Parts of Speech – Definition, Types, Examples
Parts of speech refer to the categories into which words are grouped based on their function within a sentence. English language primarily consists of eight parts of speech: nouns, which name things; pronouns, which stand in place of nouns; verbs, which express actions or states of being; adjectives, which describe nouns; adverb, which modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs; prepositions, which link words and show relationships; conjunction, which connect clauses or sentences; and interjections, which express strong emotions or reactions. Each part of speech plays a crucial role in sentence structure and meaning, contributing to the clarity and effectiveness of communication.
Download Examples of Parts of Speech
What is Parts of Speech?
Parts of speech are categories that help organize words based on their roles in sentences. There are eight main types: nouns (names of things), verbs (action or being words), adjectives (describe nouns), adverbs (modify verbs or adjectives), pronouns (replace nouns), prepositions (show relationships between words), conjunctions (connect words or phrases), and interjections (short exclamations). Understanding these helps you form clear and effective sentences, making communication easier.
Types of Parts of Speech
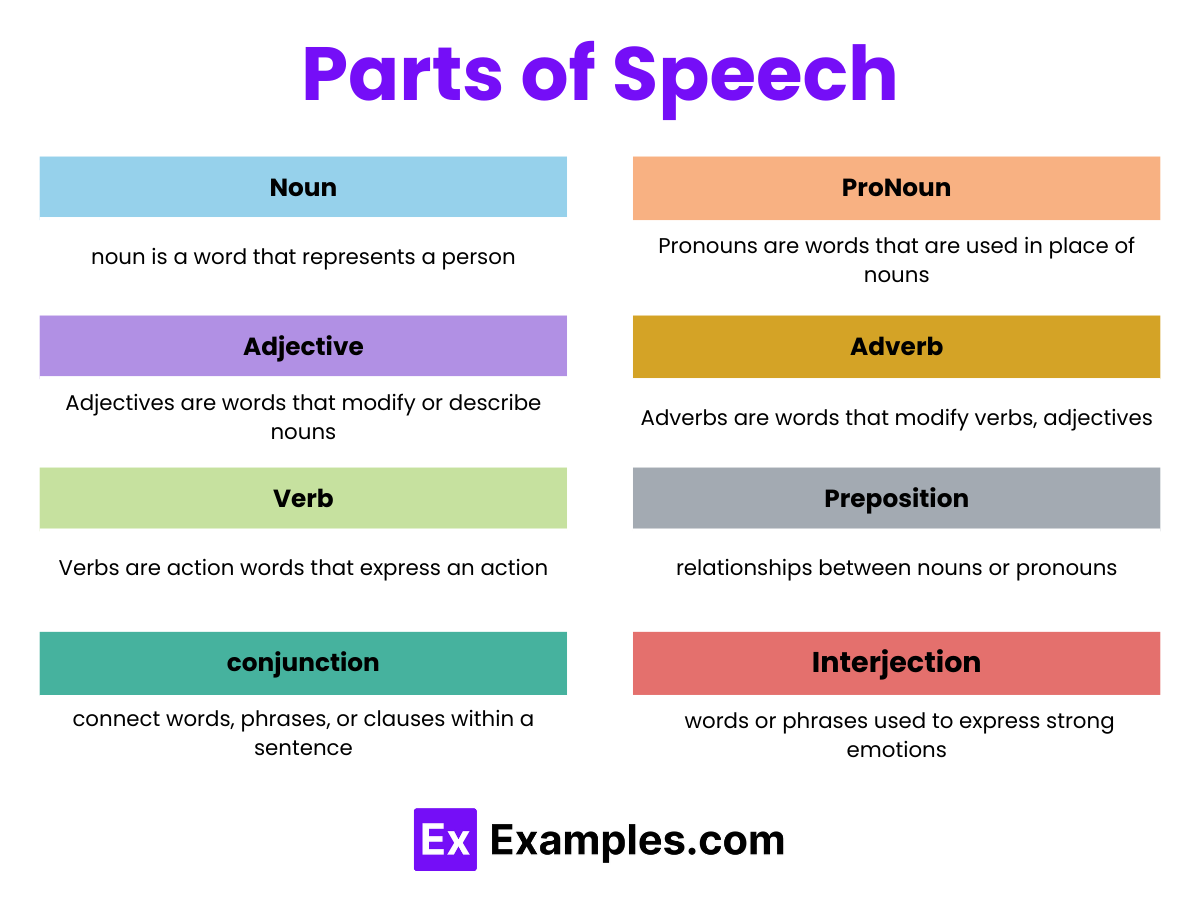
The English language includes several types of parts of speech, each serving a specific function in sentence construction:
Nouns
A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. It can be a concrete object that we can see, touch, or feel, such as “book,” “tree,” or “dog.” Alternatively, it can represent abstract concepts, emotions, or qualities, like “love,” “happiness,” or “intelligence.” Examples of Nouns in Sentences:
- The cat sat on the windowsill.
