29+ Soft Communication Skills Examples
Soft skills communication is an integral component of effective interpersonal interactions, both in personal and professional contexts. This comprehensive guide delves into various aspects of soft skills, emphasizing their role in enhancing communication efficiency. With a focus on real-world Communication Examples, the guide offers practical insights into how soft skills can be seamlessly integrated into everyday conversations and professional discourse. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply someone looking to improve your interpersonal skills, this guide provides valuable strategies and examples to refine your communicative abilities, making interactions more impactful and meaningful.
30 Examples of soft communication skills
Soft communication skills are essential in navigating the complexities of interpersonal interactions, pivotal in both personal and professional spheres. This guide focuses on 30 unique and impactful examples of soft communication skills, each illustrated with practical, real-world applications. These skills, ranging from empathy and active listening to effective negotiation and conflict resolution, play a crucial role in enhancing understanding, fostering collaboration, and building strong relationships. As we explore these examples, you will gain insights into how to apply these skills in various scenarios, thereby improving your overall communication effectiveness and fostering positive interactions in all areas of life.
- Active Listening: Show genuine interest in others’ words, encouraging open and honest communication. Example: Nod and maintain eye contact during conversations.
- Empathy: Understand and share the feelings of others.
Example: Acknowledge others’ feelings with statements like, “I can see how that would be upsetting.” - Positive Body Language: Use non-verbal cues to show engagement.
Example: Lean in slightly when someone is speaking to show interest. - Clear Articulation: Convey your message in a straightforward and understandable manner.
Example: Speak clearly and avoid using jargon when explaining concepts. - Patience: Give others the time to express themselves without rushing them.
Example: Pause before responding to show you are considering their words. - Constructive Feedback: Provide feedback that is helpful and positive.
Example: Use the sandwich method – positive, improvement, positive. - Adaptability: Adjust your communication style to match the situation.
Example: Use more formal language in a business meeting than in a casual setting. - Respect: Show consideration for others’ viewpoints.
Example: Say, “I understand your point,” even when disagreeing. - Collaboration: Work effectively with others to achieve a common goal.
Example: Encourage team brainstorming sessions. - Persuasion: Influence others while respecting their opinions.
Example: Present benefits and drawbacks when proposing an idea. - Conflict Resolution: Handle disagreements constructively.
Example: Focus on finding a middle ground in disputes. - Emotional Intelligence: Recognize and manage your own emotions and those of others.
Example: If someone is upset, offer a calm response. - Confidence: Communicate your ideas assertively without being aggressive.
Example: Stand tall and use a steady voice when presenting. - Open-mindedness: Be willing to consider different perspectives.
Example: Actively listen to ideas that differ from your own. - Negotiation Skills: Aim for solutions that benefit all parties involved.
Example: Propose compromises during discussions. - Cultural Sensitivity: Respect and adapt to diverse cultural norms.
Example: Be mindful of cultural differences in communication styles. - Storytelling: Use narratives to connect with others emotionally.
Example: Share personal experiences to illustrate points. - Reliability: Be dependable in your communication.
Example: Follow through on promises made during conversations. - Humor: Use light-heartedness to ease tensions.
Example: Share a relevant joke to lighten the mood. - Tactfulness: Communicate sensitively and diplomatically.
Example: Choose your words carefully to avoid offending others. - Active Engagement: Show enthusiasm and interest in interactions.
Example: Ask open-ended questions to encourage discussion. - Critical Thinking: Analyze information before responding.
Example: Take a moment to think before offering your opinion. - Positivity: Maintain a positive tone in your communication.
Example: Focus on solutions rather than problems. - Assertiveness: State your needs and opinions respectfully.
Example: Clearly express your viewpoint without undermining others. - Effective Questioning: Ask questions that elicit meaningful responses.
Example: Use questions to probe deeper into topics. - Feedback Reception: Be open to receiving and acting on feedback.
Example: Ask for clarification if feedback is not clear. - Presentation Skills: Communicate your ideas effectively to groups.
Example: Use visual aids to enhance your message. - Listening for Understanding: Listen to comprehend, not just to respond.
Example: Paraphrase what was said to ensure understanding. - Mentoring: Guide others through effective communication.
Example: Offer advice and feedback based on your experiences. - Networking: Build relationships through effective communication.
Example: Engage in conversations at events to make professional connections.
