29+ Interpersonal Communication Skills Examples
In today’s interconnected world, Interpersonal Communication Skills are more vital than ever. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the nuances of effective personal interactions, providing practical communication examples and strategies to enhance your ability to connect with others. Whether you’re a professional aiming to improve your workplace interactions, a student keen on developing better relationships, or simply someone looking to refine their communication skills, this guide offers invaluable insights. With examples drawn from real-life scenarios, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of how to apply these skills practically, making every conversation more meaningful and impactful.
What Are Interpersonal Communication Skills?
Interpersonal Communication Skills refer to the abilities used to effectively interact, engage, and understand others in various contexts. These skills are vital in both personal and professional settings and include both verbal and non-verbal communication techniques. Key aspects of interpersonal communication include active listening, expressing empathy, clear articulation, understanding non-verbal cues, and the ability to give and receive feedback constructively. Mastery of these skills enhances one’s ability to build and maintain relationships, resolve conflicts, and communicate effectively in diverse situations.
30 Interpersonal Communication Skills

Interpersonal Communication Skills encompass the abilities used to effectively interact, engage, and understand others in various contexts, from one-on-one conversations to group interactions. These skills involve both verbal and non-verbal communication, including listening, empathy, and clarity in conveying messages. Mastery of these skills enhances personal and professional relationships, making them crucial for success in any social setting.
- Active Listening: Paying full attention to the speaker and showing engagement.
Example: “I understand your point. Could you elaborate on that aspect?” - Empathetic Response: Showing understanding and empathy.
Example: “I can see how that situation made you feel. It must have been challenging.” - Clear Articulation: Speaking clearly and concisely.Interpersonal Communication Skills
Example: “Let me clarify my point for better understanding.” - Non-Verbal Cues: Using body language to enhance communication.
Example: Nodding while listening to show agreement or interest. - Positive Reinforcement: Offering encouragement and support.
Example: “You’re doing great. Keep up the good work!” - Constructive Feedback: Providing feedback that is helpful and non-critical.
Example: “Your idea is good. Maybe consider this perspective as well.” - Conflict Resolution: Addressing and resolving disagreements effectively.
Example: “Let’s find a common ground to resolve this issue.” - Asking Open-Ended Questions: Encouraging deeper conversation.
Example: “What are your thoughts on this topic?” - Adapting Communication Style: Modifying approach based on the audience.
Example: “For this group, I’ll use more visuals to explain.” - Expressing Gratitude: Showing appreciation in interactions.
Example: “Thank you for your input; it’s very valuable.” - Mindful Listening: Being fully present in the conversation.
Example: “I’m focused on understanding your perspective.” - Encouraging Participation: Inviting others to share their thoughts.
Example: “I’d love to hear your ideas on this.” - Tactful Assertiveness: Expressing opinions firmly but respectfully.
Example: “I firmly believe this approach will work, considering all factors.” - Cultural Sensitivity: Being aware of and respecting cultural differences.
Example: “I respect your cultural viewpoint and would like to learn more.” - Persuasive Communication: Convincing others effectively.
Example: “Consider the benefits of this strategy for our team.” - Emotional Intelligence: Recognizing and managing emotions.
Example: “I sense some hesitation; let’s discuss your concerns.” - Storytelling as a Tool: Using narratives to engage.
Example: “Let me share a story that illustrates this concept.” - Showing Empathy: Understanding others’ feelings.
Example: “It sounds like you’re feeling overwhelmed, how can I help?” - Negotiation Skills: Reaching mutual agreements.
Example: “Let’s work together to find a solution that benefits both of us.” - Presentation Skills: Communicating effectively in formal settings.
Example: “In this presentation, I will outline our key objectives.”

- Humor in Communication: Using humor appropriately.
Example: “A little humor can lighten the mood here.” - Feedback Reception: Accepting feedback positively.
Example: “I appreciate your feedback and will consider it.” - Respectful Disagreement: Disagreeing without offending.
Example: “I see your point, but I have a different view.” - Effective Questioning: Asking questions for clarity.
Example: “Could you explain that part in more detail?” - Inclusivity in Communication: Ensuring everyone feels included.
Example: “Let’s make sure everyone has a chance to speak.” - Goal-Oriented Communication: Focusing conversations on objectives.
Example: “Our main goal for this meeting is…” - Self-Disclosure: Sharing personal experiences when appropriate.
