150+ Noun Examples
When you hear the words: doctor, animals, Mary, California, Thanksgiving, actress, mice, luck, hair, scissors, eggs, oh wow!, yikes! Oh for heaven sake! and music. These words are examples of nouns.
What is Noun?
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, idea, or concept. It serves as the backbone of English sentences, acting as the subject, object, or complement within a sentence. Nouns can be classified into several categories, including proper nouns (names of specific people, places, or organizations, like “Michael” or “Paris”), common nouns (general names for things, like “dog” or “city”), countable nouns (items that can be counted, like “books”), uncountable nouns (substances or concepts that cannot be counted, like “water” or “happiness”), and collective nouns (words that represent a group of things or people, like “team” or “family”). Understanding and using nouns correctly is fundamental to constructing clear and informative sentences.
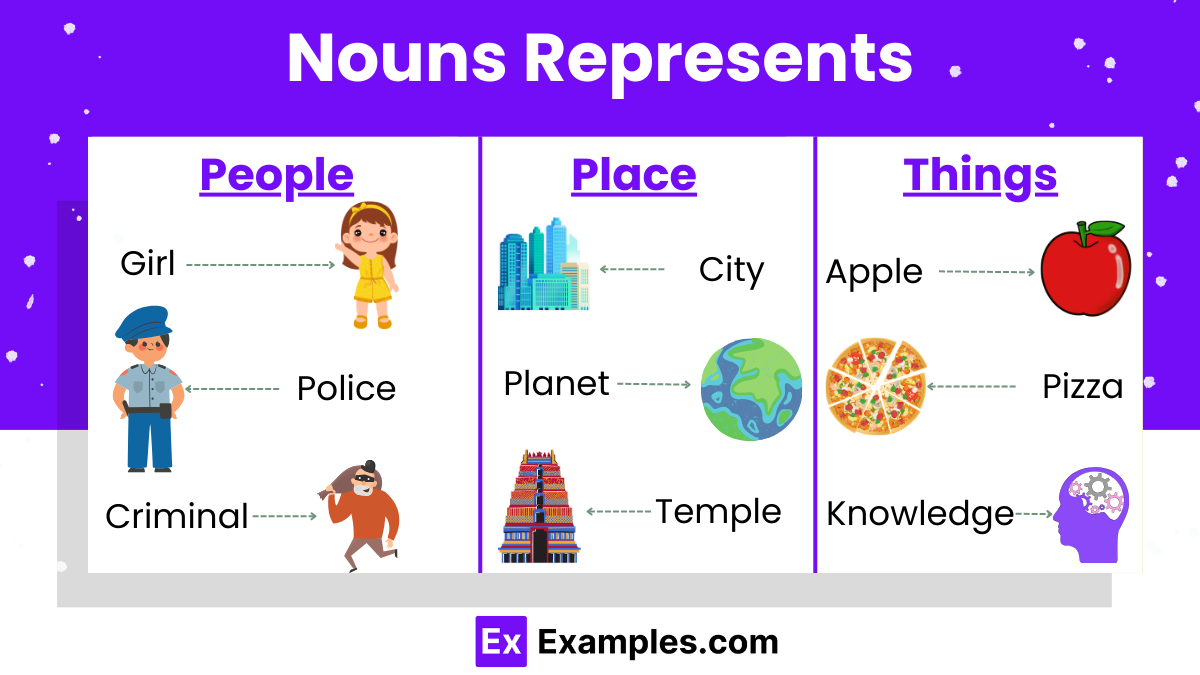
Types of Nouns
Nouns, the building blocks of sentences, come in various types to convey different meanings and functions. Here’s a breakdown of the main types:
Common Nouns
- Definition: Names general items, people, or places rather than specific ones.
- Example: dog, city, teacher
Proper Nouns
- Definition: Specific names given to particular people, places, or organizations, always capitalized.
- Example: Michael, Paris, Google
Countable Nouns
- Definition: Nouns that can be counted, allowing for a singular or plural form.
- Example: book (books), apple (apples)
Uncountable Nouns
- Definition: Mass nouns that cannot be counted and usually do not have a plural form.
- Example: information, rice, water
Concrete Nouns
- Definition: Names things that you can see, touch, hear, smell, or taste.
- Example: chocolate, thunder, perfume
Abstract Nouns
- Definition: Names ideas, qualities, or states rather than physical objects.
- Example: freedom, happiness, intelligence
Collective Nouns
- Definition: Names for a group or a collection of people or things.
- Example: team, family, herd
Compound Nouns
- Definition: Nouns formed from two or more words combined to create a new meaning.
- Example: toothpaste, basketball, greenhouse
Possessive Nouns
- Definition: Nouns that show ownership or possession.
- Example: Michael’s, cat’s, women’s
Nouns and Number
Nouns in English are closely related to number, indicating whether they refer to one item (singular) or more than one item (plural). Understanding how nouns change according to number is essential for correct grammar and clear communication. Here are key points regarding nouns and number:
Singular Nouns
- Definition: Refer to one person, place, thing, or idea.
- Example: book, cat, city
- Usage: A singular noun represents a single entity and is used with singular verbs and pronouns.
Plural Nouns
- Definition: Refer to two or more persons, places, things, or ideas.
- Example: books, cats, cities
- Formation: Generally formed by adding -s or -es to the singular form, but there are many irregular plural forms (e.g., child -> children, mouse -> mice).
- Usage: Plural nouns are used with plural verbs and pronouns to indicate more than one entity.
Special Considerations
- Irregular Plurals: Some nouns have irregular plural forms that do not follow the standard -s or -es ending pattern.
- Uncountable Nouns: These nouns (e.g., water, information) do not typically have plural forms and represent items that cannot be counted individually.
- Collective Nouns: Words that represent a group of individuals or things. They can take a singular or plural verb depending on whether the action is performed by the group as a whole or by individuals within the group (e.g., “The team is winning” vs. “The team are wearing their new uniforms”).
- Pluralia Tantum: Nouns that only exist in plural form (e.g., scissors, trousers) and refer to items that are made up of two parts.
Proper Nouns vs. Common Nouns
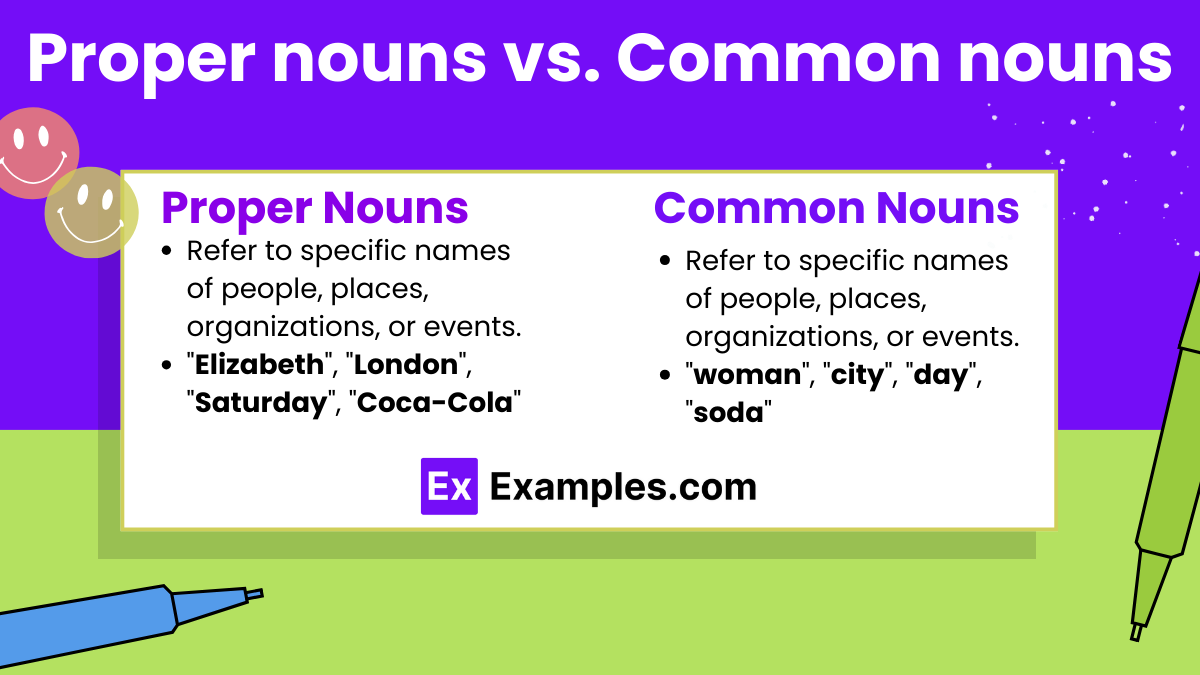
| Aspect | Proper Nouns | Common Nouns |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Refer to specific names of people, places, organizations, or events. | Refer to general names for people, places, things, or ideas. |
| Capitalization | Always capitalized. | Capitalized only if they begin a sentence or are part of a title. |
| Examples | “Elizabeth”, “London”, “Saturday”, “Coca-Cola” | “woman”, “city”, “day”, “soda” |
| Specificity | Specific and unique to the entity being referred to. | General and not specific to any one entity. |
| Usage with Articles | Often used without articles, but can include them if part of a specific title or when a common noun is included. | Can be used with definite (the) or indefinite (a, an) articles. |
| Modification | Less frequently modified by adjectives. | Often modified by adjectives to specify or quantify. |
| Plural Form | Some can be pluralized (e.g., “the Smiths”), but many remain singular. | Can be singular or plural depending on context and quantity. |
| Function | Names a particular one of its kind. | Names any one of its kind. |
Countable Nouns vs. Uncountable Nouns
Countable and uncountable nouns in English differ in how they can be quantified, affecting their use in sentences, particularly in terms of article and quantifier choice. Here’s a detailed comparison:
Countable Nouns
- Definition: Nouns that refer to items that can be counted. They have both singular and plural forms.
- Example: apple (apples), book (books), chair (chairs)
- Usage with Articles: Can use “a” or “an” with singular forms and “the” with singular or plural forms. Specific numbers can be used directly (one apple, three books).
- Quantifiers: Often used with quantifiers like many, a few, several, etc.
Uncountable Nouns
- Definition: Nouns that refer to substances, concepts, or masses that cannot be divided into separate elements. They usually do not have a plural form.
- Example: water, information, rice
- Usage with Articles: Cannot use “a” or “an” because they cannot be counted. “The” can be used to refer to the substance or concept as a whole.
- Quantifiers: Used with quantifiers like much, a little, a great deal of, etc.
Key Differences
- Plurality: Countable nouns can be singular or plural; uncountable nouns are typically treated as singular.
- Quantification: Countable nouns can be quantified with numbers directly; uncountable nouns require a unit of measurement for quantification (a cup of water, a piece of information).
- Article Usage: “A” and “an” can only be used with countable nouns in their singular form.
Nouns and the Possessive Case
The possessive case in English is used to indicate ownership or a relationship between nouns. It helps to specify who or what owns or is closely associated with something else. Here’s how nouns function within the possessive case:
Forming the Possessive Case
- Singular Nouns: Add an apostrophe followed by “s” (
's) to the end of a singular noun to make it possessive, regardless of whether the noun ends in “s.”- Example: cat’s toy, Chris’s book
- Plural Nouns Ending in “s”: Add only an apostrophe (
') after the existing “s” at the end of the plural noun.- Example: dogs’ leashes, friends’ meeting
- Plural Nouns Not Ending in “s”: Add an apostrophe followed by “s” (
's) to the end of the noun.- Example: children’s books, men’s room
Usage of the Possessive Case
- Ownership: Shows who owns something.
- Example: Maria’s car, the company’s policy
- Part of: Indicates a part of something or a relationship.
- Example: the book’s cover, today’s weather
- Associations: Signifies associations or relationships between people.
- Example: my brother’s friend, the teacher’s students
- Measurements and Time: Describes measurements or specific times, indicating duration or specific instances.
- Example: a day’s pay, two weeks’ vacation
Special Considerations
- With Inanimate Objects: While it’s common to use the possessive case with people and animals, it’s less usual with inanimate objects. Prepositional phrases are often preferred (the leg of the table rather than the table’s leg), though both forms can be grammatically correct.
- Joint Ownership: When two or more nouns share ownership, add the possessive form to the last noun only.
- Example: Alice and Bob’s apartment
- Separate Ownership: When ownership is separate, make both nouns possessive.
- Example: Alice’s and Bob’s cars
How are Nouns Used in Sentences?
Nouns play a vital role in sentence construction, serving as the foundation of English syntax. They can be used in various ways to provide clarity, detail, and depth to sentences. Here’s how nouns are typically used:
