55+ Lecture Examples
Lectures are a cornerstone of education, providing a platform for instructors to share in-depth knowledge and insights on various subjects. They offer a structured format where students can absorb information, engage with new ideas, and develop a deeper understanding of the material. Whether in classrooms, universities, or public forums, lectures foster intellectual growth and encourage active participation through discussions and questions.
What is a Lecture?
A lecture is an educational talk delivered by an expert to convey information on a specific topic. Lectures are common in schools, universities, and public forums, providing a structured method for teachers to present key concepts, theories, and knowledge. They often include visual aids and allow for audience questions and discussions to enhance understanding.
Lecture Examples for Students
1. History Lecture: The American Civil War
Description: This lecture covers the causes, major events, and consequences of the American Civil War. It includes an analysis of key battles, political decisions, and social impacts.
Visual Aids: Maps of battle sites, timelines, and photographs from the era.
Interactive Elements: Discussion questions on the impact of the war on modern America.
2. Science Lecture: The Solar System
Description: An exploration of the planets, moons, and other celestial bodies in our solar system. The lecture discusses planetary formation, orbits, and the potential for life on other planets.
Visual Aids: Planetary models, videos of space missions, and images from telescopes.
Interactive Elements: Group activity to create a scale model of the solar system.
3. Literature Lecture: Shakespeare’s Tragedies
Description: An in-depth analysis of Shakespeare’s major tragedies, focusing on themes, character development, and historical context.
Visual Aids: Excerpts from plays, video clips of performances, and character maps.
Interactive Elements: Small group discussions on the themes and their relevance today.
4. Economics Lecture: Supply and Demand
Description: Explains the fundamental principles of supply and demand, including market equilibrium, shifts in curves, and real-world applications.
Visual Aids: Graphs illustrating supply and demand curves, case studies of market changes.
Interactive Elements: Classroom polls on consumer behavior and market simulations.
5. Environmental Science Lecture: Climate Change
Description: Discusses the science behind climate change, its effects on ecosystems, and mitigation strategies. The lecture includes current data and projections.
Visual Aids: Climate models, charts showing temperature changes, and documentary clips.
Interactive Elements: Debate on the effectiveness of different climate policies.
6. Art Lecture: The Renaissance Period
Description: An overview of the Renaissance art movement, highlighting key artists, techniques, and cultural impacts.
Visual Aids: Slides of famous artworks, video tours of museums, and artist biographies.
Interactive Elements: Group analysis of a specific painting or sculpture.
7. Technology Lecture: The Evolution of the Internet
Description: Tracks the development of the internet from its inception to the present day, including major milestones, technological advances, and societal impacts.
Visual Aids: Timeline of internet development, videos of key historical moments, and diagrams of network structures.
Interactive Elements: Class discussion on how the internet has changed daily life.
8. Health Science Lecture: Nutrition and Diet
Description: Covers the basics of nutrition, the role of different nutrients, and the impact of diet on health. The lecture also addresses current dietary guidelines.
Visual Aids: Nutritional charts, food pyramid diagrams, and case studies.
Interactive Elements: Interactive quiz on nutritional knowledge and group activity to plan a balanced meal.
9. Psychology Lecture: Human Development
Description: Explores the stages of human development from infancy to adulthood, including key theories and research findings.
Visual Aids: Developmental charts, videos of developmental milestones, and excerpts from psychological studies.
Interactive Elements: Group discussions on personal development experiences and case study analyses.
10. Business Lecture: Entrepreneurship and Startups
Description: Examines the process of starting a business, including idea generation, business planning, funding, and scaling.
Visual Aids: Business model canvas templates, success stories, and market analysis tools.
Interactive Elements: Workshop to develop a business idea and pitch it to the class.
Lecture Example Sentences
1. History Lecture: The American Civil War
- “The Union and Confederate armies clashed in numerous significant battles, shaping the course of the Civil War.”