Top Soft Communication Skills Needed in the Workplace
In today’s collaborative and dynamic work environment, possessing strong soft communication skills is as important as technical know-how. These skills not only facilitate smoother interactions but also contribute significantly to building a productive and positive workplace culture. Here’s a comprehensive guide on the top soft communication skills essential in the workplace:
- Active Listening: This skill involves fully concentrating, understanding, and responding thoughtfully to what is being said, rather than just passively hearing the words.
- Empathy: Being empathetic in communication means genuinely understanding and caring about the perspectives and feelings of others, which fosters trust and openness.
- Clear Articulation: The ability to express ideas and information clearly and concisely is crucial to prevent misunderstandings and ensure efficient workflow.
- Constructive Feedback: Offering and receiving feedback in a manner that is productive and non-confrontational is essential for growth and development.
- Adaptability: Adapting your communication style to different situations and people helps in effectively conveying messages and understanding others.
- Conflict Resolution: Effectively managing and resolving disagreements is key to maintaining a harmonious work environment.
- Positive Attitude: A positive and constructive approach in communication can boost morale and foster a collaborative atmosphere.
- Cultural Sensitivity: In our globalized world, being culturally sensitive in communication is vital for inclusivity and mutual respect.
- Persuasion Skills: The ability to influence others with your ideas and viewpoints, while respecting their opinions, is an important aspect of leadership and teamwork.
- Team Collaboration: Effective communication within a team involves sharing ideas, giving and receiving support, and working towards common goals collaboratively.
Difference Between Soft Skills and Communication Skills
Understanding the difference between soft skills and communication skills is crucial for personal and professional development. While both are integral to effective workplace functioning, they encompass different aspects of interpersonal interactions. This table and description provide a clear comparison, showcasing how each set of skills plays a unique role in various contexts.
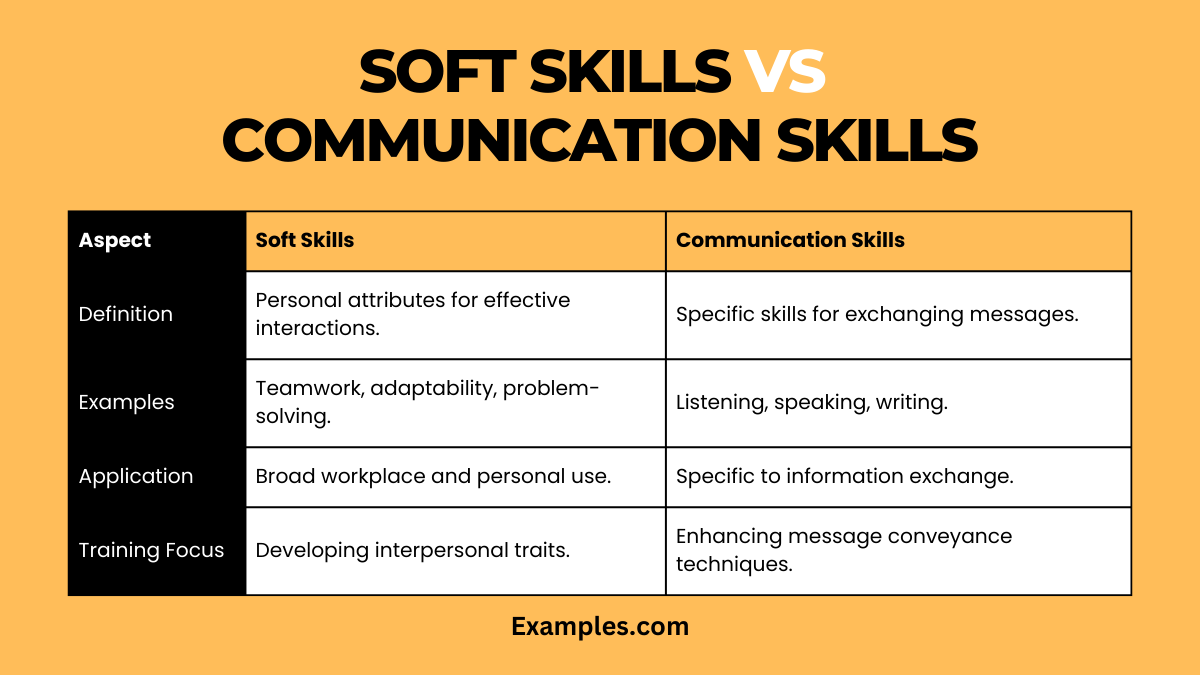
| Aspect | Soft Skills | Communication Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Broad personal attributes that enhance interactions and job performance. | Specific abilities related to the exchange of information and ideas. |
| Key Focus | Emotional intelligence, adaptability, teamwork, problem-solving. | Listening, speaking, writing, non-verbal cues. |
| Application | Across all areas of life, influencing overall effectiveness. | Predominantly in conveying and receiving messages. |
| Importance | Critical for teamwork, leadership, and adaptability in various situations. | Essential for clarity in information exchange, instruction, and feedback. |
| Development | Gained through experience, observation, and personal growth. | Improved through structured practice, training, and feedback. |
| Impact | Affects overall professional demeanor and ability to navigate workplace dynamics. | Directly influences the effectiveness of information dissemination and understanding. |
| Evaluation | Often subjective, based on observation and feedback. | More objective, can be assessed through communication outcomes. |
What Soft Communication Skills Do Employers Look For?
