70+ Participle Examples
A participle is a form of a verb that typically ends in -ing (present participle) or -ed, -d, -t, -en, or -n (past participle) and functions as an adjective or to form verb tenses. Present participles describe ongoing actions, while past participles often indicate completed actions. For example, in the sentences “The running water is cold” and “The broken vase was on the floor,” “running” and “broken” are participles modifying the nouns “water” and “vase,” respectively.
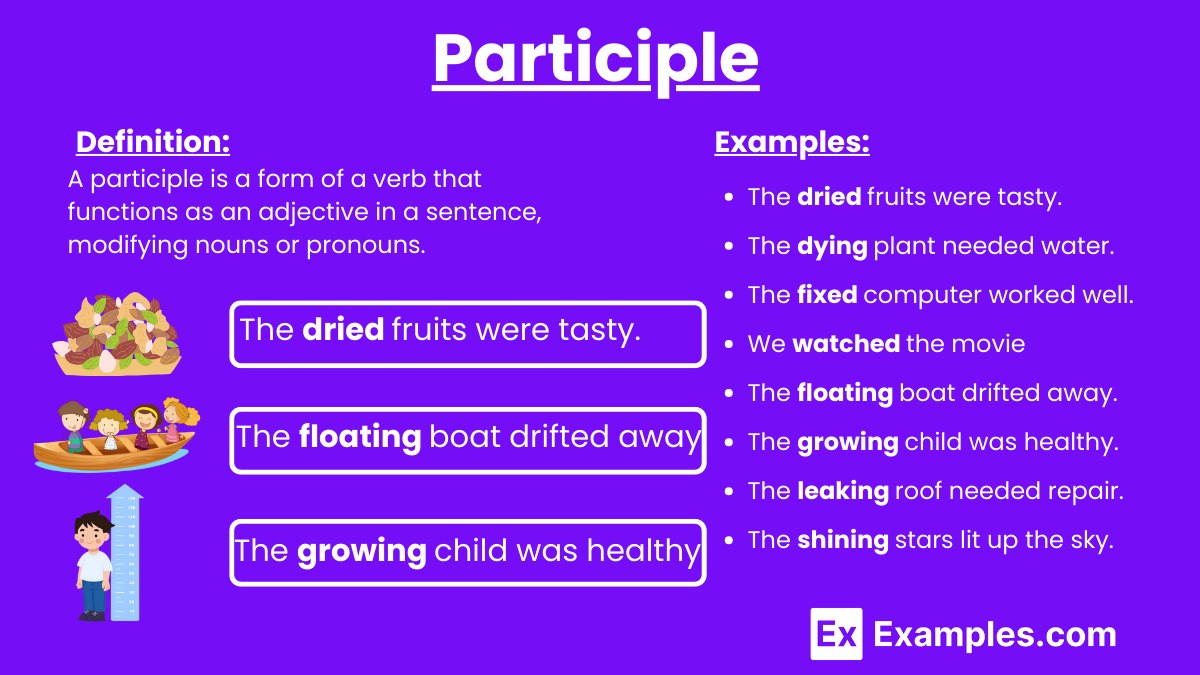
What is a Participle?
A participle is a form of a verb that functions as an adjective in a sentence, modifying nouns or pronouns. There are two types of participles: present participles, which end in “-ing” (e.g., “running”), and past participles, which typically end in “-ed” or “-en” (e.g., “baked,” “broken”). Participles can also be part of verb phrases, contributing to the formation of various tenses and aspects.
