Road vs Street – Meanings, Examples, Differences, Usage
The distinction between “road” and “street” emerges as a topic often overlooked. While these terms are frequently employed interchangeably, understanding their subtle disparities is crucial, particularly in providing accurate directions. This article aims to shed light on the differentiation between the two, offering clarity to those who encounter confusion. Exploring various aspects such as definitions, usage contexts, and distinguishing features, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how to navigate the linguistic landscape where “road” and “street” intersect.
Road and Street – Meanings
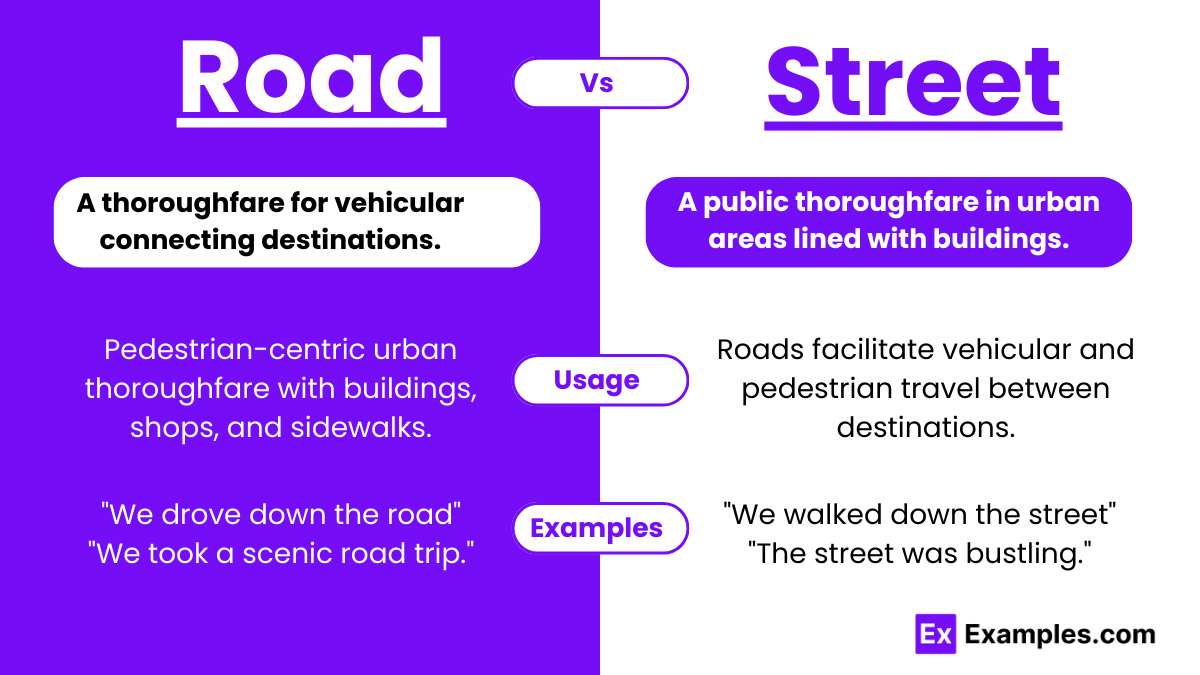
- A road typically refers to a thoroughfare, pathway, or route designed for vehicular or pedestrian travel, connecting various destinations within a geographical area. Roads can vary significantly in size, ranging from narrow rural lanes to expansive multi-lane highways, accommodating diverse modes of transportation.
- A street commonly denotes a public thoroughfare within a built environment, typically lined with buildings, residences, commercial establishments, or other structures. Unlike roads, streets often emphasize human-scale elements, fostering pedestrian activity, social interactions, and community engagement.
Summary
How To Pronounce Road and Street
- The word “road” is pronounced as /roʊd/ with the emphasis on the first syllable, rhyming with “load” or “toad.”
- The pronunciation of “street” is /striːt/ with the emphasis on the first syllable, rhyming with “treat” or “fleet.”
