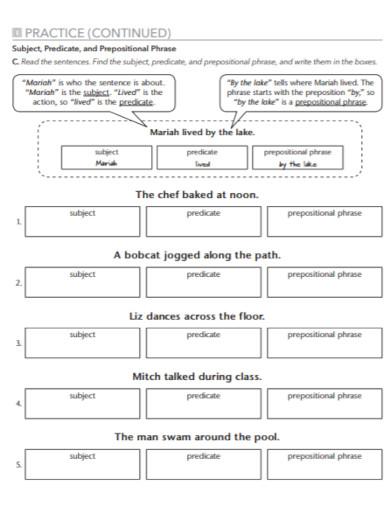
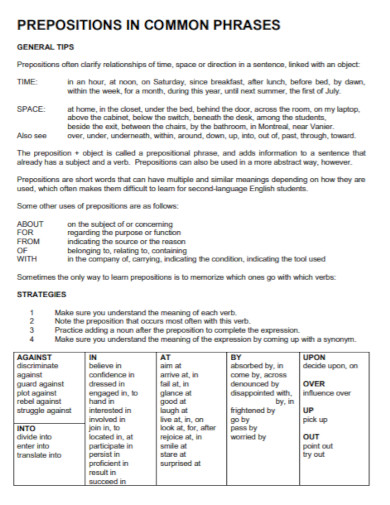
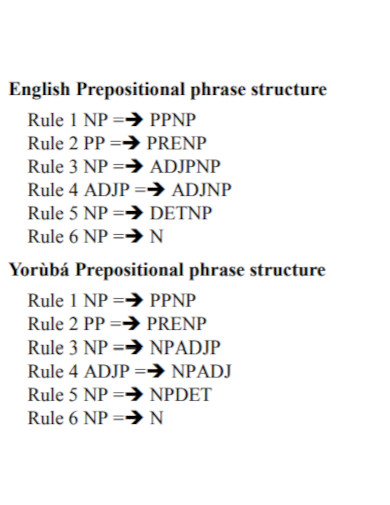
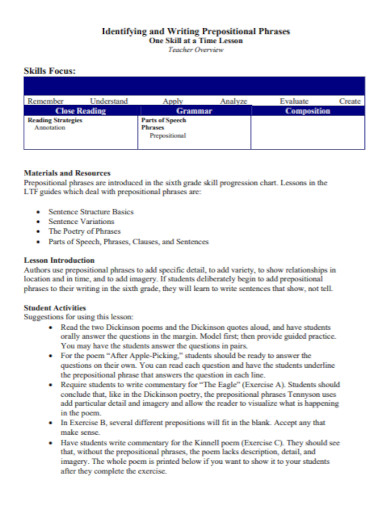
100+ Prepositional Phrase Examples
This may be familiar to you in a way that this part of speech just like nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, and prepositions. This part of speech however may be a bit confusing to some especially if it had not been discussed specifically in class. But, this should be an easy part simply by reading today’s article. So from this sample sentence, you may get an idea as to what this topic may be about. “Among the three winners, Ms. Jones thought one of us would have won the game.” If from the example sentence, you may already know what we are going to be talking about. Prepositional phrases. Yet, what do you know about them and why do you think they are necessary in our sentences? To get to know more about this, head on down the 100+ examples and straight to what you’re looking for.
