Open Communication vs Closed Communication: Examples, PDF
Dive into the realm of communication with our guide on Open vs Closed Communication. This comprehensive piece, rich with Communication Examples, breaks down the dynamics, effectiveness, and impacts of different communication styles. Understand through real-life scenarios how open dialogue can lead to success, while closed communication might hinder progress. Enhance your understanding and skills with our insightful examples and tips, tailored for an engaging, informative read.
Download Open vs Closed Communication in Workplace
What is Open Communication vs Closed Communication? – Meaning
Open Communication refers to a transparent, two-way exchange where ideas and feedback flow freely, fostering trust and collaboration. In contrast, Closed Communication is restricted, with limited information sharing, often leading to misunderstandings and a lack of trust. Understanding the difference between Open Communication and Closed Communication is crucial for effective interaction in personal and professional settings, shaping relationships and outcomes.
Difference Between Open Communication vs Closed Communication
Open Communication fosters transparency and mutual understanding, essential for trust and problem-solving in relationships and workplaces. It emphasizes the importance of open communication in nurturing healthy interactions and the specific importance of Open Communication in Relationship, enhancing connection and clarity. Contrarily, Closed Communication often leads to misunderstandings and mistrust, lacking the Open Communication Benefits seen in more collaborative environments.
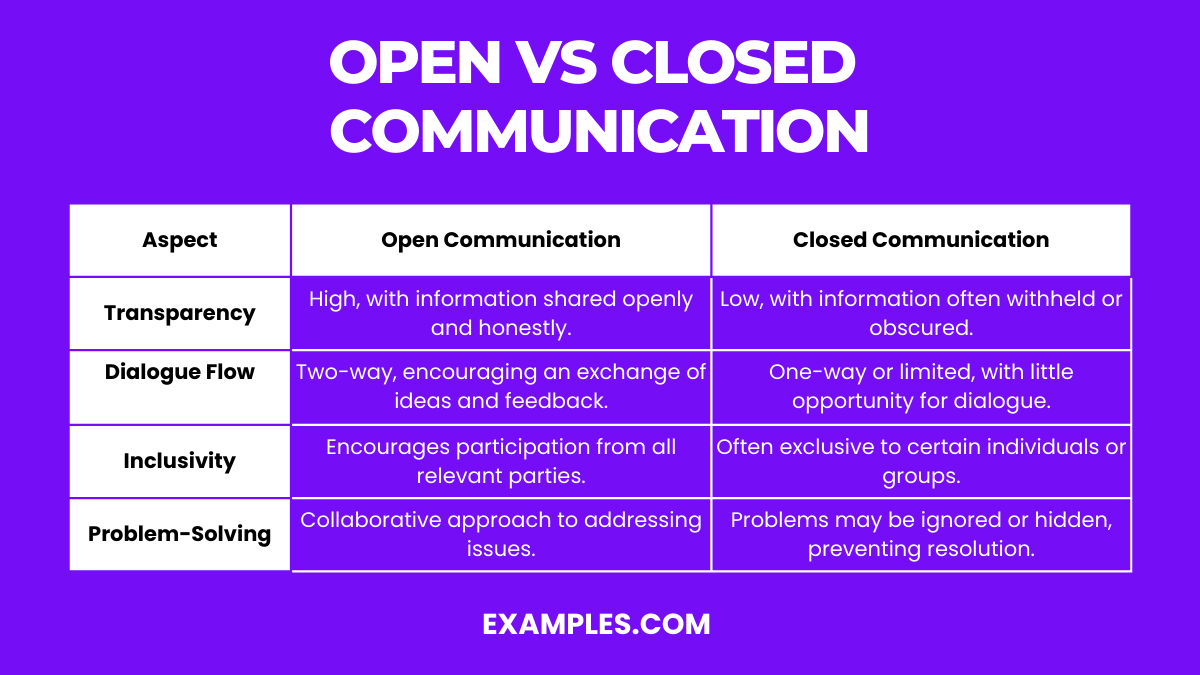
Here’s a table depicting the differences between Open Communication and Closed Communication:
| Feature | Open Communication | Closed Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | High, with information shared openly and honestly. | Low, with information often withheld or obscured. |
| Dialogue Flow | Two-way, encouraging an exchange of ideas and feedback. | One-way or limited, with little opportunity for dialogue. |
| Inclusivity | Encourages participation from all relevant parties. | Often exclusive to certain individuals or groups. |
| Problem-Solving | Collaborative approach to addressing issues. | Problems may be ignored or hidden, preventing resolution. |
| Trust | Builds and maintains trust among participants. | Can lead to mistrust and suspicion among team members. |
| Impact on Relationships | Enhances open communication in relationship, promoting understanding and collaboration. | Strains relationships, leading to misunderstandings and conflict. |
| Workplace Culture | Fosters a positive environment with open communication in the workplace. | Often leads to a negative or restrictive workplace atmosphere. |
| Benefits | Numerous, including enhanced team cohesion, creativity, and problem-solving (open communication benefits). | Limited, can lead to inefficiencies and decreased morale. |
| Importance in Personal Growth | Vital for personal development and healthy relationships (importance of open communication in relationships). | Hinders personal growth and the deepening of relationships. |
| Overall Significance | Recognized for its overall positive impact and effectiveness (importance of open communication). | Generally viewed negatively due to the barriers it creates. |
10 Open Communication Examples
