20+ Simple Past Tense Examples
Simple Past Tense is used to describe actions completed at a specific time in the past. Regular verbs add “-ed,” while irregular verbs vary, e.g., “saw,” “took,” “went.” It expresses completed actions, series of events, and past habits.
What is Simple Past Tense?
The simple past tense is a verb tense used to describe actions that were completed at a specific time in the past. This tense is typically formed by adding “-ed” to the end of a regular verb, such as “walked,” “jumped,” or “smiled.” For irregular verbs, there are unique past tense forms, such as “saw” (from “see”), “took” (from “take”), and “went” (from “go”). The simple past is not only used to describe actions that have no connection to the present, but also to narrate a series of completed actions and to describe past habits or states. It is a fundamental aspect of English grammar that enables clear communication about previous events.
Formula for Simple Past Tense
Structure of Simple Past Tense
Learning the structure of the simple past tense can be simplified by analyzing its application in positive, negative, interrogative, and negative interrogative forms. The table below provides a clear understanding of these variations.
| Format | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | Subject + Verb in the past form (base form of the verb + ed/d for regular verbs or past tense form of the irregular verbs) | He walked to the store. She enjoyed the concert. |
| Negative | Subject + Didn’t + Verb in the base form | He did not walk to the store. She did not enjoy the concert. |
| Interrogative | Did + Subject + Verb in the base form | Did he walk to the store? Did she enjoy the concert? |
| Negative Interrogative | Didn’t + Subject + Verb in the base form | Didn’t he walk to the store? Didn’t she enjoy the concert? |
Rules of Simple Past Tense
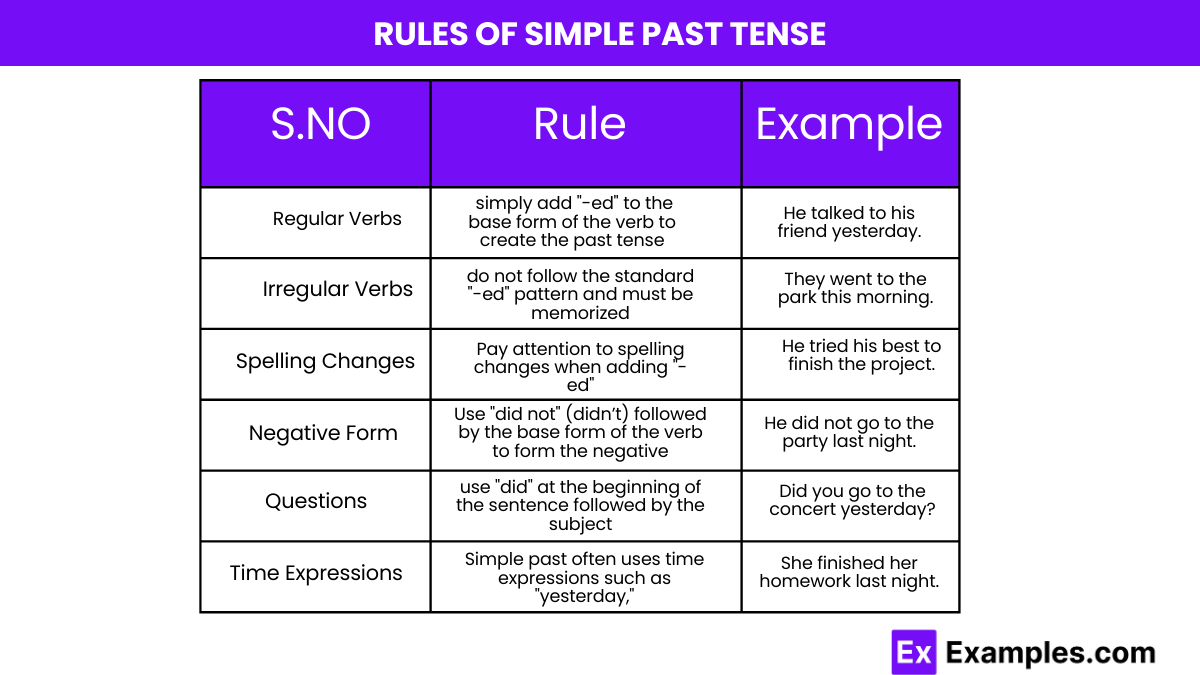
Understanding the simple past tense is essential for effective communication in English. Here’s a straightforward guide to the rules:
- Regular Verbs: For most regular verbs, simply add “-ed” to the base form of the verb to create the past tense. For example, “talk” becomes “talked” and “walk” becomes “walked.”
- Irregular Verbs: Irregular verbs do not follow the standard “-ed” pattern and must be memorized. For example, “go” becomes “went,” and “see” becomes “saw.”
- Spelling Changes: Pay attention to spelling changes when adding “-ed”:
- If the verb ends in “e,” just add “d” (e.g., “love” becomes “loved”).
- If the verb ends in a consonant followed by a “y,” change the “y” to “i” and add “ed” (e.g., “try” becomes “tried”).
- If the verb is a single-syllable word that ends in a single vowel followed by a consonant, double the consonant and add “ed” (e.g., “stop” becomes “stopped”).
- Negative Form: Use “did not” (didn’t) followed by the base form of the verb to form the negative. For example, “did not go,” “did not see.”
- Questions: For questions, use “did” at the beginning of the sentence followed by the subject and the base form of the verb. For example, “Did you go?” “Did she see?”