Example: “I’ve experienced something similar and here’s what I learned.” - Writing Skills: Conveying ideas clearly in writing.
Example: “My email outlined the main points concisely.”

- Active Encouragement: Motivating others through words.
Example: “Your progress is impressive; keep pushing forward.” - Collaborative Problem Solving: Working together to find solutions.
Example: “Let’s brainstorm to find the best solution.”
Why Interpersonal Communication Is Important
Effective interpersonal communication is crucial in various aspects of life. Here are 10 reasons why:
- Builds Strong Relationships: Enhances personal and professional connections.
- Facilitates Problem Solving: Essential in conflict resolution and negotiation.
- Improves Teamwork: Crucial for collaboration in communication skills.
- Enhances Leadership: Vital in communication skills of a leader.
- Boosts Career Prospects: Important in communication skills for workplace success.
- Aids in Emotional Intelligence: Enhances understanding and empathy in communication skills.
- Fosters Understanding: Promotes active listening communication skills.
- Improves Customer Relations: Key in brand communication.
- Encourages Openness: Reduces misunderstandings and promotes transparency.
- Supports Personal Development: Integral to communication skills training.
Interpersonal Communication in the Workplace
Interpersonal communication plays a vital role in the workplace:
- Fosters a Positive Environment: Encourages respectful and supportive interactions.
- Enhances Team Efficiency: Key to effective collaboration in communication skills.
- Improves Manager-Employee Relations: Crucial for communication skills of a manager.
- Supports Change Management: Vital in navigating workplace transitions.
- Drives Innovation: Encourages open sharing of ideas.
- Reduces Conflicts: Aids in timely and effective conflict resolution.
- Enhances Brand Image: Reflects positively in brand communication.
How to Build Interpersonal Communication Skills
Developing interpersonal communication skills involves:
- Practice Active Listening: Focus on active listening communication skills.
- Cultivate Empathy: Strengthen your empathy in communication skills.
- Seek Feedback: Utilize communication skills feedback for improvement.
- Engage in Role-Playing: Hone skills in controlled scenarios.
- Attend Workshops and Seminars: Participate in communication skills training.
- Learn from Leaders: Observe communication skills of a leader.
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice refines skills.
Difference Between Interpersonal and Intrapersonal Communication
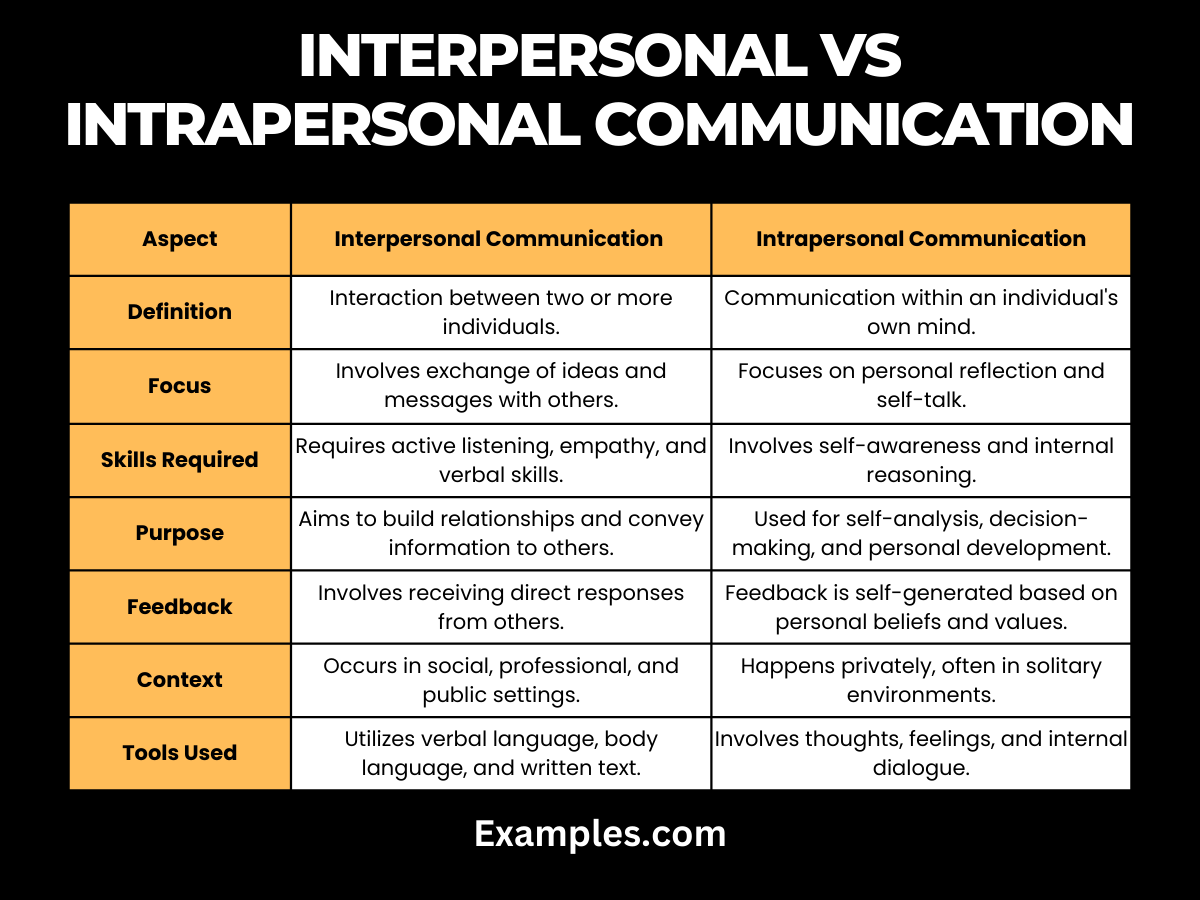
This table provides a clear comparison between interpersonal and intrapersonal communication, highlighting their distinct aspects. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective communication skills, as it helps in tailoring messages and strategies appropriately.
| Aspect | Interpersonal Communication | Intrapersonal Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interaction between two or more individuals. | Communication within an individual’s own mind. |
| Focus | Involves exchange of ideas and messages with others. | Focuses on personal reflection and self-talk. |
