29+ Media Dependency Theory in Mass Communication Examples
Explore the intriguing world of Gatekeeping Theory in Mass Communication. This comprehensive guide sheds light on how information is filtered and disseminated in the media. Understand the pivotal role gatekeepers play in shaping news and information, with real-life examples and practical tips. Ideal for students and professionals in Journalism Mass Communication and Public Relations Mass Communication, this guide is a must-read for anyone interested in media’s influential role in society.
What is Media Dependency Theory in Mass Communication?
Media Dependency Theory in Mass Communication is a concept that explains the relationship between media, audiences, and the larger social system. This theory suggests that as people increasingly depend on media for information, understanding, and entertainment, their beliefs, values, and behaviors are shaped accordingly. It’s particularly relevant in contexts like Social media Mass Communication and Broadcasting Mass Communication, where media’s influence is substantial. Understanding this theory is crucial for comprehending the impact of media in our daily lives.

History
The Gatekeeping Theory in mass communication, first introduced by Kurt Lewin in 1943, has evolved significantly over time. Originally conceptualized to understand the decision-making process in food choices, it was later applied to the mass media context. The theory explains how information is filtered and chosen for public consumption by media professionals. Over the decades, with the advent of digital media and social platforms, gatekeeping has extended beyond traditional media, encompassing new dynamics in information dissemination and control.
What is the Best Example of Media Dependency Theory in Mass Communication
The Media Dependency Theory in mass communication is best exemplified during crisis situations, such as natural disasters or pandemics. During these times, the public’s dependency on media for information significantly increases. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, people relied heavily on media outlets for updates about virus spread, safety protocols, and vaccine availability. This reliance not only illustrates Mass Communication in Real Life but also underscores the Importance of Mass Communication. Media becomes a primary source of information, guidance, and reassurance, highlighting the theory’s relevance in modern society.

30 Examples of Media Dependency Theory in Mass Communication
Media Dependency Theory in Mass Communication is a vital concept that examines how audience dependence on media shapes their perceptions and behaviors. This theory highlights the influential role of media in modern society, particularly in contexts like Public Relations Mass Communication and Social media Mass Communication. It is essential in understanding audience-media dynamics, especially in the era of digital media proliferation.
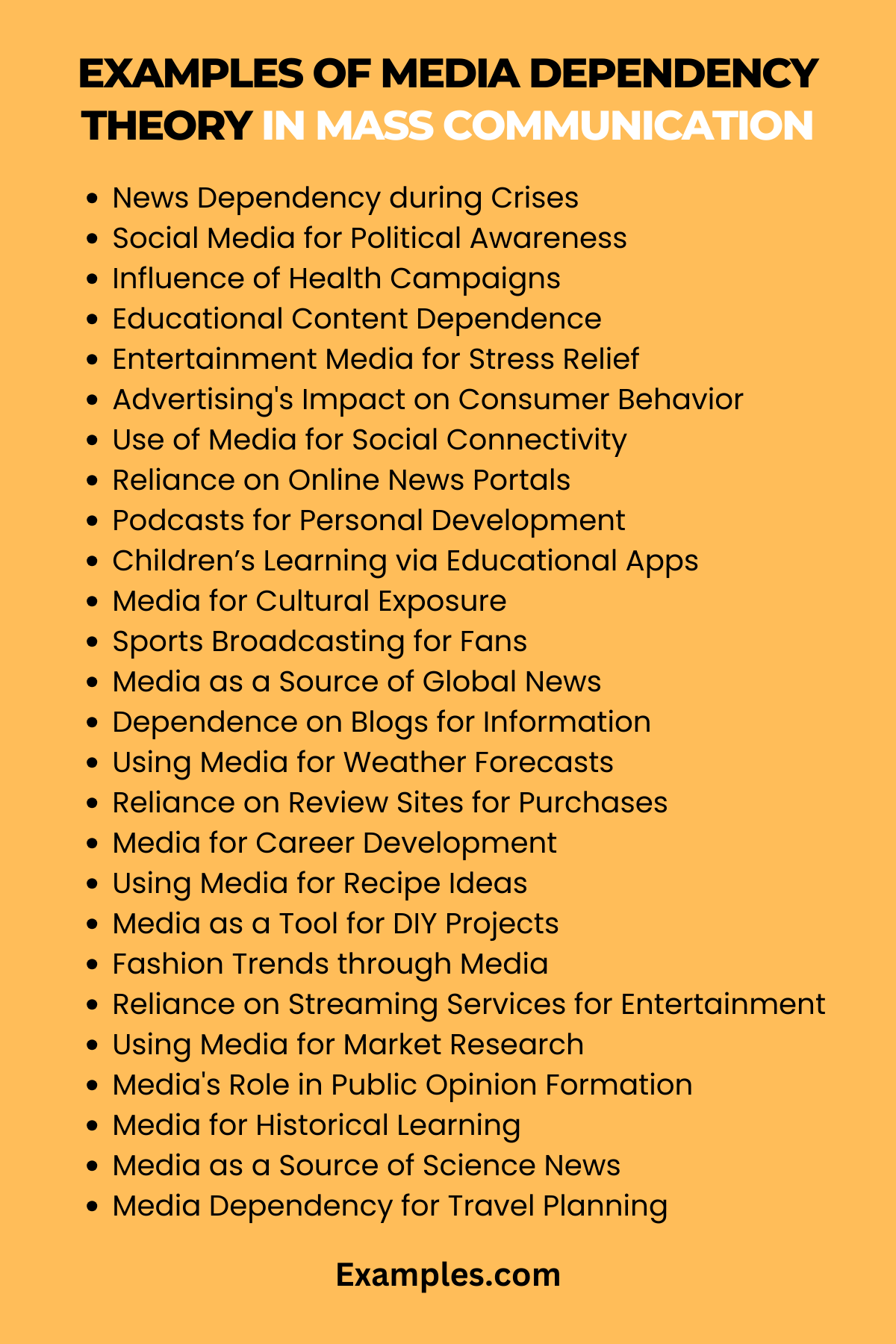
- News Dependency during Crises: People rely heavily on news media for information during emergencies.
Example: “During the hurricane, we constantly checked the news for updates on safety measures.” - Social Media for Political Awareness: Social media’s role in shaping political opinions.
Example: “I learned about the election details mostly through Twitter updates.” - Influence of Health Campaigns: Media campaigns significantly impact public health behavior.
