20+ Paragraph Examples
A paragraph is a fundamental unit of writing that focuses on a single idea or topic. It typically consists of a topic sentence, supporting sentences, and a concluding sentence. The topic sentence introduces the main idea, while the supporting sentences provide details, examples, or explanations. The concluding sentence summarizes the main point or transitions to the next paragraph. Effective paragraphs enhance the clarity and coherence of writing, making it easier for readers to understand and engage with the content. Whether in essays, articles, or reports, well-structured paragraphs are essential for effective communication.
Check Out Free Paragraph Writer Tool
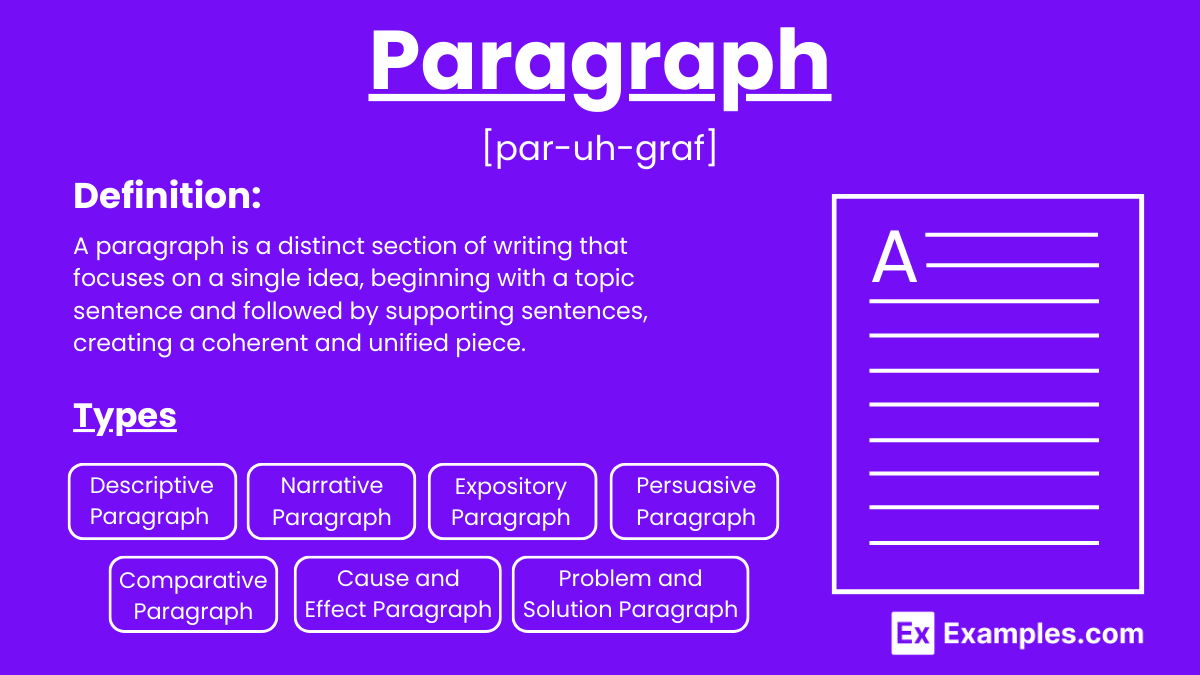
What Is a Paragraph?
A paragraph is a distinct section of writing that deals with a specific point or idea, typically consisting of several sentences. It begins with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea, followed by supporting sentences that develop this idea through details, examples, and explanations. A concluding sentence may be included to summarize the main point or provide a transition to the next paragraph. Paragraphs help organize writing, making it easier to read and understand by breaking the text into manageable sections.
Paragraph Format
1. Topic Sentence
Start with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph. It tells the reader what the paragraph will be about.
Example: “Regular exercise is essential for maintaining good health.”
2. Supporting Sentences
Add 3-5 sentences that provide details, examples, or explanations supporting the main idea. These sentences should connect logically and build on the topic sentence.
Example: “Exercise helps control weight, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and improve mental health. Physical activities like walking, running, and swimming increase cardiovascular fitness. Regular exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. It also helps improve sleep quality and boosts energy levels.”
3. Transitions
Use transition words to connect your sentences and make the paragraph flow smoothly. Examples of transition words include “furthermore,” “in addition,” “moreover,” “however,” and “therefore.”
Example: “Moreover, regular exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters.”
4. Concluding Sentence
Finish with a concluding sentence that wraps up the main idea and reinforces what you’ve discussed.
Example: “Therefore, incorporating regular exercise into your daily routine is vital for a healthy and balanced life.”
Example of a Well-Formatted Paragraph
Regular exercise is essential for maintaining good health. Exercise helps control weight, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and improve mental health. Physical activities like walking, running, and swimming increase cardiovascular fitness. Moreover, regular exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. Additionally, it helps improve sleep quality and boosts energy levels. Therefore, incorporating regular exercise into your daily routine is vital for a healthy and balanced life.
What is the Best Example of Paragraph

