100+ Sight Words List, Meaning, PDF
Sight words are common words such as “the,” “it,” and “and,” are fundamental for early readers, helping children become faster and more fluent in their reading journey. Recognized instantly by sight rather than sounded out, these words form a core part of early literacy, enabling smoother reading and comprehension. Often referred to as star words, core words, or popcorn words due to their frequent appearance in texts, mastering these words allows children to focus less on the mechanics of reading and more on understanding content. For parents eager to bolster their child’s language skills, introducing sight words like “please,” “never,” and “look” is a crucial step. This not only aids in reading fluency but also enhances communication, making sight words an essential element in teaching kids English and fostering a love for reading from an early age.
What are Sight Words?
Sight words are commonly used words that children are encouraged to recognize instantly by sight, without needing to use phonetic decoding strategies. These words, such as “the,” “and,” “it,” and “you,” frequently appear in texts and are foundational to reading fluently. Because many sight words do not follow regular phonetic rules or are used so frequently, it is more efficient for early readers to memorize them. Recognizing these words on sight helps children read more smoothly and quickly, contributing significantly to their overall reading comprehension and efficiency. Sight words are a critical component of early literacy education, aimed at helping kids build a solid foundation for reading and writing skills.
Some sight words don’t follow spelling rules
Some sight words don’t adhere to conventional spelling rules, making them challenging for children to decode using phonics alone. Words like “said,” “are,” and “was” exemplify how sight words can defy the typical patterns of English spelling, prompting the need for these words to be memorized. This memorization allows children to recognize these words instantly, facilitating smoother and faster reading, which is crucial for developing early literacy skills.
What are the most common sight word lists?
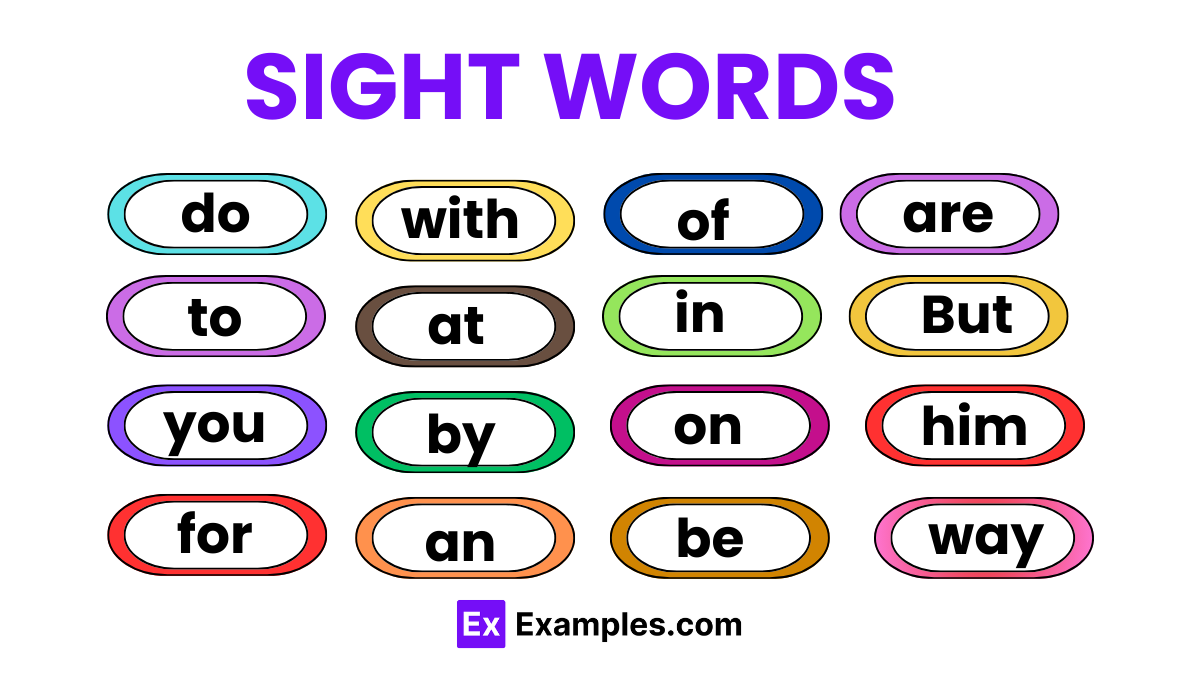
| the | of | and | a |
| to | in | is | it |
| you | that | he | was |
| for | on | are | as |
| with | his | they | I |
| at | be | this | have |
| from | or | one | had |
| by | not | but | what |
| were | we | when | your |
| can | said | there | use |
| an | each | which | she |
| do | how | their | if |
| will | up | other | about |
| many | out | so | these |
| then | them | her | would |
| make | like | him | into |
| time | has | look | two |
| more | write | go | see |
| number | no | way | could |
| people | my | than | first |
How can I teach sight words?