Examples of Participle
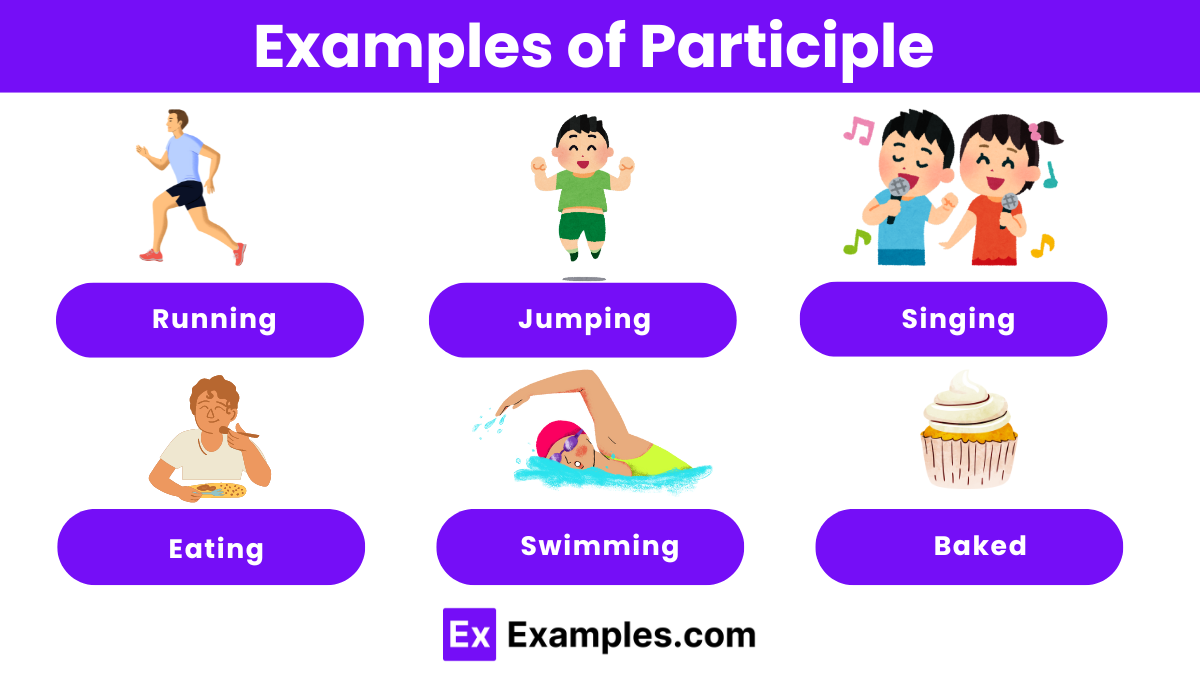
- Running
- Jumping
- Singing
- Eating
- Swimming
- Baked
- Broken
- Chosen
- Fallen
- Written
- Dancing
- Laughing
- Painted
- Taught
- Driven
- Played
- Opened
- Closed
- Cooked
- Forgotten
- Hiding
- Studying
- Shining
- Melted
- Painted
- Shattered
- Written
- Frozen
- Watched
- Prepared
Examples of Participles in Sentences
- The blooming flowers were lovely.
- The burned toast was inedible.
- The crying baby was comforted.
- The defeated team was disheartened.
- The decorated room looked festive.
- The demanding boss was intimidating.
- The destroyed building was a landmark.
- The dried fruits were tasty.
- The dripping faucet was annoying.
- The dying plant needed water.
- The excited crowd cheered loudly.
- The exhausted runner collapsed.
- The fading light signaled evening.
- The fascinated audience listened intently.
- The fixed computer worked well.
- The floating boat drifted away.
- The flying kite soared high.
- The frightened cat hid under the bed.
- The frozen pond was slippery.
- The giggling girls shared secrets.
- The growing child was healthy.
- The heated debate was intense.
- The hidden treasure was found.
- The improved design was efficient.
- The inspired artist painted furiously.
- The leaking roof needed repair.
- The loaded truck left the warehouse.
- The melting snow created puddles.
- The painted fence looked new.
- The shining stars lit up the sky.
Examples of Present Participles
| Present Participles | Present Participles |
|---|---|
| Whispering | Skipping |
| Shouting | Twinkling |
| Climbing | Exploring |
| Smiling | Fishing |
| Crying | Gathering |
| Blinking | Hanging |
| Sneezing | Ignoring |
| Running | Joking |
| Skipping | Knitting |
| Twinkling | Laughing |
| Exploring | Mixing |
| Fishing | Nodding |
| Gathering | Walking |
| Hanging | Talking |
| Ignoring | Playing |
| Joking | Cooking |
Examples of Past Participles
| Past Participles | Past Participles |
|---|---|
| Baked | Frozen |
| Broken | Sung |
| Chosen | Shown |
| Fallen | Written |
| Painted | Taken |
| Driven | Given |
| Played | Eaten |
| Opened | Known |
| Closed | Built |
| Cooked | Seen |
| Forgotten | Run |
| Taught | Grown |
| Watched | Flown |
| Prepared | Thrown |
| Melted | Spoken |
| Shattered | Shaken |
Examples of Perfect Participles
| Perfect Participles | Perfect Participles |
|---|---|
| Having eaten | Having studied |
| Having walked | Having finished |
| Having written | Having driven |
| Having played | Having chosen |
| Having cooked | Having laughed |
| Having spoken | Having broken |
| Having danced | Having opened |
| Having watched | Having seen |
| Having slept | Having known |
| Having sung | Having read |
| Having taught | Having painted |
| Having grown | Having waited |
| Having built | Having decided |
| Having run | Having traveled |
| Having jumped | Having worked |
| Having swum | Having explored |
Examples of Adjective Participles
| Adjective Participles | Adjective Participles |
|---|---|
| Boring | Excited |
| Tiring | Amused |
| Confusing | Frightened |
| Annoying | Terrified |
| Frustrating | Interested |
| Exhausting | Thrilled |
| Disappointing | Amazed |
| Surprising | Delighted |
| Shocking | Relieved |
| Embarrassing | Fascinated |
| Satisfying | Satisfied |
| Entertaining | Worried |
| Thrilling | Relaxed |
| Confused | Overwhelmed |
| Annoyed | Shocked |
| Frustrated | Embarrassed |
Types of Participles
| Participle Type | Formation | Example | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Present Participle | Base verb + “-ing” | Running | Describes ongoing actions |
| Past Participle | Base verb + “-ed” (regular) or unique form (irregular) | Walked, Written | Used in perfect tenses, passive voice, as adjectives |
| Perfect Participle | “Having” + past participle | Having walked | Indicates completed actions before another action |
Participles are verb forms that function as adjectives or parts of verb tenses. There are three main types of participles: present participles, past participles, and perfect participles.