- “The war’s economic and social impacts were profound, leading to the eventual abolition of slavery.”
- “Reconstruction after the Civil War aimed to rebuild the South and integrate freed slaves into society.”
2. Science Lecture: The Solar System
- “The discovery of water on Mars suggests the potential for past or present life on the planet.”
- “Saturn’s rings are composed mainly of ice particles, rocky debris, and dust.”
- “The Kuiper Belt is a region of the solar system beyond Neptune, populated with icy bodies and dwarf planets.”
3. Literature Lecture: Shakespeare’s Tragedies
- “Othello explores themes of jealousy, trust, and betrayal, culminating in a tragic ending.”
- “King Lear’s descent into madness highlights the devastating effects of pride and folly.”
- “In Julius Caesar, political intrigue and the struggle for power lead to betrayal and murder.”
4. Economics Lecture: Supply and Demand
- “Price elasticity of demand measures how responsive the quantity demanded is to a change in price.”
- “Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded at a given price.”
- “Government interventions, like price ceilings and floors, can lead to surpluses and shortages.”
5. Environmental Science Lecture: Climate Change
- “Deforestation contributes significantly to the increase of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.”
- “The melting of polar ice caps is a clear indicator of global warming.”
- “Renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, are vital for reducing our carbon footprint.”
6. Art Lecture: The Renaissance Period
- “Raphael’s ‘School of Athens’ is celebrated for its depiction of classical philosophers.”
- “Donatello’s sculptures demonstrate a mastery of form and movement, influencing Renaissance art.”
- “The use of perspective in Renaissance painting created a more realistic representation of space and depth.”
7. Technology Lecture: The Evolution of the Internet
- “Email revolutionized communication, making it faster and more efficient than traditional mail.”
- “The development of search engines transformed how we access and retrieve information online.”
- “E-commerce platforms have changed the way we shop, offering convenience and a wider selection of products.”
8. Health Science Lecture: Nutrition and Diet
- “Vitamins and minerals are essential micronutrients that support various bodily functions.”
- “Fiber is important for digestive health and can help prevent diseases like colon cancer.”
- “Hydration is crucial; water makes up a significant portion of our body and supports all cellular functions.”
9. Psychology Lecture: Human Development
- “Piaget’s theory of cognitive development outlines how children’s thinking evolves in stages.”
- “Attachment theory explains the bond between infants and their primary caregivers.”
- “Lifespan development studies how people change and grow from birth through old age.”
10. Business Lecture: Entrepreneurship and Startups
- “Identifying a unique value proposition is crucial for differentiating your startup from competitors.”
- “Effective networking can open doors to potential investors and business partners.”
- “Understanding market demand and customer needs is essential for developing a successful product.”
Lecture Recital Examples
1. Music History: The Baroque Period
This lecture recital explores the Baroque period, focusing on composers like Johann Sebastian Bach and George Frideric Handel. The lecture covers the characteristics of Baroque music, including the use of ornamentation, contrast, and the development of opera and instrumental music.
Performance: Excerpts from Bach’s “Brandenburg Concertos” and Handel’s “Water Music” are performed live, illustrating the lecture points.
2. Literature: The Poetry of Emily Dickinson
This lecture recital delves into the life and works of Emily Dickinson, analyzing her unique poetic style, themes of nature, death, and immortality, and her use of unconventional punctuation and capitalization.
Performance: Selected poems are read aloud, and musical settings of her poetry by contemporary composers are performed.
3. Art and Music: Impressionism
A combined art and music lecture recital that examines the Impressionist movement, featuring artists like Claude Monet and musicians like Claude Debussy. The lecture highlights how both art forms aimed to capture fleeting moments and impressions.
Performance: Piano pieces by Debussy, such as “Clair de Lune” and “La Mer,” are performed alongside a visual presentation of Impressionist paintings.
4. Theater: The Works of Shakespeare
This lecture recital focuses on the dramatic works of William Shakespeare, discussing his influence on English literature and theater. The lecture covers themes, character development, and historical context.
