Mass Communication vs Mediated Communication – 19+ Examples
Delving into the nuances of Mass Communication versus Mediated Communication offers profound insights into the evolving world of information dissemination. While mass communication encompasses a broad approach to reaching wide audiences, mediated communication refers to the specific use of mediums or channels to convey messages. This exploration sheds light on their distinct roles, impact, and strategies in today’s interconnected society, highlighting how each plays a crucial part in shaping public discourse and perception.
What is the Difference Between Mass Communication vs Mediated Communication?
Understanding the distinction between Mass Communication and Mediated Communication is crucial in the field of media studies. Below is a detailed comparison presented in a table format to highlight their differences:
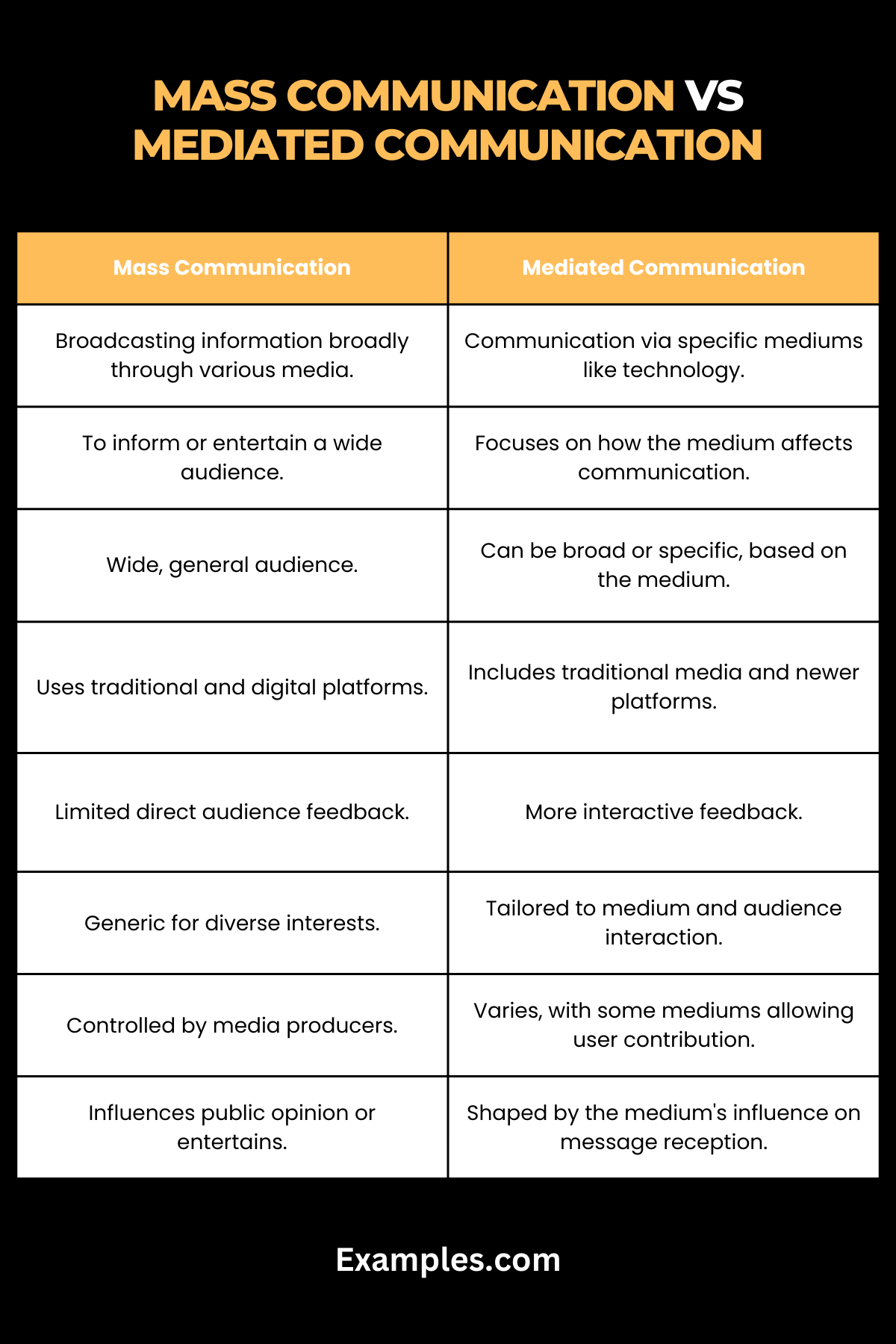
| Aspect | Mass Communication | Mediated Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Refers to the process of conveying information to a large, undifferentiated audience, typically through various media channels. | Involves communication facilitated by a medium, which could be technology, language, or cultural symbols. |
| Primary Objective | Aims to disseminate information, news, or entertainment to a broad public audience. | Focuses on the process and effects of communication through an intervening medium. |
| Scope of Audience | Targets a wide, general audience with no specific segmentation. | May target both broad and specific audiences, depending on the medium used. |
| Channels Used | Utilizes traditional and digital channels like television, radio, newspapers, and online platforms. | Includes both traditional mass media and newer forms like social media, digital platforms, and even interpersonal communication mediated through technology. |
| Feedback Mechanism | Generally offers limited direct feedback from the audience. | Often allows for more interactive and immediate feedback due to the nature of the mediums used. |
| Nature of Content | Content tends to be more generic to cater to diverse interests. | Content can be tailored and personalized, depending on the medium and audience interaction. |
| Control and Gatekeeping | Involves a higher level of control and gatekeeping by media producers and editors. | Offers varied levels of control, with some forms like social media providing more user control and contribution. |
| Message Customization | Messages are generally designed to appeal to a broad audience. | Allows for more specific and nuanced messaging, shaped by the medium and audience feedback. |
| Communication Model | Often follows a one-to-many communication model. | Can follow both one-to-many and one-to-one models, depending on the medium. |
| Impact and Influence | Aimed at influencing public opinion or providing entertainment on a large scale. | Focuses on the impact of the medium itself on the message and the audience’s reception. |
| Technological Advancements | Adapts to technological changes in terms of reach and formats. | Heavily influenced by advancements in technology, altering the way communication is mediated. |
