Interpersonal Communication vs Small Group Communication – 9+ Examples
Embark on a comprehensive exploration of communication dynamics with our guide on Interpersonal Communication vs Small Group Communication. Unveil the intricacies distinguishing one-on-one connections from collaborative group discourse. This guide provides valuable insights into effective communication within intimate relationships and small group settings, illuminating the nuances that shape meaningful interactions. Dive into the realm of interpersonal and small group communication, enriched with practical “Communication Examples” to enhance your understanding and communication skills.
Difference between Interpersonal Communication and Small Group Communication?
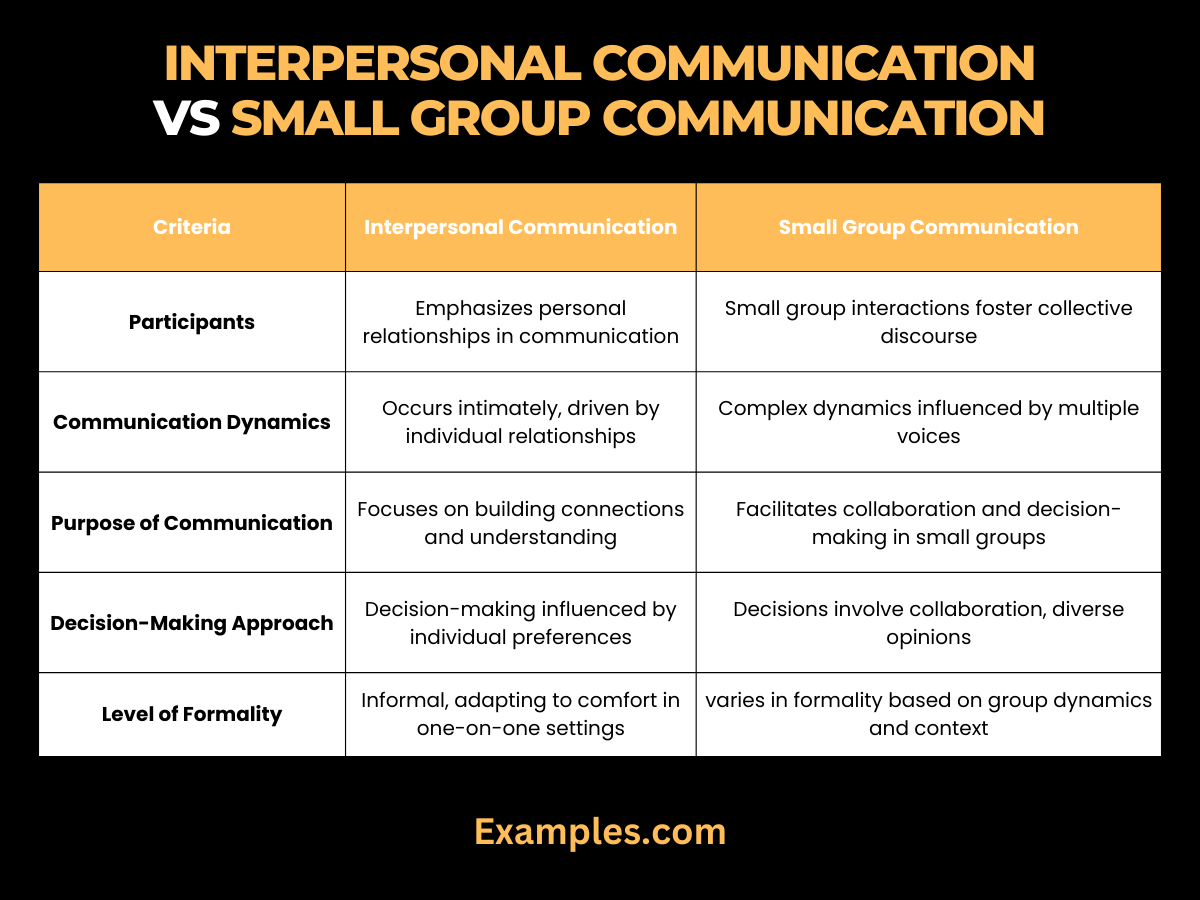
Embark on an insightful journey as we dissect and compare the nuances between Interpersonal and Small Group Communication through a detailed table:
| Criteria | Interpersonal Communication | Small Group Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Participants | Involves communication between two individuals, emphasizing personal relationships. | Encompasses interactions within a small group setting, fostering collective discourse among a limited number of participants. |
| Communication Dynamics | Occurs within a more intimate, personalized context, driven by individual relationships. | Involves complex dynamics influenced by multiple voices, perspectives, and the interplay of interactions within a small group. |
| Purpose of Communication | Primarily centered on building personal connections, understanding, and nurturing relationships. | Aims to facilitate collective understanding, decision-making, and collaboration within the dynamics of a small group. |
| Decision-Making Approach | Decision-making is often influenced by individual preferences and dynamics within the context of the interpersonal relationship. | Small group decisions involve collaborative processes, consensus-building, and consideration of diverse opinions within the limited participant pool. |
| Level of Formality | Tends to be more informal, adapting to individual preferences and comfort levels in one-on-one settings. | Can vary in formality, ranging from casual to highly structured based on the nature of the small group dynamics and the context. |
| Communication Styles | Relies on personalized, direct communication styles tailored to the individuals involved in the conversation. | Involves navigating varied communication styles within the small group, requiring adaptability and understanding of diverse perspectives. |
| Feedback Dynamics | Immediate feedback is direct and tailored to the nuances of personal relationships and emotional expressions. | Feedback is more complex within a small group, involving multiple voices and requiring facilitation and synthesis for effective communication. |
| Examples in Daily Life | Everyday interactions include one-on-one conversations, personal interactions, and relationship-building moments. | Examples encompass small group discussions, team meetings, family gatherings, and any interaction involving a limited number of participants within a shared context. |
This comprehensive guide sheds light on the distinctive features of both Interpersonal and Small Group Communication, providing insights into their varied contexts and applications in diverse social scenarios.