- Time Expressions: Simple past often uses time expressions such as “yesterday,” “last week,” “in 1990,” “two days ago,” etc.
How to use the Simple Past Tense
Using the simple past tense effectively involves understanding its application in different contexts. Here’s a guide to help you use the simple past tense correctly:
Completed Actions
- Use the simple past to talk about actions that started and finished at a specific time in the past.
- Example: She visited her grandparents last weekend.
Sequences of Actions
- When narrating a series of completed actions, use the simple past for each action.
- Example: He woke up, brushed his teeth, and went to school.
Facts or Generalizations about the Past
- Use this tense to state facts or generalizations which are no longer true.
- Example: Dinosaurs lived millions of years ago.
Past Habits
Use the simple past to describe habits or repeated actions that occurred in the past but do not happen now. Example: I walked to school every day when I was a child.
Conditions in the Past
- It’s useful for discussing conditions that were true for some time in the past.
- Example: It rained every day last week.
Polite Inquiries About Personal Experiences
- Often, it’s used to ask someone about past experiences without specifying the exact time.
- Example: Did you enjoy the concert?
Indirect Speech
- When reporting speech or thoughts from the past, shift present tense verbs in direct speech to the simple past in indirect speech.
- Example: She said she felt great.
Forming Negative Sentences and Questions
- To make a sentence negative, use “did not” followed by the base form of the verb. For questions, place “did” before the subject, followed by the base form of the verb.
- Examples: He didn’t like the movie. / Did you see that bird?
Forming the Simple Past Tense – Examples
Here are examples demonstrating the formation of the simple past tense with regular and irregular verbs, including positive, negative, and interrogative forms:
Patterns of Simple Past Tense for Regular Verbs
| Base Form | Simple Past Tense | Example |
|---|---|---|
| walk | walked | She walked to the store. |
| play | played | They played basketball. |
| wash | washed | He washed the car yesterday. |
| try | tried | I tried a new recipe. |
| stop | stopped | We stopped by your house. |
Simple Past Tense of “to be,” “to have,” “to do”
| Verb | Simple Past Tense | Example |
|---|---|---|
| be | was/were | I was happy. / They were late. |
| have | had | She had a cold last week. |
| do | did | He did his homework. |
Examples of Simple Past Tense
- She laughed at the joke.
- He cooked dinner for his family.
- They went to the park yesterday.
- We played soccer last weekend.
- You said you would call me.
- The cat slept on the sofa.
- I read an interesting book.
- She danced beautifully at the party.
- He wrote a letter to his friend.
- They watched a movie last night.
- We walked to school together.
- You drove too fast yesterday.
- The dog barked at the stranger.
- I forgot my wallet at home.
- She took her medicine this morning.
- He fixed the broken window.
- They sang their favorite songs.
- We visited our grandparents last month.
- You met her at the library.
- The teacher explained the lesson clearly.
Simple Past Tense sentences Exercises
Exercise 1: Choose the Correct Verb Form
- I (ate, eat) an apple for lunch.
- She (find, found) a lost kitten outside her house.
- They (went, goes) to the beach during their vacation.
- We (played, play) chess yesterday evening.
- He (drove, drive) his car to work last Monday.
Answers :
- I ate an apple for lunch
- She found a lost kitten outside her house.
- They went to the beach during their vacation.
- We played chess yesterday evening.
- He drove his car to work last Monday.
Exercise 2: Fill in the Blanks
Fill in the blanks with the simple past tense form of the verbs given in brackets.
- Yesterday, I __________ (run) in the park.
- Last week, she __________ (teach) us about the solar system.
- We __________ (have) a great time at the party.
- He __________ (send) a text message an hour ago.
- They __________ (build) a new house last year.
Answers :
- Yesterday,I ran in the park.
- Last week, she taught us about the solar system.
- We had a great time at the party.
- He sent a text message an hour ago.
- They built a new house last year.
FAQ’s
When do we use the Simple Past Tense?
We use the Simple Past Tense to talk about completed actions or events that happened at a specific point in the past. It is also used to describe habits or actions that were repeated in the past but are not ongoing.
Can the Simple Past Tense be used with time expressions?
Yes, the Simple Past Tense often accompanies time expressions that indicate when the action or event occurred, such as “yesterday”, “last week”, “in 2005”.
Is there any difference between regular and irregular verbs in the Simple Past Tense?
Yes, while regular verbs follow a consistent pattern for forming the Simple Past Tense, irregular verbs do not. Each irregular verb has its own unique past tense form that needs to be memorized.
Can the Simple Past Tense be used to express duration?
No, the Simple Past Tense is typically used to describe actions or events that have a definite endpoint in the past. For expressing duration, the Past Continuous Tense or other tenses may be more appropriate.
Do all sentences in the Simple Past Tense require a subject?
No, in English, it’s common to omit the subject in the Simple Past Tense if it’s clear from the context who or what is performing the action. This is particularly common in informal speech.
Are there any exceptions to the regular formation of the Simple Past Tense with “-ed”?
Yes, some verbs ending in “e” only require adding a “d” instead of “ed”. For example, “love” becomes “loved”. Additionally, some verbs undergo a vowel change, like “run” becomes “ran”.
How can I practice using the Simple Past Tense?
Practice writing sentences or stories using the Simple Past Tense, and try to incorporate both regular and irregular verbs. You can also engage in conversations or role-plays where you describe past events using this tense. Online quizzes and exercises can also be helpful for reinforcement.