Performance: Monologues and scenes from plays like “Hamlet,” “Macbeth,” and “A Midsummer Night’s Dream” are performed by actors, bringing the text to life.
5. Cultural Studies: Traditional Japanese Music
This lecture recital explores traditional Japanese music, including instruments like the koto, shamisen, and shakuhachi. The lecture discusses the historical and cultural significance of these instruments and the music they produce.
Performance: Live performances of traditional pieces demonstrate the unique sounds and techniques of each instrument.
6. History: The Harlem Renaissance
This lecture recital examines the Harlem Renaissance, a cultural movement in the 1920s and 1930s that celebrated African American cultural expression in literature, music, and art.
Performance: Jazz and blues music from artists like Duke Ellington and Bessie Smith are performed, along with readings from poets like Langston Hughes.
7. Film Studies: The Evolution of Film Music
This lecture recital traces the development of film music from silent films to contemporary scores. The lecture covers key composers, techniques, and the impact of music on the cinematic experience.
Performance: Iconic film scores by composers such as Max Steiner, John Williams, and Hans Zimmer are performed, showcasing the evolution of film music.
8. Literature and Music: The Romantics
This lecture recital explores the Romantic period in both literature and music, highlighting the works of poets like Lord Byron and composers like Franz Schubert.
Performance: Poetry readings and live performances of Lieder (art songs) by Schubert illustrate the emotional and expressive qualities of Romanticism.
9. History of Jazz: From Ragtime to Bebop
This lecture recital covers the history of jazz, from its roots in ragtime to the bebop era. The lecture discusses key figures, stylistic developments, and cultural impact.
Performance: Live jazz performances, including pieces by Scott Joplin, Louis Armstrong, and Charlie Parker, demonstrate the evolution of the genre.
10. Opera: The Magic of Mozart
This lecture recital focuses on the operas of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, examining his compositional style, librettos, and the historical context of his works.
Performance: Arias and ensembles from operas like “The Magic Flute,” “Don Giovanni,” and “The Marriage of Figaro” are performed, highlighting Mozart’s genius.
Lecture Forum Examples
1. Education Forum: Innovative Teaching Strategies
In this forum, educators gather to discuss and share innovative teaching strategies. Lectures cover topics like integrating technology in the classroom, project-based learning, and fostering student engagement.
Interactive Element: Breakout sessions where teachers collaborate to develop new lesson plans.
2. Business Forum: Entrepreneurship and Startup Culture
Entrepreneurs and business leaders discuss the challenges and opportunities of starting and growing a business. Topics include funding strategies, market analysis, and leadership skills.
Interactive Element: Panel discussions with successful entrepreneurs followed by Q&A sessions.
3. Health and Wellness Forum: Mental Health Awareness
Mental health professionals provide lectures on recognizing and addressing mental health issues. Topics include anxiety, depression, and stress management techniques.
Interactive Element: Workshops on mindfulness practices and coping strategies.
4. Technology Forum: The Future of Artificial Intelligence
Experts in AI discuss the latest advancements, ethical considerations, and future applications of artificial intelligence. Lectures cover machine learning, robotics, and AI in healthcare.
Interactive Element: Live demonstrations of AI technology and interactive coding sessions.
5. Environmental Forum: Climate Change Solutions
Scientists and environmental activists present lectures on current climate change research and potential solutions. Topics include renewable energy, conservation efforts, and policy changes.
Interactive Element: Group discussions on local environmental initiatives and action plans.
6. Cultural Forum: Global Literature and Storytelling
Authors and literary scholars discuss the impact of literature across cultures. Lectures focus on storytelling traditions, contemporary global literature, and the role of literature in social change.
Interactive Element: Readings and discussions of selected literary works from various cultures.
7. Science Forum: Advances in Biotechnology
Biotechnology experts share insights on the latest developments in the field. Lectures cover gene editing, bioengineering, and medical breakthroughs.