10 Examples of Interpersonal Communication
Embark on a journey through the art of meaningful connections with these 10 exemplary instances of Interpersonal Communication. Each example unfolds the intricacies of effective dialogue, showcasing scenarios where understanding and building relationships play a pivotal role in daily life.
- Active Listening: Demonstrate active listening by maintaining eye contact, nodding, and responding appropriately, fostering a deeper connection.
- Expressing Empathy: Show empathy by saying, “I understand how you feel; your perspective is essential to me,” fostering emotional understanding.
- Conflict Resolution: Navigate conflicts by addressing concerns openly, seeking common ground, and finding resolutions that benefit both parties.
- Non-Verbal Affirmation: Express affection through non-verbal cues like smiles and hugs, reinforcing emotional connections without words.
- Effective Questioning: Enhance conversations by asking open-ended questions, encouraging thoughtful and detailed responses for richer interactions.
- Building Trust: Cultivate trust through transparent and honest communication, fostering a strong foundation in personal and professional relationships.
- Setting Boundaries: Clearly communicate personal boundaries, ensuring mutual understanding and respect in interpersonal dynamics.
- Giving Constructive Feedback: Provide constructive feedback with tact and specificity, guiding improvement without causing defensiveness.
- Expressing Gratitude: Show appreciation by saying, “Thank you for your efforts; your contributions are invaluable to the team,” reinforcing positive actions.
- Apologizing Sincerely: Apologize sincerely when necessary, acknowledging mistakes and expressing a genuine commitment to improvement for relational harmony.
10 Examples of Small Group Communication
Dive into the realm of collaborative discourse with these 10 exceptional examples of Small Group Communication. Uncover the dynamics that shape effective group interactions, where collective understanding and shared decision-making take center stage, fostering cohesive collaboration within limited participant pools.
- Brainstorming Sessions: Energize small groups by fostering an open exchange of ideas, encouraging creativity and innovative solutions through collaborative brainstorming sessions.
- Consensus Building: Facilitate decision-making through consensus-building, where each member contributes, ensuring collective agreement and commitment to the chosen course of action.
- Team Meetings: Conduct efficient team meetings, allowing members to share updates, discuss goals, and collaboratively plan strategies for enhanced group performance.
- Problem-Solving Groups: Tackle challenges collectively in problem-solving groups, leveraging diverse perspectives to analyze issues and formulate effective solutions.
- Study Groups: Enhance learning through study groups, where members collaboratively review material, discuss concepts, and deepen their understanding of academic subjects.
- Project Planning: Coordinate projects seamlessly with small group communication, allocating tasks, setting timelines, and ensuring everyone is on the same page for successful execution.
- Focus Group Discussions: Gather insights through focus group discussions, where participants share opinions, perceptions, and preferences on specific topics, informing decision-making.
- Feedback Sessions: Conduct constructive feedback sessions within small groups, providing a platform for open dialogue and improvement in various aspects, from projects to personal development.
- Committee Meetings: Efficiently manage committees by facilitating purpose-driven meetings, ensuring collaboration and coordination among members for achieving common goals.
- Training Workshops: Conduct interactive training workshops within small groups, promoting active participation, knowledge exchange, and skill development for collective growth.
Comparison between Interpersonal Communication and Small Group Communication
Embark on a comprehensive exploration of communication dynamics as we delve into the distinctions between Interpersonal Communication and Small Group Communication, presented in a detailed point-by-point guide:
1. Number of Participants:
- Interpersonal Communication: Involves direct interaction between two individuals, fostering personal connections.
- Small Group Communication: Extends beyond one-on-one interactions, involving communication within a limited number of participants, typically up to around 10 individuals.
2. Nature of Interaction:
- Interpersonal Communication: Emphasizes personal connections and relationships on an individual level.
- Small Group Communication: Focuses on interactions within a collective, emphasizing shared goals, discussions, and collaboration among a select number of participants.
3. Communication Dynamics:
- Interpersonal Communication: Characterized by a more intimate and personalized dynamic, allowing for in-depth exchanges.