As the Subject of a Sentence
- Function: Indicates who or what is performing the action or being described.
- Example: The dog barks loudly.
As the Object of a Verb
- Function: Receives the action of the verb.
- Example: She reads the book.
As the Object of a Preposition
- Function: Follows a preposition to form a prepositional phrase, indicating location, direction, time, or method.
- Example: They sat on the bench.
As a Complement
- Function: Follows a linking verb (such as be, seem, look) and renames or describes the subject.
- Example: He is a teacher.
As a Possessive Modifier
- Function: Shows ownership, association, or a relationship to another noun.
- Example: Sara’s book is on the table.
In Apposition
- Function: A noun or noun phrase that renames another noun right beside it, providing additional information about it.
- Example: My brother, the doctor, is visiting.
Noun Phrases
A noun phrase is a group of words that functions in a sentence as a subject, object, or prepositional object, with a noun or pronoun being its central element. Noun phrases provide detailed information about the people, places, and things in sentences, including who or what is involved, and any additional description or specification. Here’s a deeper look into noun phrases:
Components of Noun Phrases
- Head: The central noun or pronoun that determines the core meaning of the phrase.
- Determiners: Articles (a, an, the), possessive pronouns (my, your, their), demonstratives (this, that, these, those), quantifiers (some, many, a lot of), and numbers. They specify and identify the noun.
- Modifiers: Adjectives, participles, or even other noun phrases that describe or qualify the head noun. Prepositional phrases and relative clauses can also serve as modifiers.
Functions of Noun Phrases
- Subject: The noun phrase can act as the subject of a sentence.
- Example: The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.
- Object: The noun phrase can serve as the direct or indirect object of a verb.
- Example: She found a lost golden ring in the park.
- Complement: The noun phrase can complement the subject or object, often following linking verbs.
- Example: The winner of the competition is my best friend.
- Prepositional Object: The noun phrase can act as the object of a preposition.
- Example: They walked through the dense forest.
Common Mistakes with Nouns
Navigating the use of nouns in English can sometimes be tricky, leading to common mistakes. Here are several typical errors to watch out for:
1. Incorrect Plural Forms
- Mistake: Adding an incorrect ending to make a noun plural, especially with irregular nouns.
- Example: Incorrect: “childs” | Correct: “children”
2. Misuse of Countable and Uncountable Nouns
- Mistake: Treating uncountable nouns as countable, and vice versa.
- Example: Incorrect: “informations” | Correct: “information”
3. Confusing Similar Nouns
- Mistake: Mixing up nouns that are similar in form or meaning.
- Example: Incorrect: “effect” (when you mean result) vs. Correct: “affect” (when you mean influence)
4. Incorrect Use of Articles with Nouns
- Mistake: Using the wrong article (“a”, “an”, “the”) or omitting it where necessary.
- Example: Incorrect: “She has cat.” | Correct: “She has a cat.”
5. Errors in Possessive Forms
- Mistake: Misplacing the apostrophe in possessive nouns or using it with possessive pronouns.
- Example: Incorrect: “its tail” (possessive pronoun) as “it’s tail” | Correct: “its tail”
6. Overgeneralization of Rules
- Mistake: Applying a rule too broadly, especially with irregular nouns and foreign-derived words.
- Example: Incorrect: “cactuses” | Correct: “cacti”
7. Mixing Up Proper and Common Nouns
- Mistake: Failing to capitalize proper nouns or unnecessarily capitalizing common nouns.
- Example: Incorrect: “spanish food” | Correct: “Spanish food”
8. Forgetting Noun-Verb Agreement
- Mistake: Using a singular noun with a plural verb or vice versa.
- Example: Incorrect: “The list of items are on the table.” | Correct: “The list of items is on the table.”
9. Misusing Collective Nouns
- Mistake: Confusion over whether to treat collective nouns as singular or plural.
- Example: Incorrect (depending on context): “The team are winning.” | Correct: “The team is winning.” or “The team are winning.” (UK English can treat collective nouns as plural)
How to Use Nouns
Nouns are fundamental to English language sentences, serving various roles to convey meaning and information. Here’s how to effectively use nouns in your writing and speaking:
1. Identifying Entities
- Purpose: Nouns name people, places, things, and ideas, providing clarity about what or whom you’re discussing.
- Example: “The computer on the desk belongs to Daniel.”
2. Serving as the Subject
- Purpose: The subject of a sentence performs the action or is described. Nouns often serve this role.
- Example: “The cat sleeps on the sofa.”
3. Acting as an Object
- Purpose: Nouns can be direct objects (receiving the action) or indirect objects (to whom/for whom the action is done).
- Example: “She gave the teacher a gift.”
4. Describing Possession
- Purpose: Use possessive nouns to show ownership or relationships.
- Example: “Sara’s book is on the table.”
5. Working within Prepositional Phrases
- Purpose: Nouns often follow prepositions in a sentence to create a prepositional phrase, adding detail about time, location, or manner.
- Example: “They sat in the park.”
6. Complementing Linking Verbs
- Purpose: After a linking verb (like “is” or “becomes”), a noun can rename or describe the subject (known as a predicate nominative).
- Example: “Karl is a teacher.”
7. Using in Apposition
- Purpose: An appositive is a noun or noun phrase that renames another noun right beside it, providing additional information about it.
- Example: “My brother, a doctor, works at the hospital.”
8. Forming Compound Nouns
- Purpose: Combine two or more words to create a compound noun, offering a specific name for objects, places, or concepts.
- Example: “She always forgets her credit card.”
9. Creating Noun Phrases
- Purpose: Expand a simple noun with modifiers (like adjectives) and determiners to form a noun phrase, adding detail.
- Example: “The tall, old tree in the backyard is my favorite.”
Tips for Effective Noun Usage
- Ensure agreement between nouns and verbs in terms of number.
- Be aware of the difference between countable and uncountable nouns, especially when using articles and quantifiers.
- Use specific nouns for clarity and detailed descriptions in your writing.\
Nouns vs. Pronouns
| Aspect | Nouns | Pronouns |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Words that name people, places, things, ideas, or concepts. | Words used to replace nouns to avoid repetition and make sentences smoother. |
| Examples | dog, city, happiness | he, she, it, they, this, who |
| Types | Common, proper, countable, uncountable, concrete, abstract, collective, compound. | Personal, possessive, demonstrative, relative, reflexive, interrogative, indefinite. |
| Capitalization | Proper nouns are capitalized. | Pronouns are not usually capitalized, except “I” and when beginning sentences. |
| Function | Serve as the subject, object, or complement in a sentence, indicating what the sentence is about. | Refer back to nouns mentioned previously or about to be mentioned, serving as subjects, objects, possessives, or complements. |
| Specificity | Can be specific (proper nouns) or general (common nouns). | Are generally non-specific, referring to nouns mentioned elsewhere in the text for context. |
| Variety | Vast array of nouns exists to name a multitude of things, emotions, ideas, etc. | Limited set of pronouns, each serving a specific grammatical purpose. |
| Modification | Can be modified by adjectives and possessive forms. | Cannot be modified by adjectives; possessive pronouns serve a similar function to adjectives. |
| Agreement | Nouns agree with verbs in number and sometimes gender (in gendered languages). |
Pronouns agree with the nouns they replace in number, gender (in some languages), and case |
A to Z Noun Examples list
| Letter | Examples |
|---|---|
| A | Apple, Artist, Airplane, Animal, Author |
| B | Book, Beach, Bird, Bread, Bicycle |
| C | Car, Cat, City, Chair, Cake |
| D | Dog, Doctor, Desk, Door, Dish |
| E | Elephant, Egg, Engine, Earth, Envelope |
| F | Flower, Fish, Farmer, Forest, Friend |
| G | Garden, Guitar, Girl, Glass, Game |
| H | House, Horse, Hospital, Hat, Honey |
| I | Ice, Island, Insect, Idea, Iron |
| J | Juice, Jacket, Jungle, Jar, Jewel |
| K | Kite, Kangaroo, Kitchen, Key, King |
| L | Lion, Lamp, Lake, Leaf, Lemon |