- We visited New York City last summer.
- His honesty is admirable.
- She bought a beautiful dress for the party.
- They drank cold water after the game.
- Integrity is essential in leadership roles.
Pronouns
Pronouns are words that are used in place of nouns to avoid repetition and make sentences clearer and more concise. They can refer to people, places, things, or ideas mentioned earlier in the discourse. Examples of Pronouns in Sentences:
- Personal Pronouns: She is going to the store.
- Possessive Pronouns: The coat is mine.
- Demonstrative Pronouns: This is my favorite book.
- Relative Pronouns: The person who called left a message.
- Interrogative Pronouns: What is your name?
- Indefinite Pronouns: Everybody enjoyed the party.
Verbs
Verbs are action words that express an action, occurrence, or state of being within a sentence. They are essential for conveying actions, events, or conditions and are conjugated to indicate tense, mood, voice, and agreement with the subject.Examples of Verbs in Sentences:
- Action Verbs: She dances gracefully.
- Linking Verbs: The flowers are beautiful.
- Auxiliary Verbs: He has finished his homework.
Adjectives
Adjectives are words that modify or describe nouns or pronouns by providing additional information about their qualities, characteristics, or attributes. They add detail and specificity to nouns and help create vivid imagery in writing. Examples of Adjectives in Sentences:
- Descriptive Adjectives: The blue sky looked beautiful.
- Demonstrative Adjectives: That book is mine.
- Possessive Adjectives: Her cat is very playful.
- Quantitative Adjectives: There are many books on the shelf.
- Interrogative Adjectives: Whose bag is this?
Adverbs
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing additional information about time, place, manner, frequency, degree, or certainty. They enhance the meaning of a sentence by answering questions such as “how,” “when,” “where,” “why,” “to what extent,” or “under what conditions.”Examples of Adverbs in Sentences:
- Adverbs of Time: They will arrive soon.
- Adverbs of Place: The cat is sleeping there.
- Adverbs of Manner: She sings beautifully.
- Adverbs of Frequency: He always arrives early.
- Adverbs of Degree: She is very talented.
Prepositions
Prepositions are words that establish relationships between nouns or pronouns and other words in a sentence, indicating direction, location, time, or manner. They often come before a noun or pronoun and form phrases known as prepositional phrases.Examples of Prepositions in Sentences:
- He is sitting on the chair.
- The book is under the table.
- She walked to the store.
- They went for a walk in the park.
- The cat jumped off the bed.
- We traveled across the country.
Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses within a sentence, allowing for smooth transitions and logical relationships between different parts of the sentence. They help coordinate ideas, express contrast, or show cause and effect. Examples of Conjunctions in Sentences:
- Coordinating Conjunctions: She likes tea and coffee.
- Subordinating Conjunctions: He left early because he was tired.
- Correlative Conjunctions: You can have either cake or ice cream.
- She will go to the party if she finishes her work.
- He didn’t study, so he failed the exam.
- We can go for a walk unless it rains.
Interjections
Interjections are words or phrases used to express strong emotions, feelings, or reactions. They often stand alone and are punctuated with an exclamation mark to convey excitement, surprise, joy, frustration, or other sentiments. Examples of Interjections:
- Wow! That was an amazing performance!
- Ouch! That hurt!
- Yay! We won the game!
- Oops! I dropped my phone.
- Oh no! I forgot my keys.
- Bravo! Well done!