- Small Group Communication: Involves a more complex dynamic with the potential for diverse perspectives, group roles, and collaborative decision-making.
4. Adaptability to Participants:
- Interpersonal Communication: Adapts to the unique needs and preferences of two individuals, considering personal connections.
- Small Group Communication: Requires adaptability to cater to the diverse communication styles, opinions, and roles within the small group setting.
5. Communication Channels:
- Interpersonal Communication: Utilizes various channels such as face-to-face interactions, calls, and personalized messages.
- Small Group Communication: Involves multiple communication channels, including group discussions, meetings, and collaborative platforms.
6. Examples in Daily Life:
- Interpersonal Communication: Everyday conversations with friends, family, and colleagues, focusing on personal bonds.
- Small Group Communication: Team meetings, family discussions, study groups, and collaborative projects involving a limited number of participants.
7. Communication Objectives:
- Interpersonal Communication: Primarily focused on building individual relationships, sharing emotions, and resolving conflicts.
- Small Group Communication: Aims to achieve shared goals, facilitate decision-making, and foster effective collaboration within the small group setting.
8. Role of Non-Verbal Cues:
- Interpersonal Communication: Non-verbal cues like body language and facial expressions play a significant role in conveying emotions and messages.
- Small Group Communication: Non-verbal cues contribute to understanding group dynamics, cohesion, and the reception of shared ideas among the limited participants.
9. Impact on Social Dynamics:
- Interpersonal Communication: Shapes personal relationships on an individual level, contributing to intimate connections.
- Small Group Communication: Influences the dynamics and cohesion of the small group, impacting collective success, harmony, and shared understanding.
10. Decision-Making Process:
- Interpersonal Communication: Decisions often involve only the two individuals in the interaction, with a focus on mutual agreement.
- Small Group Communication: Decision-making involves group discussions, considerations of diverse perspectives, and collaborative consensus-building.
By understanding these key points, individuals can navigate the intricacies of both interpersonal and small group communication, adapting their approach to the specific context and goals of the interaction.
Relationship between Interpersonal Communication and Small Group Communication
Embark on a nuanced exploration of the interconnected dynamics between Interpersonal Communication and Small Group Communication through this detailed point-by-point guide:
1. Interactive Scale:
- Interpersonal Communication: Limited to direct interactions between two individuals, fostering personal connections.
- Small Group Communication: Expands beyond one-on-one interactions, involving communication within a select group of participants, typically up to around 10 individuals.
2. Nature of Connections:
- Interpersonal Communication: Emphasizes intimate and personal connections on an individual level.
- Small Group Communication: Cultivates connections within a collective, accentuating shared goals, discussions, and collaboration among a limited number of participants.
3. Complexity in Dynamics:
- Interpersonal Communication: Characterized by a simpler, more one-on-one dynamic, facilitating in-depth exchanges.
- Small Group Communication: Involves a more intricate dynamic with the potential for diverse perspectives, roles, and collaborative decision-making within the small group setting.
4. Adaptability to Participants’ Dynamics:
- Interpersonal Communication: Adapts to the unique needs and preferences of two individuals, focusing on the nuances of personal connections.
- Small Group Communication: Requires adaptability to cater to diverse communication styles, opinions, and roles within the small group, demanding a collective approach.
5. Communication Channels and Mediums:
- Interpersonal Communication: Utilizes various channels such as face-to-face interactions, calls, and personalized messages.
- Small Group Communication: Encompasses multiple communication channels, including group discussions, meetings, and collaborative platforms tailored for a small collective.
6. Daily Life Scenarios:
- Interpersonal Communication: Everyday conversations with friends, family, and colleagues, centering on personal bonds.
- Small Group Communication: Examples include team meetings, family discussions, study groups, and collaborative projects involving a select number of participants.
7. Objectives of Communication:
- Interpersonal Communication: Primarily focused on building individual relationships, sharing emotions, and resolving conflicts on a personal level.
- Small Group Communication: Aims to achieve shared goals, facilitate decision-making, and foster effective collaboration within the limited small group setting.
8. Non-Verbal Cues in Interaction:
- Interpersonal Communication: Non-verbal cues like body language and facial expressions significantly impact understanding at an individual level.
- Small Group Communication: Non-verbal cues contribute to understanding group dynamics, cohesion, and the reception of shared ideas among the limited participants.
9. Impact on Social Dynamics:
- Interpersonal Communication: Shapes personal relationships individually, contributing to intimate connections.
- Small Group Communication: Influences the dynamics and cohesion of the small group, impacting collective success, harmony, and shared understanding.
10. Decision-Making Dynamics:
- Interpersonal Communication: Decisions typically involve only the two individuals in the interaction, with a focus on mutual agreement.
- Small Group Communication: Decision-making entails group discussions, considerations of diverse perspectives, and collaborative consensus-building within the small group context.
Understanding the interplay between interpersonal and small group communication allows individuals to navigate diverse social contexts effectively, fostering meaningful connections at both personal and collective levels.