The Importance of Reading
Reading is a fundamental skill that significantly impacts personal and academic growth. It enhances vocabulary, improves comprehension, and fosters critical thinking. When individuals read regularly, they are exposed to new ideas and perspectives, which broadens their understanding of the world. Additionally, reading stimulates the brain, keeping it active and engaged, which can help prevent cognitive decline. It also provides a means of relaxation and stress reduction, as immersing oneself in a good book can be a soothing escape from daily pressures. Therefore, cultivating a habit of reading not only contributes to intellectual development but also promotes overall well-being.
Paragraph Examples
Example 1: Benefits of Regular Exercise
Regular exercise offers numerous benefits, both physically and mentally. Engaging in physical activities like jogging, swimming, or cycling helps improve cardiovascular health, strengthen muscles, and enhance flexibility. Exercise also plays a crucial role in weight management and reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypertension. Moreover, regular physical activity is known to boost mental health by alleviating symptoms of depression and anxiety, promoting better sleep, and enhancing overall mood. By making exercise a part of your daily routine, you can significantly improve your quality of life and longevity.
Example 2: Importance of Time Management
Effective time management is essential for achieving success and maintaining a balanced life. By prioritizing tasks and setting clear goals, individuals can maximize productivity and reduce stress. Time management involves creating schedules, setting deadlines, and avoiding procrastination. It also requires the ability to delegate tasks when necessary and to focus on one task at a time. Proper time management not only helps in completing tasks efficiently but also allows for more free time to relax and pursue personal interests. Developing good time management skills is key to achieving both professional and personal goals.
Example 3: The Impact of Social Media on Society
Social media has revolutionized the way we communicate and interact with one another. Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have made it easier to stay connected with friends and family, share information, and express opinions. However, social media also has its downsides. It can lead to issues such as cyberbullying, privacy concerns, and the spread of misinformation. Additionally, excessive use of social media can contribute to mental health problems like anxiety and depression. It is important for users to be mindful of their social media habits and strive for a healthy balance between online and offline interactions.
Example 4: The Importance of Environmental Conservation
Environmental conservation is crucial for the health and sustainability of our planet. Protecting natural habitats, preserving biodiversity, and reducing pollution are essential steps in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Conservation efforts help ensure clean air and water, fertile soil, and a stable climate. Individuals can contribute to environmental conservation by adopting eco-friendly practices such as recycling, reducing energy consumption, and supporting sustainable products. Governments and organizations also play a vital role by implementing policies and initiatives aimed at protecting the environment. By working together, we can safeguard our planet for future generations.
Example 5: The Role of Technology in Education
Technology has transformed the field of education, making learning more accessible and engaging. Online courses, interactive learning platforms, and educational apps provide students with a wealth of resources at their fingertips. Technology enables personalized learning, allowing students to learn at their own pace and according to their individual needs. It also facilitates collaboration and communication among students and teachers, enhancing the overall learning experience. However, it is important to use technology responsibly and ensure that it complements traditional teaching methods. By integrating technology effectively, we can create a more dynamic and inclusive educational environment.
Short Paragraph Examples
Paragraph on Value of Time
Time is an invaluable resource, one that we cannot reclaim once it’s lost. Every moment holds the potential for growth, learning, and creating meaningful experiences. Time management enables us to maximize our productivity and achieve our goals efficiently. By valuing time, we make conscious decisions about how we spend it, prioritizing tasks that align with our long-term aspirations. Understanding the worth of time fosters discipline, reduces stress, and enhances our overall well-being. In essence, appreciating time empowers us to live a more purposeful and fulfilling life.
- paragraph on internet
- paragraph on drug addiction
- paragraph on climate change
- paragraph on food adulteration
- paragraph on air pollution
- paragraph on environment
- paragraph on save water
- paragraph on water
- paragraph on books are our best friends
- paragraph on nature
- paragraph on hard work
- paragraph on health
- paragraph on games and sports
- paragraph on technology
- paragraph on social media
- paragraph on success
- paragraph on work is worship
- paragraph on disaster management
- paragraph on laughter is the best medicine
- paragraph on noise pollution
- paragraph on kindness