| Skills Required | Requires active listening, empathy, and verbal skills. | Involves self-awareness and internal reasoning. |
| Purpose | Aims to build relationships and convey information to others. | Used for self-analysis, decision-making, and personal development. |
| Feedback | Involves receiving direct responses from others. | Feedback is self-generated based on personal beliefs and values. |
| Context | Occurs in social, professional, and public settings. | Happens privately, often in solitary environments. |
| Tools Used | Utilizes verbal language, body language, and written text. | Involves thoughts, feelings, and internal dialogue. |
| Impact | Influences and is influenced by social interactions and group dynamics. | Impacts one’s self-esteem, motivation, and personal goals. |
| Development | Enhanced through social interactions and communication skills training. | Improved through introspection and communication skills in psychology. |
| Examples | Conversations, meetings, communication skills for team. | Self-reflection, planning, setting goals for communication skills. |
Interpersonal Communication Tips for Remote Workers
For remote workers, effective interpersonal communication is key:
- Regular Check-Ins: Maintain connection with team members.
- Clear and Concise Messages: Emphasize clarity in communication.
- Use of Technology: Leverage digital tools for effective communication.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Respect diverse backgrounds.
- Feedback Channels: Establish avenues for communication skills feedback.
- Work-Life Balance: Respect personal boundaries.
This comprehensive guide on Interpersonal Communication Skills offers insights and practical tips for enhancing these essential skills. Whether in a personal, professional, or remote work setting, understanding and effectively applying these skills can significantly improve interactions and relationships, fostering a more connected and productive environment.
In professional settings, effective interpersonal communication is pivotal for creating a well-functioning and high-performing team. These skills are not just about conveying information; they are also about managing social interactions within various levels of an organization. By fostering better workplace relationships, these skills contribute to a more connected and productive environment, which is integral to any organization’s success. For more insights on the impact of interpersonal communication in the workplace, Roubler provides a detailed exploration of this topic.
Similarly, in the realm of education, teachers with strong interpersonal skills can profoundly influence their students. These skills enable teachers to connect effectively with a diverse range of students, accommodating various mindsets and motivations. By doing so, teachers not only enhance their teaching quality but also contribute positively to their students’ personal and academic growth. Understanding and implementing these skills can be challenging, yet they are crucial for educators to foster a conducive learning environment. For a deeper understanding of how interpersonal skills benefit teachers and students alike, visit Teachmint for more information.



