29+ Public communication in Oral Communication Examples
Public communication in oral communication is a vital skill, encompassing the ability to effectively convey messages to larger audiences. It blends articulate speaking, engaging storytelling, and persuasive techniques, crucial for impactful presentations and speeches. Mastering this form of oral communication not only enhances public speaking skills but also boosts confidence and audience engagement. In today’s interconnected world, excelling in public communication is essential, whether for professional presentations, academic lectures, or social advocacy, making it a key component of successful oral communication.
What is Public Communication in Oral Communication?

Public communication in oral communication refers to the process of sharing information, ideas, or messages with a large group of people, typically in a formal or structured setting. This involves speaking to an audience, whether it’s giving a presentation, delivering a speech, or leading a discussion in a public forum. The key focus is on effectively conveying a message to many people at once, requiring skills in clear expression, audience engagement, and persuasive techniques. It’s a form of oral communication that emphasizes reaching and influencing a broader audience.
30 Public Communication in Oral Communication Examples

Public communication in oral communication is a dynamic skill that involves engaging and addressing a large audience effectively. This form of communication combines clear articulation, persuasive storytelling, and impactful nonverbal cues like eye contact and gestures. It’s essential in various settings, from business presentations to public speeches, requiring mastery in audience engagement, clarity, and confidence. Effective public communication not only conveys information but also influences, motivates, and connects with the audience, making it a pivotal skill in oral communication.
- “Exploring New Strategies Today”: Engage with an informative, forward-looking opening.
- “Storytelling for Clarity”: Use relatable stories to illustrate points.
- “Audience Involvement”: Directly engage the audience for inclusivity.
- “Inspiring Visions”: Use imaginative scenarios to motivate.
- “Introducing Thought-Provoking Topics”: Transition to new ideas smoothly.

- “Encouraging Dialogue”: Invite audience questions and participation.
- “Citing Credible Evidence”: Reinforce messages with factual data.
- “Framing Challenges Positively”: Present obstacles as opportunities.
- “Delving Into Details”: Provide in-depth explanations of goals.
- “Valuing Audience Expertise”: Acknowledge and respect the audience’s insights.