Interactive Element: Lab tours and hands-on experiments demonstrating biotechnological techniques.
8. History Forum: Revisiting Ancient Civilizations
Historians and archaeologists explore the achievements and legacies of ancient civilizations such as Egypt, Greece, and Rome. Lectures include recent archaeological findings and historical analyses.
Interactive Element: Virtual reality tours of ancient sites and interactive artifact exhibits.
9. Arts Forum: Contemporary Art Movements
Artists and critics discuss recent trends in contemporary art, including digital art, street art, and installation art. Lectures highlight influential artists and key exhibitions.
Interactive Element: Art workshops where participants create their own contemporary artworks.
10. Social Sciences Forum: Urban Development and Planning
Urban planners and sociologists examine the challenges of modern urban development. Topics include sustainable cities, smart infrastructure, and community engagement.
Interactive Element: Interactive mapping exercises and group discussions on urban planning projects.
Examples of Lecture Notes
1. History Lecture: The American Civil War
Date: June 26, 2024
Lecturer: Dr. John Smith
Introduction:
- The American Civil War (1861-1865)
- Main causes: slavery, states’ rights, economic differences
Key Battles:
- Battle of Gettysburg (1863): Turning point, Union victory
- Battle of Antietam (1862): Bloodiest single-day battle, led to the Emancipation Proclamation
Consequences:
- Abolition of slavery (13th Amendment)
- Reconstruction Era: integrating freed slaves into society
Discussion Points:
- Impact on modern America
- How economic factors influenced the war
2. Science Lecture: The Solar System
Date: June 26, 2024
Lecturer: Dr. Emily Johnson
Introduction:
- Overview of the solar system
- Sun as the central star
Planets:
- Mercury: Smallest, closest to the Sun
- Venus: Similar size to Earth, thick atmosphere
- Earth: Only planet with known life
- Mars: Potential for past/present life, polar ice caps
- Jupiter: Largest, Great Red Spot storm
- Saturn: Known for its rings
- Uranus: Rotates on its side
- Neptune: Strong winds, dark spots
Other Celestial Bodies:
- Asteroids: Mainly found in the asteroid belt
- Comets: Icy bodies with tails
Discussion Points:
- Future of human exploration on Mars
- Differences between terrestrial and gas giant planets
3. Literature Lecture: Shakespeare’s Tragedies
Date: June 26, 2024
Lecturer: Prof. Anne Williams
Introduction:
- Overview of Shakespeare’s works
- Focus on tragedies
Major Tragedies:
- Hamlet: Themes of revenge and madness
- Macbeth: Ambition and moral corruption
- Othello: Jealousy and betrayal
- King Lear: Power, family dynamics, madness
Literary Devices:
- Use of soliloquies to reveal inner thoughts
- Symbolism and motifs (e.g., blood in Macbeth)
Discussion Points:
- Relevance of Shakespeare’s themes today
- Interpretation of characters across different productions
4. Economics Lecture: Supply and Demand
Date: June 26, 2024
Lecturer: Prof. Mark Thompson
Introduction:
- Fundamental principles of supply and demand
Key Concepts:
- Law of Demand: Inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded
- Law of Supply: Direct relationship between price and quantity supplied
- Market Equilibrium: Point where supply equals demand
Graph Analysis:
- Shifts in demand/supply curves due to external factors (e.g., income, technology)
Real-World Applications:
- Pricing strategies in businesses
- Government interventions (price ceilings/floors)
Discussion Points:
- How supply and demand affect everyday life
- Examples of market changes (e.g., tech industry)
5. Environmental Science Lecture: Climate Change
Date: June 26, 2024
Lecturer: Dr. Lisa Green
Introduction:
- Overview of climate change and global warming
Causes:
- Greenhouse gases (CO2, methane)
- Deforestation, industrial activities
Effects:
- Rising global temperatures
- Melting polar ice caps, rising sea levels
- Increased frequency of extreme weather events
Mitigation Strategies:
- Renewable energy sources (solar, wind)
- Carbon footprint reduction
- Policy changes and international agreements (e.g., Paris Agreement)
Discussion Points:
- Impact of climate change on ecosystems
- Individual actions to combat climate change
Lecture Objectives Examples
1. History Lecture: The American Civil War
Objectives:
- Examine the political, economic, and social causes leading to the Civil War.
