Interpersonal Communication vs Intercultural Communication – 19+ Examples
Embark on a comprehensive exploration of communication dynamics with our guide on Interpersonal Communication vs Intercultural Communication. Unravel the intricacies of human connection within diverse cultural contexts, discovering how these communication dimensions differ. Dive into real-world scenarios and illuminating instances, delving into the realm of “Communication Examples.” Enhance your understanding of effective communication strategies, whether in personal relationships or navigating the complexities of intercultural interactions. This guide navigates the subtleties, emphasizing the significance of clear, meaningful communication across diverse cultural landscapes.
Difference between Interpersonal Communication and Intercultural Communication?
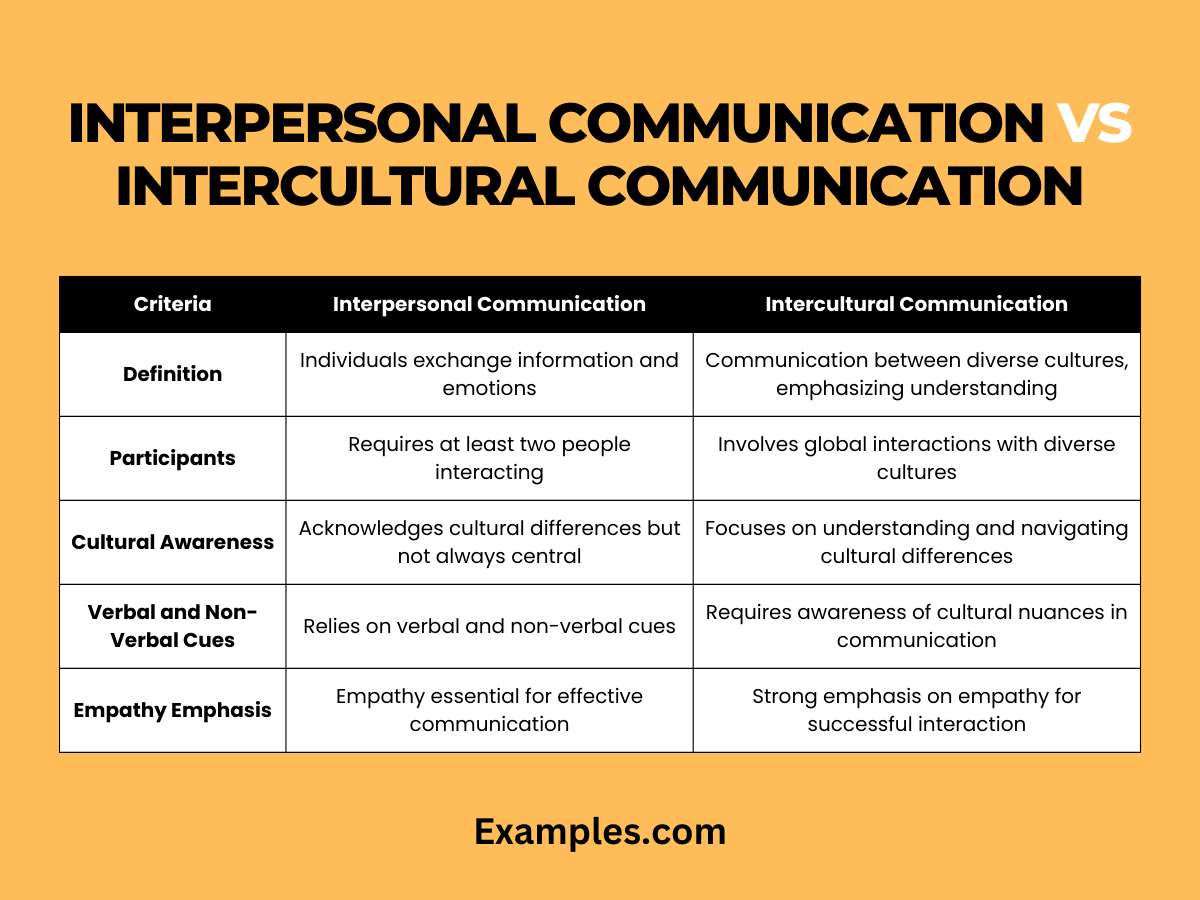
Understanding the nuances between Interpersonal Communication and Intercultural Communication is crucial in our interconnected world. Delve into a detailed table that highlights the distinctive features of each:
| Criteria | Interpersonal Communication | Intercultural Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Communication between individuals, involving exchange of information, emotions, and thoughts. | Communication that occurs between individuals from different cultural backgrounds, emphasizing understanding and respect. |
| Participants | Involves at least two people interacting with each other. | Encompasses interactions between individuals from diverse cultural backgrounds, potentially within a global context. |
| Cultural Awareness | Acknowledges cultural differences but may not be the central focus. | Centrally focused on understanding and navigating cultural differences to facilitate effective communication. |
| Verbal and Non-Verbal Cues | Relies on both verbal and non-verbal cues to convey thoughts and emotions. | Requires heightened awareness of cultural nuances in verbal and non-verbal communication to avoid misunderstandings. |
| Empathy Emphasis | Empathy is essential for effective communication, emphasizing understanding of others’ perspectives. | Places a strong emphasis on empathy, requiring individuals to empathize with diverse cultural viewpoints for successful interaction. |
| Language Dynamics | Language may vary but is not always a significant barrier. | Language differences play a crucial role, requiring strategies for effective communication in multilingual settings. |
| Conflict Resolution | Conflict resolution is approached based on personal dynamics. | Cultural differences impact conflict resolution, necessitating cultural sensitivity and unique approaches. |
| Examples in Daily Life | Everyday conversations, social interactions, and personal relationships. | Collaborating on international projects, navigating diverse workplace environments, or engaging in cross-cultural friendships. |
This comprehensive guide illuminates the distinct characteristics of Interpersonal Communication and Intercultural Communication, offering insights into effective communication across diverse cultural landscapes.