100+ Prepositional Phrase
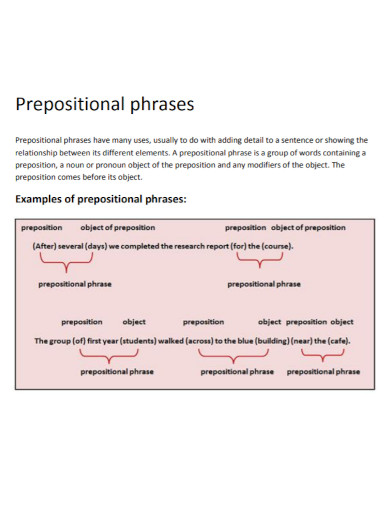
1. Preposition and Prepositional Phrase
2. Recognizing Prepositional Phrase
3. Prepositional Phrase Template
4. The Prepositional Phrase
5. Types of Prepositional Phrases
6. Printable Prepositional Phrases
7. Simple Prepositional Phrase
8. Prepositional Phrase Example
9. Basic Prepositional Phrase
10. Commonly Used Prepositional Phrase
11. English Prepositional Phrase
12. Prepositional Phrase Attachment
13. Group Prepositional Phrases
14. Prepositional Phrases Grammar Preview
15. General Prepositional Phrase
16. Recognising Prepositional Phrases Example
17. Prepositional Phrases Agreement
18. Prepositions and Phrasal Verbs
19. Facts About Prepositional Phrases
20. Intervening Prepositional Phrases
21. Prepositional and Transitional Phrases
22. Common Prepositional Phrases
23. Prepositional Phrases with Example
24. Compound Prepositional Phrases
25. Range of Prepositional Phrases
26. Multiple Prepositional Phrases
27. Words with Prepositional Phrases
28. Prepositional Phrases Worksheet Example
29. Diagramming Prepositional Phrases
30. Prepositional Phrases in PDF
31. Prepositional Phrases Practice
32. Prepositional Phrases Syntax
33. Prepositional Phrases Sentences
34. Draft Prepositional Phrases
35. Sample Prepositional Phrases
36. Punctuating Prepositional Phrases
37. Learning to Use Prepositional Phrase
38. Prepositional Phrase Template in PDF
39. Draft Prepositional Phrase Example
40. Student Prepositional Phrases
41. Prepositional Phrases and their Objects
42. More Work with Prepositional Phrases
43. Prepositional Phrases Lesson Plan
44. Example of Prepositional Phrases
