19+ Technological barriers in Communication Examples
Technological barriers in communication refer to obstacles created by tools and platforms when people try to exchange information. These barriers can include issues like poor internet connectivity, outdated software, or incompatible devices that make it difficult for users to connect and communicate effectively. Such barriers often hinder the flow of information and can lead to misunderstandings or delays in communication
What are Technological Barriers in Communication?
20 Examples of Technological Barriers in Communication

In the digital era, Technological barriers in Communication can significantly disrupt the flow of information and hinder effective interaction. These barriers encompass a wide range of issues, from hardware malfunctions to software incompatibilities and beyond. Understanding these examples is key to identifying and resolving common technological obstacles, ensuring smoother and more efficient communication in various settings.
- Poor Internet Connectivity During a Video Conference: Causes disruptions and misunderstandings.
Example: “Your video is freezing; can we switch to a voice call?” - Incompatible Software Platforms Between Teams: Hinders file sharing and collaboration.
Example: “Let’s find a common platform for file sharing.” - Limited Access to Technology in Remote Areas: Affects the ability to communicate effectively.
Example: “Can we use offline methods to share this information?” - Language Barriers in Global Virtual Teams: Non-native speakers struggle with English-dominated software.
Example: “Let’s use a translation tool to aid our communication.” - Overreliance on Email for Urgent Matters: Delays in reading emails can cause issues.
Example: “For urgent matters, let’s use instant messaging.” - Data Privacy Concerns in Sharing Sensitive Information: Fear of data breaches affects communication openness.
Example: “Let’s ensure our communication channels are secure for this information.” - Technical Jargon Confusing Non-Tech Savvy Individuals: Creates misunderstandings in discussions.
Example: “I’ll explain these technical terms in simpler language.” - Misinterpretation of Tone in Text-Based Communication: Leads to misunderstandings.
Example: “To avoid confusion, let’s discuss this over a call.” - Outdated Communication Systems Slowing Down Processes: Reduces efficiency and productivity.
Example: “Upgrading our systems will help us communicate more effectively.” - Lack of Digital Literacy Hindering Online Collaboration: Affects participation in digital projects.
Example: “Let’s provide training on using these collaboration tools.” - Noise and Distractions in Virtual Meetings: Impairs the quality of communication.
Example: “Please find a quiet space during our virtual meeting.” - Hardware Malfunctions During Presentations: Disrupts the flow of information.
Example: “I’ll email the presentation in case of technical issues.” - Slow Response Time in Asynchronous Communication: Leads to delays in decision-making.
Example: “Let’s set a timeframe for email responses.” - Difficulty in Managing Large Volumes of Digital Communication: Overwhelms recipients.
Example: “We should streamline our digital communication channels.” - Lack of Personal Touch in Electronic Communication: Can lead to disengagement.
Example: “Periodic face-to-face meetings can enhance our team’s connection.” - Cybersecurity Threats in Online Communication: Creates reluctance to share information.
Example: “We need to discuss cybersecurity measures for our communications.” - Bandwidth Limitations Affecting Online Activities: Restricts the quality of digital interactions.
Example: “Let’s schedule our high-bandwidth activities during off-peak hours.” - Complex User Interfaces Leading to Avoidance: Non-intuitive tools deter usage.
Example: “A user-friendly interface would encourage more participation.” - Visual and Hearing Impairments in Digital Platforms: Accessibility issues for differently-abled individuals.
Example: “Let’s ensure our platforms are accessible to everyone.” - Frequent Software Updates Interrupting Workflows: Causes disruptions and learning curves.
Example: “We’ll allocate time for adapting to new software updates.”
Addressing these Technological barriers in Communication is crucial for maintaining effective, efficient, and inclusive communication in our increasingly digital world.
