Types of Nouns with 90+ Examples in English, Easy to Learn
Nouns are categorized into various types, each serving a unique function in sentences. Common nouns refer to general items (e.g., city, car). Proper nouns name specific entities (e.g., New York, Toyota). Abstract nouns denote intangible concepts (e.g., love, freedom). Concrete nouns identify physical objects (e.g., book, apple). Collective nouns represent groups (e.g., team, flock). Understanding these types enhances clarity and precision in communication.
What is a Noun?
A noun is a word that identifies a person, place, thing, or idea. There are various types of nouns: common nouns refer to general items (e.g., city), proper nouns name specific entities (e.g., New York), abstract nouns denote concepts (e.g., freedom), concrete nouns identify physical objects (e.g., apple), and collective nouns represent groups (e.g., team).
Different Types of Nouns with Examples
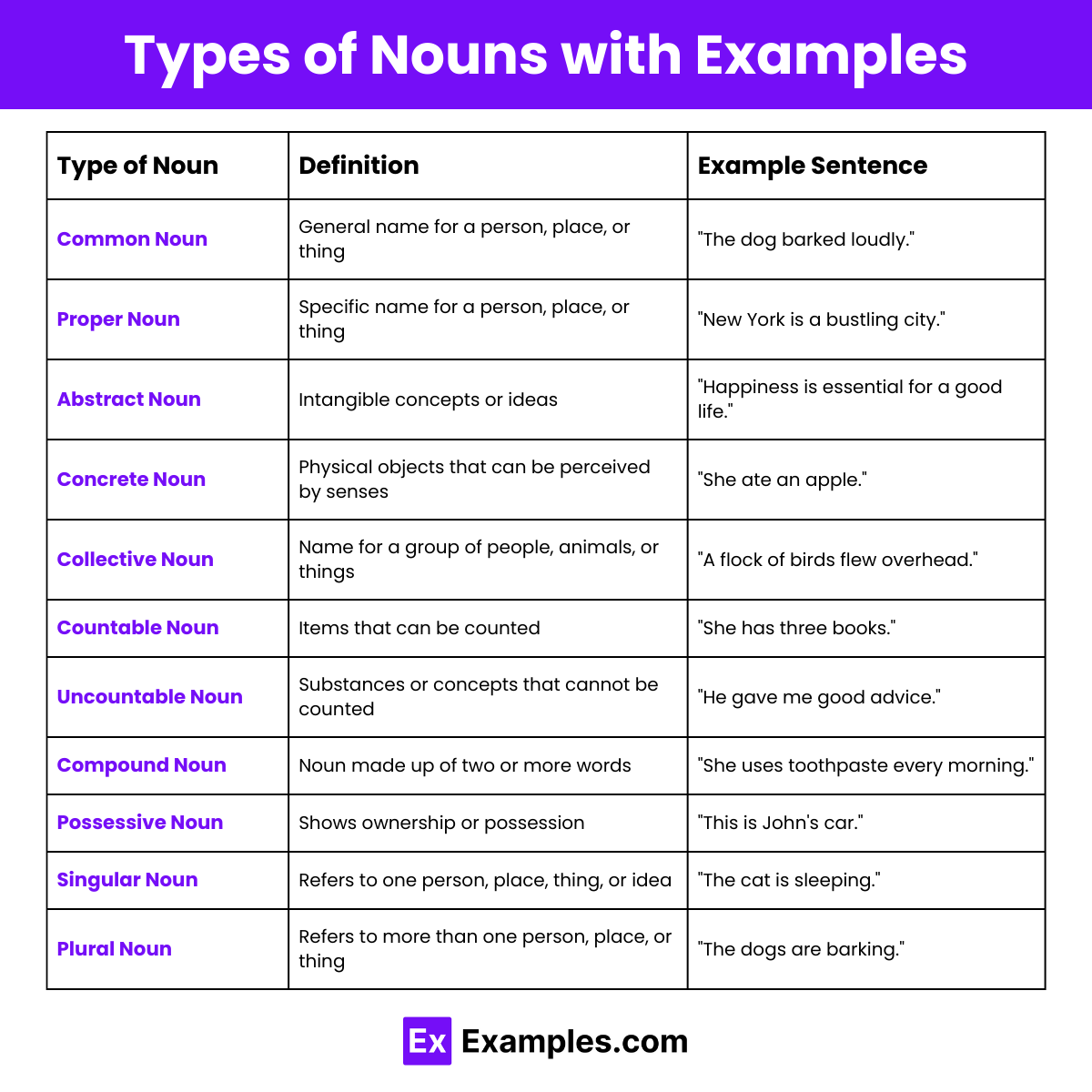
Nouns are words that name people, places, things, or ideas. They can be categorized into several types based on their characteristics and usage. Here are the main types of nouns:
Common Nouns
Common nouns are general names for people, places, things, or ideas. Unlike proper nouns, they are not capitalized unless they begin a sentence. Common nouns refer to general items rather than specific ones.