45. One Page Prepositional Phrases
46. Underlining Prepositional Phrases
47. Noun and Prepositional Phrases
48. Grammar Prepositional Phrases
49. University Prepositional Phrases
50. Prepositional Phrases Case Study
51. Learning About Prepositional Phrases
52. Prepositional Phrases Format
53. Individual Prepositional Phrases
54. Prepositional Phrases in English
55. Prepositional Phrases Lesson
56. Prepositional Phrases with Modifiers
57. Prepositional Phrases Handout
58. Prepositional Phrases Document
59. Short Prepositional Phrases
60. Prepositional Phrases Passage
61. Prepositional Phrase Exercises
62. Prepositional Phrases Types
63. Prepositional Phrases Structure
64. Typical Prepositional Phrases
65. Prepositional Phrases with Grammar
66. Academic Prepositional Phrases
67. Prepositional Phrases Classifications
68. Prepositional Phrases for College
69. Prepositional Phrases Comprehension
70. Preposition in Common Phrases
71. Prepositional Phrases in Sentence Example
72. Identifying Preposition and Prepositional Phrases
73. Spotting Prepositional Phrases
74. Internal Structure of Prepositional Phrases
75. Starting Sentences with Prepositional Phrases
76. Underlined Prepositional Phrases Worksheet
77. English Prepositional Phrase Structure
78. Prepositional Phrases Sample Example
79. Annotation for Prepositional Phrases
80. Prepositional Phrases Research
81. Prepositional Phrases Workbook
82. Prepositional Phrases Example in PDF
83. Prepositional Phrases Grammar Handbook
84. Prepositional Phrases in DOC
85. Prepositional Phrases Examples in DOC
86. Prepositional Phrases for Students
87. Basic Prepositional Phrases Format
