Passive Communication vs Active Communication – 19+ Examples
Embark on a transformative journey through Passive vs Active Communication. This comprehensive guide illuminates the intricacies of communication dynamics. Uncover real-life “Communication Examples,” offering actionable insights and strategies to enhance your interactive prowess. Dive into the art of engagement, master the nuances, and elevate your communication skills with this illuminating guide.
Difference Between Passive Communication and Active Communication
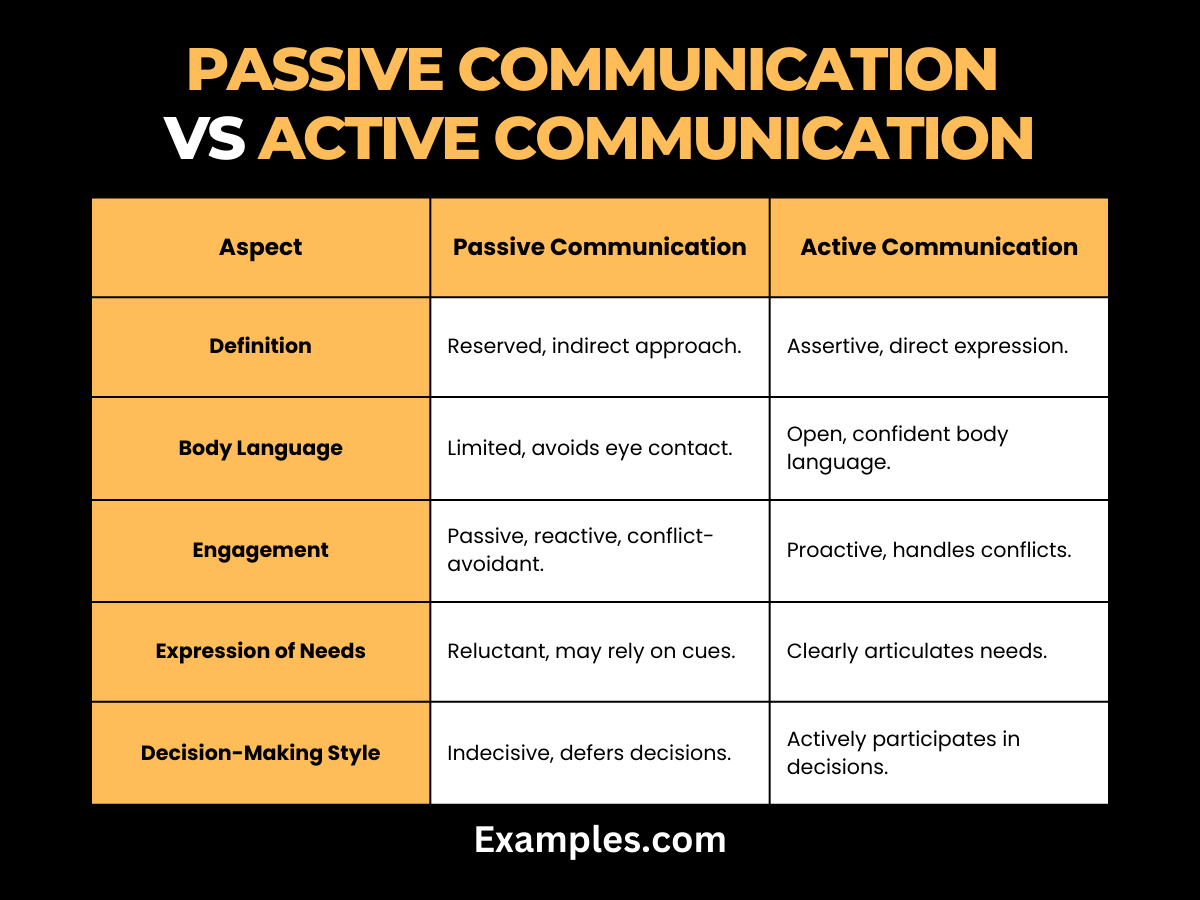
| Aspect | Passive Communication | Active Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Passive communication involves a reserved, indirect approach in conveying thoughts or feelings. | Active communication is characterized by assertiveness, direct expression, and open engagement. |
| Body Language | Limited body language, often avoiding eye contact and displaying closed postures. | Open and confident body language, maintaining eye contact, and using expressive gestures. |
| Engagement | Tends to be passive, reactive, and may avoid conflicts, leading to unexpressed concerns. | Proactively engages, expresses thoughts, and handles conflicts assertively for resolution. |
| Expression of Needs | Reluctant to express needs directly, may rely on subtle cues, leading to potential misunderstandings. | Clearly articulates needs and desires, fostering effective understanding and collaboration. |
| Decision-Making Style | May be indecisive, deferring decisions to others, and avoiding taking the lead. | Actively participates in decision-making, provides input, and takes responsibility for choices. |
| Conflict Resolution | May avoid conflicts, leading to unresolved issues. Often complies to maintain peace. | Addresses conflicts directly, seeks resolution, and values open communication for growth. |
| Impact on Relationships | Can lead to unmet expectations, misunderstandings, and challenges in building strong connections. | Enhances relationships by fostering transparency, mutual understanding, and effective collaboration. |
| Benefits | Reduced confrontation, avoids potential conflicts. | Improved clarity, stronger relationships, and effective problem-solving. |
| Challenges | Limited self-expression, potential for misunderstandings. | Need for assertiveness, handling conflicts openly. |
10 Passive Communication Examples
Passive communication, while subtle, offers distinct benefits in certain scenarios. By promoting a non-confrontational approach, it helps maintain harmony and reduce stress. Individuals utilizing passive communication often display empathy and attentiveness, fostering positive relationships. Here are ten examples illustrating the benefits
- Conflict Avoidance: Choosing to avoid conflicts to maintain a peaceful environment.