This table shows that while Mass Communication and Mediated Communication overlap, they have distinct characteristics. Mass Communication is about reaching a large audience with a broad message, whereas Mediated Communication focuses more on the medium through which the message is conveyed and how it shapes the communication process.
10 Mass Communication Examples
Exploring various examples of mass communication offers insights into its expansive reach and diverse applications. From traditional media to digital platforms, these examples highlight how mass communication effectively disseminates information, influences public opinion, and entertains a wide audience. Each instance illustrates unique approaches and strategies within the field, reflecting the dynamic and influential nature of mass communication.
- National Television Broadcasts:
National TV broadcasts reach millions, offering news, entertainment, and educational content. They exemplify mass communication’s ability to inform and engage a vast audience simultaneously. - Radio Talk Shows:
Radio talk shows provide a platform for discussion on various topics, reaching commuters and listeners nationwide. They demonstrate mass communication’s role in shaping public discourse and opinion. - Newspaper Publications:
Newspapers have been a cornerstone of mass communication, delivering news, opinions, and advertisements to a wide readership, showcasing the traditional approach to mass information dissemination. - Online News Portals:
Online news portals offer real-time news updates, accessible globally. They represent mass communication’s evolution in the digital age, providing instant access to information. - Social Media Platforms:
Platforms like Facebook and Twitter facilitate rapid information sharing, reaching billions worldwide. They highlight how mass communication has expanded into the digital and interactive realm. - Public Service Announcements (PSAs):
PSAs broadcasted on various media channels raise awareness about important social issues, exemplifying mass communication’s role in public education and welfare. - Podcasts:
Podcasts cover a myriad of subjects, accessible globally. They showcase mass communication’s adaptability and reach in the digital era, catering to diverse interests. - Film and Cinema:
Films are distributed globally, influencing culture and societal norms. This medium demonstrates mass communication’s power in storytelling and cultural impact. - Educational Webinars and Online Courses:
These digital platforms provide learning opportunities to a global audience, highlighting mass communication’s role in education and skill development. - Advertising Campaigns on Multiple Platforms:
These campaigns, spanning TV, radio, and online, illustrate mass communication’s commercial aspect, influencing consumer behavior and market trends.
10 Mediated Communication Examples
Exploring examples of mediated communication reveals its diverse applications and profound impact on how we exchange information. Mediated communication, using various mediums to facilitate the exchange of messages, is an integral part of our digital and interconnected world. Each example below illustrates a unique facet of how mediated communication functions, showcasing its role in shaping interactions, perceptions, and experiences.