- Evaluate the strategic significance and outcomes of major battles like Gettysburg and Antietam.
- Assess the impact of the Civil War on the abolition of slavery and civil rights movements.
- Analyze the challenges and successes of the Reconstruction Era in integrating freed slaves into American society.
2. Science Lecture: The Solar System
Objectives:
- Describe the formation and structure of the solar system.
- Compare the atmospheric and geological features of terrestrial and gas giant planets.
- Investigate the role of the Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud in the solar system.
- Explore current missions and research focused on Mars and the potential for human colonization.
3. Literature Lecture: Shakespeare’s Tragedies
Objectives:
- Explore the thematic elements of ambition, power, and human frailty in Shakespeare’s tragedies.
- Analyze the character development and motivations in plays like “Othello” and “King Lear.”
- Examine Shakespeare’s use of dramatic irony and foreshadowing.
- Discuss the cultural and historical context of Shakespeare’s works and their influence on modern literature.
4. Economics Lecture: Supply and Demand
Objectives:
- Illustrate the principles of supply and demand with real-world examples.
- Analyze how external factors, such as technological advancements and government policies, affect supply and demand curves.
- Evaluate the concept of market equilibrium and how it is achieved in different markets.
- Investigate the effects of price controls, such as rent ceilings and minimum wage laws, on market outcomes.
5. Environmental Science Lecture: Climate Change
Objectives:
- Explain the greenhouse effect and its role in global warming.
- Identify human activities contributing to increased greenhouse gas emissions.
- Assess the ecological and socioeconomic impacts of climate change on various regions.
- Evaluate mitigation and adaptation strategies, including renewable energy, conservation efforts, and international agreements.
6. Art Lecture: The Renaissance Period
Objectives:
- Analyze the key characteristics and innovations of Renaissance art and how they differed from Medieval art.
- Explore the contributions of major artists like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael.
- Examine the influence of humanism and classical antiquity on Renaissance art.
- Discuss the legacy of the Renaissance in shaping Western art and cultural history.
7. Technology Lecture: The Evolution of the Internet
Objectives:
- Trace the historical milestones in the development of the internet, from ARPANET to the modern web.
- Understand the technological breakthroughs that enabled the growth of the internet, such as packet switching and the World Wide Web.
- Discuss the transformative effects of the internet on communication, commerce, and society.
- Predict future trends in internet technology, including the impact of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things.
8. Health Science Lecture: Nutrition and Diet
Objectives:
- Explore the biochemical roles of vitamins and minerals in maintaining health.
- Analyze the impact of dietary patterns on chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
- Discuss the principles of balanced diets and nutritional guidelines for different age groups.
- Evaluate the effects of emerging dietary trends, such as plant-based diets and intermittent fasting.
9. Psychology Lecture: Human Development
Objectives:
- Investigate the major stages of cognitive development according to Piaget’s theory.
- Explore the attachment styles and their impact on later relationships based on Bowlby’s attachment theory.
- Examine the influence of genetic and environmental factors on physical and psychological growth.
- Discuss the role of cultural practices in shaping developmental milestones and behaviors.
10. Business Lecture: Entrepreneurship and Startups
Objectives:
- Identify the essential components of a successful business plan.
- Analyze the risks and rewards associated with different types of entrepreneurial ventures.
- Explore various funding sources for startups, including venture capital, crowdfunding, and bootstrapping.
- Develop strategies for scaling a startup and maintaining competitive advantage in the market.