- Politeness and Respect: Expressing opinions politely to show respect for others’ perspectives.
- Listening Actively: Providing full attention during conversations to understand others.
- Reduced Tension: Minimizing tension through a calm and composed demeanour.
- Avoiding Blame: Steering clear of blaming language to prevent escalation.
- Open to Suggestions: Remaining open to others’ suggestions without resistance.
- Promoting Harmony: Prioritizing harmony in group dynamics over personal preferences.
- Non-Verbal Cues: Using non-verbal cues like nodding to affirm understanding.
- Flexibility: Being adaptable and willing to compromise for the greater good.
- Encouraging Cooperation: Fostering a cooperative atmosphere by considering others’ needs.
10 Active Communication Examples
Engaging in active communication enhances interpersonal connections. It promotes clear expression of thoughts and feelings, fostering mutual understanding. Active communicators exhibit confidence, contributing to effective collaboration and conflict resolution. This proactive approach builds trust and cultivates positive relationships. Mastering active communication is vital for leadership and personal development.
- Boldly Expressing Opinions:
- Active communicators confidently voice opinions, encouraging open dialogue.
- Clarifying Expectations:
- Clearly stating expectations reduces misunderstandings and promotes productivity.
- Empathetic Listening:
- Actively listening and responding empathetically strengthens connections.
- Resolving Conflicts Directly:
- Addressing conflicts head-on leads to quicker resolutions and stronger relationships.
- Giving Constructive Feedback:
- Providing feedback constructively contributes to individual and team improvement.
- Initiating Conversations:
- Active communicators take the lead in initiating meaningful conversations.
- Encouraging Participation:
- Fostering active participation creates an inclusive and collaborative environment.
- Asking Clarifying Questions:
- Seeking clarification through questions ensures a shared understanding.
- Setting Clear Boundaries:
- Clearly defining boundaries maintains respect and avoids misunderstandings.
- Expressing Gratitude:
- Active communicators express appreciation, strengthening interpersonal bonds.
Comparison Between Passive Communication and Active Communication
Effective communication is a dynamic process influenced by various styles. Passive and active communication represent two ends of the spectrum, each with distinct characteristics. Understanding the differences is crucial for enhancing interpersonal skills and fostering healthier relationships.
Passive Communication:
Passive communicators tend to avoid expressing their needs or opinions clearly. They may withhold thoughts, leading to misunderstandings. Passivity often results from a fear of conflict or rejection, hindering effective collaboration. Passive individuals may prioritize others’ needs over their own, sacrificing personal goals.
Active Communication:
Active communicators, on the other hand, engage openly and express thoughts and feelings clearly. They actively listen, seek feedback, and contribute to conversations. Active communication fosters collaboration, as individuals share ideas and work collectively towards common goals. It involves assertiveness, clear expression, and a willingness to address conflicts directly.
Key Differences:
- Expression of Needs:
- Passive: Avoids expressing needs directly.
- Active: Clearly articulates needs and desires.
- Handling Conflict:
- Passive: Avoids conflict, leading to unaddressed issues.
- Active: Addresses conflicts directly for resolution.
- Engagement in Conversations:
- Passive: Often silent or minimal contribution.
- Active: Actively participates, contributing ideas and feedback.
- Assertiveness:
- Passive: Lacks assertiveness in expressing opinions.
- Active: Demonstrates assertiveness in communication.
- Decision-Making Involvement:
- Passive: May not actively engage in decision-making.
- Active: Participates actively in decision-making processes.
Relationship between Passive and Active Communication
Understanding the dynamic interplay between passive and active communication is crucial for effective interpersonal dynamics. Both styles influence how messages are conveyed and received, impacting relationships in various contexts. Let’s delve into the nuanced relationship between passive and active communication:
1. Complementary Nature:
- Passive and active communication often coexist, complementing each other based on situational demands. A balanced approach integrates elements of both styles.
2. Impact on Relationships:
- Passive communication may lead to misinterpretations, while active communication fosters clarity. Striking a balance enhances relationship dynamics and mutual understanding.
3. Communication Styles in Conflict:
- During conflicts, passive communicators may avoid confrontation, while active communicators seek resolution through open dialogue. Navigating these differences is essential for conflict resolution.
4. Influence on Team Dynamics:
- In team settings, passive contributors may hinder progress, while active participants drive collaboration. Recognizing each style’s role promotes effective teamwork.
5. Adaptability in Communication:
- Individuals who can seamlessly shift between passive and active communication exhibit adaptability, enhancing their ability to connect with diverse personalities.
6. Building Trust:
- Trust is integral to relationships. Passive communication may lead to misconceptions, while active communication establishes transparency, reinforcing trust bonds.
7. Recognizing Nonverbal Cues:
- Passive communicators may rely heavily on nonverbal cues. Active communicators recognize and interpret these cues, enhancing their understanding of underlying messages.
8. Enhancing Emotional Intelligence:
- Balancing passive and active communication contributes to emotional intelligence. Individuals adept in both styles navigate social situations with finesse.
9. Creating a Communicative Bridge:
- Effectively combining passive and active elements forms a communicative bridge, fostering nuanced and empathetic exchanges.
10. Continuous Personal Growth:
- Individuals consciously navigating the passive-active dynamic experience ongoing personal growth, refining their communication skills for diverse contexts.
In the intricate dance of communication, finding harmony between passive and active styles is key. Embrace the versatility of both approaches, leveraging passive reflection and active engagement judiciously. The interplay between these styles enhances relationships, fostering a nuanced understanding of diverse communication contexts. Strive for balance, allowing the synergistic blend to guide you in varied interactions for enriched connections and effective communication.