- “Personal Experience Sharing”: Create connections through personal stories.
- “Collective Endeavor Invitation”: Invite the audience on a joint journey.
- “Data-Driven Perspectives”: Introduce data for a factual basis.
- “Highlighting Solution Urgency”: Emphasize the critical nature of solutions.
- “Celebrating Milestones”: Focus on achievements to build confidence.
- “Seeking Audience Feedback”: Emphasize the importance of audience input.
- “Discussing Practical Implications”: Relate topics to daily operations.
- “Simplifying Complex Concepts”: Make complex ideas accessible.
- “Motivational Conclusions”: Summarize with an inspiring call to action.
- “Personalizing Audience Roles”: Make each listener feel essential.
- “Recalling Past Successes”: Boost confidence with reminders of achievements.
- “Emphasizing Audience Impact”: Highlight the audience’s role in success.
- “Aligning with Organizational Goals”: Connect topics to broader visions.
- “Stressing Change Necessity”: Underline the importance of proposed changes.
- “Addressing Concerns Proactively”: Discuss and alleviate potential worries.
- “Unity and Overcoming Challenges”: Promote collective strength and resilience.
- “Valuing Audience Insights”: Appreciate contributions from listeners.
- “Broader Implications Consideration”: Urge consideration of wider effects.
- “Gratitude and Interaction”: Thank listeners and open up for questions.
- “Collective Strength Harnessing”: Motivate joint efforts towards a goal.
What are the Types of Public communication in Oral Communication?
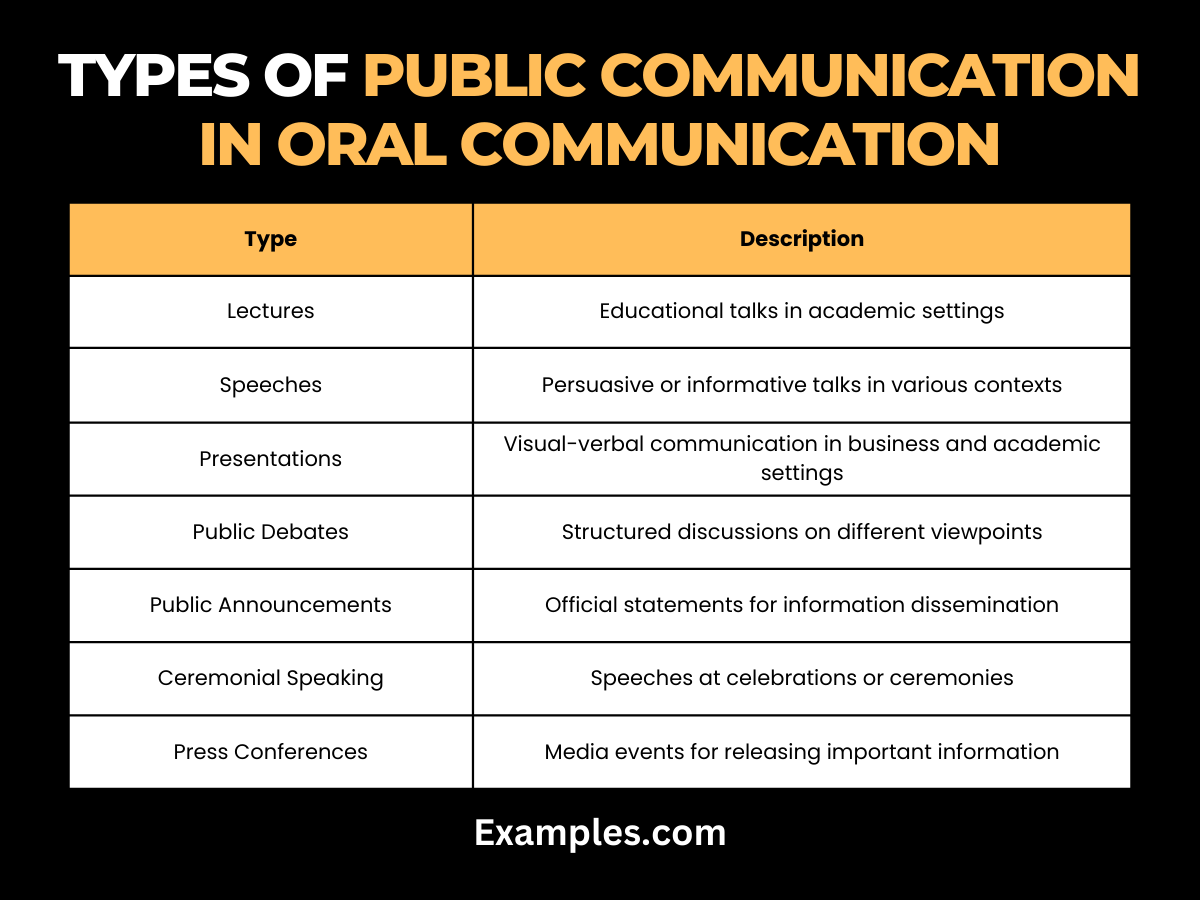
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Lectures | Formal educational talks, crucial in oral communication in college and other academic institutions. |
| Speeches | Talks for persuasion or information sharing, key in oral communication in business and social settings. |
| Presentations | Combining visual and verbal elements, vital in oral communication in the workplace for conveying ideas. |
| Public Debates | Structured argumentative discussions, important in oral communication for academic purposes. |
| Public Announcements | Official statements, essential in oral communication for information dissemination. |
| Ceremonial Speaking | Speeches at events, reflecting cultural aspects of oral communication. |
| Press Conferences | Media-addressing events, significant in oral communication for public figures and organizations. |
| Political Campaign Speeches | Persuasive speeches by politicians, a critical aspect of oral communication in political campaigns. |
| Workshops and Seminars | Educational sessions, playing a role in oral communication for practical purposes. |
| Keynote Addresses | Inspirational speeches that outline the theme of events, important in oral communication for public speaking. |
What is the importance of Public communication in Oral Communication?
Public communication in oral communication holds immense importance:
- Dissemination of Information: It’s essential for spreading knowledge, particularly in oral communication for grade levels and community education.
- Influence and Persuasion: Effective public communication can shape opinions and motivate actions, crucial in oral communication for social purposes.
- Educational Role: In academic contexts, it facilitates learning and discussion, demonstrating the value of oral communication in college.
- Professional Skill: Public communication skills are indispensable for success in various careers, highlighting the role of oral communication in the workplace.
- Community Mobilization: It’s key in engaging communities, especially in oral communication for civic engagement.
- Cultural Sharing: Public speaking allows for cultural expression and sharing, an aspect of oral communication in cultural contexts.
- Crisis Communication: In emergencies, it’s critical for providing instructions and information, underscoring the importance of oral communication in crisis management.
What is the Purpose of Public Communication in Oral Communication?
Public communication in oral communication serves several key purposes, each contributing to the effectiveness and impact of the message delivered to a broad audience.
- Informing and Educating: One of the primary purposes is to inform or educate an audience about specific topics, ideas, or issues. This aspect is vital in settings like academic lectures, informational briefings, or public awareness campaigns.