Discover the power of open communication with these ten illustrative examples. This guide highlights the transformative effect of transparent, two-way dialogue in various settings, from healthcare to personal relationships. Understanding the Importance of Open Communication is crucial in fostering environments of trust, collaboration, and efficiency. Each example demonstrates the positive impact of openness and provides insights into fostering such communication effectively.
- Team Collaboration Meetings: Regular team meetings encourage sharing and problem-solving. Open Communication in the Workplace prevents misunderstandings and promotes unity.
- Patient Consultations: Doctors engaging in honest, clear conversations with patients highlight the Open Communication in Healthcare, leading to better health outcomes.
- Weekly Staff Feedback Sessions: Encourages employees to share ideas and concerns, illustrating Why is Open Communication Important in Workplace for innovation and satisfaction.
- Family Meetings: Regular discussions about plans and issues reinforce Open Communication in Family, strengthening bonds and understanding.
- Couples Therapy: Facilitates open dialogue between partners, showcasing the Importance of Open Communication in Relationships for emotional health.
- Community Forums: Public meetings for community members to voice opinions and propose solutions, demonstrating civic engagement.
- User Feedback Channels: Platforms for customers to provide product/service feedback, critical for business improvement.
- Management ‘Open Door’ Policy: Leaders making themselves available for any discussions, enhancing trust and transparency.
- Peer Review Sessions: Colleagues providing constructive feedback on work, fostering a culture of growth and learning.
- Conflict Resolution Meetings: Addressing and resolving conflicts through mediated discussions, ensuring long-term harmony and cooperation.
10 Closed Communication Examples
Explore the detrimental effects of closed communication with these ten examples, illustrating the challenges it poses in various environments. This guide emphasizes the need for Honest Communication and the consequences of its absence. Each example shows how closed communication can lead to misunderstanding, mistrust, and inefficiency, along with strategies for overcoming these barriers and moving towards an open Communication Model.
- Silent Treatment in Families: Avoiding discussions about issues leads to unresolved conflicts. Open Communication in Family can be encouraged through family counseling or mediation.
- Ignoring Employee Feedback: Disregarding employee suggestions can demotivate staff. How to Create Culture of Open Communication at Workplace involves establishing regular feedback mechanisms.
- Withholding Patient Information: Not sharing full medical details with patients can lead to poor health outcomes. Promoting Open Communication in Healthcare ensures better patient care.
- Leaders Not Sharing Vision: When leaders don’t communicate the company’s direction, it creates confusion. Open Communication in Leadership can be fostered by regular strategic updates.
- Restrictive Parenting: Not allowing children to express themselves freely can hinder their development. Open Communication with Parents involves listening and validating their feelings.
- No Public Consultation: Failing to involve the community in decision-making leads to public dissatisfaction. How to Promote Open Communication includes holding community forums and surveys.
- Dismissive Classroom Environment: Teachers ignoring or belittling student questions stifles learning. Encouraging Open Communication with Students involves creating a more interactive classroom.
- Censorship in Media: Suppressing information or news creates a misinformed public. Advocating for Open Mind Communication and freedom of the press is vital.