Types of Technological Barriers in Communication
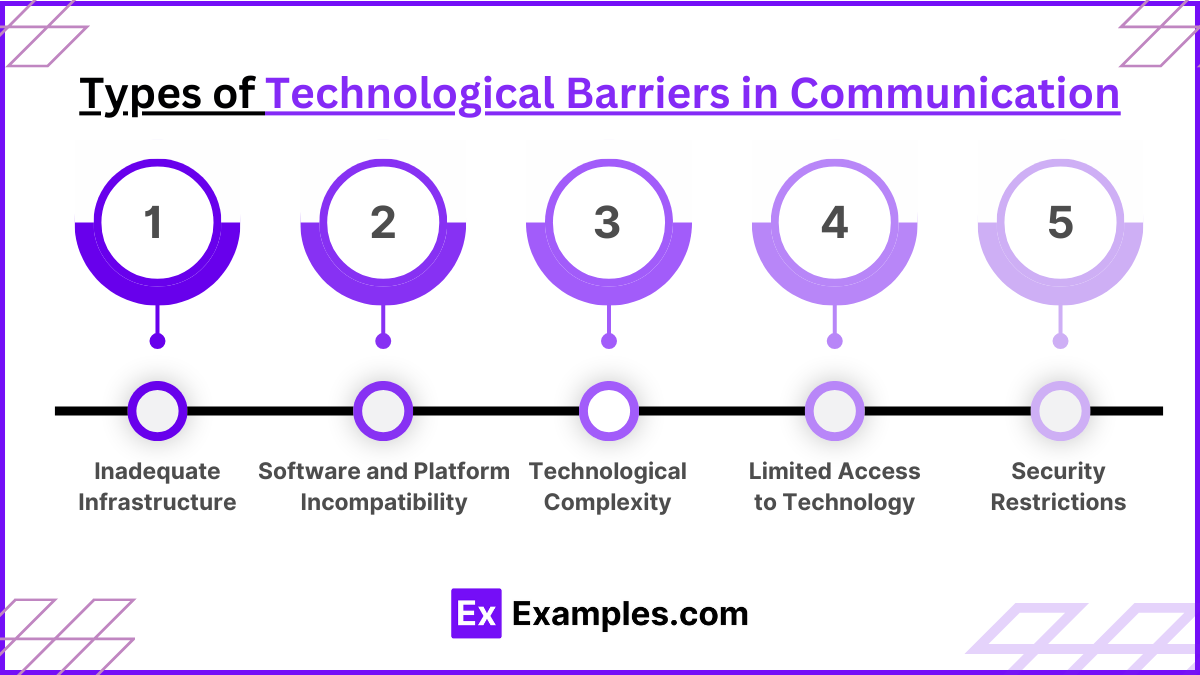
1. Inadequate Infrastructure
Lack of essential technological infrastructure, such as poor internet connectivity or outdated communication hardware, can severely limit effective communication.
2. Software and Platform Incompatibility
Issues arise when different communication systems or software are not compatible, preventing seamless interaction between users.
3. Technological Complexity
Complex systems or user interfaces can confuse users, reducing their ability to communicate effectively.
4. Limited Access to Technology
Barriers faced by individuals who do not have sufficient access to modern digital tools or the internet, often due to economic or geographic constraints.
5. Security Restrictions
Strict security measures, like firewalls or communication filters, can restrict the flow of communication by blocking certain types of data exchanges.
How to Overcome Technological Barriers in Communication

Overcoming Technological barriers in Communication requires strategic efforts and a willingness to adapt to changing technological landscapes.
- Invest in Modern Technology: Update and maintain current communication tools.
- Enhance Digital Literacy: Provide training to improve tech skills.
- Ensure Compatibility and Integration: Use universally compatible communication tools.
- Strengthen Internet Connectivity: Invest in reliable internet services.
- Prioritize Data Security: Implement robust security measures.
- Balance Electronic and Personal Communication: Encourage face-to-face interactions when possible.
- Manage Digital Workload: Develop strategies to handle digital communication effectively.
- Regular Technology Assessments and Updates: Continuously evaluate and update technology.
Tackling Technological barriers in Communication is essential in our increasingly digital world. By identifying the types of barriers, understanding their impact on collaboration, exploring their causes, and implementing strategies to overcome them, we can enhance our communication efficiency and effectiveness. This guide offers insights and practical tips to navigate the challenges posed by technology in communication, fostering smoother and more productive interactions.
Technological Barriers in Communication that Affects Team Collaboration
Technological barriers in Communication can significantly impact team collaboration, especially in remote or virtual settings.
- Inconsistent Technology Access: Team members having unequal access to technology.
- Diverse Technology Preferences: Different preferences for communication tools.
- Miscommunications Due to Technology Failures: Misunderstandings arising from technical glitches.
- Time Zone Differences in Virtual Teams: Challenges in synchronizing communication.
- Lack of Non-Verbal Cues in Digital Communication: Missing out on body language cues.
- Information Overload: Difficulty in managing a large volume of digital information.
- Reliance on Written Communication: Misinterpretation of tone in texts and emails.
- Delayed Responses: Slow response time affecting team dynamics.
Causes of Technological Barriers in Communication
Understanding the causes of Technological barriers in Communication is crucial for identifying and addressing these issues effectively.
- Rapid Technological Changes: Difficulty in keeping up with fast-evolving tech.
- Economic Constraints: Limited budget for technology upgrades.
- Lack of Training and Support: Inadequate training in new technologies.
- Cultural and Language Differences in Technology Use: Variations in tech usage across cultures.
- Generational Differences in Tech Savviness: Gap in comfort and skills with technology.
- Resistance to Change: Hesitance in adopting new communication technologies.
- Inadequate IT Support: Lack of sufficient technical support.
- Poorly Designed User Interfaces: User-unfriendly technology designs.