Examples:
- Teacher
- “The teacher explained the lesson clearly.”
- Car
- “She drove her car to work every day.”
- Book
- “He borrowed a book from the library.”
- City
- “They moved to a new city last year.”
- Dog
- “The dog barked at the stranger.”
- Chair
- “There is a comfortable chair in the living room.”
- House
- “They bought a house in the suburbs.”
- Restaurant
- “We had dinner at a new restaurant downtown.”
- Laptop
- “His laptop is essential for his work.”
- Garden
- “She planted flowers in her garden.”
Proper Nouns
Proper nouns are specific names given to individual people, places, organizations, or sometimes things. They are always capitalized, regardless of where they appear in a sentence, to distinguish them from common nouns.
Examples:
- New York
- “New York is known for its skyscrapers and vibrant culture.”
- Albert Einstein
- “Albert Einstein developed the theory of relativity.”
- Amazon
- “Amazon is one of the largest online retailers in the world.”
- Christmas
- “Christmas is celebrated on December 25th each year.”
- Shakespeare
- “Shakespeare wrote many famous plays, including ‘Hamlet’ and ‘Macbeth.'”
- Mount Everest
- “Mount Everest is the highest mountain in the world.”
- Google
- “Google is the most widely used search engine.”
- Paris
- “Paris is known as the City of Light and is famous for the Eiffel Tower.”
- Coca-Cola
- “Coca-Cola is a popular soft drink brand.”
- Harvard University
- “Harvard University is one of the most prestigious universities in the world.”
Concrete Nouns
Concrete nouns are nouns that refer to physical objects, substances, or entities that can be perceived by the senses. They are tangible and have a physical form that can be seen, touched, smelled, heard, or tasted.
Examples:
- Apple
- “She ate a red apple for breakfast.”
- Car
- “He washed his car every Saturday.”
- Book
- “The book on the shelf is very interesting.”
- Dog
- “The dog barked at the mailman.”
- Chair
- “She sat on a wooden chair by the window.”
- House
- “They live in a beautiful house by the beach.”
- Tree
- “The tree in the backyard provides a lot of shade.”
- Laptop
- “He uses his laptop for both work and entertainment.”
- Table
- “The table in the dining room is made of oak.”
- Pen
- “She wrote the letter with a blue pen.”
Abstract Nouns
Abstract nouns refer to intangible concepts, ideas, or feelings that cannot be perceived with the five senses. They represent things that do not have a physical form and cannot be seen, touched, heard, smelled, or tasted.
Examples:
- Love
- “Her love for her family is unconditional.”
- Freedom
- “Freedom of speech is a fundamental right.”
- Happiness
- “Happiness is often found in simple things.”
- Courage
- “He showed great courage during the rescue mission.”
- Knowledge
- “Knowledge is power.”
- Wisdom
- “Wisdom comes with experience and age.”
- Friendship
- “Their friendship has lasted over two decades.”
- Justice
- “Justice must be served in this case.”
- Peace
- “The country has been in a state of peace for many years.”
- Honesty
- “Honesty is one of the most important values.”
Collective Nouns
Collective nouns are words that represent a group of people, animals, or things as a single entity. Even though the noun is singular, it encompasses multiple members within the group.
Examples:
- Team
- “The soccer team won the championship.”
- Flock
- “A flock of birds flew over the field.”
- Class
- “The class took a field trip to the museum.”