| M | Mountain, Monkey, Moon, Music, Map |
| N | Nurse, Nest, Notebook, Night, Name |
| O | Ocean, Owl, Orange, Office, Oil |
| P | Pencil, Park, Penguin, Pizza, Planet |
| Q | Queen, Quilt, Quail, Quarter, Quiz |
| R | River, Rabbit, Rainbow, Rose, Room |
| S | Sun, School, Star, Ship, Stone |
| T | Tree, Train, Tiger, Table, Town |
| U | Umbrella, Unicorn, Uniform, University, Urn |
| V | Violin, Village, Vase, Volcano, Van |
| W | Water, Whale, Window, Watch, Wood |
| X | Xylophone, X-ray, Xerus, Xenon, Xylem |
| Y | Yacht, Yard, Yarn, Year, Youth |
| Z | Zebra, Zoo, Zigzag, Zucchini, Zenith |
Noun Examples in Sentences by Types
1. Common Nouns
- Dog: “The dog barked loudly.”
- City: “She moved to a new city.”
- Book: “He read an interesting book.”
- Chair: “There is a comfortable chair in the room.”
- Teacher: “The teacher explained the lesson.”
2. Proper Nouns
- John: “John is my best friend.”
- Paris: “They visited Paris last summer.”
- Monday: “We have a meeting on Monday.”
- Nike: “She bought new Nike shoes.”
- Eiffel Tower: “The Eiffel Tower is a famous landmark.”
3. Abstract Nouns
- Love: “Love can conquer all.”
- Happiness: “His happiness was evident.”
- Freedom: “They fought for their freedom.”
- Courage: “She showed great courage.”
- Knowledge: “Knowledge is power.”
4. Concrete Nouns
- Apple: “She ate a red apple.”
- Car: “He drives a fast car.”
- House: “They live in a big house.”
- Tree: “A tall tree stood in the yard.”
- Laptop: “Her laptop is brand new.”
5. Collective Nouns
- Team: “The team won the match.”
- Class: “The class went on a field trip.”
- Flock: “A flock of birds flew overhead.”
- Family: “Her family gathers every Sunday.”
- Committee: “The committee meets monthly.”
6. Countable Nouns
- Book: “She borrowed three books from the library.”
- Cat: “He has two cats.”
- Chair: “We need five chairs for the dining table.”
- Pen: “I bought a new pen.”
- Egg: “She used a dozen eggs for the recipe.”
7. Uncountable Nouns
- Water: “She drank a glass of water.”
- Rice: “We need more rice.”
- Information: “He provided useful information.”
- Sugar: “There is no sugar left.”
- Music: “I love listening to music.”
8. Compound Nouns
- Toothbrush: “Don’t forget your toothbrush.”
- Basketball: “They played basketball after school.”
- Sunflower: “The sunflower bloomed in the garden.”
- Firefighter: “The firefighter saved the cat.”
- Laptop: “She worked on her laptop.”
9. Possessive Nouns
- Child’s: “The child’s toy was broken.”
- Teacher’s: “The teacher’s desk is organized.”
- Dogs’: “The dogs’ owner is friendly.”
- Men’s: “The men’s restroom is on the left.”
- Alice’s: “This is Alice’s book.”
10. Singular Nouns
- Dog: “The dog is barking.”
- City: “The city is crowded.”
- Book: “The book is on the table.”
- Tree: “The tree is tall.”
- Laptop: “The laptop is new.”
11. Plural Nouns
- Dogs: “The dogs are barking.”
- Cities: “The cities are crowded.”
- Books: “The books are on the table.”
- Trees: “The trees are tall.”
- Laptops: “The laptops are new.”
More Noun Examples
1. Noun Plurals
2. Noun Template
3. Nouns and Determiners
4. Grammatical Nouns
5. Articles and Nouns
6. General Nouns
7. Nouns, Pronouns, and Articles
8. Parts of Speech Noun
9. Noun Phrases
10. Noun Types
11. Noun-Verb Ambiguity
12. Noun Sort
13. Common Nouns
14. Articles With Nouns
15. The Noun Group
16. Noun-Adjective Memory Game
17. Noun Notes
18. Noun Types with Exercises
19. Verb and Adverb in DOC
20. Articles and Noun Phrases
21. Standard Nouns
22. Countable and Uncountable Nouns
23. Plural Possessives Nouns
24. Nouns and Noun Groups
25. Professional Nouns
26. Grammar Nouns
27. Nouns Worksheet
28. Noun and Verb
29. Knowledge Acquisition Nouns
30. Identifying Nouns
31. English Grammar Nouns
32. Nouns in PDF
33. Case Study Nouns
34. Kinds of Nouns
35. Noun Phrase Appositives
36. Noun Sentences
37. School Nouns and Verbs
38. The Basic Nouns
39. Concrete and Abstract Nouns
40. Apostrophes With Plural Nouns
41. Simple Nouns
42. First 300 Nouns
43. Wolof Noun Class System
44. Grammar Basics Nouns
45. Noun Exercises
46. Comparison of Noun and Verb
47. Printable Nouns
48. Nouns in the English System
49. Apostrophe Nouns
50. Noun Paradigm
51. Noun Game in DOC
52. Standard Noun Practice
53. Grammar Compound Nouns
54. Collective Nouns
55. Fry’s Picture Noun
56. Analysis of Noun Phrases
57. Draft Nouns
58. Nouns Worksheet in PDF
59. Noun Driven Paradigm
60. Types of Noun
61. Pronoun and Noun
62. Skimming for Base Noun Phrases
63. The Noun
64. Abstract Nouns
65. Noun Classes for Children’s
66. Noun Extraction
67. Student Nouns
68. Noun Agreement
69. Noun Examples
70. Noun Project
71. Noun Filter Table
72. Noun or Verb
73. Basic Noun in DOC
74. Noun Poem
75. Expanded Noun Phrases
76. Common and Proper Nouns Example
77. English Nouns Format
78. Possessive Nouns
79. Formal Nouns
80. Nouns as Variables
81. Nouns Handout
82. Zombie Nouns
83. Nouns, Adjectives and Verbs
84. Verb-Noun Language List
85. Noun Examples in PDF
86. Two-Way Nouns
87. Simple Noun Phrases
88. School English Nouns
89. Noun Clauses
90. Nouns List
91. Noun Sorting
92. Noun Words
93. Syntax of Noun
94. Vocabulary Nouns
95. Nouns in Speech
96. Nouns in DOC
97. Singular and Plural Nouns
98. Noun Phrase Generator
99. Noun Words in DOC
100. Sematic Nouns
101. Noun Template in DOC
Importance of Nouns
Nouns hold a fundamental place in the structure and expression of the English language, serving as the cornerstone for conveying clear and specific information. Here are key reasons highlighting their importance:
Foundation for Communication
- Nouns provide the essential details in our conversations and writings, naming the key components of our messages. Without nouns, it would be challenging to specify subjects and objects in our discussions.
Convey Specificity and Detail
- Through the use of nouns, speakers and writers can convey specific information, offering clarity and precision. Nouns allow for the description of concrete and abstract concepts, enabling detailed expression of thoughts and ideas.
Serve Multiple Roles in Sentences
- Nouns are versatile, serving as subjects, objects, and complements within sentences. This flexibility allows for varied sentence structures, enhancing the dynamism and richness of language.
Enable Description and Identification
- Nouns work in tandem with adjectives and other modifiers to provide detailed descriptions, allowing for the vivid depiction of scenes, emotions, and narratives.
Facilitate Clear Communication Across Disciplines
- In academic and professional contexts, nouns are crucial for naming theories, principles, and materials, facilitating precise and unambiguous communication across various fields.
Support Language Development and Learning
- Learning nouns is a foundational aspect of language acquisition, helping individuals categorize and understand the world around them. Mastery of nouns and their functions is essential for language learners at all levels.
Cultural and Conceptual Significance
- Nouns also carry cultural and conceptual significance, encapsulating ideas, traditions, and beliefs specific to different languages and societies. They are pivotal in sharing and preserving cultural heritage.
What is a noun?
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. Examples: cat, city, book, happiness.
What are common nouns?
Common nouns are general names for people, places, or things. Examples: dog, city, book, teacher.
What are proper nouns?
Proper nouns are specific names for particular people, places, or things and are always capitalized. Examples: John, Paris, Monday, Nike.
What are abstract nouns?
Abstract nouns refer to intangible concepts or ideas that cannot be seen or touched. Examples: love, happiness, freedom, courage.
What are concrete nouns?
Concrete nouns are physical objects that can be perceived by the senses. Examples: apple, car, house, tree.
What are collective nouns?
Collective nouns refer to groups of people, animals, or things as a single unit. Examples: “team,” “class,” “flock.”
What are countable nouns?
Countable nouns can be counted as individual units and have singular and plural forms. Examples: “book/books,” “cat/cats,” “chair/chairs.”
What are uncountable nouns?
Uncountable nouns cannot be counted and do not have a plural form. Examples: “water,” “rice,” “music.”
What are compound nouns?
Compound nouns are formed by combining two or more words to create a single noun. Examples: “toothbrush,” “basketball,” “sunflower.”
What are possessive nouns?
Possessive nouns show ownership or possession, typically formed by adding an apostrophe and “s” or just an apostrophe for plural nouns. Examples: “child’s,” “teacher’s,” “dogs’.”
150+ Noun Examples