- Introduction in Context: Introduce new sight words within the context of sentences or stories. This helps children understand the word’s meaning and usage.
- Flashcards: Use flashcards to practice sight words. Show the word, say it out loud, and use it in a sentence. Repeat this process regularly to reinforce memory.
- Word Walls: Create a word wall in your classroom or home. Add new sight words to the wall as they are learned, and encourage children to read them often.
- Games and Activities: Incorporate sight words into games and activities. For example, sight word bingo, memory match games, and word hunts can make learning fun and interactive.
- Use of Technology: There are many apps and online games designed to help children learn sight words through interactive play.
- Writing Practice: Encourage children to write sentences using sight words. This not only reinforces recognition but also helps with spelling and grammar skills.
- Reading Together: Read books together and point out sight words as you come across them. This reinforces the words’ importance and shows them in various contexts.
- Consistent Review: Regular review is key to mastery. Spend a few minutes each day reviewing sight words, gradually increasing the words’ difficulty as children become more proficient.
- Positive Reinforcement: Use praise and positive reinforcement to encourage and motivate children as they learn new sight words.
What Are The Types Of Sight Words?
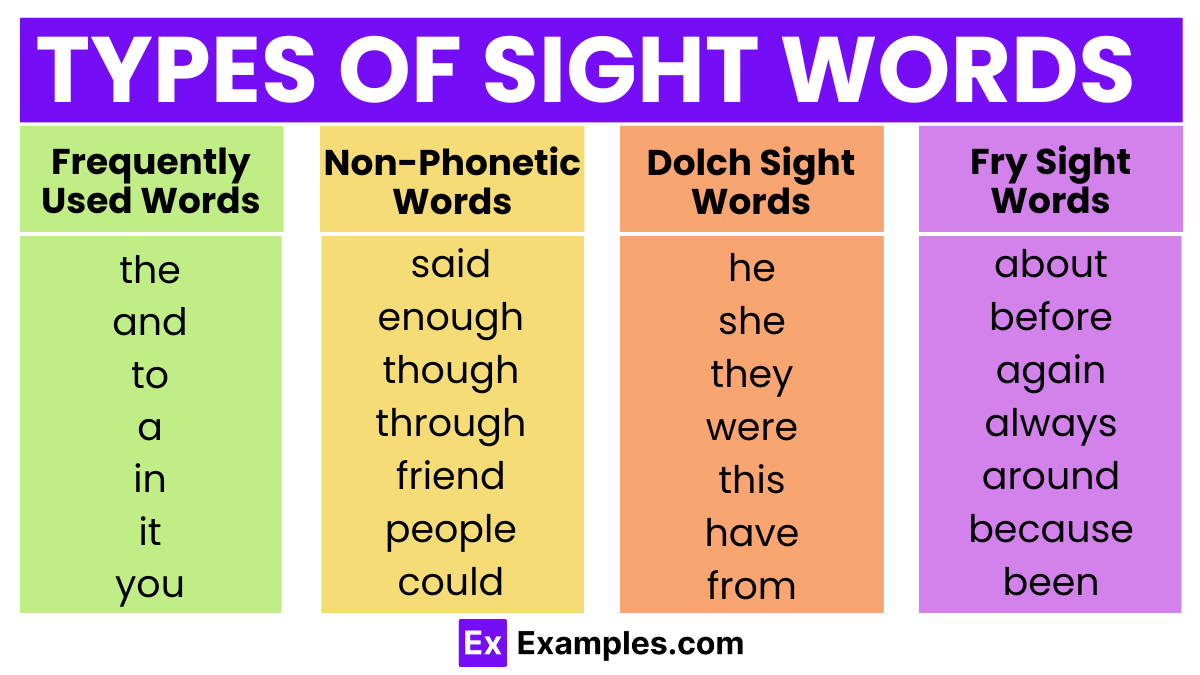
1. Frequently Used Words
These are words that appear with high frequency in written English across various types of texts, including books, magazines, and online articles. Teaching children these words helps improve reading fluency because they encounter them often. Examples include “and,” “the,” “he,” and “it.” Recognizing these words quickly allows readers to comprehend texts more smoothly and with greater speed.
2. Non-Phonetic Words
Non-phonetic words do not follow standard phonetic rules, making them difficult to decode through sounding out. These words can be particularly challenging for beginning readers, as their pronunciation and spelling do not match in a predictable way. Examples of non-phonetic sight words include “said,” “enough,” and “women.” Memorizing these words as whole units enables readers to recognize them instantly, aiding in reading comprehension and fluency.
