10 Styles of Interpersonal Communication Examples
In this complete guide, we delve into the fascinating world of interpersonal communication, exploring its varied styles with practical Interpersonal Communication Examples. From verbal to non-verbal cues, and from digital interactions to emotional expressions, we cover the full spectrum. Each style is illuminated with real-life examples, making this guide a valuable resource for anyone looking to enhance their communication skills. Whether for personal growth or professional development, understanding these styles is key to effective and meaningful interactions.
What are Interpersonal Communication Styles? – Definition
Interpersonal Communication Styles are the varied methods through which people exchange information and emotions with others. These styles encompass everything from verbal and non-verbal cues to listening and emotional expression. Each style is a unique combination of how we use words, tone, body language, and even silence in our interactions. Recognizing and understanding these styles is essential in enhancing Interpersonal Communication Skills and is a fundamental aspect of Elements of Interpersonal Communication. They play a pivotal role in how we connect, understand, and build relationships with those around us.
10 Types of Interpersonal Communication Styles
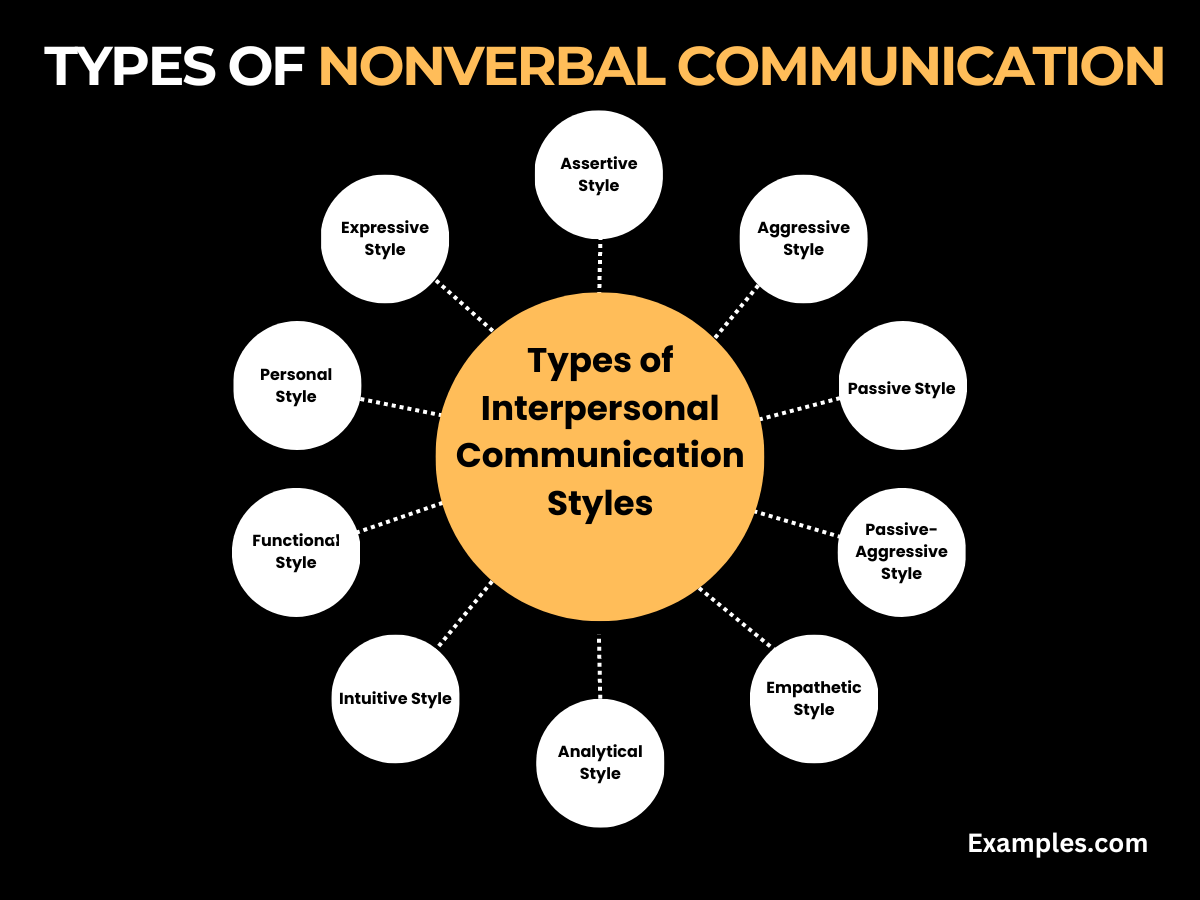
Understanding the Styles of Interpersonal Communication is key to mastering effective and meaningful exchanges. Here, we explore ten distinct styles, each playing a crucial role in how we interact in various contexts:
- Assertive Style: This style is direct, honest, and respectful, ideal for effective interpersonal communication. Assertive communicators balance their needs with others’, promoting healthy interactions.
- Aggressive Style: Characterized by dominating conversations and expressing opinions forcefully, often leading to interpersonal conflict communication.
- Passive Style: Passive communicators often avoid confrontation, which can lead to misunderstandings and hinder interpersonal communication skills development.
- Passive-Aggressive Style: Involves expressing negativity indirectly, creating challenges in types of interpersonal communication.
- Empathetic Style: Focused on understanding others’ emotions, this style is crucial in emotional expression in interpersonal communication.
- Analytical Style: Relies on facts, data, and logic, often seen in digital communication in interpersonal communication where data is key.
- Intuitive Style: This style emphasizes quick decisions based on gut feelings rather than detailed analysis, important in dynamic communication settings.
- Functional Style: Focuses on process and detail, emphasizing clear steps and organization, a key aspect in written communication in interpersonal communication.
- Personal Style: Values emotional connection and personal relationships, often utilizing personal narratives in verbal communication in interpersonal communication.
- Expressive Style: Known for enthusiasm and storytelling, this style is effective in engaging audiences, particularly in public communication in interpersonal communication.
Each style contributes uniquely to the fabric of our daily interactions, whether in personal conversations or professional settings. By understanding and adapting these Styles of Interpersonal Communication, we can enhance our ability to communicate effectively, building stronger relationships and achieving clearer understanding in various contexts.
Different Interpersonal Communication Styles

