10+ Past Perfect Continuous Tense Examples
Past Perfect Continuous Tense refers to actions or events that were ongoing in the past and continued up to another point in the past. It’s formed using “had been” + verb + “-ing.” This tense emphasizes the duration of an action that occurred before another action or point in the past. For example, “She had been studying for hours before the exam.”
What is Past Perfect Continuous Tense?
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense is a verb form used to describe actions or situations that were ongoing in the past and continued up to a specific point in the past. It is formed by combining “had been” with the present participle form of the main verb (-ing form). This tense emphasizes the duration of an action that occurred before another action or point in the past.
For example, consider the sentence: “She had been waiting for the bus for over an hour when it finally arrived.” In this sentence, the Past Perfect Continuous Tense “had been waiting” indicates that the action of waiting started before a specific time in the past and continued up to that point, which is when the bus finally arrived.
Formula of Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Rules of Past Perfect Continuous Tense
The rules for using the Past Perfect Continuous Tense are as follows:
- Formation: It is formed by using the auxiliary verb “had been” followed by the present participle (verb + “-ing”).
- Continuous Action in the Past: It is used to describe actions or events that were ongoing in the past and continued up to a specific point in the past.
- Duration Emphasis: It emphasizes the duration of an action that occurred before another action or point in the past.
- Time Reference: It often involves time expressions such as “for” (indicating duration) and “since” (indicating starting point).
- Narrative Past: It is commonly used in storytelling to provide background information or set the scene for past events.
- Multiple Actions: It can be used to show that one action was in progress while another action or event occurred.
Uses of the Past Perfect Continuous Tense
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense is used in English for several purposes:
- Continuous Actions in the Past: It describes actions or events that were ongoing in the past and continued up to a specific point or another action in the past.
- Duration Emphasis: It emphasizes the duration of an action that occurred before another action or point in the past.
- Background Information: It provides background information in storytelling or narratives, setting the scene for past events.
- Time Reference: It often involves time expressions such as “for” (indicating duration) and “since” (indicating starting point).
- Multiple Actions: It can be used to show that one action was in progress while another action or event occurred.
Examples of the Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- She had been studying for hours before the exam.
- They had been waiting at the bus stop when the bus finally arrived.
- He had been working on the project for weeks before he completed it.
- By the time they arrived, she had been cooking dinner for two hours.
- The children had been playing outside all afternoon before it started raining.
- We had been driving for hours when we finally reached our destination.
- By the time I woke up, she had been practicing the piano for hours.
- They had been hiking for days before they reached the summit.
- She had been talking on the phone for hours before it suddenly disconnected.
- The team had been training hard for months before the competition.
Differences between Past Continuous Tense and Past Perfect Continuous Tense
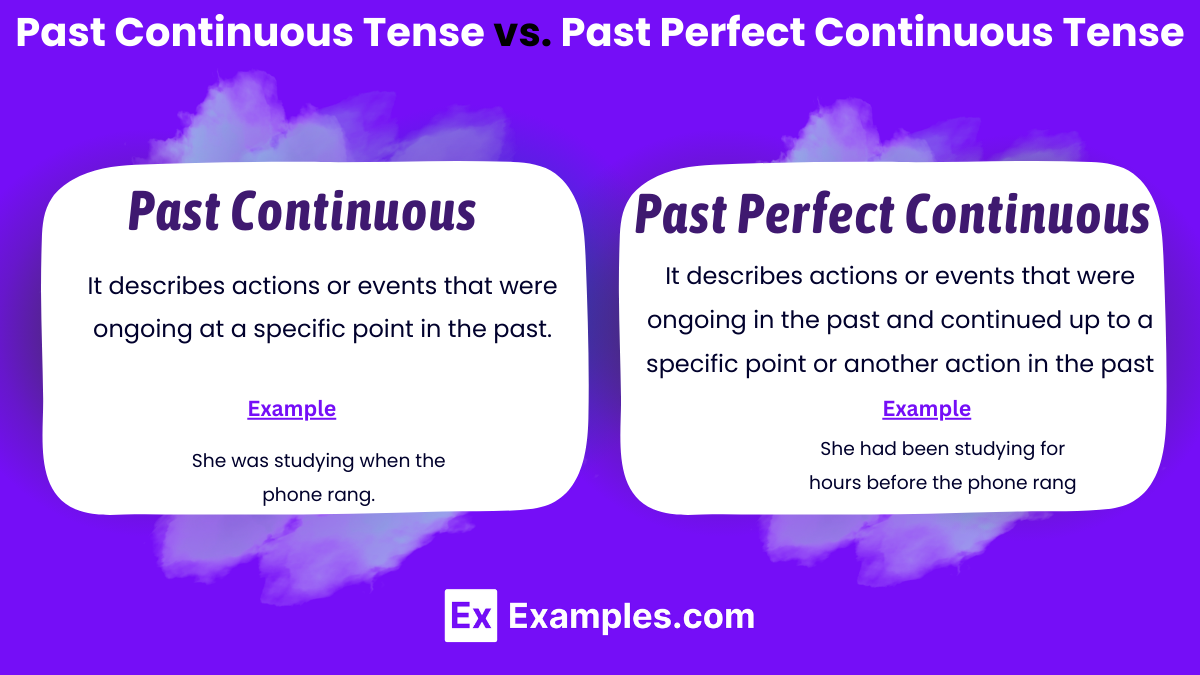
The main differences between the Past Continuous Tense and the Past Perfect Continuous Tense are as follows:
1.Timing of the Action:
Past Continuous Tense: It describes actions or events that were ongoing at a specific point in the past.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense: It describes actions or events that were ongoing in the past and continued up to a specific point or another action in the past.
2.Formation:
Past Continuous Tense: It is formed by using the past tense of the verb “to be” (was/were) with the base form of the main verb plus the “-ing” suffix.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense: It is formed by using “had been” with the present participle (verb + “-ing”).
3.Usage:
Past Continuous Tense: It is used to describe ongoing actions or events in the past, often with a specific time reference.
4.Past Perfect Continuous Tense: It is used to emphasize the duration of an action that occurred before another action or point in the past.
Example:
Past Continuous Tense: “She was studying when the phone rang.”
Past Perfect Continuous Tense: “She had been studying for hours before the phone rang.”
FAQ’s
What are some common time expressions used with the Past Perfect Continuous Tense?
Time expressions such as “for” (indicating duration) and “since” (indicating starting point) are commonly used with this tense.
Is the Past Perfect Continuous Tense commonly used in everyday conversation?
While it is not as commonly used as other tenses in everyday conversation, it is frequently found in written narratives, storytelling, and formal writing.
How does the Past Perfect Continuous Tense differ from the Past Continuous Tense?
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense emphasizes the duration of an action leading up to another point in the past, while the Past Continuous Tense describes ongoing actions at a specific time in the past.
Can the Past Perfect Continuous Tense be used with all verbs?
Yes, the Past Perfect Continuous Tense can be used with all verbs to describe ongoing actions in the past.