10+ Introduction Examples to Download
The first paragraph of an essay or research paper is traditionally designated as the introduction, and its purpose is to introduce the subject matter and set the stage for the remainder of the documentary research. Because it’s responsible for both the reader’s first impression and set the stage for the rest of the work, the introduction paragraph, without prejudice to the conclusion paragraph, is arguably the most important paragraph writing in the work.
Writing a strong introductory paragraph is a valuable skill for students and academics to have. Here, we go over all you need to know to create the finest introduction, including what to include and a step-by-step procedure, as well as some samples of introductory paragraphs.
1. Sample Introductions Template
2. Self Introduction Speech Examples
3. Writing an Introduction Template
4. Giving an Introduction Speech
5. Writing an Effective Introduction
6. Survey Introduction Example
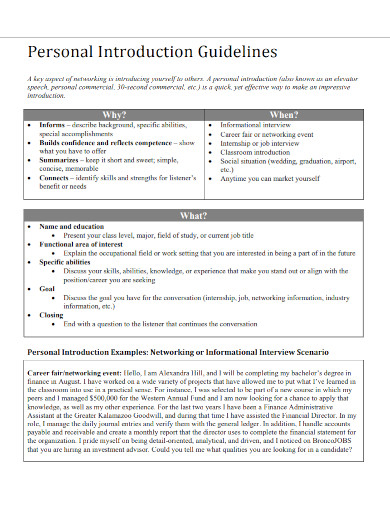
7. Personal Introduction Guidelines
8. Thesis Statements and Introductions
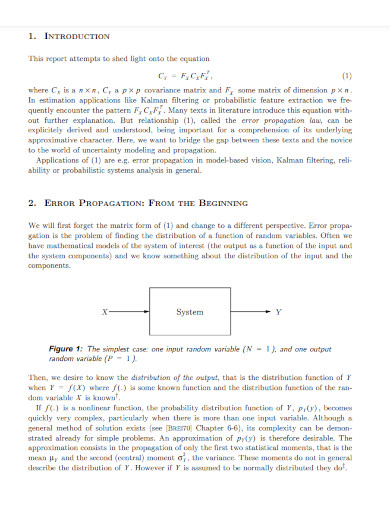
9. An Introduction To Error Propagation
10. Introduction to Hypothesis Testing
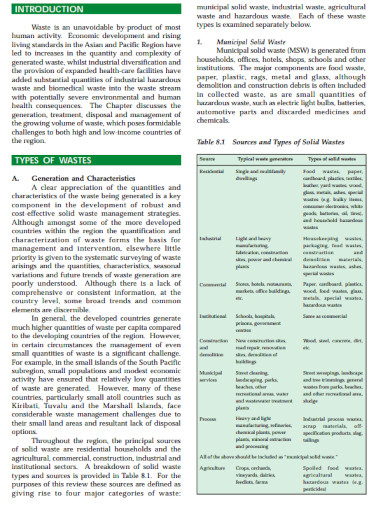
11. Introduction Types of Wastes
What is an Introduction?
Essentially, the introduction serves to prime the reader for the rest of your work. A piece’s opening paragraph establishes the tone, voice, and writing style the reader may anticipate from the rest of the piece. The reader won’t be able to grasp your paper’s aim and main points unless they have the context provided by your introduction.
How to make a good Introduction?
An author’s tone and the requirements of the assignment (for instance, an essay can benefit from an amusing start, while a research paper would be better off with a more formal tone) determine how the document’s introduction is structured. It doesn’t matter what sort of paper you’re writing or what kind of writer you are; a solid introduction always has a hook, some background for context, and a thesis statement or primary argument.
Step 1: Establish the level of seriousness and style you’d want to use throughout your work.
Usually, the subject matter will dictate the tone: Writing an introduction for a report follows a different set of rules than writing an opening for an English essay. Even within essays of the same genre, there are linguistic boundaries; slang, for instance, might work in a reflective piece but not in an academically serious arguing one.
Step 2: Write your thesis statement.
Despite their brevity, thesis statements are often the single most crucial phrase in any given piece of writing. If your thesis statement is well-stated, your readers may utilize it as a point of reference for the essay as they read further.
Step 3: Think about what your reader needs to know about the context.
Provide some background on the discussion itself, even if your issue is an instance of abstractionism like an ethical dispute. How long has the ethical discussion been going on? Was there a particular occurrence that sparked it? In order to prevent your reader from feeling as if they are missing anything, information like this might assist create the scene.
Step 4: Think of a good hook.
The most challenging aspect of writing an introduction is likely to be coming up with a catchy hook. Although the body of your paper may consist mostly of providing facts, the introduction’s hook often demands you to spin a yarn out of thin air.
Step 5: Don’t feel rushed when you write a rough draft of your introduction.
If you become nervous just thinking about writing your introduction, don’t worry. As the introduction is traditionally the first section written, that’s where you start.
Step 6: Revise your introduction after you’ve written your whole paper.
After writing the first draft of your paper, you may find that you need to make some adjustments to the overall structure; if this is the case, be sure to update the introduction to reflect these changes. Editing for things like spelling and punctuation errors becomes much simpler when the first draft is complete.
FAQs
How do I start my introduction?
The best introductions include all three of these elements: a hook to get the reader interested, some context for the issue so they can follow along, and a thesis statement that succinctly and clearly conveys your major argument.
What is a good introduction?
It is common practice for an essay’s opening to provide background information about the issue at hand, before moving on to outline the more narrowly focused arguments that will be developed in the essay’s body.
What is a good opening sentence for an essay?
You should just provide a brief overview of your subject and explain its significance. Optionally, you may additionally offer some of the essay’s supporting arguments or examples. No need to go into great detail here; this is only an introduction to your issue, not a thesis statement.
In conclusion, it takes time and effort to learn how to write an excellent introduction. It’s possible that you’ll have to rewrite them multiple times before you’re happy with the final product. Keep in mind that if you can hold on to just a few more readers, the effort will have been well worth it. You may also check out our free article on examples of essay writing and How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay.