Internal vs Interpersonal Communication – Examples, How to Improve
This comprehensive guide delves into the differences and synergies between Internal and Interpersonal Communication, complete with vivid Internal Communication Examples. It provides an in-depth exploration of how these two forms of communication operate within an organizational context and their significance in fostering a productive and harmonious work environment. From the structured exchanges of internal communication to the nuanced interactions of interpersonal communication, this guide offers key insights and practical examples to enhance both in your professional sphere.
What is Internal vs Interpersonal Communication

Internal Communication and Interpersonal Communication, though similar, serve different purposes within an organization. Internal Communication refers to the exchange of information and ideas that occurs within an organization, typically between teams or departments. It’s key for ensuring that everyone in a company is aligned and informed about organizational goals, policies, and activities. In contrast, Interpersonal Communication involves direct, face-to-face interaction between individuals. It’s about how people convey and receive messages on a personal level, crucial for building relationships and effective teamwork within an organization. Both forms are integral to maintaining Internal Communication Functions and enhancing Internal Communication in the Workplace.
Differences Between Internal and Interpersonal Communication
Understanding the differences between Internal and Interpersonal Communication is crucial for effective communication management within any organization. Both play significant roles but cater to different aspects of organizational and personal interactions.
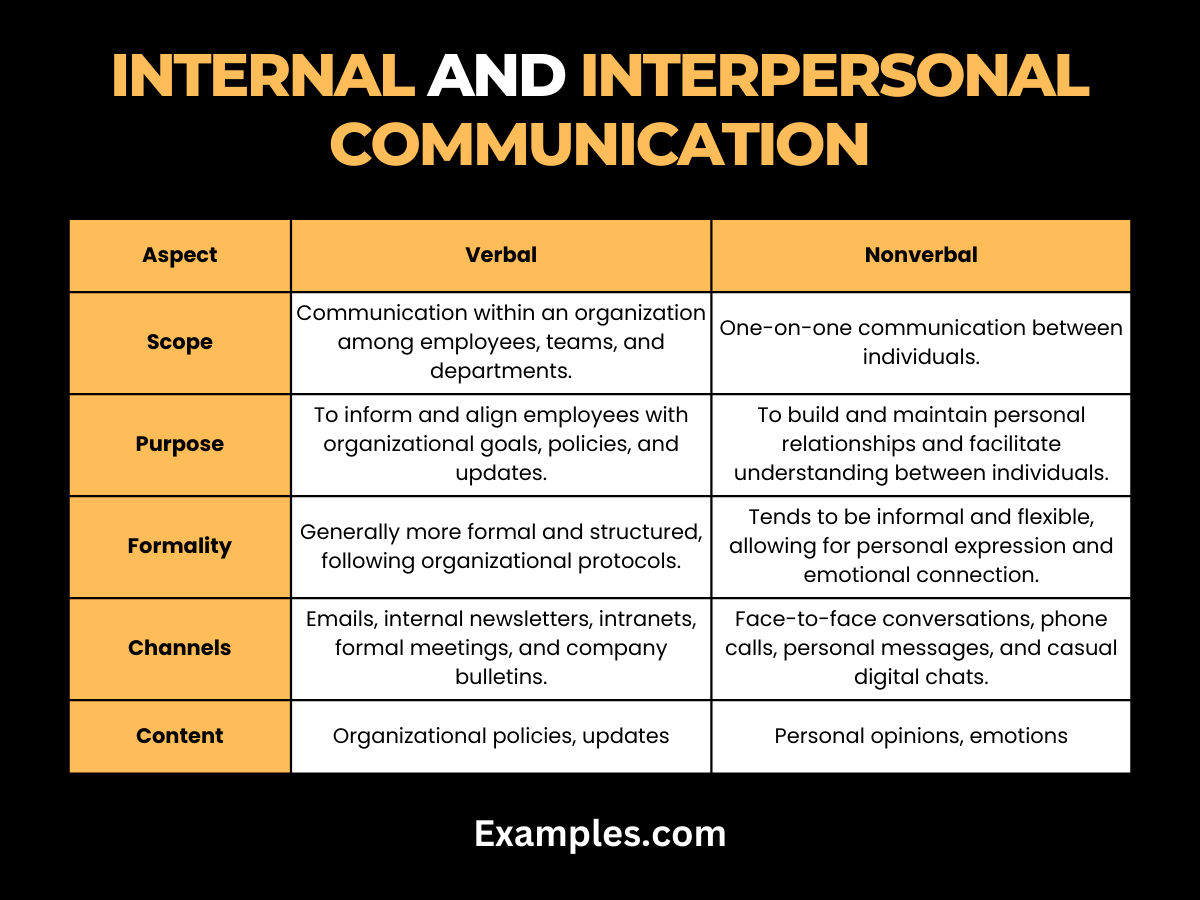
| Aspect | Internal Communication | Interpersonal Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Communication within an organization among employees, teams, and departments. | One-on-one communication between individuals. |
| Purpose | To inform and align employees with organizational goals, policies, and updates. | To build and maintain personal relationships and facilitate understanding between individuals. |
| Formality | Generally more formal and structured, following organizational protocols. | Tends to be informal and flexible, allowing for personal expression and emotional connection. |
| Channels | Emails, internal newsletters, intranets, formal meetings, and company bulletins. | Face-to-face conversations, phone calls, personal messages, and casual digital chats. |
| Content | Related to company policies, internal goals, operational details, and employee information. | Personal opinions, emotions, individual perspectives, and mutual understanding. |
| Tone | Professional and aligned with the company’s culture and values. | Personal, empathetic, and relaxed. |