- Persuading and Influencing: Public communication is often used to persuade or influence an audience, such as in political speeches, marketing presentations, or advocacy efforts. It aims to shape opinions, encourage action, or change behaviors.
- Entertaining: At times, the purpose is to entertain, as seen in storytelling, theatrical performances, or certain types of speeches. This use of oral communication aims to engage and captivate the audience.
- Building Connections: Public communication helps in building connections between the speaker and the audience, fostering a sense of community or shared understanding. It’s crucial in creating rapport and establishing trust.
- Inspiring and Motivating: It is also used to inspire and motivate people, especially in motivational talks, keynote speeches, or inspirational addresses. This form of oral communication seeks to uplift and energize the audience.
- Initiating Dialogue and Discussion: Lastly, it can initiate broader dialogue and discussion on various topics, promoting public discourse and democratic participation.
What are the Skills of Public Communication in Oral Communication?
To effectively engage in public communication in oral communication, several key skills are essential:
- Clarity and Articulation: The ability to articulate thoughts clearly and concisely is crucial. This involves using precise language and a well-structured flow of ideas.
- Audience Engagement: Skilled public communicators know how to engage and hold the audience’s attention, using techniques like storytelling, humor, and rhetorical questions.
- Nonverbal Communication: Effective use of body language, gestures, facial expressions, and eye contact enhances the message and keeps the audience engaged.
- Voice Modulation and Projection: Good control over voice modulation and the ability to project one’s voice ensures that the message is heard clearly by everyone in the audience.
- Persuasive Techniques: Understanding and utilizing persuasive techniques are vital for influencing the audience’s thoughts and actions.
- Preparation and Research: Thorough preparation and research on the topic provide depth and authenticity to the communication.
- Listening and Responsiveness: Being responsive to the audience’s reactions and adapting the message accordingly is a crucial skill in oral communication.
- Emotional Intelligence: The ability to connect emotionally with the audience, understanding their mood and expectations, is key to successful public communication.
- Confidence and Presence: Lastly, confidence and a strong stage presence help in establishing credibility and keeping the audience’s attention.
How to Improve Public Communication in Oral Communication?
Improving public communication skills in oral communication involves several steps:
- Practice Regularly: Like any skill, public speaking improves with practice. Seek opportunities to speak in public.
- Seek Constructive Feedback: Constructive criticism from peers or mentors is invaluable for improvement.
- Join Speaking Clubs or Workshops: Organizations like Toastmasters provide a platform for practicing and improving public speaking skills.
- Study Effective Speakers: Analyze speeches by accomplished public speakers to learn techniques and styles.
- Work on Nonverbal Skills: Practice body language, facial expressions, and gestures that complement your verbal message.
- Record and Review: Record your speeches and presentations to identify areas for improvement.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with current topics and trends relevant to your field for more engaging discussions.
- Manage Anxiety: Learn techniques to manage public speaking anxiety, such as deep breathing and positive visualization.
By following these steps, you can continuously improve your public communication abilities, making your oral communication more impactful and effective.
For further enrichment in public communication skills, the Toastmasters International website offers an array of resources and opportunities to practice and refine public speaking skills in a supportive environment. Additionally, Harvard University’s Public Speaking Course provides invaluable insights and strategies to enhance one’s ability to speak confidently and effectively in public settings. These resources complement the knowledge and skills discussed in this guide, providing practical avenues for applying and advancing your public communication abilities.
29+ Public communication in Oral Communication Examples