Differences Between Road and Street
| Aspect | Road | Street |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A thoroughfare for vehicular or pedestrian travel, typically connecting destinations. | A public thoroughfare within urban areas, often lined with buildings and fostering pedestrian activity. |
| Location | Found in both rural and urban environments, varying in size and capacity. | Primarily located in urban settings, integrated with surrounding infrastructure and amenities. |
| Usage | Emphasizes transportation efficiency and connectivity between regions or communities. | Prioritizes pedestrian activity, community engagement, and urban aesthetics. |
| Characteristics | Can range from narrow rural lanes to expansive multi-lane highways, accommodating diverse modes of transportation. | Integrates with surrounding buildings and infrastructure, featuring sidewalks, street furniture, and architectural aesthetics. |
| Importance | Vital for facilitating economic activities, social interactions, and cultural exchange across regions. | Contributes to the vibrancy and character of urban areas, enhancing walkability and quality of life for residents. |
How to Remember the Differences Between “Road” and “Street”
- Rural vs. Urban: Think of “Road” as primarily rural, connecting distant places, while “Street” is urban, weaving through buildings.
- Purpose: “Road” emphasizes long-distance travel and transportation efficiency, like highways. “Street” emphasizes local navigation, with sidewalks and shops.
- Setting: “Roads” are often wide and open, while “Streets” are narrower, bustling with activity, and lined with buildings.
When to use Road and Street
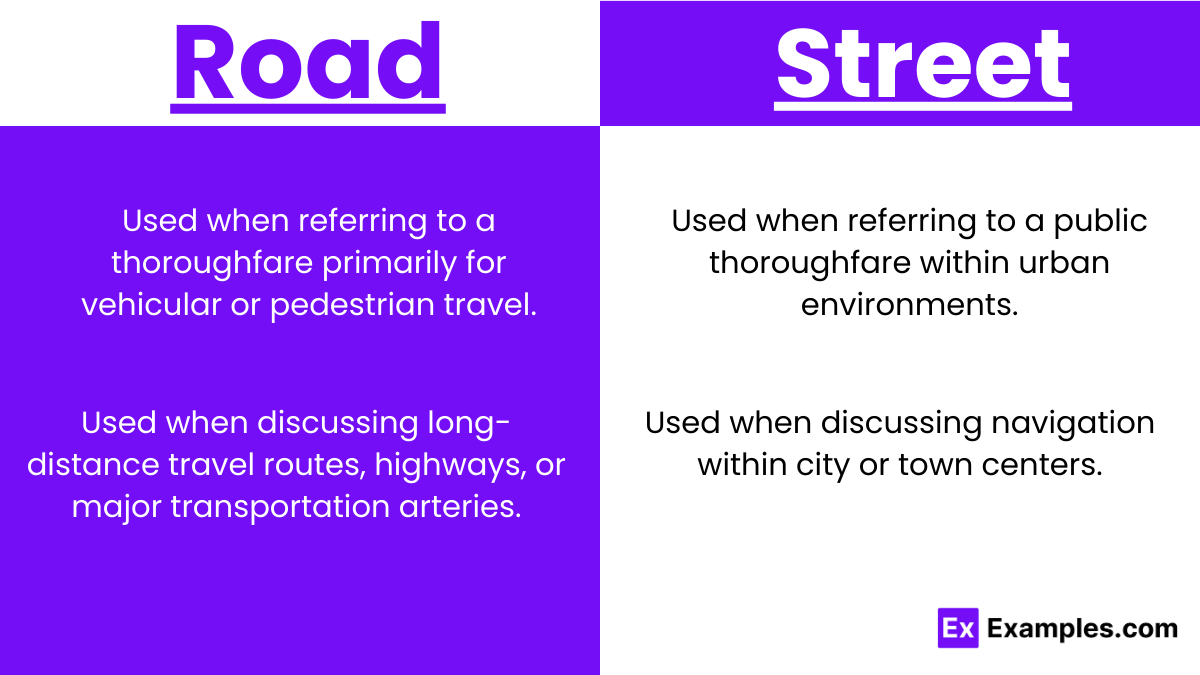
Usage of “Road”:
- When referring to a thoroughfare primarily for vehicular or pedestrian travel, especially in rural or suburban areas.