When you hear the words: doctor, animals, Mary, California, Thanksgiving, actress, mice, luck, hair, scissors, eggs, oh wow!, yikes! Oh for heaven sake! and music. These words are examples of nouns.
What is Noun?
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, idea, or concept. It serves as the backbone of English sentences, acting as the subject, object, or complement within a sentence. Nouns can be classified into several categories, including proper nouns (names of specific people, places, or organizations, like “Michael” or “Paris”), common nouns (general names for things, like “dog” or “city”), countable nouns (items that can be counted, like “books”), uncountable nouns (substances or concepts that cannot be counted, like “water” or “happiness”), and collective nouns (words that represent a group of things or people, like “team” or “family”). Understanding and using nouns correctly is fundamental to constructing clear and informative sentences.
Types of Nouns
Nouns, the building blocks of sentences, come in various types to convey different meanings and functions. Here’s a breakdown of the main types:
Common Nouns
Definition: Names general items, people, or places rather than specific ones.
Example: dog, city, teacher
Proper Nouns
Definition: Specific names given to particular people, places, or organizations, always capitalized.
Example: Michael, Paris, Google
Countable Nouns
Definition: Nouns that can be counted, allowing for a singular or plural form.
Example: book (books), apple (apples)
Uncountable Nouns
Definition: Mass nouns that cannot be counted and usually do not have a plural form.
Example: information, rice, water
Concrete Nouns
Definition: Names things that you can see, touch, hear, smell, or taste.
Example: chocolate, thunder, perfume
Abstract Nouns
Definition: Names ideas, qualities, or states rather than physical objects.
Example: freedom, happiness, intelligence
Collective Nouns
Definition: Names for a group or a collection of people or things.
Example: team, family, herd
Compound Nouns
Definition: Nouns formed from two or more words combined to create a new meaning.
Example: toothpaste, basketball, greenhouse
Possessive Nouns
Definition: Nouns that show ownership or possession.
Example: Michael’s, cat’s, women’s
Nouns and Number
Nouns in English are closely related to number, indicating whether they refer to one item (singular) or more than one item (plural). Understanding how nouns change according to number is essential for correct grammar and clear communication. Here are key points regarding nouns and number:
Singular Nouns
Definition: Refer to one person, place, thing, or idea.
Example: book, cat, city
Usage: A singular noun represents a single entity and is used with singular verbs and pronouns.
Plural Nouns
Definition: Refer to two or more persons, places, things, or ideas.
Example: books, cats, cities
Formation: Generally formed by adding -s or -es to the singular form, but there are many irregular plural forms (e.g., child -> children, mouse -> mice).
Usage: Plural nouns are used with plural verbs and pronouns to indicate more than one entity.
Special Considerations
Irregular Plurals: Some nouns have irregular plural forms that do not follow the standard -s or -es ending pattern.
Uncountable Nouns: These nouns (e.g., water, information) do not typically have plural forms and represent items that cannot be counted individually.
Collective Nouns: Words that represent a group of individuals or things. They can take a singular or plural verb depending on whether the action is performed by the group as a whole or by individuals within the group (e.g., “The team is winning” vs. “The team are wearing their new uniforms”).
Pluralia Tantum: Nouns that only exist in plural form (e.g., scissors, trousers) and refer to items that are made up of two parts.
Proper Nouns vs. Common Nouns
Aspect | Proper Nouns | Common Nouns |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Refer to specific names of people, places, organizations, or events. | Refer to general names for people, places, things, or ideas. |
Capitalization | Always capitalized. | Capitalized only if they begin a sentence or are part of a title. |
Examples | “Elizabeth”, “London”, “Saturday”, “Coca-Cola” | “woman”, “city”, “day”, “soda” |
Specificity | Specific and unique to the entity being referred to. | General and not specific to any one entity. |
Usage with Articles | Often used without articles, but can include them if part of a specific title or when a common noun is included. | Can be used with definite (the) or indefinite (a, an) articles. |
Modification | Less frequently modified by adjectives. | Often modified by adjectives to specify or quantify. |
Plural Form | Some can be pluralized (e.g., “the Smiths”), but many remain singular. | Can be singular or plural depending on context and quantity. |
Function | Names a particular one of its kind. | Names any one of its kind. |
Countable Nouns vs. Uncountable Nouns
Countable and uncountable nouns in English differ in how they can be quantified, affecting their use in sentences, particularly in terms of article and quantifier choice. Here’s a detailed comparison:
Countable Nouns
Definition: Nouns that refer to items that can be counted. They have both singular and plural forms.
Example: apple (apples), book (books), chair (chairs)
Usage with Articles: Can use “a” or “an” with singular forms and “the” with singular or plural forms. Specific numbers can be used directly (one apple, three books).
Quantifiers: Often used with quantifiers like many, a few, several, etc.
Uncountable Nouns
Definition: Nouns that refer to substances, concepts, or masses that cannot be divided into separate elements. They usually do not have a plural form.
Example: water, information, rice
Usage with Articles: Cannot use “a” or “an” because they cannot be counted. “The” can be used to refer to the substance or concept as a whole.
Quantifiers: Used with quantifiers like much, a little, a great deal of, etc.
Key Differences
Plurality: Countable nouns can be singular or plural; uncountable nouns are typically treated as singular.
Quantification: Countable nouns can be quantified with numbers directly; uncountable nouns require a unit of measurement for quantification (a cup of water, a piece of information).
Article Usage: “A” and “an” can only be used with countable nouns in their singular form.
Nouns and the Possessive Case
The possessive case in English is used to indicate ownership or a relationship between nouns. It helps to specify who or what owns or is closely associated with something else. Here’s how nouns function within the possessive case:
Forming the Possessive Case
Singular Nouns: Add an apostrophe followed by “s” (
's) to the end of a singular noun to make it possessive, regardless of whether the noun ends in “s.”Example: cat’s toy, Chris’s book
Plural Nouns Ending in “s”: Add only an apostrophe (
') after the existing “s” at the end of the plural noun.Example: dogs’ leashes, friends’ meeting
Plural Nouns Not Ending in “s”: Add an apostrophe followed by “s” (
's) to the end of the noun.Example: children’s books, men’s room
Usage of the Possessive Case
Ownership: Shows who owns something.
Example: Maria’s car, the company’s policy
Part of: Indicates a part of something or a relationship.
Example: the book’s cover, today’s weather
Associations: Signifies associations or relationships between people.
Example: my brother’s friend, the teacher’s students
Measurements and Time: Describes measurements or specific times, indicating duration or specific instances.
Example: a day’s pay, two weeks’ vacation
Special Considerations
With Inanimate Objects: While it’s common to use the possessive case with people and animals, it’s less usual with inanimate objects. Prepositional phrases are often preferred (the leg of the table rather than the table’s leg), though both forms can be grammatically correct.
Joint Ownership: When two or more nouns share ownership, add the possessive form to the last noun only.
Example: Alice and Bob’s apartment
Separate Ownership: When ownership is separate, make both nouns possessive.
Example: Alice’s and Bob’s cars
How are Nouns Used in Sentences?
Nouns play a vital role in sentence construction, serving as the foundation of English syntax. They can be used in various ways to provide clarity, detail, and depth to sentences. Here’s how nouns are typically used:
As the Subject of a Sentence
Function: Indicates who or what is performing the action or being described.
Example: The dog barks loudly.
As the Object of a Verb
Function: Receives the action of the verb.
Example: She reads the book.
As the Object of a Preposition
Function: Follows a preposition to form a prepositional phrase, indicating location, direction, time, or method.
Example: They sat on the bench.
As a Complement
Function: Follows a linking verb (such as be, seem, look) and renames or describes the subject.
Example: He is a teacher.
As a Possessive Modifier
Function: Shows ownership, association, or a relationship to another noun.
Example: Sara’s book is on the table.
In Apposition
Function: A noun or noun phrase that renames another noun right beside it, providing additional information about it.
Example: My brother, the doctor, is visiting.
Noun Phrases
A noun phrase is a group of words that functions in a sentence as a subject, object, or prepositional object, with a noun or pronoun being its central element. Noun phrases provide detailed information about the people, places, and things in sentences, including who or what is involved, and any additional description or specification. Here’s a deeper look into noun phrases:
Components of Noun Phrases
Head: The central noun or pronoun that determines the core meaning of the phrase.
Determiners: Articles (a, an, the), possessive pronouns (my, your, their), demonstratives (this, that, these, those), quantifiers (some, many, a lot of), and numbers. They specify and identify the noun.