Types of Lectures
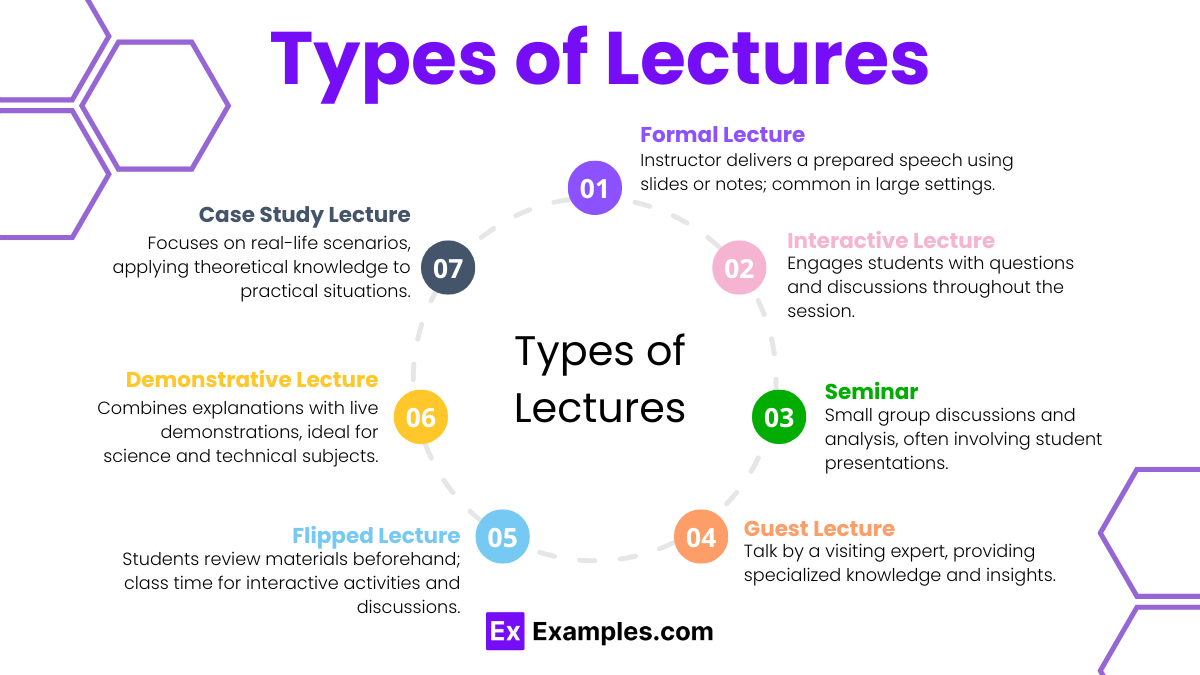
Lectures are a fundamental part of education, offering a structured way to convey information to students. Here are some common types of lectures used in various educational settings:
1. Formal Lecture
A traditional approach where the instructor speaks without interruption, often using slides or notes. This type is common in large classrooms and conferences.
Example: A history professor delivers a detailed talk on the events leading up to World War II, using a prepared slide presentation to outline key dates and events.
2. Interactive Lecture
Incorporates questions and discussions throughout the session to engage students actively. It encourages participation and immediate feedback.
Example: A biology lecturer pauses frequently to ask students questions about cell structure, encouraging group discussions and immediate responses.
3. Seminar
A more intimate setting where students and the instructor discuss and analyze topics in-depth. Often involves student presentations and collaborative learning.
Example: A graduate literature seminar where students discuss and debate interpretations of Shakespeare’s plays, with each student presenting their analysis.
4. Guest Lecture
Delivered by a visiting expert or industry professional, providing specialized knowledge and real-world insights on a particular subject.
Example: An entrepreneur from the tech industry gives a lecture on startup culture and innovation to a business class, sharing firsthand experiences and insights.