- When discussing long-distance travel routes, highways, or major transportation arteries.
- In contexts emphasizing transportation infrastructure, such as discussions about road construction, maintenance, or traffic flow.
Usage of “Street”:
- When referring to a public thoroughfare within urban environments, often lined with buildings and accommodating pedestrian activity.
- When discussing navigation within city or town centers, including addresses, intersections, or landmarks.
- In contexts emphasizing urban planning, community development, or the social dynamics of city life.
Road and Street Examples

Examples of “Road”
- We live on Pine road, just off the highway.
- The scenic road meandered through the countryside, offering breathtaking views.
- Elm road was closed for repairs, so we had to take an alternative route.
- The road ahead was lined with tall trees, creating a picturesque tunnel.
- Main road is always busy during rush hour, so we try to avoid it.
Examples of “Street”
- Let’s meet at the café on Maple street for lunch.
- The bustling street was filled with shoppers browsing through the market stalls.
- Oak street is known for its charming Victorian houses and tree-lined sidewalks.
- We strolled down the cobblestone street, admiring the historic architecture.
- We walked hand in hand down the cobblestone street.
Synonyms For Road and Street
| Road Synonyms | Street Synonyms |
|---|---|
| Highway | Avenue |
| Freeway | Boulevard |
| Expressway | Lane |
| Thoroughfare | Alley |
| Route | Way |
| Path | Lane |
| Boulevard | Drive |
| Motorway | Cul-de-sac |
| Lane | Terrace |
| Byway | Crescent |
Exercise
Instructions: Fill in the blanks with the appropriate word, “road” or “street,” to complete each sentence correctly.
- We took a leisurely drive down the scenic _______________.
- The shops on Main _______________ were bustling with activity.
- Elm _______________ is known for its charming tree-lined sidewalks.
- The construction crew worked tirelessly to repair the damaged _______________.
- Fifth _______________ is famous for its upscale boutiques and designer stores.
Answers:
- road
- street
- street
- road
- street
FAQ’S
What is the difference between a road and a street?
A street is usually found in a city or town, and therefore often has houses or buildings on both sides. A road can be in the countryside and might go through a forest or field.
What makes a “road” a place?
A road with no throughway that ends in a loop or cul-de-sac.
Are “street” and “road” interchangeable?
There is a difference. Streets are generally in an urban setting, while roads are rural or sometimes suburban.
What structure is a road?
Yes, a road is civil structure or the structure which is constructed by concrete, sand, aggregate and metel are civil structure like bridge, dam, road, runway, port, house, etc.
Road vs Street – Meanings, Examples, Differences, Usage
The distinction between “road” and “street” emerges as a topic often overlooked. While these terms are frequently employed interchangeably, understanding their subtle disparities is crucial, particularly in providing accurate directions. This article aims to shed light on the differentiation between the two, offering clarity to those who encounter confusion. Exploring various aspects such as definitions, usage contexts, and distinguishing features, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how to navigate the linguistic landscape where “road” and “street” intersect.
Road and Street – Meanings
A road typically refers to a thoroughfare, pathway, or route designed for vehicular or pedestrian travel, connecting various destinations within a geographical area. Roads can vary significantly in size, ranging from narrow rural lanes to expansive multi-lane highways, accommodating diverse modes of transportation.
A street commonly denotes a public thoroughfare within a built environment, typically lined with buildings, residences, commercial establishments, or other structures. Unlike roads, streets often emphasize human-scale elements, fostering pedestrian activity, social interactions, and community engagement.
Summary
A “Road” serves as a designated route for vehicular and pedestrian travel, connecting various destinations and playing a pivotal role in transportation infrastructure. Conversely, a “Street” represents a public thoroughfare within urban environments, characterized by its integration with surrounding buildings and infrastructure. Both “Roads” and “Streets” contribute uniquely to the fabric of human civilization, serving as conduits for mobility, interaction, and connectivity across landscapes and cityscapes alike.
How To Pronounce Road and Street
The word “road” is pronounced as /roʊd/ with the emphasis on the first syllable, rhyming with “load” or “toad.”