Modifiers: Adjectives, participles, or even other noun phrases that describe or qualify the head noun. Prepositional phrases and relative clauses can also serve as modifiers.
Functions of Noun Phrases
Subject: The noun phrase can act as the subject of a sentence.
Example: The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.
Object: The noun phrase can serve as the direct or indirect object of a verb.
Example: She found a lost golden ring in the park.
Complement: The noun phrase can complement the subject or object, often following linking verbs.
Example: The winner of the competition is my best friend.
Prepositional Object: The noun phrase can act as the object of a preposition.
Example: They walked through the dense forest.
Common Mistakes with Nouns
Navigating the use of nouns in English can sometimes be tricky, leading to common mistakes. Here are several typical errors to watch out for:
1. Incorrect Plural Forms
Mistake: Adding an incorrect ending to make a noun plural, especially with irregular nouns.
Example: Incorrect: “childs” | Correct: “children”
2. Misuse of Countable and Uncountable Nouns
Mistake: Treating uncountable nouns as countable, and vice versa.
Example: Incorrect: “informations” | Correct: “information”
3. Confusing Similar Nouns
Mistake: Mixing up nouns that are similar in form or meaning.
Example: Incorrect: “effect” (when you mean result) vs. Correct: “affect” (when you mean influence)
4. Incorrect Use of Articles with Nouns
Mistake: Using the wrong article (“a”, “an”, “the”) or omitting it where necessary.
Example: Incorrect: “She has cat.” | Correct: “She has a cat.”
5. Errors in Possessive Forms
Mistake: Misplacing the apostrophe in possessive nouns or using it with possessive pronouns.
Example: Incorrect: “its tail” (possessive pronoun) as “it’s tail” | Correct: “its tail”
6. Overgeneralization of Rules
Mistake: Applying a rule too broadly, especially with irregular nouns and foreign-derived words.
Example: Incorrect: “cactuses” | Correct: “cacti”
7. Mixing Up Proper and Common Nouns
Mistake: Failing to capitalize proper nouns or unnecessarily capitalizing common nouns.
Example: Incorrect: “spanish food” | Correct: “Spanish food”
8. Forgetting Noun-Verb Agreement
Mistake: Using a singular noun with a plural verb or vice versa.
Example: Incorrect: “The list of items are on the table.” | Correct: “The list of items is on the table.”
9. Misusing Collective Nouns
Mistake: Confusion over whether to treat collective nouns as singular or plural.
Example: Incorrect (depending on context): “The team are winning.” | Correct: “The team is winning.” or “The team are winning.” (UK English can treat collective nouns as plural)
How to Use Nouns
Nouns are fundamental to English language sentences, serving various roles to convey meaning and information. Here’s how to effectively use nouns in your writing and speaking:
1. Identifying Entities
Purpose: Nouns name people, places, things, and ideas, providing clarity about what or whom you’re discussing.
Example: “The computer on the desk belongs to Daniel.”
2. Serving as the Subject
Purpose: The subject of a sentence performs the action or is described. Nouns often serve this role.
Example: “The cat sleeps on the sofa.”
3. Acting as an Object
Purpose: Nouns can be direct objects (receiving the action) or indirect objects (to whom/for whom the action is done).
Example: “She gave the teacher a gift.”
4. Describing Possession
Purpose: Use possessive nouns to show ownership or relationships.
Example: “Sara’s book is on the table.”
5. Working within Prepositional Phrases
Purpose: Nouns often follow prepositions in a sentence to create a prepositional phrase, adding detail about time, location, or manner.
Example: “They sat in the park.”
6. Complementing Linking Verbs
Purpose: After a linking verb (like “is” or “becomes”), a noun can rename or describe the subject (known as a predicate nominative).
Example: “Karl is a teacher.”
7. Using in Apposition
Purpose: An appositive is a noun or noun phrase that renames another noun right beside it, providing additional information about it.
Example: “My brother, a doctor, works at the hospital.”
8. Forming Compound Nouns
Purpose: Combine two or more words to create a compound noun, offering a specific name for objects, places, or concepts.
Example: “She always forgets her credit card.”
9. Creating Noun Phrases
Purpose: Expand a simple noun with modifiers (like adjectives) and determiners to form a noun phrase, adding detail.
Example: “The tall, old tree in the backyard is my favorite.”
Tips for Effective Noun Usage
Ensure agreement between nouns and verbs in terms of number.
Be aware of the difference between countable and uncountable nouns, especially when using articles and quantifiers.
Use specific nouns for clarity and detailed descriptions in your writing.\
Nouns vs. Pronouns
Aspect | Nouns | Pronouns |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Words that name people, places, things, ideas, or concepts. | Words used to replace nouns to avoid repetition and make sentences smoother. |
Examples | dog, city, happiness | he, she, it, they, this, who |
Types | Common, proper, countable, uncountable, concrete, abstract, collective, compound. | Personal, possessive, demonstrative, relative, reflexive, interrogative, indefinite. |
Capitalization | Proper nouns are capitalized. | Pronouns are not usually capitalized, except “I” and when beginning sentences. |
Function | Serve as the subject, object, or complement in a sentence, indicating what the sentence is about. | Refer back to nouns mentioned previously or about to be mentioned, serving as subjects, objects, possessives, or complements. |
Specificity | Can be specific (proper nouns) or general (common nouns). | Are generally non-specific, referring to nouns mentioned elsewhere in the text for context. |
Variety | Vast array of nouns exists to name a multitude of things, emotions, ideas, etc. | Limited set of pronouns, each serving a specific grammatical purpose. |
Modification | Can be modified by adjectives and possessive forms. | Cannot be modified by adjectives; possessive pronouns serve a similar function to adjectives. |
Agreement | Nouns agree with verbs in number and sometimes gender (in gendered languages). | Pronouns agree with the nouns they replace in number, gender (in some languages), and case |
A to Z Noun Examples list
Letter | Examples |
|---|---|
A | Apple, Artist, Airplane, Animal, Author |
B | Book, Beach, Bird, Bread, Bicycle |
C | Car, Cat, City, Chair, Cake |
D | Dog, Doctor, Desk, Door, Dish |
E | Elephant, Egg, Engine, Earth, Envelope |
F | Flower, Fish, Farmer, Forest, Friend |
G | Garden, Guitar, Girl, Glass, Game |
H | House, Horse, Hospital, Hat, Honey |
I | Ice, Island, Insect, Idea, Iron |
J | Juice, Jacket, Jungle, Jar, Jewel |
K | Kite, Kangaroo, Kitchen, Key, King |
L | Lion, Lamp, Lake, Leaf, Lemon |
M | Mountain, Monkey, Moon, Music, Map |
N | Nurse, Nest, Notebook, Night, Name |
O | Ocean, Owl, Orange, Office, Oil |
P | Pencil, Park, Penguin, Pizza, Planet |
Q | Queen, Quilt, Quail, Quarter, Quiz |
R | River, Rabbit, Rainbow, Rose, Room |
S | Sun, School, Star, Ship, Stone |
T | Tree, Train, Tiger, Table, Town |
U | Umbrella, Unicorn, Uniform, University, Urn |
V | Violin, Village, Vase, Volcano, Van |
W | Water, Whale, Window, Watch, Wood |
X | Xylophone, X-ray, Xerus, Xenon, Xylem |
Y | Yacht, Yard, Yarn, Year, Youth |
Z | Zebra, Zoo, Zigzag, Zucchini, Zenith |
Noun Examples in Sentences by Types
1. Common Nouns
Dog: “The dog barked loudly.”
City: “She moved to a new city.”
Book: “He read an interesting book.”
Chair: “There is a comfortable chair in the room.”
Teacher: “The teacher explained the lesson.”
2. Proper Nouns
John: “John is my best friend.”
Paris: “They visited Paris last summer.”
Monday: “We have a meeting on Monday.”
Nike: “She bought new Nike shoes.”
Eiffel Tower: “The Eiffel Tower is a famous landmark.”
3. Abstract Nouns
Love: “Love can conquer all.”
Happiness: “His happiness was evident.”
Freedom: “They fought for their freedom.”
Courage: “She showed great courage.”
Knowledge: “Knowledge is power.”
4. Concrete Nouns
Apple: “She ate a red apple.”
Car: “He drives a fast car.”
House: “They live in a big house.”
Tree: “A tall tree stood in the yard.”
Laptop: “Her laptop is brand new.”
5. Collective Nouns
Team: “The team won the match.”
Class: “The class went on a field trip.”
Flock: “A flock of birds flew overhead.”
Family: “Her family gathers every Sunday.”
Committee: “The committee meets monthly.”
6. Countable Nouns
Book: “She borrowed three books from the library.”
Cat: “He has two cats.”
Chair: “We need five chairs for the dining table.”
Pen: “I bought a new pen.”
Egg: “She used a dozen eggs for the recipe.”
7. Uncountable Nouns
Water: “She drank a glass of water.”
Rice: “We need more rice.”
Information: “He provided useful information.”
Sugar: “There is no sugar left.”
Music: “I love listening to music.”
8. Compound Nouns
Toothbrush: “Don’t forget your toothbrush.”
Basketball: “They played basketball after school.”
Sunflower: “The sunflower bloomed in the garden.”
Firefighter: “The firefighter saved the cat.”
Laptop: “She worked on her laptop.”
9. Possessive Nouns
Child’s: “The child’s toy was broken.”
Teacher’s: “The teacher’s desk is organized.”
Dogs’: “The dogs’ owner is friendly.”
Men’s: “The men’s restroom is on the left.”
Alice’s: “This is Alice’s book.”
10. Singular Nouns
Dog: “The dog is barking.”
City: “The city is crowded.”
Book: “The book is on the table.”
Tree: “The tree is tall.”
Laptop: “The laptop is new.”
11. Plural Nouns
Dogs: “The dogs are barking.”
Cities: “The cities are crowded.”
Books: “The books are on the table.”
Trees: “The trees are tall.”
Laptops: “The laptops are new.”
More Noun Examples
1. Noun Plurals