5. Flipped Lecture
Students review lecture materials beforehand and use class time for interactive activities, problem-solving, and discussions. This method promotes active learning.
Example: Engineering students watch recorded lectures on fluid dynamics before class and then work on related problems and experiments during in-person sessions.
6. Demonstrative Lecture
Combines explanation with live demonstrations, often used in science and technical courses to illustrate concepts practically.
Example: A chemistry professor performs live chemical reactions to show how different substances interact, explaining each step and outcome to the class.
7. Case Study Lecture
Focuses on real-life scenarios and case studies, encouraging students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations and develop critical thinking skills.
Example: A business ethics class analyzes the Enron scandal, discussing the ethical breaches and their implications, and applying theoretical principles to understand what went wrong.
Functions of Lecture
A lecture serves several essential functions in education and professional development:
1. Knowledge Dissemination
Lectures are a primary method for transmitting information and knowledge from an expert to a broader audience. They help condense large amounts of information into digestible segments.
2. Concept Explanation
Lectures allow instructors to break down complex concepts, theories, and ideas into understandable parts. Through structured presentation and examples, students can grasp difficult material more effectively.
3. Engagement and Inspiration
A well-delivered lecture can captivate and motivate students, sparking interest and curiosity in the subject matter. Engaging lectures often lead to increased student participation and enthusiasm.
4. Structured Learning
Lectures provide a clear, organized framework for learning. They follow a logical sequence, making it easier for students to follow the progression of ideas and build upon their knowledge systematically.
5. Interactive Learning
Interactive elements within lectures, such as Q&A sessions, discussions, and multimedia presentations, enhance student engagement and facilitate active learning. These interactions help reinforce understanding and retention of the material.
6. Assessment and Feedback
Lectures can include quizzes, polls, and other formative assessments to gauge student understanding and provide immediate feedback. This helps identify areas where students may need additional support.
7. Skill Development
Lectures often emphasize critical thinking, note-taking, and listening skills. By actively engaging with the lecture content, students develop these essential academic and professional skills.
8. Expert Insight
Lectures delivered by guest speakers or professionals offer valuable real-world insights and experiences that enrich the learning experience. They provide students with perspectives beyond textbook knowledge.
Benefits of Lecture
1. Efficient Knowledge Transfer
Lectures allow instructors to convey a large amount of information in a structured and concise manner, ensuring students receive essential knowledge within a limited time frame.
2. Expert Insight
Lectures provide students access to the expertise and experiences of instructors, who can offer in-depth explanations and real-world applications that textbooks may not provide.
3. Engagement and Motivation
A well-delivered lecture can inspire and engage students, sparking interest and enthusiasm in the subject matter. Dynamic presentations and passionate delivery can motivate students to delve deeper into topics.
4. Clarification of Complex Concepts
Instructors can break down complicated theories and ideas into more manageable parts, using examples and analogies to make them easier to understand.
5. Structured Learning
Lectures offer a clear and organized framework for learning, following a logical progression that helps students build upon their knowledge systematically.
6. Active Learning Opportunities
Incorporating interactive elements like questions, discussions, and multimedia can enhance student engagement and participation, making learning more dynamic and effective.
7. Critical Thinking and Note-Taking Skills
Lectures encourage students to listen actively, take notes, and synthesize information, which are essential skills for academic success and lifelong learning.
8. Immediate Feedback
Through in-class questions and discussions, students can receive immediate feedback from instructors, clarifying any misunderstandings and reinforcing their learning.
9. Flexibility in Delivery
Lectures can be adapted to various formats, including traditional in-person, online, or hybrid models, making them versatile tools for education in diverse settings.
10. Community Building
Lectures bring students together in a shared learning experience, fostering a sense of community and collaboration. Group discussions and peer interactions during lectures can strengthen social and academic bonds.