The pronunciation of “street” is /striːt/ with the emphasis on the first syllable, rhyming with “treat” or “fleet.”
Differences Between Road and Street
Aspect | Road | Street |
|---|---|---|
Definition | A thoroughfare for vehicular or pedestrian travel, typically connecting destinations. | A public thoroughfare within urban areas, often lined with buildings and fostering pedestrian activity. |
Location | Found in both rural and urban environments, varying in size and capacity. | Primarily located in urban settings, integrated with surrounding infrastructure and amenities. |
Usage | Emphasizes transportation efficiency and connectivity between regions or communities. | Prioritizes pedestrian activity, community engagement, and urban aesthetics. |
Characteristics | Can range from narrow rural lanes to expansive multi-lane highways, accommodating diverse modes of transportation. | Integrates with surrounding buildings and infrastructure, featuring sidewalks, street furniture, and architectural aesthetics. |
Importance | Vital for facilitating economic activities, social interactions, and cultural exchange across regions. | Contributes to the vibrancy and character of urban areas, enhancing walkability and quality of life for residents. |
How to Remember the Differences Between “Road” and “Street”
Rural vs. Urban: Think of “Road” as primarily rural, connecting distant places, while “Street” is urban, weaving through buildings.
Purpose: “Road” emphasizes long-distance travel and transportation efficiency, like highways. “Street” emphasizes local navigation, with sidewalks and shops.
Setting: “Roads” are often wide and open, while “Streets” are narrower, bustling with activity, and lined with buildings.
When to use Road and Street

Usage of “Road”:
When referring to a thoroughfare primarily for vehicular or pedestrian travel, especially in rural or suburban areas.
When discussing long-distance travel routes, highways, or major transportation arteries.
In contexts emphasizing transportation infrastructure, such as discussions about road construction, maintenance, or traffic flow.
Usage of “Street”:
When referring to a public thoroughfare within urban environments, often lined with buildings and accommodating pedestrian activity.
When discussing navigation within city or town centers, including addresses, intersections, or landmarks.
In contexts emphasizing urban planning, community development, or the social dynamics of city life.
Road and Street Examples

Examples of “Road”
We live on Pine road, just off the highway.
The scenic road meandered through the countryside, offering breathtaking views.
Elm road was closed for repairs, so we had to take an alternative route.
The road ahead was lined with tall trees, creating a picturesque tunnel.
Main road is always busy during rush hour, so we try to avoid it.
Examples of “Street”
Let’s meet at the café on Maple street for lunch.
The bustling street was filled with shoppers browsing through the market stalls.
Oak street is known for its charming Victorian houses and tree-lined sidewalks.
We strolled down the cobblestone street, admiring the historic architecture.
We walked hand in hand down the cobblestone street.
Synonyms For Road and Street
Road Synonyms | Street Synonyms |
|---|---|
Highway | Avenue |
Freeway | Boulevard |
Expressway | Lane |
Thoroughfare | Alley |
Route | Way |
Path | Lane |
Boulevard | Drive |
Motorway | Cul-de-sac |
Lane | Terrace |
Byway | Crescent |
Exercise
Instructions: Fill in the blanks with the appropriate word, “road” or “street,” to complete each sentence correctly.
We took a leisurely drive down the scenic _______________.
The shops on Main _______________ were bustling with activity.
Elm _______________ is known for its charming tree-lined sidewalks.
The construction crew worked tirelessly to repair the damaged _______________.
Fifth _______________ is famous for its upscale boutiques and designer stores.
Answers:
road
street
street
road
street
FAQ’S
What is the difference between a road and a street?
A street is usually found in a city or town, and therefore often has houses or buildings on both sides. A road can be in the countryside and might go through a forest or field.
What makes a “road” a place?
A road with no throughway that ends in a loop or cul-de-sac.
Are “street” and “road” interchangeable?
There is a difference. Streets are generally in an urban setting, while roads are rural or sometimes suburban.
What structure is a road?
Yes, a road is civil structure or the structure which is constructed by concrete, sand, aggregate and metel are civil structure like bridge, dam, road, runway, port, house, etc.