Public communication in oral communication is a vital skill, encompassing the ability to effectively convey messages to larger audiences. It blends articulate speaking, engaging storytelling, and persuasive techniques, crucial for impactful presentations and speeches. Mastering this form of oral communication not only enhances public speaking skills but also boosts confidence and audience engagement. In today’s interconnected world, excelling in public communication is essential, whether for professional presentations, academic lectures, or social advocacy, making it a key component of successful oral communication.
What is Public Communication in Oral Communication?

Public communication in oral communication refers to the process of sharing information, ideas, or messages with a large group of people, typically in a formal or structured setting. This involves speaking to an audience, whether it’s giving a presentation, delivering a speech, or leading a discussion in a public forum. The key focus is on effectively conveying a message to many people at once, requiring skills in clear expression, audience engagement, and persuasive techniques. It’s a form of oral communication that emphasizes reaching and influencing a broader audience.
30 Public Communication in Oral Communication Examples

Public communication in oral communication is a dynamic skill that involves engaging and addressing a large audience effectively. This form of communication combines clear articulation, persuasive storytelling, and impactful nonverbal cues like eye contact and gestures. It’s essential in various settings, from business presentations to public speeches, requiring mastery in audience engagement, clarity, and confidence. Effective public communication not only conveys information but also influences, motivates, and connects with the audience, making it a pivotal skill in oral communication.
“Exploring New Strategies Today”: Engage with an informative, forward-looking opening.
“Storytelling for Clarity”: Use relatable stories to illustrate points.
“Audience Involvement”: Directly engage the audience for inclusivity.
“Inspiring Visions”: Use imaginative scenarios to motivate.
“Introducing Thought-Provoking Topics”: Transition to new ideas smoothly.

“Encouraging Dialogue”: Invite audience questions and participation.
“Citing Credible Evidence”: Reinforce messages with factual data.
“Framing Challenges Positively”: Present obstacles as opportunities.
“Delving Into Details”: Provide in-depth explanations of goals.
“Valuing Audience Expertise”: Acknowledge and respect the audience’s insights.

“Personal Experience Sharing”: Create connections through personal stories.
“Collective Endeavor Invitation”: Invite the audience on a joint journey.
“Data-Driven Perspectives”: Introduce data for a factual basis.
“Highlighting Solution Urgency”: Emphasize the critical nature of solutions.
“Celebrating Milestones”: Focus on achievements to build confidence.
“Seeking Audience Feedback”: Emphasize the importance of audience input.
“Discussing Practical Implications”: Relate topics to daily operations.
“Simplifying Complex Concepts”: Make complex ideas accessible.
“Motivational Conclusions”: Summarize with an inspiring call to action.
“Personalizing Audience Roles”: Make each listener feel essential.
“Recalling Past Successes”: Boost confidence with reminders of achievements.
“Emphasizing Audience Impact”: Highlight the audience’s role in success.
“Aligning with Organizational Goals”: Connect topics to broader visions.
“Stressing Change Necessity”: Underline the importance of proposed changes.
“Addressing Concerns Proactively”: Discuss and alleviate potential worries.
“Unity and Overcoming Challenges”: Promote collective strength and resilience.
“Valuing Audience Insights”: Appreciate contributions from listeners.
“Broader Implications Consideration”: Urge consideration of wider effects.
“Gratitude and Interaction”: Thank listeners and open up for questions.
“Collective Strength Harnessing”: Motivate joint efforts towards a goal.
What are the Types of Public communication in Oral Communication?