Present Participles
Present participles are formed by adding -ing to the base form of a verb. They describe ongoing actions or states.
Examples:
The running water was refreshing.
She saw him writing a letter.
Past Participles
Past participles are typically formed by adding -ed to the base form of regular verbs, though irregular verbs have unique forms. They describe completed actions or states.
Examples:
The broken vase lay on the floor.
They have finished the project.
Perfect Participles
Perfect participles are formed by combining having with the past participle of a verb. They describe actions that were completed before another action.
Examples:
Having finished the homework, he went to bed.
Having eaten, they felt satisfied.
Uses of Participle
Participles are versatile verb forms that can function in various roles within sentences. They can act as adjectives, form verb tenses, and create participial phrases. Here are the primary uses of participles:
1. As Adjectives
Participles can modify nouns and pronouns, describing characteristics or states. Using participles as adjectives adds descriptive detail to your writing, making it more vivid and engaging.
Example: The barking dog woke up the neighborhood. (Present participle)
2. Forming Continuous Tenses
Present participles are used with auxiliary verbs to form continuous tenses, indicating ongoing actions. Continuous tenses are useful for expressing actions that are in progress at a specific time or for describing repeated actions.
Example: She is running in the marathon. (Present continuous)
3. Forming Perfect Tenses
Past participles are used with auxiliary verbs to form perfect tenses, indicating completed actions. Perfect tenses are useful for showing that an action was completed before another action or time.
Example: She has finished her homework. (Present perfect)
4. Forming Passive Voice
Past participles are used with auxiliary verbs to form the passive voice, indicating that the subject is acted upon. Passive voice can be useful for emphasizing the action or the recipient of the action rather than the doer.
Example: The book was written by a famous author. (Past simple passive)
5. Participial Phrases
Participial phrases provide additional information about a noun or pronoun, often adding detail or background to the main clause. Participial phrases can make your writing more dynamic and detailed.
Example: Running down the street, she waved at her friend.
6. As Gerunds (Verbals)
Present participles can also function as gerunds, acting as nouns in sentences. Gerunds can be the subject, object, or complement of a sentence, adding variety to sentence structures.
Example: Swimming is my favorite sport
FAQ’s
How is a present participle formed?
A present participle is formed by adding -ing to the base form of a verb.
How is a past participle formed?
A past participle is usually formed by adding -ed to regular verbs, though irregular verbs vary.
What is the function of a present participle?
Present participles describe ongoing actions or states and can act as adjectives or form continuous tenses.
What is the function of a past participle?
Past participles describe completed actions or states and are used in perfect tenses and passive voice.
Can participles act as adjectives?
Yes, participles can modify nouns or pronouns, providing descriptive detail.
How are participles used in continuous tenses?
Present participles are used with auxiliary verbs to form continuous tenses, indicating ongoing actions.
How are participles used in perfect tenses?
Past participles are used with auxiliary verbs to form perfect tenses, indicating completed actions.
How are participles used in passive voice?
Past participles are used with auxiliary verbs to form passive voice, indicating the subject is acted upon.
What is the difference between a gerund and a present participle?
A gerund functions as a noun, while a present participle functions as an adjective or forms continuous tenses.
Can participles be used in all tenses?
Yes, present and past participles can be used to form various tenses, including continuous and perfect tenses.