10 Examples of Interpersonal Communication
Embark on a journey through the intricacies of Interpersonal Communication with these 10 compelling examples, each showcasing the art of meaningful connection. Explore diverse scenarios that illustrate the power of effective interpersonal dynamics, shaping relationships and fostering understanding.
- Expressing Empathy: In challenging moments, displaying empathy by saying, “I understand what you’re going through; I’m here to support you.”
- Active Listening: During conversations, active listening involves nodding, maintaining eye contact, and responding thoughtfully for deeper understanding.
- Conflict Resolution: Colleagues navigate disagreements by openly communicating, finding common ground for a resolution that benefits everyone.
- Constructive Feedback: Mentors provide constructive feedback, emphasizing strengths and offering guidance for improvement.
- Non-Verbal Affirmation: In relationships, partners communicate affection through non-verbal cues like smiles, hugs, and supportive gestures.
10 Examples of Intercultural Communication
Embark on a cultural odyssey with these 10 illuminating examples of Intercultural Communication, showcasing the art of bridging diverse perspectives. Each scenario unfolds the complexities and triumphs of effective communication across cultural boundaries, fostering mutual understanding and harmony.
- Cross-Cultural Collaboration: In global teams, effective intercultural communication fosters collaboration by valuing diverse opinions and approaches.
- Language Adaptation: Navigating language differences, intercultural communicators adeptly adapt language nuances for clear and respectful dialogue.
- Cultural Empathy: Displaying cultural empathy involves understanding and appreciating diverse traditions, customs, and societal norms.
- Interpreting Non-Verbal Cues: Intercultural communicators skillfully interpret non-verbal cues, recognizing cultural subtleties in body language and facial expressions.
- Global Business Negotiation: In international negotiations, intercultural awareness is key, ensuring mutual respect and successful deal-making.
- Cultural Sensitivity in Hospitality: In hospitality, recognizing and respecting guests’ cultural preferences enhances the overall experience and satisfaction.
- Virtual Intercultural Meetings: Navigating virtual meetings across cultures involves considering time zones, cultural norms, and communication styles.
- Navigating Taboos Respectfully: Effective intercultural communicators navigate potentially sensitive topics with cultural awareness and tact.
- Celebrating Diversity: In multicultural societies, intercultural communication celebrates diversity, fostering a sense of inclusivity and shared identity.
- Educational Cross-Cultural Exchanges: In educational settings, intercultural communication enhances learning by incorporating diverse perspectives, enriching the educational experience.
Comparison between Interpersonal Communication and Intercultural Communication
Embark on a journey of understanding as we draw comparisons between Interpersonal and Intercultural Communication, presented in a detailed point-by-point guide:
1. Participants and Diversity:
- Interpersonal Communication: Involves direct interaction between individuals, irrespective of cultural backgrounds.
- Intercultural Communication: Encompasses interactions between individuals from different cultural contexts, emphasizing diversity.
2. Cultural Sensitivity:
- Interpersonal Communication: Cultural considerations may be present, but the primary focus is on personal connections.
- Intercultural Communication: Requires heightened cultural sensitivity, considering diverse norms, values, and communication styles.
3. Contextual Nuances:
- Interpersonal Communication: Context is influenced by personal history and individual dynamics.