monmouth.edu
2. Noun Template

assets.vmou.ac.in
3. Nouns and Determiners

southeastern.edu
4. Grammatical Nouns
jcu.edu.au
5. Articles and Nouns

strose.edu
6. General Nouns

sac.edu
7. Nouns, Pronouns, and Articles

walton.uark.edu
8. Parts of Speech Noun

hfhighschool.org
9. Noun Phrases

public.wsu.edu
10. Noun Types
qub.ac.uk
11. Noun-Verb Ambiguity

aclanthology.org
12. Noun Sort
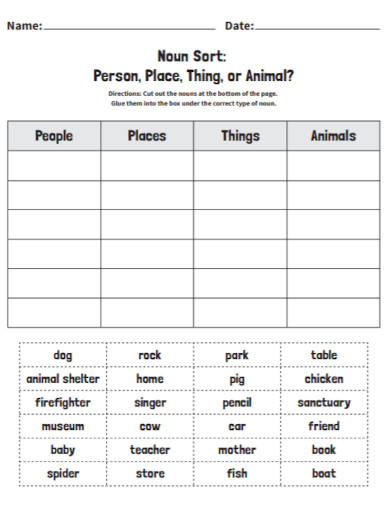
peta.org
13. Common Nouns

poorvucenter.yale.edu
14. Articles With Nouns

sass.uottawa.ca
15. The Noun Group

sydney.edu.au
16. Noun-Adjective Memory Game
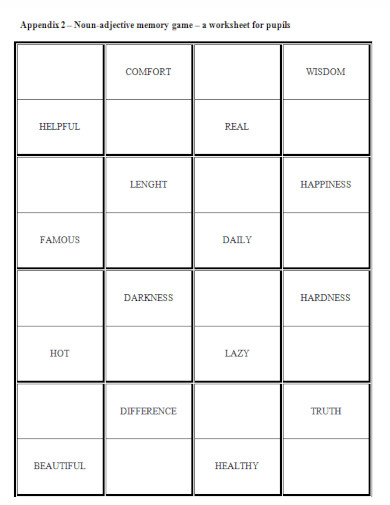
clanky.rvp.cz
17. Noun Notes