- Social Media Platforms:
Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter revolutionize personal and professional interactions. They allow users to share content, engage in discussions, and foster communities, exemplifying mediated communication in the digital age. - Virtual Reality (VR) Experiences:
VR immerses users in a digitally created environment, offering unique, mediated experiences. It’s used for entertainment, education, and training, demonstrating the power of technology in creating new communication dimensions. - Online Educational Courses:
E-learning platforms exemplify mediated communication in education, connecting students and educators globally. They offer interactive courses and resources, making education accessible and flexible. - Teleconferencing and Video Calls:
Tools like Zoom and Skype facilitate real-time, visual communication over distances. They have become essential in business and personal communication, exemplifying mediated interaction in a globalized world. - Blogs and Online Articles:
Blogs and online articles are prime examples of mediated communication in digital journalism and personal expression. They allow writers to reach global audiences with diverse content. - Podcasts:
Podcasts offer audio-based content on various topics, representing a significant shift in how we consume information and entertainment, showcasing a unique form of mediated auditory communication. - Email and Electronic Newsletters:
Email communication and electronic newsletters are crucial in business and personal communication. They offer direct and targeted content delivery, representing efficient mediated written communication. - Digital Billboards and Advertising Displays:
Digital billboards demonstrate mediated communication in advertising, using technology to present dynamic and interactive content in public spaces, enhancing message delivery and audience engagement. - Mobile Messaging Apps:
Apps like WhatsApp and Telegram have transformed personal communication, offering instant and convenient text, voice, and video messaging, exemplifying the evolution of mediated communication. - E-commerce Platforms:
Online shopping sites like Amazon and eBay use mediated communication to facilitate transactions, customer interaction, and product exploration, highlighting its role in modern commerce.
What is the Comparison Between Mass and Mediated Communication?
In the realm of Mass Communication, understanding the distinction from Mediated Communication is crucial. This comprehensive table outlines their differences, focusing on various aspects that highlight their unique characteristics and functions:
| Aspect | Mass Communication | Mediated Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Involves disseminating information broadly across public platforms to a large audience. | Focuses on communication through specific mediums, which influence the message delivery and reception. |
| Primary Objective | Aims to inform, educate, or entertain the general public. | Seeks to examine and utilize the medium’s role in shaping and delivering the message. |
| Target Audience | Broad and undifferentiated, reaching as many people as possible. | Can be broad but is often more targeted, depending on the medium’s nature. |
| Channels Used | Utilizes traditional media (like television and radio), print, and digital platforms. | Employs both mass media channels and newer digital platforms, focusing on the medium’s specific attributes. |
| Feedback and Interaction | Generally limited direct feedback; relies on audience ratings and surveys. | Offers potential for more direct and interactive feedback, especially in digital mediums. |
| Content Nature | Typically generic and diverse to cater to a wide range of interests. | Often more specialized and tailored, influenced by the medium and audience feedback. |
| Control and Gatekeeping | Higher level of control by media producers, editors, and institutions. | Varies; some mediums like social media offer more user control and contribution. |
| Message Customization | Generalized messages designed for broad appeal. | Messages are often more nuanced and personalized. |
| Communication Model | Largely a one-to-many model. | Can be both one-to-many and one-to-one, influenced by the medium. |
| Impact and Influence | Aimed at wide public influence, shaping opinion or providing entertainment. | Focused on the medium’s role in message interpretation and audience engagement. |
| Technological Influence | Rapidly adapting to new technologies in terms of reach and format. | Highly influenced by technological advancements, which directly shape the medium. |
| Content Strategy | Involves planning content for mass appeal and wide dissemination. | Involves strategic content planning based on medium-specific characteristics. |
| Audience Analysis | Focuses on understanding broad audience demographics and preferences. | Involves deeper analysis of audience behavior and interaction with the medium. |
| Measurement of Effectiveness | Assessed through reach, viewership, and audience engagement metrics. | Measured by the effectiveness of the medium in message delivery and audience response. |
| Adaptability and Flexibility | Adapts content based on broad audience trends and general feedback. | Highly adaptable, especially in digital mediums, to respond to specific audience interactions. |
This comparison table elucidates that while Mass Communication is about disseminating information to a large audience, Mediated Communication emphasizes the role and influence of the specific medium used in the communication process. Both are integral to the media landscape but operate under different paradigms and strategies.
The distinction between Mass Communication and Mediated Communication is fundamental in understanding the media landscape. Mass Communication broadly reaches wide audiences, while Mediated Communication focuses on how mediums shape message delivery and audience reception. Recognizing these differences is crucial for effectively navigating and employing various communication strategies in an increasingly media-centric world, as outlined in this comprehensive guide.