| Impact | Affects overall organizational functioning, employee engagement, and operational efficiency. | Influences the quality of work relationships, team dynamics, and individual employee satisfaction. |
| Feedback Mechanism | Typically involves formal feedback channels like surveys, suggestion boxes, and performance reviews. | Often includes direct and immediate feedback during conversations. |
| Skill Development | Focuses on developing skills related to professional communication, team collaboration, and leadership. | Centers on improving personal communication skills, emotional intelligence, and conflict resolution. |
| Measurement of Success | Measured through employee engagement surveys, productivity metrics, and achievement of organizational objectives. | Gauged by the quality of relationships, individual satisfaction, and effective conflict resolution. |
- Scope of Communication:
- Internal Communication typically refers to the formal exchange of information and ideas within an organization. It involves communication between teams, departments, and across the entire company.
- Interpersonal Communication, on the other hand, is the one-on-one communication that occurs between individuals, whether within a professional or personal context.
- Purpose and Objectives:
- The primary goal of Internal Communication is to ensure all members of an organization are informed and aligned with company goals, policies, and procedures. It plays a crucial role in Internal Communication Functions.
- Interpersonal Communication focuses more on building and maintaining relationships, exchanging personal ideas, and mutual understanding between individuals.
- Formality and Structure:
- Internal Communication often follows a more formal and structured format, adhering to organizational norms and protocols. This includes official memos, corporate announcements, and structured meetings.
- Interpersonal Communication tends to be more informal and flexible, allowing for a personal and emotional connection. This includes casual conversations, personal feedback, and empathetic exchanges.
- Channels Used:
- In Internal Communication, standard channels like emails, company newsletters, internal portals, and formal meetings are commonly used.
- For Interpersonal Communication, more direct channels are employed, such as face-to-face discussions, phone calls, or personal messages.
- Content and Tone:
- The content of Internal Communication is typically related to organizational activities, updates, and directives. The tone is more professional and aligned with Internal Communication Best Practices.
- The content in Interpersonal Communication is more varied, often including personal opinions, emotions, and individual perspectives. The tone is more personal and relaxed.
- Impact on Organization:
- Effective Internal Communication impacts the overall functioning and success of the organization. It’s integral to Internal Communication in the Workplace and affects employee engagement and operational efficiency.