88. Prepositional Phrase Map Worksheet
89. Phrases and Prepositional Phrases
90. The Prepositional Phrases in DOC
91. The Functions of Prepositional Phrases
92. Prepositional Phrases as Subject Complements
93. Prepositional Phrases with Directions
94. Prepositional Phrases Convections
95. Prepositional Phrases Review
96. Prepositional Phrases List
97. Subjects in Prepositional Phrases
98. Speech’s of Prepositional Phrases
99. Prepositional Phrases in DOC Template
100. Prepositional Phrases Levels with Example
101. Standard Prepositional Phrases Worksheet
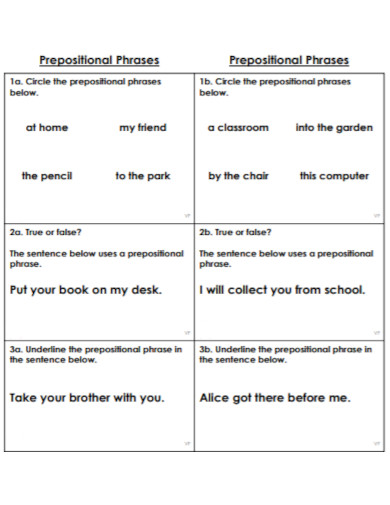
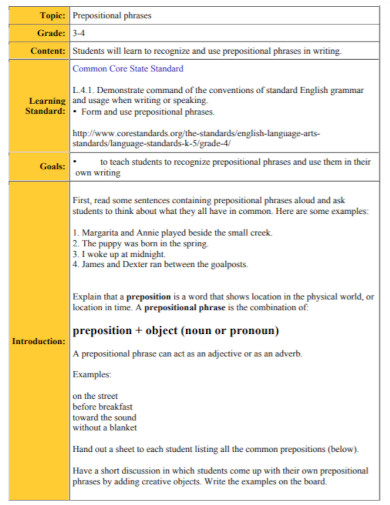
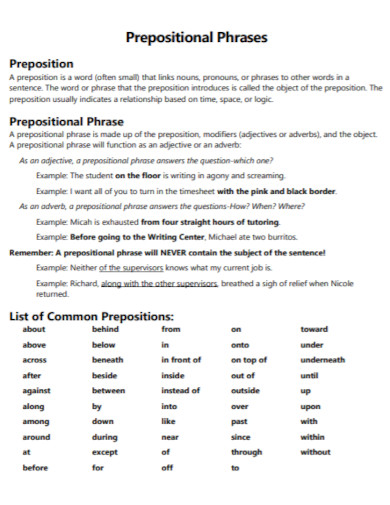
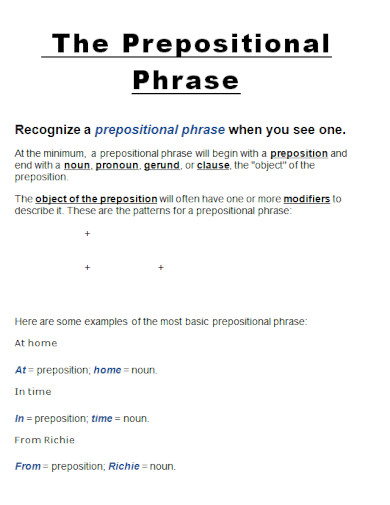
What Is a Prepositional Phrase?
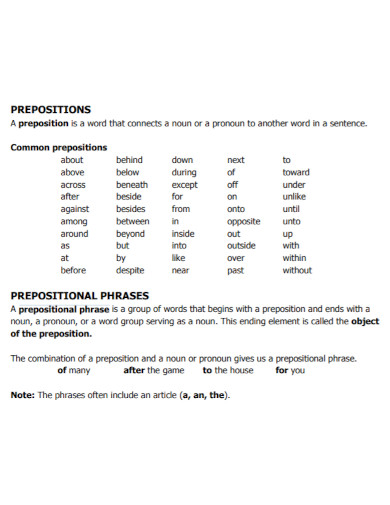
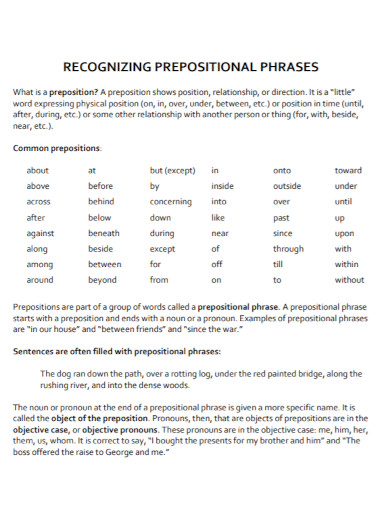
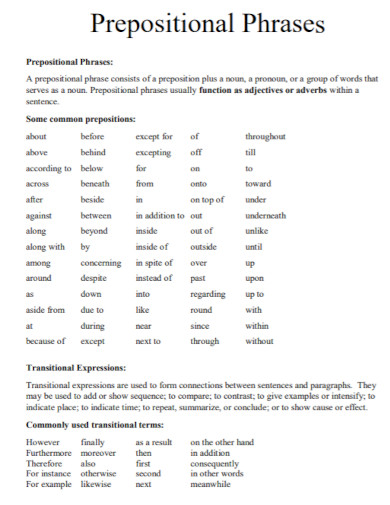
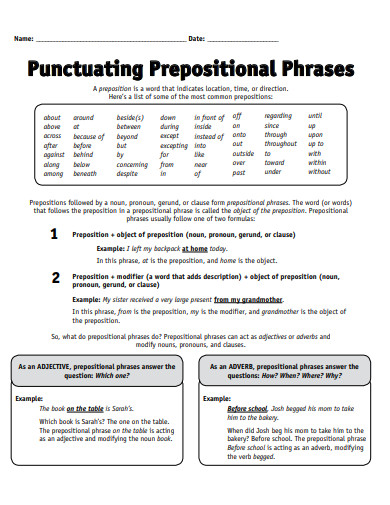
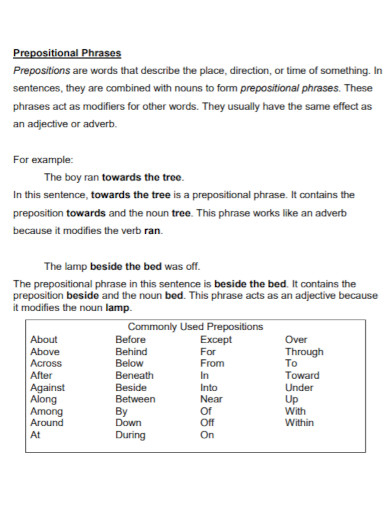
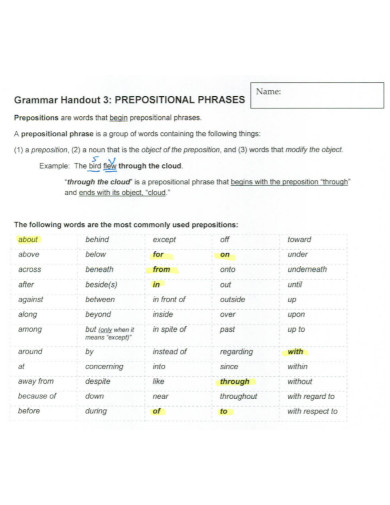
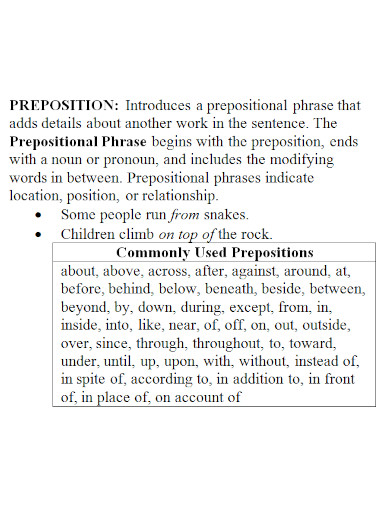
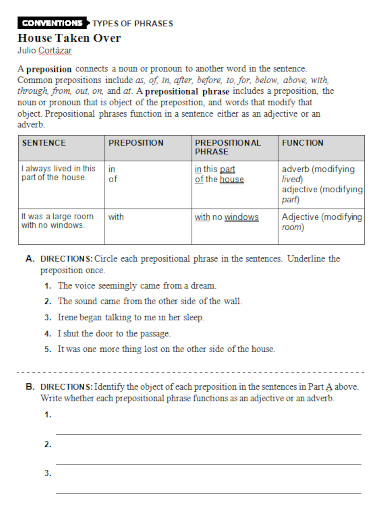
A preposition is a type of speech that connects phrases or ideas to a sentence. It is also mostly used before a noun and a pronoun. In addition to that, a preposition is present to show time, a place, direction, etc. An example of prepositions are “with, to, at, in”. A prepositional phrase is a word, a group of words or ideas that consists of the preposition and the object. What this means is a prepositional phrase has a preposition and the object or a word along with it to modify within the sentence. Prepositional phrases mostly modify verbs or nouns.