Examples of Parts of Speech
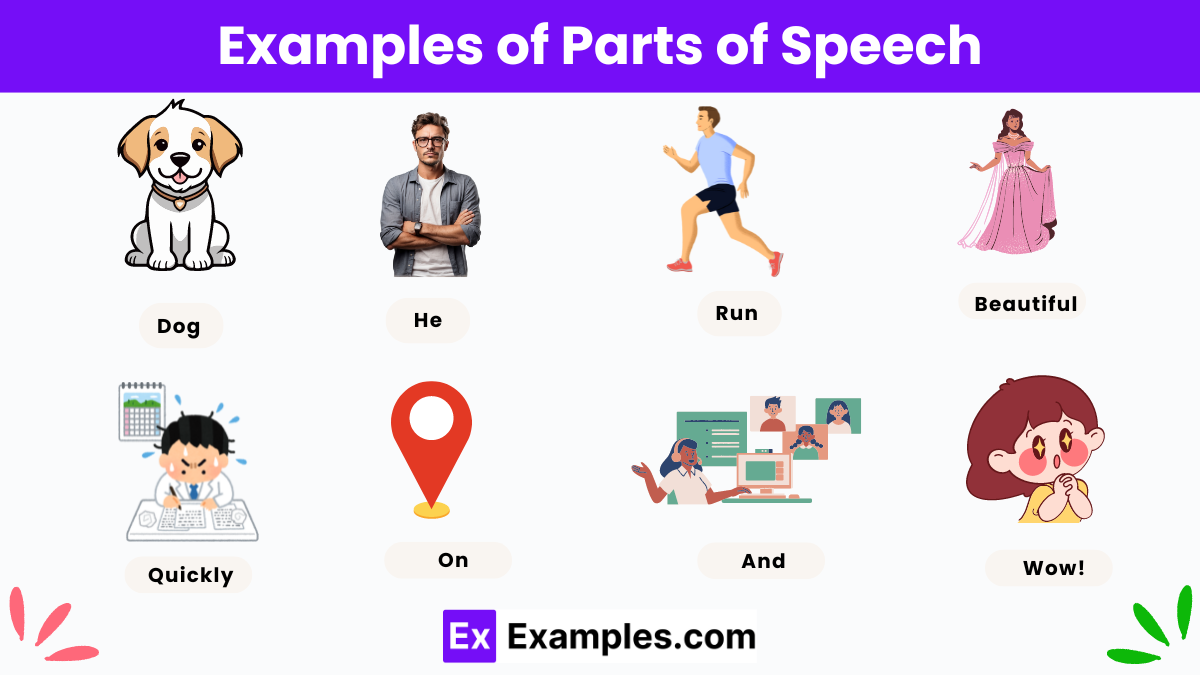
Dog : A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. In this example, “dog” is a noun because it represents a specific animal.
He : A pronoun is a word that is used in place of a noun to avoid repetition. In this example, “he” is a pronoun that replaces the noun representing a male person.
Run :A verb is a word that expresses an action, occurrence, or state of being. In this example, “run” is a verb because it describes the action of moving quickly.
Beautiful : An adjective is a word that modifies or describes a noun or pronoun by providing additional information about its qualities or attributes. In this example, “beautiful” is an adjective that describes the noun it modifies.
Quickly : An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb by providing information about time, place, manner, degree, or frequency. In this example, “quickly” is an adverb that describes how an action is performed.
On : A preposition is a word that establishes a relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence, indicating direction, location, time, or manner. In this example, “on” is a preposition that indicates the location of something.
And : A conjunction is a word that connects words, phrases, or clauses within a sentence, allowing for smooth transitions and logical relationships between different parts of the sentence. In this example, “and” is a conjunction that connects two ideas or elements.
Wow!: An interjection is a word or phrase used to express strong emotions, feelings, or reactions. In this example, “wow” is an interjection that conveys surprise, excitement, or admiration.
Sentences Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
- Noun: The cat sat on the mat.
- “Cat” and “mat” are nouns, referring to a specific animal and an item.
- Pronoun: She loves to read books.
- “She” is a pronoun that replaces a noun, possibly referring to a known female.
- Verb: The teacher writes on the board.
- “Writes” is a verb that describes the action being performed by the subject.
- Adjective: He bought a red car.
- “Red” is an adjective that describes the noun “car.”
- Adverb: She sings beautifully.
- “Beautifully” is an adverb modifying the verb “sings,” describing how she sings.
- Preposition: The book is on the table.
- “On” is a preposition that shows the relationship between “book” and “table.”
- Conjunction: I wanted to go out, but it was raining.
- “But” is a conjunction that connects two independent clauses.
- Interjection: Wow!, that’s a huge pumpkin!
- “Wow” is an interjection expressing surprise.
Why are parts of speech important?
Understanding parts of speech helps in structuring sentences correctly, enhancing clarity, and improving communication skills.
Can words belong to more than one part of speech?
Yes, some words can function as more than one part of speech depending on their use in a sentence, such as “love” (noun and verb).
How do nouns function in a sentence?
Nouns serve as the subject or object in sentences, representing people, places, things, or ideas.
What is the role of verbs?
Verbs express action or a state of being and are central to the predicate of a sentence.