- Intercultural Communication: Context is shaped by cultural norms, traditions, and the collective history of involved cultures.
4. Communication Challenges:
- Interpersonal Communication: Challenges may arise based on individual differences and communication preferences.
- Intercultural Communication: Challenges include navigating language barriers, differing communication norms, and cultural misunderstandings.
5. Adaptability in Interaction:
- Interpersonal Communication: Adapts to the unique needs and preferences of individuals.
- Intercultural Communication: Requires adaptability to diverse communication styles and cultural nuances.
6. Communication Channels:
- Interpersonal Communication: Utilizes various channels based on personal preferences, including face-to-face and digital interactions.
- Intercultural Communication: Involves diverse channels but may emphasize verbal and non-verbal cues to bridge cultural gaps.
7. Examples in Daily Life:
- Interpersonal Communication: Everyday conversations with friends, family, and colleagues.
- Intercultural Communication: Collaborative efforts in multicultural workplaces, international business negotiations, or interactions within diverse communities.
8. Objective of Communication:
- Interpersonal Communication: Primarily focuses on building personal relationships, sharing emotions, and resolving conflicts.
- Intercultural Communication: Aims to foster understanding, bridge cultural gaps, and achieve effective cross-cultural collaboration.
9. Role of Non-Verbal Cues:
- Interpersonal Communication: Non-verbal cues are significant, conveying emotions and enhancing understanding.
- Intercultural Communication: Non-verbal cues play a crucial role in navigating cultural nuances and conveying respect.
10. Impact on Global Dynamics:
- Interpersonal Communication: Shapes personal relationships and connections on an individual level.
- Intercultural Communication: Influences global dynamics by fostering cross-cultural understanding, diversity appreciation, and international collaboration.
By exploring these distinctions, individuals can enhance their ability to navigate both interpersonal and intercultural communication, fostering meaningful connections in diverse and globalized contexts.
Relationship between Interpersonal Communication and Intercultural Communication
Explore the intricate relationship between Interpersonal and Intercultural Communication through this comprehensive point-by-point guide, offering a fresh perspective:
1. Participants’ Cultural Identities:
- Interpersonal Communication: Participants may share a common cultural background, but communication focuses on individual connections.
- Intercultural Communication: Involves participants from diverse cultural backgrounds, highlighting the significance of cultural identities.
2. Cultural Awareness and Sensitivity:
- Interpersonal Communication: Cultural awareness may play a role, but sensitivity is more individually focused.
- Intercultural Communication: Demands heightened cultural awareness and sensitivity to navigate diverse norms and values.
3. Contextual Influence:
- Interpersonal Communication: Context is shaped by personal histories and the dynamics between individuals.
- Intercultural Communication: Context is deeply influenced by the cultural norms, traditions, and histories of the involved cultures.
4. Challenges in Communication:
- Interpersonal Communication: Challenges may arise based on individual differences and communication preferences.
- Intercultural Communication: Challenges include navigating language barriers, differing communication norms, and potential cultural misunderstandings.
5. Adaptability to Cultural Nuances:
- Interpersonal Communication: Adapts to individual preferences and styles, with a focus on personal connections.
- Intercultural Communication: Requires adaptability to diverse communication styles, cultural nuances, and a collective understanding.
6. Communication Channels and Styles:
- Interpersonal Communication: Utilizes various channels based on personal preferences, including face-to-face and digital interactions.
- Intercultural Communication: Involves diverse channels, placing emphasis on effective verbal and non-verbal communication to bridge cultural gaps.
7. Daily Life Examples:
- Interpersonal Communication: Everyday conversations within personal circles such as friends, family, and colleagues.
- Intercultural Communication: Collaborative efforts in multicultural workplaces, international business negotiations, or interactions within diverse communities.
8. Communication Objectives:
- Interpersonal Communication: Primarily focuses on building personal relationships, sharing emotions, and resolving conflicts.
- Intercultural Communication: Aims to foster understanding, bridge cultural gaps, and achieve effective cross-cultural collaboration.
9. Non-Verbal Cues in Cultural Context:
- Interpersonal Communication: Non-verbal cues enhance personal communication, conveying emotions and understanding.
- Intercultural Communication: Non-verbal cues play a crucial role in navigating cultural nuances, conveying respect, and establishing cross-cultural rapport.
10. Global Impact:
- Interpersonal Communication: Shapes personal relationships and connections on an individual level.
- Intercultural Communication: Influences global dynamics by fostering cross-cultural understanding, diversity appreciation, and international collaboration.
By navigating the distinctive intricacies of interpersonal and intercultural communication, individuals can foster meaningful connections and contribute to a more interconnected and culturally aware global landscape.