3. Dolch Sight Words
The Dolch Sight Words list was compiled by Edward William Dolch, PhD, in 1936 and includes 220 service words (words with no pictures possible) and 95 high-frequency nouns. These words were identified as the most common and necessary words for reading and are divided by grade levels, ranging from pre-kindergarten to second grade, with an additional list of nouns. The Dolch list is still widely used in education for teaching reading and emphasizes words that students need to recognize effortlessly to achieve reading fluency.
4. Fry Sight Words
Developed by Dr. Edward Fry in the 1950s (and updated in 1980), the Fry Sight Words list expands on the Dolch list and includes 1,000 of the most common English words arranged by frequency. Fry’s research highlighted these words as covering a significant portion of material kids encounter in their reading. The list is divided into groups of 100, making it easier for students to tackle in segments. Mastery of the Fry Sight Words supports reading fluency across more diverse texts and grade levels.
Benefits Of Learning Sight Words For Kids
Learning sight words offers several key benefits for children:
- Improves Reading Fluency: Recognizing sight words quickly allows children to read more fluidly, increasing their speed and comprehension.
- Enhances Comprehension: By not having to decode every word, children can focus better on the meaning of the text.
- Builds Confidence: Mastery of sight words can boost children’s confidence in their reading abilities, encouraging them to explore more challenging texts.
- Provides a Foundation: Sight words serve as building blocks for early literacy, supporting further language development and reading skills.
At What Age Should Your Child Start Learning Sight Words?
Children can start learning sight words as early as preschool, around ages 4 to 5. At this stage, focus on introducing a few simple words in a fun and engaging way. The learning process should continue into kindergarten and the early grades, as children become more capable of handling a larger vocabulary. It’s important to adjust the pace based on the child’s individual development, interest, and readiness to ensure a positive learning experience.
Benefits Of Learning Sight Words For Kids
- Improves Reading Fluency: Recognizing sight words by sight rather than sounding them out can significantly speed up the reading process. This improved fluency makes reading more enjoyable and less frustrating for early readers.
- Boosts Reading Comprehension: When children don’t have to spend time decoding every word, they can focus more on the meaning of the text. This leads to better understanding and retention of the material they read.
- Enhances Confidence: Mastery of sight words can give children a sense of achievement and boost their confidence in their reading abilities. This increased self-assurance can encourage them to explore more challenging texts and enjoy reading as a leisure activity.
- Facilitates Writing Skills: Knowing sight words by memory also aids in writing. Children who are familiar with these words can write more fluently and expressively because they don’t have to spend as much time thinking about how to spell common words.
- Provides a Foundation for Learning New Words: Understanding and recognizing sight words helps children learn new words more easily. They can use the context surrounding known sight words to decipher the meaning of new vocabulary.
- Supports Academic Success: Since sight words make up a large percentage of the text in early reading materials, being able to recognize these words is closely linked to overall academic success. Children who master sight words early on are often better prepared for the reading and writing demands of later grades.
Teaching Sight Words To Your Child
eaching sight words to your child is a crucial step in their reading development. Sight words are common words that appear frequently in text but may not follow conventional phonetic rules, making them challenging for children to decode. Recognizing these words on sight helps children read more fluently and confidently. Here’s how to effectively teach sight words to your child:
Start Simple
Begin with a small, manageable list of sight words. Choose words that are most common in the books your child is reading or will read. Words like “the,” “and,” “a,” “to,” and “in” are good starting points.
Use Flashcards
Create or buy sight word flashcards. Flashcards are a versatile tool for teaching sight words. Show the word, say it aloud, and use it in a sentence. Encourage your child to repeat after you.
Incorporate Words into Daily Activities
Label objects around the house with sight words or play games that involve finding and reading sight words in context. This immersion strategy helps children recognize these words in their environment.
Make Learning Interactive
Engage your child with activities like sight word bingo, memory games, or word hunts. Apps and online games designed for sight word learning can also be effective, offering a fun and interactive way to practice.
Practice with Books
Choose books that are appropriate for your child’s reading level and contain a good number of sight words. Read together, pointing out sight words as you go along. Ask your child to find sight words on each page.
Consistent Practice
Dedicate a few minutes each day to practice sight words. Consistency is key to reinforcing what your child learns and ensuring they remember the words.
Use Creative Methods
Encourage your child to write sight words in sand, with finger paint, or using magnetic letters. These tactile activities can make learning more engaging and memorable.
How Many Sight Words Can You Teach To Your Child?
The number of sight words you can teach your child varies significantly depending on their age, developmental stage, and readiness to learn. However, there are general guidelines you can follow to ensure the learning process is effective and not overwhelming for your child.
For Preschoolers (Ages 3-4)
Start with a small set of about 5-10 sight words. At this age, the focus should be on introducing the concept of sight words and building interest in word recognition.