In the ever-evolving job market, employers are increasingly valuing a range of soft communication skills that facilitate effective and harmonious workplace interactions. Here are some of the key skills that stand out:
- Emotional Intelligence: The capacity to be aware of, control, and express one’s emotions judiciously and empathetically.
- Conflict Management: The ability to address disagreements or misunderstandings constructively, without escalating tension.
- Active Listening and Responsiveness: Prioritizing understanding in communication, which involves listening actively and responding appropriately.
- Constructive Criticism: The skill of offering feedback that is helpful and promotes growth, rather than demoralizing the recipient.
- Inclusivity and Diversity Awareness: Being able to communicate respectfully with individuals from diverse backgrounds and perspectives.
- Persuasive Communication: The art of influencing others while maintaining respect for their opinions and needs.
- Team-Building Communication: Fostering a sense of collaboration and mutual support within a team.
- Nonverbal Communication: The ability to read and use body language, facial expressions, and other nonverbal cues effectively.
- Resilience and Adaptability: Being flexible and resilient in communication, especially in times of change or stress.
- Clear and Concise Communication: Conveying messages in a straightforward, uncomplicated manner that is easily understood by all.
How to Develop Communication Soft Skills?
Enhancing your communication soft skills can be a transformative process, impacting both your professional and personal life. Here’s a guide to developing these skills:
- Participate in Diverse Teams: Engage in projects or activities that involve collaboration with people from various backgrounds. This experience broadens your perspective and enhances your ability to communicate effectively in diverse settings.
- Practice Empathetic Listening: In conversations, focus more on understanding the speaker’s perspective than on formulating your response. This practice not only improves your listening skills but also builds deeper connections.
- Role-Playing Exercises: Engage in role-playing scenarios to simulate different communication situations. This can be particularly effective in learning how to handle difficult conversations or conflicts.
- Join Communication Skills Workshops: Enroll in workshops or seminars that focus specifically on developing soft communication skills. These programs often provide practical exercises and expert feedback.
- Mindfulness and Emotional Regulation: Practice mindfulness techniques to enhance your emotional intelligence. Being aware of your emotions and how they influence your communication is crucial.
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback loop with trusted colleagues or mentors. Regular constructive feedback is invaluable for recognizing your strengths and areas for improvement.
- Expand Your Reading: Broaden your reading to include books and articles on psychology, communication, and emotional intelligence. This will provide theoretical knowledge that can be applied practically.
- Public Speaking Practice: Regularly practicing public speaking, perhaps in a group like Toastmasters, helps in refining your verbal communication skills and boosts confidence.
- Reflect on Your Interactions: After important conversations or meetings, take time to reflect on what went well and what could be improved. This self-reflection is a powerful tool for continuous learning and development.
- Leverage Technology: Use technology, such as communication apps or online platforms, to practice and improve your soft skills. Many apps now offer scenarios and tips for effective communication.
In conclusion, soft communication skills are a vital asset in any professional setting, enhancing both individual performance and overall workplace dynamics. To further develop these skills, resources like MindTools, which offers extensive articles and tips on various aspects of soft skills and communication, can be immensely helpful.
Additionally, the American Management Association provides a range of training and resources focused on professional development, including communication and soft skills training. These external resources offer valuable guidance and tools to refine your soft skills, contributing significantly to your career growth and professional success. Remember, continuous learning and practice are key to mastering these skills and thriving in any collaborative environment.