- paragraph on rainwater harvesting
- paragraph on desert
Paragraph Examples for Students
- paragraph on discipline
- paragraph on my aim in life
- paragraph on importance of education
- paragraph on early rising
- paragraph on daily routine
- paragraph on morning walk
- paragraph on newspaper
- paragraph on if i were a bird
- paragraph about football
- paragraph on a visit to a zoo
- paragraph on a visit to a hill station
- paragraph on grandparents
- paragraph on morning assembly in my school
- paragraph on a house on fire
Paragraph Examples for Middle School
- paragraph on my favourite teacher
- paragraph on winter morning
- paragraph on my place
- paragraph on my house
- paragraph on summer vacation
- paragraph on christmas
- paragraph on an ideal student
- paragraph writing on covid 19
- paragraph on mother teresa
- paragraph on elephant
- paragraph on computer
- paragraph on flood
- paragraph on gandhi jayanti
- paragraph on festival
- paragraph on doctor
- paragraph on solar system
- paragraph on red fort
- paragraph on earth day
- paragraph on plants
- paragraph on sikkim
- paragraph on unsung heroes of freedom struggle
- paragraph on tsunami
Paragraph Examples for High School
- paragraph on mobile phone
- paragraph on artificial intelligence
- paragraph on early to bed
- paragraph on our national flag
- paragraph on road accident
- paragraph on online classes
- paragraph on lion
- paragraph on forest
- paragraph on earth
Paragraph Examples for Kids
- paragraph on my mother
- paragraph on my sister
- paragraph on my father
- paragraph on my brother
- paragraph on myself
- paragraph on my school
- paragraph on my grandmother
- paragraph on parrot
- paragraph on badminton
Paragraph Examples for 2nd Grade
- paragraph on raksha bandhan
- paragraph on janmashtami
- Paragraph on My Pet
- Paragraph on My Best Friend
- Paragraph on My Favorite Toy
Paragraph Examples for 3rd Grade
- paragraph on my family
- paragraph on my hobby
- Paragraph on My Favorite Game
- Paragraph on A Trip to the Park
Paragraph Examples for 4th Grade
Paragraph Examples for 5th Grade
Paragraph Examples for Grade 6
Paragraph Examples for Grade 7
Paragraph Examples for Grade 8
- paragraph on desert
- Paragraph on A Historical Figure I Admire
- Paragraph on The Impact of Technology on Education
Paragraph Examples for Grade 9
- paragraph on disaster management
- Paragraph on The Role of Social Media in Our Lives
- Paragraph on The Benefits of Reading
Paragraph Examples for Grade 10
- paragraph on save water
- Paragraph on The Importance of Healthy Eating
- Paragraph on The Effects of Global Warming
Paragraph Examples for Grade 11
- paragraph on laughter is the best medicine
- Paragraph on The Influence of Music on Culture
- Paragraph on The Benefits of Learning a Second Language
Paragraph Examples for Grade 12
Paragraph Examples College Students
Narrative Paragraph Examples
- happy birthday paragraph
- paragraph for her
- paragraph for him
- Paragraph Transitions
Types of Paragraphs
Understanding the different types of paragraphs can help enhance your writing by using the most effective structure for each part of your text. Here are the main types of paragraphs:
1. Descriptive Paragraph
A descriptive paragraph paints a vivid picture of a person, place, thing, or idea using detailed observations and sensory descriptions. It focuses on creating an immersive experience for the reader, helping them visualize and experience the subject through words.
2. Narrative Paragraph
A narrative paragraph tells a story or recounts events in a chronological order. It includes characters, a setting, and a plot, guiding the reader through the sequence of events. This type of paragraph aims to engage and entertain the reader with a clear storyline.
3. Expository Paragraph
An expository paragraph aims to explain, inform, or clarify a topic. It presents facts, definitions, and explanations in a logical and straightforward manner. The goal is to provide the reader with a clear understanding of the subject, using evidence and examples to support the information.
4. Persuasive Paragraph
A persuasive paragraph seeks to convince the reader of a particular viewpoint or argument. It presents reasons, evidence, and examples to support the writer’s position. The goal is to persuade the reader to agree with the writer’s perspective through logical reasoning and emotional appeal.
5. Comparative Paragraph
A comparative paragraph compares and contrasts two or more items, ideas, or concepts. It highlights similarities and differences, helping the reader understand the relative characteristics of each subject. This type of paragraph often uses transitional words to clearly indicate comparisons and contrasts.
6. Cause and Effect Paragraph
A cause and effect paragraph explains the reasons why something happened (cause) and the results that followed (effect). It analyzes the relationship between events, helping the reader understand the sequence and consequences. This type of paragraph often explores multiple causes and their effects.
7. Problem and Solution Paragraph
A problem and solution paragraph identifies a specific problem and proposes one or more solutions. It describes the issue in detail, explains its significance, and then offers practical and feasible solutions. The goal is to address the problem effectively and persuade the reader of the proposed solutions’ viability.
5-Paragraph Essay Template
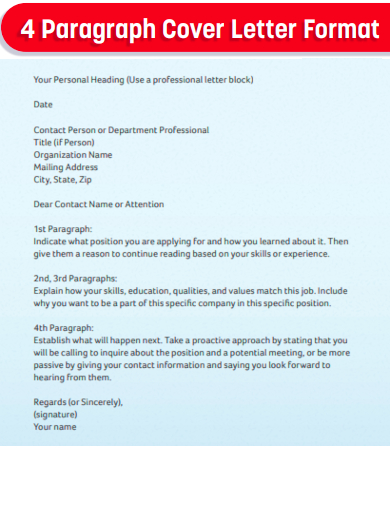
4 Paragraph Cover Letter Format
csueastbay.edu
Introduction Paragraph Format

