Celebrating Cultural Festivals: Acknowledging and participating in the cultural festivals of colleagues.
Example: “Happy Diwali! I’d love to learn more about this festival.”
8. Constructive Feedback Across Cultures: Providing feedback that is culturally sensitive.
Example: “I want to give feedback in a way that’s respectful of your cultural norms. How should I approach this?”
9. Global Team Collaboration: Facilitating effective collaboration in culturally diverse teams.
Example: “Let’s discuss how we can leverage our diverse backgrounds to enhance our project.”
10. Cultural Adaptability in Relocation: Adapting quickly to a new cultural environment when relocating.
Example: “I’m researching local customs to better integrate into my new community.”
11. Intercultural Negotiation Skills: Negotiating deals while respecting cultural differences.
Example: “I understand the importance of relationship-building in your culture before we proceed with negotiations.”
12. Respect for Cultural Time Perceptions: Being mindful of different cultural perceptions of time.
Example: “I realize punctuality can have different meanings in various cultures. What’s your perspective?”
13. Cultural Awareness Training: Participating in or conducting cultural sensitivity training.
Example: “This training helped me understand the nuances of intercultural communication.”
14. Addressing Stereotypes: Actively challenging and avoiding cultural stereotypes.
Example: “I know it’s a common stereotype, but let’s not make assumptions about their culture.”
15. Intercultural Mentoring: Mentoring someone from a different cultural background.
Example: “As your mentor, I’m here to help you navigate the cultural aspects of our workplace.”
16. Diverse Hiring Practices: Implementing hiring practices that value cultural diversity.
Example: “We’re looking for candidates who can bring a diverse cultural perspective to our team.”
17. Cross-Cultural Customer Service: Providing customer service that considers cultural nuances.
Example: “I understand your concern. Let me explain this in a way that might be more aligned with your cultural expectations.”
18. Cultural Immersion Experiences: Engaging in experiences to deeply understand different cultures.
Example: “Living in Japan for a month really opened my eyes to different ways of working and living.”
19. Reflecting on Personal Biases: Regularly reflecting on and challenging one’s own cultural biases.
Example: “I’m constantly trying to be aware of my biases and how they affect my interactions.”
20. Embracing Diverse Cultural Perspectives: Actively seeking out and valuing diverse cultural viewpoints.
Example: “Your perspective is unique and valuable. Can you share more about your cultural background?”
These examples underscore the importance of intercultural competency in fostering effective and respectful communication across diverse cultural landscapes
Types of Intercultural Competency

Intercultural Competency in the realm of Intercultural Communication can be categorized into several types, each addressing different aspects of cultural interactions.
Cognitive Competency: Involves knowledge and understanding of different cultures and worldviews.
Affective Competency: Relates to attitudes, emotions, and values towards cultural differences.
Behavioral Competency: Encompasses skills and behaviors for effective intercultural interactions.
Communication Competency: Focuses on language skills and non-verbal communication understanding.
Empathy Competency: The ability to empathize with individuals from diverse backgrounds.
Adaptability Competency: Flexibility in adapting to new cultural environments.
Self-awareness Competency: Recognizing one’s own cultural biases and perspectives.
Conflict Resolution Competency: Skills in resolving misunderstandings and conflicts in a culturally sensitive manner.
Each type plays a crucial role in enhancing Intercultural Communication and fostering meaningful cross-cultural interactions.
Components of Intercultural Competency
Intercultural Competency consists of several key components that contribute to effective and respectful Intercultural Communication.
Cultural Awareness: Understanding one’s own culture and recognizing its influence on perceptions.
Cultural Knowledge: Acquiring knowledge about different cultural practices and norms.
Communication Skills: Developing skills to convey and interpret messages across cultures.
Empathy: Ability to see situations from others’ cultural perspectives.
Cultural Sensitivity: Showing respect and consideration for different cultural practices.
Adaptability: Flexibility in adjusting behaviors and attitudes in diverse settings.
Open-mindedness: Being open to new cultural experiences and ideas.
Tolerance for Ambiguity: Comfort with cultural uncertainties and complexities.
These components are essential for developing Intercultural Competency and navigating the complexities of diverse cultural landscapes.
Importance of Intercultural Competency
Intercultural Competency is increasingly crucial in today’s globalized world, particularly in the context of Intercultural Communication.
Enhances Global Business Relations: Facilitates successful international business negotiations and partnerships.
Improves Cross-Cultural Understanding: Promotes deeper understanding and appreciation of diverse cultures.
Supports Effective Communication: Reduces misunderstandings and improves communication effectiveness.
Fosters Inclusive Environments: Essential for creating inclusive workplaces and social spaces.
Enhances Personal and Professional Growth: Broadens personal perspectives and professional opportunities.
Reduces Cultural Conflicts: Helps in navigating and resolving cultural misunderstandings.
Strengthens Global Networks: Aids in building robust and diverse professional networks.
Promotes Global Citizenship: Encourages responsible and informed interactions in a global context.
The importance of developing Intercultural Competency cannot be overstated, as it is key to thriving in an interconnected and culturally diverse world.
Intercultural Competency is vital for effective Intercultural Communication in our increasingly interconnected world. This guide has explored the types, components, and importance of developing such competencies, emphasizing their role in fostering successful cross-cultural interactions. Whether in personal growth, professional development, or global business relations, Intercultural Competency is a fundamental skill set that enhances understanding, respect, and collaboration across diverse cultural landscapes.