Example: “The anti-smoking ads on TV really made me think about quitting.” - Educational Content Dependence: Reliance on educational broadcasts for learning.
Example: “My kids learn a lot from educational programs on public television.” - Entertainment Media for Stress Relief: Using TV shows and movies as a primary stress relief method. ?
Example: “Watching comedies on Netflix is my go-to way to unwind after work.” - Advertising’s Impact on Consumer Behavior: Media advertisements sway shopping habits.
Example: “The repeated ads on Instagram influenced me to buy this skincare product.” - Use of Media for Social Connectivity: Dependence on social media for maintaining personal relationships.
Example: “I stay connected with my college friends primarily through Facebook.” - Reliance on Online News Portals: Preferring digital news over traditional newspapers.
Example: “I get all my daily news from online portals now, instead of the paper.” - Podcasts for Personal Development: Relying on podcasts for inspiration and self-improvement.
Example: “I listen to motivational podcasts every morning during my commute.” - Children’s Learning via Educational Apps: Kids’ dependence on apps for learning.
Example: “My daughter has learned so much from educational apps on the tablet.”

- Media for Cultural Exposure: Using media to learn about different cultures.
Example: “I explore different cultures through documentaries and international films.” - Sports Broadcasting for Fans: Sports enthusiasts’ reliance on media for game updates.
Example: “I follow every game of the season through live sports broadcasts.” - Media as a Source of Global News: Relying on international news channels for world events.
Example: “For global news, I always turn to international news channels.” - Dependence on Blogs for Information: Regular following of blogs for niche information.
Example: “I keep up with the latest tech trends through specific tech blogs.” - Using Media for Weather Forecasts: Dependence on media for weather updates.
Example: “I check the weather app every morning to plan my day.” - Reliance on Review Sites for Purchases: Using online reviews to inform buying decisions.
Example: “Before buying any gadget, I always read reviews on tech forums.” - Media for Career Development: Using media platforms for professional growth and job searches.
Example: “I often use LinkedIn to look for job opportunities and networking.” - Using Media for Recipe Ideas: Relying on cooking shows and blogs for culinary inspiration.
Example: “I get most of my recipe ideas from food blogs and cooking channels.” - Media as a Tool for DIY Projects: Following DIY channels and blogs for project ideas.
Example: “For my home DIY projects, I often refer to tutorials on YouTube.” - Fashion Trends through Media: Media influencing fashion and lifestyle choices.
Example: “I keep up with the latest fashion trends through Instagram influencers.” - Reliance on Streaming Services for Entertainment: Preferring streaming services over traditional TV.
Example: “I’ve completely switched to streaming services like Netflix for movies and shows.” - Using Media for Market Research: Businesses relying on media for consumer insights.
Example: “We use social media trends to understand customer preferences better.” - Media’s Role in Public Opinion Formation: How media shapes public opinion on societal issues.
Example: “Public opinion on environmental issues has been largely shaped by media documentaries.” - Media for Historical Learning: Using documentaries and historical channels for learning about history.