Elements of a Prepositional Phrase
Just as nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, prepositions and adverbs have elements, so does a prepositional phrase. However, unlike the ones mentioned above, these elements are only a few but still worth learning about. So why don’t we check it below to see what these elements may be.
1. Preposition
To make a short review, a preposition is a type of speech that connects phrases or ideas to a sentence. In the sentence, the main purpose of a preposition is to answer the questions of who, what, when, where, why and how. To make a prepositional phrase, you must of course add the preposition to the mix. Some prepositional words include “on, between, in, of, at, by, etc. An example sentence for the following prepositions would be: “Between the two of them, one is a suspect for murder.” “I will be coming at around noon tomorrow.” “She had her glasses on her head the whole time.” “The boss told me to submit my work by tomorrow or I would be fired.”
2. Object of the Preposition
To give you an idea, let us first define what an object of the preposition is. So the object of the preposition is basically a word, a group of words, an idea or a phrase. The object of the preposition is found beside the preposition and it explains what is going on in the sentence. In other words, it specifies about the intention, the place, the time and the manner of the idea. To make it simpler, here is an example for an object of the preposition. “The oranges are in the basket.” For this sentence, the object of the preposition is “the basket.” As for the preposition, the word “in.” The preposition in is basically explaining where you can find the oranges.
3. Multiple Prepositions
What are multiple prepositions? Well, there are actually instances wherein in a sentence, you get more than just one preposition and the object of the preposition. In this case, it’s called multiple prepositions. The combination of more than one or two prepositions to expound a better if not different meaning than the single prepositions often found in sentences. To keep it easier to understand, take this as an example. “With regards to the current issues, a lot of companies decide to lay off their employees, except for those who have been working in the company for more than a year.”
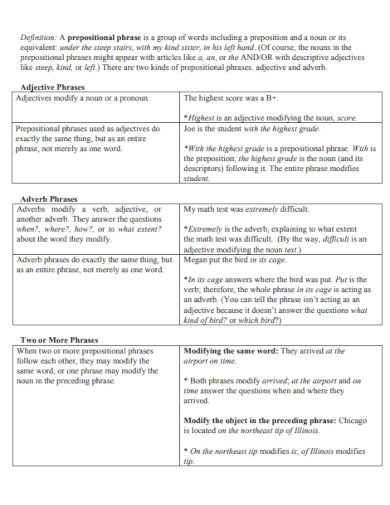
Types of Prepositional Phrases
Have a fun fact while we carry on with the discussion about prepositional phrases. Did you know that prepositional phrases can be used as information? If you wonder what kind of information, this type of information goes with nouns, pronouns and even verbs! However, the majority role of the prepositional phrase would usually or most of the time answer WH questions, location, time, and manner. Check these ones below.
1. Who Did the Action
So the first type of prepositional phrase we have is who did the action or to whom was the action made for. For this to be answered, your prepositional phrase must be based on a person rather than on a thing. The person being addressed is the one who did the action or the one whom the prepositional phrase was meant for. In this case, an example for that would be: “Tyson was punched in the face.” For the first example, this would mean who received the punch to the face. So your prepositional phrase is the word in. To whom it was directed to would be Tyson. Another example would be “Jenna gave a basketball to Luke for his birthday.” The one doing the action is Jenna but to whom the action was addressed to would be Luke.
2. Why Did They Do the Action
The second one we have is why. Why did they do the action? So this prepositional phrase is going to explain the reason as to why the object or the subject of the phrase is doing the action. To give out a reason for the activity being done. An example for this would be: “Mary went to the market to buy some fresh vegetables.” This sentence let’s you ask why did Mary go? It gives out the explanation in the sentence or better yet what was her reason for going. Another example would be “Lucy studied for the whole weekend for an exam on Monday.” Why did Lucy study would be the exact question for this second example.