asd.org
18. Noun Types with Exercises

broughtonhall.com
19. Verb and Adverb in DOC

unit.org
20. Articles and Noun Phrases

methodist.edu
21. Standard Nouns

kngac.ac.in
22. Countable and Uncountable Nouns
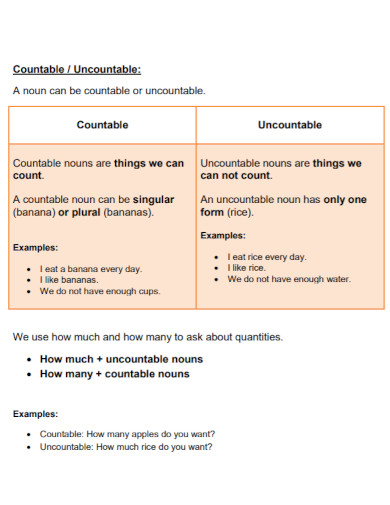
qu.edu.qa
23. Plural Possessives Nouns
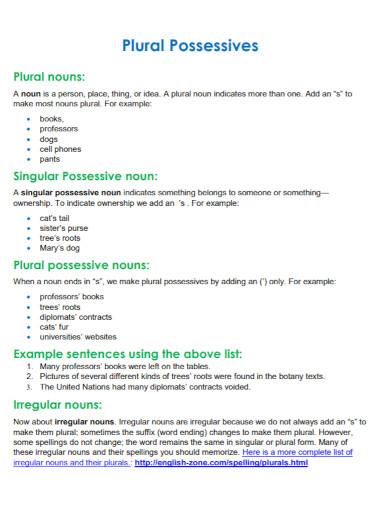
uhcl.edu
24. Nouns and Noun Groups

ugr.es
25. Professional Nouns

iseahs.rnu.tn
26. Grammar Nouns

timeeducation.com
27. Nouns Worksheet

zeeschoolhyd.com
28. Noun and Verb

sendat.academy
29. Knowledge Acquisition Nouns

ijcai.org
30. Identifying Nouns

cambridge.org
31. English Grammar Nouns

perfect-english-grammar.com
32. Nouns in PDF

scholastic.com
33. Case Study Nouns

notredamebarh.co.in
34. Kinds of Nouns

manasquanschools.org
35. Noun Phrase Appositives
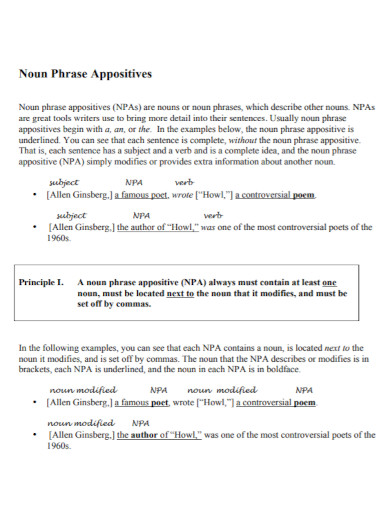
collegeofsanmateo.edu
36. Noun Sentences

mdc.edu
37. School Nouns and Verbs

apsva.us
38. The Basic Nouns

uwgb.edu
39. Concrete and Abstract Nouns

houstonisd.org
40. Apostrophes With Plural Nouns

oasisacademywoodview.org
41. Simple Nouns

soas.ac.uk
42. First 300 Nouns
pattan.net
43. Wolof Noun Class System

linguisticsociety.org
44. Grammar Basics Nouns

ou.edu
45. Noun Exercises

stfrancisschool.edu.in
46. Comparison of Noun and Verb
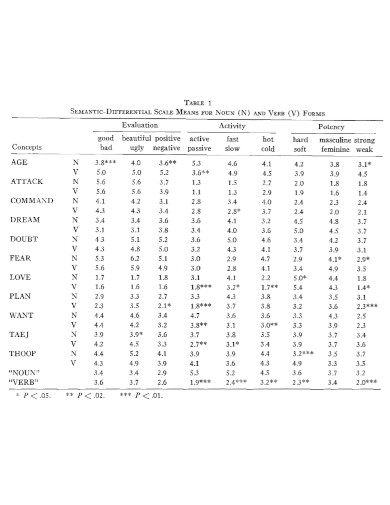
deepblue.lib.umich.edu
47. Printable Nouns

old.amu.ac.in
48. Nouns in the English System

staffnew.uny.ac.id
49. Apostrophe Nouns
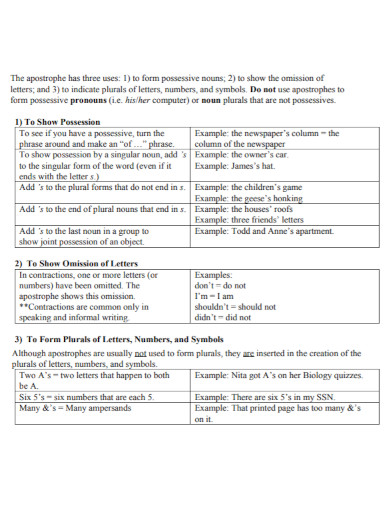
suu.edu
50. Noun Paradigm

myheritage.heritage.edu
51. Noun Game in DOC
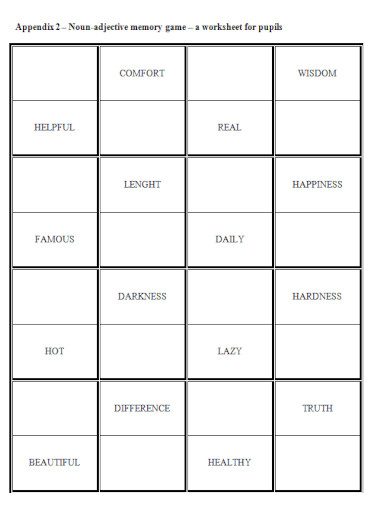
clanky.rvp.cz
52. Standard Noun Practice

warrenhills.org
53. Grammar Compound Nouns
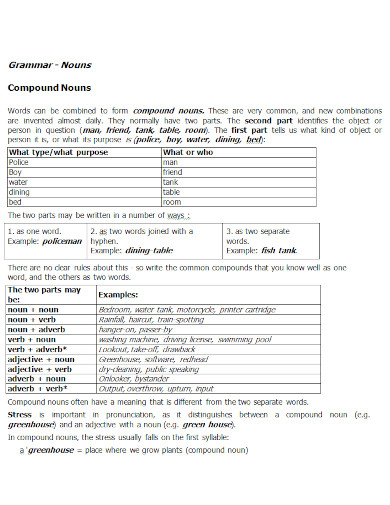
profs.info.uaic.ro
54. Collective Nouns
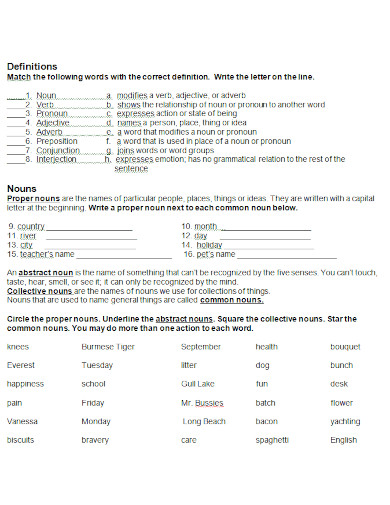
htsdnj.org
55. Fry’s Picture Noun
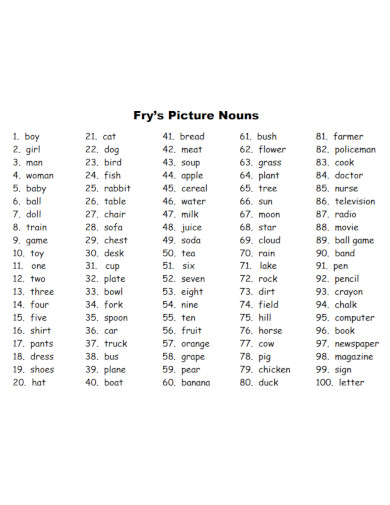
nrcs.net
56. Analysis of Noun Phrases

web.stanford.edu
57. Draft Nouns

itcaonline.com
58. Nouns Worksheet in PDF

learning.com
59. Noun Driven Paradigm

escholarship.org
60. Types of Noun

palomar.edu
61. Pronoun and Noun

evansville.edu
62. Skimming for Base Noun Phrases

citeseerx.ist.psu.edu
63. The Noun

oup.com.au
64. Abstract Nouns

starnoldsvijaynagar.com
65. Noun Classes for Children’s
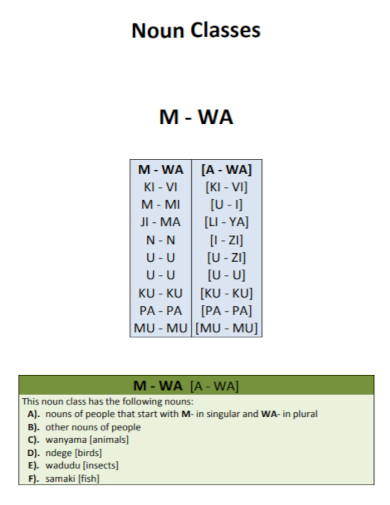
kiswahili.ku.edu
66. Noun Extraction