- Effective Interpersonal Communication primarily impacts the quality of work relationships and individual employee satisfaction. It plays a key role in team dynamics and collaboration.
By understanding these differences, organizations can better manage their communication strategies, ensuring both internal cohesiveness and strong interpersonal relationships among employees. This understanding is essential for maintaining a balanced and effective communication environment within any business setting.
Comparison for Internal and Interpersonal Communication
Comparing Internal and Interpersonal Communication helps in understanding how each contributes to the overall functioning of an organization.
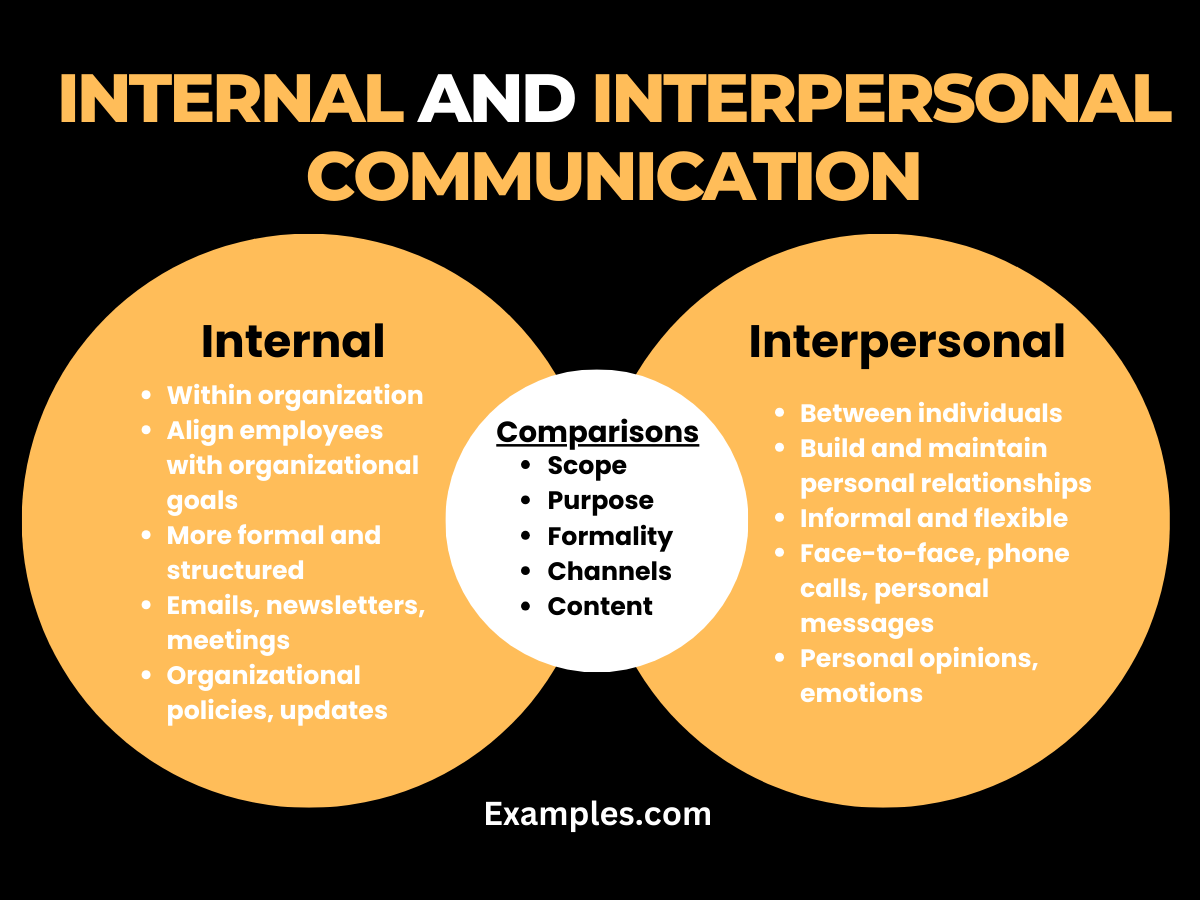
| Aspect | Internal Communication | Interpersonal Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Organizational goals, policies, and updates. | Personal interactions and relationships. |
| Formality | More formal and structured. | More informal and personal. |
| Scale | Broad, often involving entire departments or the organization. | Typically one-on-one or small groups. |
| Tools/Channels | Emails, intranets, newsletters, formal meetings. | Face-to-face interactions, phone calls, casual digital chats. |
| Primary Objective | To inform and align employees with organizational directives. | To build and maintain personal relationships and collaboration. |
Both Internal and Interpersonal Communication are essential in an organization but cater to different needs and scenarios. While internal communication ensures coherence and alignment with organizational objectives, interpersonal communication is key to building strong, collaborative relationships among individuals. Balancing these two forms of communication is crucial for a healthy, productive, and cohesive workplace
Importance of Internal and Intrapersonal Communication
Understanding the importance of both Internal and Intrapersonal Communication is vital for creating a productive and well-functioning workplace. Each type of communication contributes uniquely to the organizational and personal development of employees.
- Importance of Internal Communication:
- Promotes Cohesion and Collaboration: Effective internal communication fosters teamwork and unity within an organization, essential for achieving Internal Communication Functions.
- Ensures Efficient Information Flow: It plays a key role in disseminating information about Internal Communication Policies, company updates, and strategic changes.
- Boosts Employee Engagement: Regular and transparent communication improves morale and engagement, a key aspect of Internal Communication in the Workplace.