Example: “I learn about historical events through documentaries on the History Channel.” - Media as a Source of Science News: Relying on media for the latest science discoveries and news.
Example: “I follow science news primarily through specialized online science news portals.”

- Media Dependency for Travel Planning: Using travel blogs and shows for vacation planning.
Example: “I plan my trips based on recommendations from travel vlogs and articles.” - Media for Language Learning: Using media to learn and practice new languages.
Example: “I improve my Spanish by watching Spanish movies and TV shows.” - Media as a Source for Self-Help Content: Depending on self-help books, podcasts, and videos.
Example: “I often turn to self-help podcasts for personal growth advice.” - Media for Keeping Up with Technology Trends: Following tech news to stay updated with the latest in technology.
Example: “I keep up with the latest in AI through tech news sites.” - Media for Real Estate Market Trends: Using media to understand and follow real estate trends.
Example: “For real estate investments, I closely follow market trends through specialized media platforms.”
Role of Media Dependency Theory in Mass Communication
The Media Dependency Theory plays a pivotal role in understanding the dynamics of mass communication, especially in how audiences interact with media and are influenced by it.
- Source of Information: In scenarios where alternative information sources are limited, media becomes the primary source. For example, during emergencies, people rely on media for crucial updates.
- Shaping Perceptions: The theory suggests that media can shape public perception, especially in matters where the audience has no direct experience or knowledge, such as foreign affairs or scientific developments.
- Influence on Public Opinion: Media has the power to influence public opinion by selecting which issues to highlight. This can be seen in Political Campaigns Mass Communication, where media coverage can sway voter opinions.
- Role in Socialization: Media plays a crucial role in the socialization process, disseminating cultural norms and values. This is evident in Television Mass Communication, where TV shows reflect and shape societal norms.
- Interplay with Societal Changes: The theory also acknowledges that the influence of media evolves with societal changes. The rise of Social media Mass Communication has altered the way information is consumed and shared, leading to a more active audience participation.
- Dependency in Digital Age: In the digital age, dependency on media has grown with the proliferation of Mass Communication in a Digital Age. The internet and social media platforms have become integral in daily life, further cementing the theory’s relevance.
- Critical in Decision-Making: Media plays a critical role in public decision-making processes. For instance, in health crises, people depend on media for health-related decisions, showing the practical applications of Mass Communication Examples in Real Life.
- Impact on Public Behavior: The theory also highlights how media can influence public behavior. This is particularly evident in advertising and marketing strategies that shape consumer behaviors.
Importance of Media Dependency Theory in Mass Communication
The Media Dependency Theory plays a crucial role in understanding the dynamics of Mass Communication in Real Life. This theory suggests that the more a person depends on media to meet their needs, the more important that media becomes to them. Here’s why it’s significant:
- Influences Public Perception: Media Dependency Theory highlights how media shapes public perception, especially in situations where the audience has no direct experience or knowledge.
- Adaptation to Changing Media Environments: It explains how individuals and societies adapt to new and evolving media technologies.
- Critical in Crisis Management: During crises, people’s dependency on media for information increases, making it a vital tool for effective communication and management.
- Understanding Audience Behavior: This theory helps in predicting audience behavior, which is essential for developing targeted media content and strategies.
- Role in Policy Making: Understanding media dependency assists policymakers in crafting regulations that affect media consumption and content.
- Impact on Socialization: Media plays a significant role in socialization, and this theory underscores its influence in shaping cultural norms and values.
How to Use Media Dependency Theory in Mass Communication
Applying the Media Dependency Theory in mass communication involves several strategic approaches:
- Target Audience Analysis: Identify the level of dependency your target audience has on specific media channels and tailor your content accordingly.
- Content Strategy Development: Develop content that meets the informational, personal, and social needs of your audience, enhancing their dependency on your media.
- Crisis Communication: Utilize media channels effectively during crises to provide reliable information, thereby increasing audience dependency and trust.
- Influencing Public Opinion: Create and disseminate content that influences public opinion, recognizing the media’s role as a primary source of information for many individuals.
- Adapting to Media Changes: Stay abreast of changes in media technology and consumption habits to maintain and enhance audience dependency.
- Educational and Awareness Campaigns: Use media to educate and raise awareness, capitalizing on the audience’s dependency for information dissemination.
- Evaluating Media Effects: Regularly assess how changes in media affect audience behavior and preferences to fine-tune communication strategies.
The Media Dependency Theory in Mass Communication offers insightful perspectives on the relationship between media and its audience. By understanding and leveraging this theory, professionals in Journalism Mass Communication and Public Relations Mass Communication can craft more impactful messages and strategies. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the theory’s application, enhancing the effectiveness of communication in various media domains.