Lecture vs. Seminar
| Aspect | Lecture | Seminar |
|---|---|---|
| Format | Instructor-led presentation | Interactive, discussion-based session |
| Audience Size | Large groups | Small groups |
| Interaction Level | Limited interaction | High interaction, active participation |
| Content Delivery | Structured, formal delivery | Collaborative exploration, often student-led |
| Duration | Longer, 50 minutes to several hours | Shorter, typically 1-2 hours |
| Preparation | Instructor prepares detailed content | Participants prepare readings or presentations |
| Focus | Broad coverage of subject matter | In-depth analysis of specific topics |
| Learning Style | Passive learning | Active learning |
| Assessment | Quizzes, tests, exams | Presentations, papers, group projects |
| Environment | Formal setting | Informal setting |
| Instructor Role | Central figure delivering information | Facilitator guiding discussion |
How to Prepare for a Lecture
1. Understand the Topic
- Research Thoroughly: Gather comprehensive information on the topic from credible sources like textbooks, academic journals, and reputable websites.
- Identify Key Points: Focus on the main ideas and concepts that you want to convey during the lecture.
2. Organize Your Content
- Create an Outline: Develop a structured outline that includes an introduction, main body, and conclusion.
- Segment the Material: Break down the content into manageable sections to ensure a logical flow of information.
3. Develop Visual Aids
- Create Slides: Use PowerPoint or similar tools to create slides that highlight key points, include visuals, and maintain engagement.
- Include Diagrams and Charts: Visual aids like diagrams, charts, and videos can help illustrate complex concepts effectively.
4. Prepare Speaking Notes
- Detailed Notes: Prepare detailed notes or cue cards to guide your presentation and ensure you cover all important points.
- Practice Speaking: Rehearse your lecture to become familiar with the material and improve your delivery.
5. Engage Your Audience
- Plan Interactive Elements: Incorporate questions, discussions, or activities to encourage audience participation.
- Prepare Questions: Anticipate possible questions from the audience and prepare answers.
6. Check Technical Requirements
- Test Equipment: Ensure that all technical equipment, such as microphones, projectors, and computers, are working properly.
- Backup Plans: Have backup plans for technical issues, like printed handouts or alternate ways to present visuals.
7. Time Management
- Set Time Limits: Allocate specific time for each section of your lecture to ensure you cover all material within the allotted time.
- Practice Timing: Rehearse your lecture to ensure it fits within the time constraints.
8. Final Review
- Review Content: Go through your content multiple times to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Seek Feedback: If possible, practice in front of a colleague or mentor and seek feedback to improve your delivery.
How should I prepare for a lecture?
Review the material beforehand, take detailed notes, ask questions, and actively participate in discussions to maximize understanding and retention.
What are the benefits of attending lectures?
Lectures provide expert knowledge, structured learning, interactive discussions, and opportunities for immediate feedback and clarification of complex concepts.
How can I stay engaged during long lectures?
Stay engaged by taking notes, asking questions, participating in discussions, and reviewing the material periodically to stay focused and attentive.
What types of lectures are there?
Types of lectures include formal, interactive, seminar, guest, flipped, demonstrative, and case study lectures, each with unique formats and engagement methods.
How can lecturers make their sessions more engaging?
Use visual aids, interactive elements, real-life examples, and encourage questions and discussions to keep students engaged and enhance learning.
What is the role of visual aids in lectures?
Visual aids help illustrate concepts, maintain interest, and enhance understanding by providing visual representations of the material.
How do interactive lectures benefit students?
Interactive lectures encourage active participation, immediate feedback, and a deeper understanding of the material through engagement and discussion.
What are common challenges in delivering effective lectures?
Common challenges include maintaining student engagement, managing time effectively, and ensuring clear communication of complex concepts.
How can students effectively take notes during a lecture?
Use a structured format, highlight key points, and summarize information in your own words to create useful and organized notes.
How should students review lecture material after class?
Review notes, summarize key points, discuss with peers, and seek clarification on any unclear topics to reinforce understanding and retention.