towson.edu
Basic Paragraph Format

mtroyal.ca
Organization Paragraph Format

canadacollege.edu
Paragraph and Page Formatting

dcf.wisconsin.gov
Essay and Paragraph Format

uvu.edu
Paragraph & Line Spacing Format

grad.mst.edu
Body Paragraph Structure and Development

ivcc.edu
Chunked Paragraph Format

lcps.org
Dos and Don’ts of Paragraph
Paragraph is crucial for clear and impactful communication. A well-structured paragraph helps convey your ideas logically and keeps the reader engaged. Here are some key dos and don’ts to keep in mind when crafting a paragraph.
| Dos | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| 1. Start with a clear topic sentence. Introduce the main idea of the paragraph clearly and concisely. | 1. Don’t introduce multiple ideas. Stick to one main idea per paragraph to maintain focus. |
| 2. Use supporting details and examples. Include relevant facts, examples, and explanations to support your main idea. | 2. Don’t include irrelevant information. Ensure all details are directly related to the main idea. |
| 3. Maintain logical coherence. Ensure sentences flow logically from one to the next. | 3. Don’t make the paragraph too long. Keep it concise to enhance readability. |
| 4. Use transitional words for flow. Use words like “furthermore,” “however,” and “therefore” to connect ideas smoothly. | 4. Don’t neglect proofreading. Always check for grammatical, spelling, and punctuation errors. |
| 5. Keep sentences concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary words and overly complex sentences. | 5. Don’t use clichés or jargon. Avoid overused phrases and confusing technical terms. |
| 6. Maintain a logical structure. Organize sentences in a clear, logical order that supports the main idea. | 6. Don’t overuse passive voice. Prefer active voice to make your writing more engaging. |
| 7. Vary sentence length. Use a mix of short and long sentences to keep the reader engaged. | 7. Don’t repeat ideas unnecessarily. Avoid redundancy by not repeating the same ideas. |
| 8. Ensure consistency in tense and tone. Maintain the same tense and tone throughout the paragraph. | 8. Don’t use inconsistent tense. Stick to the same tense to avoid confusing the reader. |
| 9. Provide evidence and examples. Use statistics, quotes, or examples to support your points. | 9. Don’t rely on unsupported opinions. Base your points on facts and evidence, not just personal opinions. |
| 10. Conclude with a reinforcing sentence. End with a sentence that reinforces the main idea or provides a transition to the next paragraph. | 10. Don’t leave sentences incomplete. Ensure each sentence is complete and contributes to the paragraph’s purpose. |
How to Format/Write a Perfect Paragraph?
Before diving into the depths of paragraph formatting, it’s essential to recognize that the specific requirements may vary depending on the intended format of your writing. Whether you’re composing an email, working on a book, designing an outline format, or crafting a one-pager, understanding the purpose and context of your writing will guide your paragraph formatting decisions.
Step 1: Determine the Context:
Before delving into paragraph formatting, understand the context and purpose of your writing. Consider whether you’re writing an email, a book, an outline format, a one-pager, or an informative essay outline. Each format may have specific formatting requirements.