3. With Whom Did They Do the Action
For this type of prepositional phrase, the prepositional phrase explains what kind was being used. In a way that the object must be specific along with another object. To make this as clearer as possible, here is an example. “Jane and her sister bathed their dog with a hose.” So this sentence here explains with what they were doing. Another example sentence would be “My mother washed the dishes with soap and water.” This phrase is explaining as to what is used or with whom the action was being done.
4. When Did the Action Take Place
This type simply asks where. Where did the action take place. So the prepositional phrase is accompanied by either the location or place. An example would be “My friends and I are going to the beach.” “My parents are traveling to Madrid this week.” Your prepositional phrase + the location.
5. Where Did the Action Take Place
Just like the fourth one, for where did the action take place, it simply states the location of where the prepositional phrase took place. It does not necessarily mean that you have to be specific with where the location is as long as it still answers the question “where”. An example would be: “My parents are off to a vacation in Madrid.” “I will spend my summer vacation in Europe.”
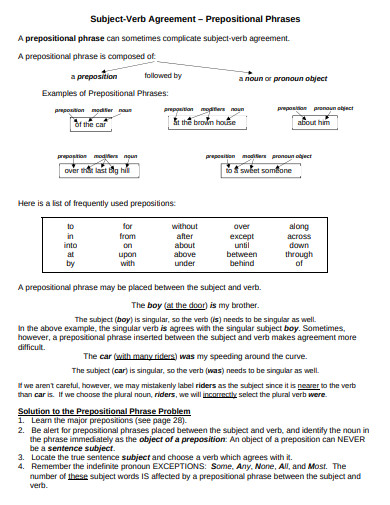
How to Avoid Mistakes with Prepositional Phrases
We are all guilty at some point over making a lot of mistakes with prepositional phrases in sentences. Especially when we use them in a lot of documents that need active voice. So here are some tips to avoid mistakes.
1. Phrasal Verbs are not Prepositional Phrases
Some verbs seem to have a specific meaning especially when they are combined with certain prepositions. These multi-word verbs are called phrasal verbs. The two are quite similar, but phrasal verbs shouldn’t be confused with prepositional phrases. To has many uses especially in different situations and as different parts of speech. Although to is often used as a preposition, it can also be used to form infinitives.
2. Infinitives are not Prepositional Phrases
Infinitives and prepositional phrases most often seem to be quite identical. However, an infinitive is practically the basic form of a verb that is not have a connection to the subject of a sentence. Infinitives are formed by combining the word to and the stem of a verb.
3. Don’t Overdo It
There are times that we often make the mistake of overdoing our prepositional phrases. One thing that should be taken to consideration is to stop overdoing it. If the sentence does not need any more prepositional phrases, do not add them.
4. Use Active Voice
The more prepositional phrases in your sentences, the more it gets confusing. To avoid having to go through that, it is best to use some into active voice instead. Active voice in your sentences can not just lessen the use of a lot of prepositional phrases in your sentence, it can also make your sentences look and sound nicer.
5. Take Out Unnecessary Phrases
Taking out unnecessary phrases or those that are redundant not only makes your sentences look neater, it also helps by making your prepositional phrases less all over the place.
FAQs
What is a prepositional phrase?
A preposition is a type of speech that connects phrases or ideas to a sentence. Prepositional phrases help the sentence make more sense.
What are some examples of a prepositional phrase?
Some examples of prepositional phrases in a sentence are: At the back of the line. In the apple tree. With my sister. Across the pond.
What should be avoided in prepositional phrases?
Do not overdo your sentences by adding a lot of prepositional phrases. As this would make your sentences look odd or dull. Adding just the exact amount of prepositional phrases is fine, but overdoing it would make your sentence confusing.
When writing your sentences, always remember to not overdo anything. Do not make your sentences sound passive when they are okay to sound active. Always choose the correct prepositional phrase for your sentence.