- Unshared Organizational Changes: Not informing employees about changes leads to rumors and fear. Adopting Open Communication Quotes and transparent change management strategies can help.
- Non-Participatory Meetings: Meetings where only a few speak and others are passive lead to disengagement. Implementing round-table discussions can ensure everyone’s voice is heard.
Comparison between Open Communication vs Closed Communication
Open Communication vs Closed Communication refers to distinct approaches in various contexts, such as parenting and healthcare. Open communication emphasizes transparency and active dialogue, allowing individuals, including children or patients, to express themselves freely. It nurtures trust and understanding. In contrast, closed communication involves limited information sharing, hindering meaningful interactions. For instance, in open communication with a child, parents encourage dialogue, while in healthcare, open communication with patients involves clear explanations and listening. Recognizing the differences between these approaches is vital for effective relationships, whether within families or in healthcare settings, promoting better understanding and decision-making. Here’s a detailed comparison:
1. Transparency:
- Open Communication: There is a high level of transparency. Information is shared freely and openly, with stakeholders having access to the information they need.
- Closed Communication: Information is often withheld or shared selectively, leading to a lack of transparency and possible mistrust among stakeholders.
2. Flow of Dialogue:
- Open Communication: Encourages two-way, multi-directional dialogue where feedback is sought, valued, and acted upon.
- Closed Communication: Typically features One-way Communication, where feedback channels are limited or non-existent, stifling dialogue.
3. Inclusivity:
- Open Communication: All relevant parties are encouraged to participate, fostering inclusivity and diverse perspectives.
- Closed Communication: Often exclusive to certain individuals or groups, leading to a narrow viewpoint and potential for groupthink.
4. Approach to Problem-Solving:
- Open Communication: Encourages collaborative problem-solving, where issues are discussed openly and solutions are developed collectively.
- Closed Communication: Problems may be ignored, hidden, or addressed in a top-down manner without input from others.
5. Trust and Relationship Building:
- Open Communication: Builds and maintains trust, leading to stronger, more resilient relationships.
- Closed Communication: Can lead to mistrust and suspicion, weakening relationships and collaboration.
6. Flexibility and Adaptation:
- Open Communication: Facilitates a more adaptive and flexible environment where changes can be discussed and implemented smoothly.
- Closed Communication: Often rigid and resistant to change, leading to a slower response to new challenges.
Relationship between Verbal vs Written Communication
Verbal and written communication are essential forms of expression, each with its unique strengths and nuances. Verbal communication, whether face-to-face or through digital means, allows for real-time interaction and immediate feedback. It’s valuable for open communication with managers and stakeholders, fostering engagement and clarity. Written communication, on the other hand, offers permanence and precision. It can be crucial in documenting agreements and ensuring transparency in open communication with stakeholders. Understanding when to use each mode is vital in navigating open communication vs direct communication scenarios, as both play distinct roles in effective interpersonal and professional relationships. The relationship between verbal and written communication can be described in five key points:
- Medium and Clarity: Verbal communication allows for immediate feedback and clarification, making it dynamic and adaptive. In contrast, written communication is static but provides a permanent record that can be referred back to for clarity and proof.
- Tone and Nuance: Verbal communication carries tone, pace, and emotion, making it rich in nuances. Written communication relies on word choice and punctuation to convey tone, which can sometimes lead to misunderstandings if not crafted carefully.
- Formality and Structure: Written communication often follows a more formal structure and is used in professional or official capacities. Verbal communication can be more informal and spontaneous, suitable for immediate or personal interactions.
- Speed and Revision: Verbal communication is instantaneous, whereas written communication can be drafted, revised, and edited before sending, allowing for more thought and organization.
- Accessibility and Reach: Verbal communication requires the presence or real-time connection of parties, limiting its reach. Written communication can be distributed to a wider audience and is accessible over time and distance. Both forms complement each other and are used interchangeably depending on the context and requirement.
In Conclusion, the choice between open communication vs. closed communication can significantly impact relationships and outcomes. As seen through examples and their effects, open communication with students and colleagues enhances trust and collaboration. Recognizing signs of ineffective communication is crucial. To improve, prioritize transparency, active listening, and adaptability. By fostering open communication, individuals and organizations can cultivate stronger connections and achieve more positive results.