Step 2: Indentation:
Indentation plays a crucial role in paragraph formatting. For most formats, including books and essays, indent the first line of each paragraph. This indentation visually separates paragraphs and aids in readability. Use the tab key or the ruler in your word processing software to apply consistent indentation.
Step 3: Alignment
Ensure your paragraphs are aligned consistently throughout your writing. The most common alignment is left-aligned, where the left margin of each line is straight. Avoid center-aligning or right-aligning paragraphs unless the format specifically calls for it.
Step 4: Spacing
Consider the spacing between paragraphs to enhance readability. In some formats, such as emails or one-pagers, it’s beneficial to include blank lines or line breaks between paragraphs to create visual separation. However, in other formats like books or essays, single spacing without additional blank lines is typically preferred.
Step 5: Coherence and Unity
Maintain coherence and unity within each paragraph. A well-formatted paragraph should contain a clear topic sentence or main idea, followed by supporting sentences that expand on the main idea. Ensure there is a logical flow between sentences, guiding readers through your thoughts smoothly.
Step 6: Length and Consistency
Keep your paragraphs concise and focused. Long paragraphs can be overwhelming for readers, while short paragraphs can disrupt the flow of ideas. Aim for a balanced length and strive for consistency throughout your writing.
Is a paragraph 3 or 5 sentences?
A paragraph typically consists of 3 to 5 sentences. This range allows for a clear and concise expression of ideas, ensuring that each paragraph contains a complete thought or topic. While some paragraphs may extend beyond five sentences, especially in more complex writing, 3 to 5 sentences is a standard guideline.
How long is a paragraph?
A paragraph usually ranges from 100 to 200 words. This length allows for sufficient development of ideas while maintaining readability. Longer paragraphs may be appropriate in academic or detailed writing, but in general, keeping paragraphs within this word range ensures that the text remains accessible and engaging for readers.
Can a paragraph be 300 words?
Yes, a paragraph can be 300 words if it is well-structured and coherent. Longer paragraphs are often found in academic or technical writing where detailed explanations are necessary. However, for most writing, shorter paragraphs are preferred as they are easier to read and help maintain the reader’s interest and engagement.
Is a 150-word paragraph too short?
No, a 150-word paragraph is not too short; it is within the typical length range. Concise paragraphs can be very effective in conveying clear and focused ideas. In fact, shorter paragraphs are often used in digital content and journalism to enhance readability and ensure that key points are communicated efficiently.
In conclusion, maintaining a well-organized approach to tasks enhances productivity and efficiency. By prioritizing activities and managing time effectively, individuals can achieve their goals more successfully. Developing a disciplined routine fosters personal growth, reduces stress, and ensures steady progress in both professional and personal endeavors, leading to overall satisfaction and fulfillment.