- Facilitates Organizational Change: Efficient internal communication is crucial for managing change within a company, highlighting the Importance of Internal Communication during transitions.
- Importance of Intrapersonal Communication:
- Enhances Self-Awareness and Decision-Making: Effective intrapersonal communication, or self-dialogue, helps individuals in making informed and thoughtful decisions.
- Improves Personal Effectiveness: Through self-reflection, employees can enhance their personal skills and workplace performance.
- Aids in Personal Goal Setting: Clear self-communication enables individuals to set realistic personal and professional goals.
- Contributes to Emotional Intelligence: It is vital for developing emotional intelligence, improving interpersonal skills and Internal vs Interpersonal Communication.
How to Improve Internal and Intrapersonal Communication
Enhancing both Internal and Intrapersonal Communication is key to a more effective and mentally resilient workplace.
- Strategies to Improve Internal Communication:
- Clear Communication Channels: Establish transparent channels for sharing information related to Internal Communication in Organizations.
- Feedback and Open Dialogue: Encourage a culture where feedback is welcomed, enhancing Internal Communication Techniques.
- Leverage Digital Tools: Utilize Internal Communication Platforms/ Tools for efficient communication.
- Regular Team Meetings: Hold meetings to ensure alignment with organizational goals and employee well-being.
- Strategies to Improve Intrapersonal Communication:
- Mindfulness and Reflection: Practice mindfulness to enhance self-awareness, an important aspect of Internal vs Interpersonal Communication.
- Personal Development Goals: Set and pursue personal goals, fostering a culture of growth and Internal Communication for Employee Engagement.
- Emotional Intelligence Training: Offer workshops on emotional intelligence and personal communication skills.
- Supportive Environment: Promote a work environment that values mental health and personal development.
Improving both forms of communication is crucial for fostering a productive, engaged, and emotionally intelligent workforce. These efforts lead to enhanced organizational efficiency and a positive work culture.
Internal vs Interpersonal Communication play crucial yet distinct roles in the fabric of organizational life. This guide has illuminated their differences, importance, and enhancement strategies. By understanding and effectively implementing both forms of communication, organizations can foster a more cohesive, efficient, and emotionally intelligent workplace. Embracing these communication dynamics is key to building a strong organizational culture and enhancing overall business success.