In the realm of Styles of Interpersonal Communication, it’s essential to recognize the diversity in how we convey and interpret messages. This section explores various interpersonal communication styles, each with its unique characteristics and applications:
- Direct vs. Indirect Communication: Direct communication is straightforward and clear, leaving little room for misinterpretation. In contrast, indirect communication relies more on context and non-verbal cues, often to maintain harmony or avoid conflict.
- Formal vs. Informal Communication: Formal communication follows established conventions and is often used in professional settings. Informal communication is more relaxed, typically used among friends or in casual settings.
- Emotional vs. Reserved Communication: Emotional communicators express feelings openly, whereas reserved communicators tend to keep their emotions subdued, focusing more on facts and logic.
- Detailed vs. Big-Picture Communication: Some prefer discussing topics with thorough detail and precision, while others communicate in broad strokes, focusing on the overall picture rather than specifics.
Understanding these different interpersonal communication styles helps in adapting our approach to various situations, enhancing both personal and professional interpersonal communication.
What are the three interpersonal Communication Styles Used at Work?

In professional environments, three primary interpersonal communication styles are commonly observed, each playing a vital role in workplace dynamics:
- Assertive Communication: This style is characterized by clarity, directness, and respect for others. Assertive communicators express their thoughts and needs confidently without infringing on others’ rights, making it a key style in effective workplace communication.
- Passive Communication: Passive communicators often avoid expressing their opinions or needs, prioritizing others’ preferences. This style can lead to challenges in workplace interpersonal communication, as it might hinder clear expression of ideas and needs.
- Aggressive Communication: In this style, individuals express themselves in a forceful and sometimes overpowering manner. Aggressive communication can disrupt workplace harmony and is often counterproductive in team-based interpersonal communication.
Recognizing and understanding these styles at work is crucial for maintaining a positive and productive work environment. It aids in navigating interpersonal communication in business and fosters effective collaboration and conflict resolution. By mastering these styles, individuals can enhance their interpersonal communication skills and contribute more effectively to their professional roles.
Interpersonal Communication Styles & Conflict

Understanding Styles of Interpersonal Communication is crucial in managing and resolving conflicts. Conflict is a natural part of human interaction, and the way we communicate plays a pivotal role in its resolution. Here’s how different interpersonal communication styles impact conflict:
- Assertive Style in Conflict Resolution: Assertiveness is often the most effective style in conflict situations. It involves expressing one’s viewpoint clearly and respectfully, while also considering others’ perspectives. This style promotes constructive dialogue and problem-solving, essential in resolving interpersonal conflict communication.
- Passive Style and Conflict Avoidance: Passive communicators often avoid conflicts, which can lead to unresolved issues and increased tension. This avoidance may prevent the healthy resolution of disputes, impacting the overall interpersonal communication in relationships.
- Aggressive Style and Escalation of Conflict: Aggressive communication can exacerbate conflicts. This style, characterized by dominating and forceful communication, often leads to defensive responses and hinders effective interpersonal communication in conflict resolution.
- Passive-Aggressive Style and Indirect Conflict: This style involves expressing dissatisfaction indirectly, often leading to misunderstandings and prolonged conflicts. Recognizing and addressing passive-aggressive tendencies is important for healthy interpersonal communication.
- Compromising as a Middle Ground: A compromising style aims to find a middle ground where both parties can agree. While it may not satisfy all needs, it can be an effective temporary solution in interpersonal communication and conflict management.
- Collaborative Style for Win-Win Solutions: Collaboration involves working together to find a mutually beneficial solution. It is a highly effective style in interpersonal communication, especially in complex conflicts where all parties’ needs are considered.
Effective conflict resolution requires understanding and adapting to various communication styles. By mastering these styles, individuals can enhance their ability to navigate conflicts, whether in personal relationships or professional settings. This guide not only explains the different styles but also offers insights into applying them effectively in conflict situations, a crucial aspect of interpersonal communication skills in both personal and professional contexts.
In conclusion, understanding the diverse Styles of Interpersonal Communication is key to effective and meaningful interactions. By recognizing and adapting to these styles, we can enhance our communication skills, resolve conflicts more effectively, and build stronger relationships. This guide offers valuable insights and practical tips, empowering you to navigate the complex world of interpersonal communication with confidence and skill.