For Kindergarteners (Ages 5-6)
Aim to teach around 20-50 sight words throughout the year. Kindergarten curriculums often include lists of sight words that are introduced gradually over the school year.
For First Graders (Ages 6-7)
First graders can typically handle learning 100-150 sight words throughout the year. This builds on their kindergarten foundation and prepares them for more complex reading.
For Second Graders and Beyond (Ages 7+)
By second grade, children can learn an additional 100-200 sight words, as their reading skills become more advanced. At this stage, the focus shifts to more complex words and phrases that appear frequently in their reading materials.
List of sight words for Children
| Sight Words for Preschool | Sight Words for Kindergarten | Sight Words for 1st Grade | Sight Words for 2nd Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | all | after | always |
| a | am | again | around |
| and | are | an | because |
| the | can | any | been |
| to | do | as | before |
| is | go | ask | best |
| you | he | by | both |
| we | it | could | buy |
| see | like | every | call |
| my | me | fly | cold |
Examples Of Sentences With Sight Words For Kids
- I see the cat.
- You are my best friend.
- We go to the park.
- He has a red ball.
- Can you play with me?
- She likes to read books.
- It is time for lunch.
- Look at the big dog.
- The sun is very bright.
- They have two apples.
- Do you like to draw?
- What is your name?
- Please sit here.
- This is my house.
- That was a fun game.
- Where is my hat?
- Who are you?
- Why is the sky blue?
- When will we go home?
- How do you do that
Tips to Remember Sight Words
Sight words are critical for early readers to recognize instantly without needing to use decoding strategies. Here are several effective tips for helping learners remember sight words, enhancing their reading fluency and comprehension:
1. Visual Memory
- Encourage the use of flashcards. Colorful cards with the word displayed prominently can make learning more engaging.
- Use word walls in the classroom or at home. Regularly adding new words and referring to them can reinforce memory.
2. Repetition and Routine
- Practice sight words daily. Short, frequent sessions are more effective than less frequent, longer sessions.
- Incorporate sight words into everyday activities. Label objects around the house or classroom with sight words to integrate learning into daily life.
3. Engaging Methods
- Utilize games and apps that focus on sight words. Interactive and fun methods can enhance engagement and retention.
- Sing sight word songs. Music and rhythm can help memorize words more easily.
4. Contextual Learning
- Read books that emphasize sight words. Contextualizing words within stories can aid in understanding and memorization.
- Write simple sentences using sight words. This helps in understanding the usage and function of the words in language.
5. Multi-Sensory Approaches
- Practice writing words in sand, shaving cream, or with finger paint. The tactile experience can help in memorizing words.
- Use letter tiles or magnets to build words. Physically manipulating letters to form words can reinforce learning through touch.
6. Personal Connection
- Encourage learners to write their own stories using sight words. Personalization of learning can increase interest and motivation.
- Customize learning materials with the child’s interests. Using words in sentences or stories about their favorite characters or activities can make learning more relevant and engaging.
What’s the difference between sight words and high-frequency words?
| Aspect | Sight Words | High-Frequency Words |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Words that are taught to be recognized by sight without sounding them out. | Words that appear most frequently in written language. |
| Purpose | To enhance reading fluency by enabling instant recognition. | To identify words that readers are most likely to encounter, aiding in reading efficiency. |
| Examples | “the,” “and,” “it” | “the,” “of,” “and” |
| Teaching Approach | Often memorized due to their irregular phonetic patterns or because they are essential for sentence structure. | Taught for recognition, but may also be decoded phonetically. |
| Overlap | Many sight words are also high-frequency words due to their common use in text. | Not all high-frequency words are considered sight words, especially if they can be easily phonetically decoded. |
Exercise to Practice
1. I want to __ to the park.
- go
- goes
- gone
- going
2. She __ a beautiful flower in the garden.
- see
- sees
- saw
- seed
3. Can you __ me the book, please?
- passed
- pass
- pace
- paste
4. They are __ to the zoo tomorrow.
- go
- goes
- gone
- going
5. We have a cat and a __.
- dog
- dig
- dug
- dogs
6. He can __ really fast.
- ran
- run
- runs
- ring
7. I __ my homework after school.
- do
- does
- did
- done
8. It is __ outside today.
- sun
- sunny
- suns
- sunlight
9. Please __ quietly.
- sit
- sits
- sat
- seat
10. She likes to __ stories.
- tell
- tells
- told
- telling
Answers
- go – The correct answer is A. go.
- see – The correct answer is B. see.
- can – The correct answer is D. can.
- the – The correct answer is C. the.
- we – The correct answer is A. we.
- to – The correct answer is B. to.
- and – The correct answer is C. and.
- you – The correct answer is D. you.
- is – The correct answer is A. is.
- in – The correct answer is B. in.