arxiv.org
67. Student Nouns

writing.umn.edu
68. Noun Agreement

powerscore.com
69. Noun Examples
eit.ac.nz
70. Noun Project

warwicksd.org
71. Noun Filter Table
ict.senecacollege.ca
72. Noun or Verb

repository.unikom.ac.id
73. Basic Noun in DOC

lcps.org
74. Noun Poem

parkside.herts.sch.uk
75. Expanded Noun Phrases

st-thomas-more.oxon.sch.uk
76. Common and Proper Nouns Example

nfei.org
77. English Nouns Format

ristekdikti.go.id
78. Possessive Nouns
cattlv.wnyric.org
79. Formal Nouns

little-lever.bolton.sch.uk
80. Nouns as Variables

semanticsarchive.net
81. Nouns Handout

ndu.edu.lb
82. Zombie Nouns

lsu.edu
83. Nouns, Adjectives and Verbs

thecoombes.com
84. Verb-Noun Language List
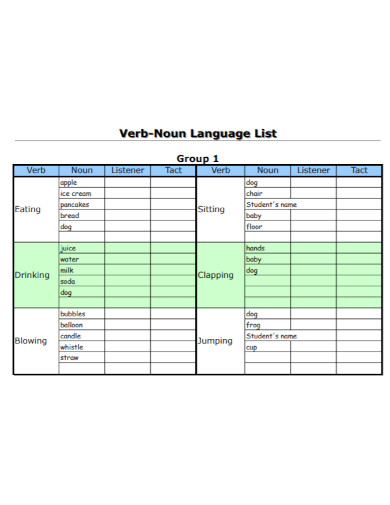
pattan.net
85. Noun Examples in PDF

english.fullerton.edu
86. Two-Way Nouns

queensu.ca
87. Simple Noun Phrases

exeterschool.co.uk
88. School English Nouns

sunfloweragra.com
89. Noun Clauses

glendale.edu
90. Nouns List

kilburnjunior.school
91. Noun Sorting
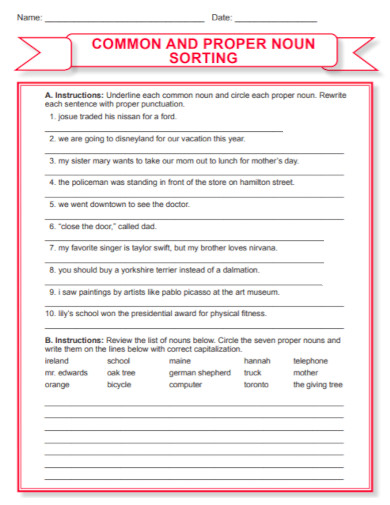
assets.ltkcontent.com
92. Noun Words
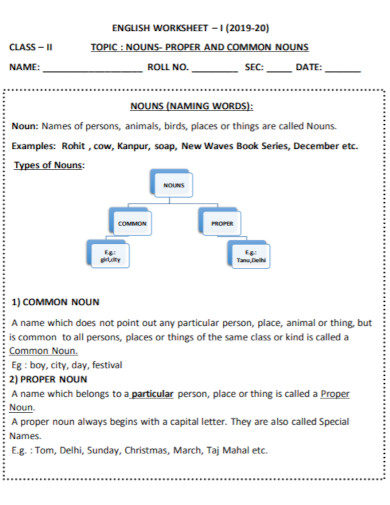
qmsmodeltown.com
93. Syntax of Noun

library.oapen.org
94. Vocabulary Nouns

hunter.cuny.edu
95. Nouns in Speech
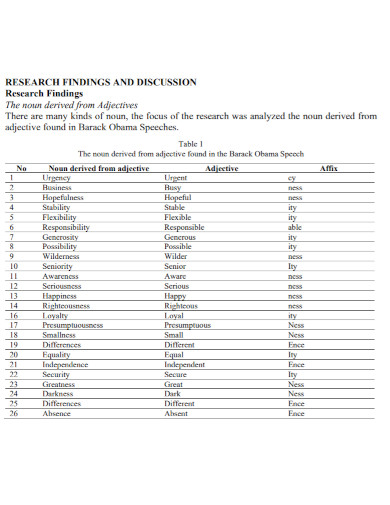
journal.undikma.ac.id
96. Nouns in DOC

boone.kyschools.us
97. Singular and Plural Nouns

mile.org
98. Noun Phrase Generator
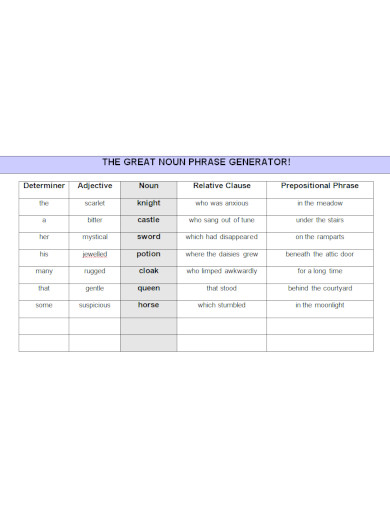
socialsciences.exeter.ac.uk
99. Noun Words in DOC

jackson.us
100. Sematic Nouns

bspu.by
101. Noun Template in DOC

blogs.glowscotland.org
Importance of Nouns
Nouns hold a fundamental place in the structure and expression of the English language, serving as the cornerstone for conveying clear and specific information. Here are key reasons highlighting their importance:
Foundation for Communication
Nouns provide the essential details in our conversations and writings, naming the key components of our messages. Without nouns, it would be challenging to specify subjects and objects in our discussions.
Convey Specificity and Detail
Through the use of nouns, speakers and writers can convey specific information, offering clarity and precision. Nouns allow for the description of concrete and abstract concepts, enabling detailed expression of thoughts and ideas.
Serve Multiple Roles in Sentences
Nouns are versatile, serving as subjects, objects, and complements within sentences. This flexibility allows for varied sentence structures, enhancing the dynamism and richness of language.
Enable Description and Identification
Nouns work in tandem with adjectives and other modifiers to provide detailed descriptions, allowing for the vivid depiction of scenes, emotions, and narratives.
Facilitate Clear Communication Across Disciplines
In academic and professional contexts, nouns are crucial for naming theories, principles, and materials, facilitating precise and unambiguous communication across various fields.
Support Language Development and Learning
Learning nouns is a foundational aspect of language acquisition, helping individuals categorize and understand the world around them. Mastery of nouns and their functions is essential for language learners at all levels.
Cultural and Conceptual Significance
Nouns also carry cultural and conceptual significance, encapsulating ideas, traditions, and beliefs specific to different languages and societies. They are pivotal in sharing and preserving cultural heritage.
What is a noun?
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. Examples: cat, city, book, happiness.
What are common nouns?
Common nouns are general names for people, places, or things. Examples: dog, city, book, teacher.
What are proper nouns?
Proper nouns are specific names for particular people, places, or things and are always capitalized. Examples: John, Paris, Monday, Nike.
What are abstract nouns?
Abstract nouns refer to intangible concepts or ideas that cannot be seen or touched. Examples: love, happiness, freedom, courage.
What are concrete nouns?
Concrete nouns are physical objects that can be perceived by the senses. Examples: apple, car, house, tree.
What are collective nouns?
Collective nouns refer to groups of people, animals, or things as a single unit. Examples: “team,” “class,” “flock.”
What are countable nouns?
Countable nouns can be counted as individual units and have singular and plural forms. Examples: “book/books,” “cat/cats,” “chair/chairs.”
What are uncountable nouns?
Uncountable nouns cannot be counted and do not have a plural form. Examples: “water,” “rice,” “music.”
What are compound nouns?
Compound nouns are formed by combining two or more words to create a single noun. Examples: “toothbrush,” “basketball,” “sunflower.”
What are possessive nouns?
Possessive nouns show ownership or possession, typically formed by adding an apostrophe and “s” or just an apostrophe for plural nouns. Examples: “child’s,” “teacher’s,” “dogs’.”