Type | Description |
|---|---|
Lectures | Formal educational talks, crucial in oral communication in college and other academic institutions. |
Speeches | Talks for persuasion or information sharing, key in oral communication in business and social settings. |
Presentations | Combining visual and verbal elements, vital in oral communication in the workplace for conveying ideas. |
Public Debates | Structured argumentative discussions, important in oral communication for academic purposes. |
Public Announcements | Official statements, essential in oral communication for information dissemination. |
Ceremonial Speaking | Speeches at events, reflecting cultural aspects of oral communication. |
Press Conferences | Media-addressing events, significant in oral communication for public figures and organizations. |
Political Campaign Speeches | Persuasive speeches by politicians, a critical aspect of oral communication in political campaigns. |
Workshops and Seminars | Educational sessions, playing a role in oral communication for practical purposes. |
Keynote Addresses | Inspirational speeches that outline the theme of events, important in oral communication for public speaking. |
What is the importance of Public communication in Oral Communication?
Public communication in oral communication holds immense importance:
Dissemination of Information: It’s essential for spreading knowledge, particularly in oral communication for grade levels and community education.
Influence and Persuasion: Effective public communication can shape opinions and motivate actions, crucial in oral communication for social purposes.
Educational Role: In academic contexts, it facilitates learning and discussion, demonstrating the value of oral communication in college.
Professional Skill: Public communication skills are indispensable for success in various careers, highlighting the role of oral communication in the workplace.
Community Mobilization: It’s key in engaging communities, especially in oral communication for civic engagement.
Cultural Sharing: Public speaking allows for cultural expression and sharing, an aspect of oral communication in cultural contexts.
Crisis Communication: In emergencies, it’s critical for providing instructions and information, underscoring the importance of oral communication in crisis management.
What is the Purpose of Public Communication in Oral Communication?
Public communication in oral communication serves several key purposes, each contributing to the effectiveness and impact of the message delivered to a broad audience.
Informing and Educating: One of the primary purposes is to inform or educate an audience about specific topics, ideas, or issues. This aspect is vital in settings like academic lectures, informational briefings, or public awareness campaigns.
Persuading and Influencing: Public communication is often used to persuade or influence an audience, such as in political speeches, marketing presentations, or advocacy efforts. It aims to shape opinions, encourage action, or change behaviors.
Entertaining: At times, the purpose is to entertain, as seen in storytelling, theatrical performances, or certain types of speeches. This use of oral communication aims to engage and captivate the audience.
Building Connections: Public communication helps in building connections between the speaker and the audience, fostering a sense of community or shared understanding. It’s crucial in creating rapport and establishing trust.
Inspiring and Motivating: It is also used to inspire and motivate people, especially in motivational talks, keynote speeches, or inspirational addresses. This form of oral communication seeks to uplift and energize the audience.
Initiating Dialogue and Discussion: Lastly, it can initiate broader dialogue and discussion on various topics, promoting public discourse and democratic participation.
What are the Skills of Public Communication in Oral Communication?
To effectively engage in public communication in oral communication, several key skills are essential:
Clarity and Articulation: The ability to articulate thoughts clearly and concisely is crucial. This involves using precise language and a well-structured flow of ideas.
Audience Engagement: Skilled public communicators know how to engage and hold the audience’s attention, using techniques like storytelling, humor, and rhetorical questions.
Nonverbal Communication: Effective use of body language, gestures, facial expressions, and eye contact enhances the message and keeps the audience engaged.
Voice Modulation and Projection: Good control over voice modulation and the ability to project one’s voice ensures that the message is heard clearly by everyone in the audience.
Persuasive Techniques: Understanding and utilizing persuasive techniques are vital for influencing the audience’s thoughts and actions.
Preparation and Research: Thorough preparation and research on the topic provide depth and authenticity to the communication.
Listening and Responsiveness: Being responsive to the audience’s reactions and adapting the message accordingly is a crucial skill in oral communication.
Emotional Intelligence: The ability to connect emotionally with the audience, understanding their mood and expectations, is key to successful public communication.
Confidence and Presence: Lastly, confidence and a strong stage presence help in establishing credibility and keeping the audience’s attention.
How to Improve Public Communication in Oral Communication?
Improving public communication skills in oral communication involves several steps:
Practice Regularly: Like any skill, public speaking improves with practice. Seek opportunities to speak in public.
Seek Constructive Feedback: Constructive criticism from peers or mentors is invaluable for improvement.
Join Speaking Clubs or Workshops: Organizations like Toastmasters provide a platform for practicing and improving public speaking skills.
Study Effective Speakers: Analyze speeches by accomplished public speakers to learn techniques and styles.
Work on Nonverbal Skills: Practice body language, facial expressions, and gestures that complement your verbal message.
Record and Review: Record your speeches and presentations to identify areas for improvement.
Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with current topics and trends relevant to your field for more engaging discussions.
Manage Anxiety: Learn techniques to manage public speaking anxiety, such as deep breathing and positive visualization.
By following these steps, you can continuously improve your public communication abilities, making your oral communication more impactful and effective.
For further enrichment in public communication skills, the Toastmasters International website offers an array of resources and opportunities to practice and refine public speaking skills in a supportive environment. Additionally, Harvard University’s Public Speaking Course provides invaluable insights and strategies to enhance one’s ability to speak confidently and effectively in public settings. These resources complement the knowledge and skills discussed in this guide, providing practical avenues for applying and advancing your public communication abilities.