- Herd
- “A herd of elephants roamed the savannah.”
- Committee
- “The planning committee organized the event.”
- Family
- “Her family gathers for a reunion every year.”
- Audience
- “The audience clapped loudly after the performance.”
- Bunch
- “She bought a bunch of bananas from the market.”
- Choir
- “The choir sang beautifully during the concert.”
- Pack
- “A pack of wolves was spotted near the forest.”
Countable Nouns
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted as individual units. They have both singular and plural forms, and you can use numbers or quantifiers with them.
Examples:
- Cat
- Singular: “A cat sat on the windowsill.”
- Plural: “Several cats were playing in the yard.”
- Book
- Singular: “She borrowed a book from the library.”
- Plural: “He has many books on his shelf.”
- Chair
- Singular: “There is a chair in the corner.”
- Plural: “We need five chairs for the dining table.”
- House
- Singular: “They bought a new house.”
- Plural: “The neighborhood has many houses.”
- Apple
- Singular: “He ate an apple for lunch.”
- Plural: “She bought a dozen apples.”
- Car
- Singular: “He owns a new car.”
- Plural: “They saw several cars at the dealership.”
- Pen
- Singular: “She wrote with a blue pen.”
- Plural: “He collected different pens from various countries.”
- Student
- Singular: “A student asked a question during the lecture.”
- Plural: “The professor answered questions from several students.”
- Tree
- Singular: “A tree fell during the storm.”
- Plural: “The park is full of tall trees.”
- Idea
- Singular: “She had an interesting idea for the project.”
- Plural: “They shared their ideas during the brainstorming session.”
Uncountable Nouns
Uncountable nouns (also known as mass nouns) refer to substances, concepts, or items that cannot be counted as individual units. They do not have a plural form and are often used with quantifiers like “some,” “much,” “a lot of,” or “a little.”
Examples:
- Water
- “She drank a glass of water.”
- Information
- “He provided valuable information during the meeting.”
- Rice
- “They served rice with every meal.”
- Advice
- “She gave me good advice about my career.”
- Furniture
- “The furniture in the living room is modern and stylish.”
- Money
- “He saved a lot of money for his vacation.”
- Knowledge
- “Knowledge is power.”
- Milk
- “She poured some milk into her cereal.”
- Music
- “They enjoyed listening to classical music.”
- Sand
- “The beach was covered in fine, white sand.”
Compound Nouns
Compound nouns are nouns made up of two or more words that function as a single unit to name a person, place, thing, or idea. These words can be written as one word, hyphenated, or as separate words.
Examples:
- Toothpaste
- “She squeezed toothpaste onto her brush.”
- Mother-in-law
- “Her mother-in-law is visiting for the holidays.”
- Basketball
- “They played basketball at the gym.”
- Coffee table
- “There are magazines on the coffee table.”
- Sunflower
- “The garden is full of blooming sunflowers.”
- Ice cream
- “He loves to eat ice cream in the summer.”
- Bedroom
- “She cleaned her bedroom over the weekend.”
- Firefighter
- “The firefighter bravely entered the burning building.”
- Notebook
- “He wrote his notes in a new notebook.”
- Haircut
- “She got a stylish haircut at the salon.”
Possessive Nouns
Possessive nouns show ownership or possession of something. They typically involve adding an apostrophe and an “s” to a noun, though the placement of the apostrophe can vary depending on whether the noun is singular or plural.
Examples:
- Child’s
- “The child’s toy was left on the floor.”
- Teacher’s
- “The teacher’s desk was neatly organized.”
- Dogs’
- “The dogs’ owner took them for a walk.”
- Men’s
- “The men’s restroom is down the hall.”
- Alice’s
- “Alice’s book was on the table.”
- Students’
- “The students’ homework was graded by the teacher.”
- Boss’s
- “The boss’s office is at the end of the hallway.”
- Cats’
- “The cats’ food bowls were lined up in the kitchen.”
- Doctor’s
- “The doctor’s appointment was scheduled for next week.”
- Parents’
- “The parents’ meeting will be held in the school auditorium.”
Singular Nouns
Singular nouns refer to one person, place, thing, or idea. They are used to indicate a single entity and typically do not have an “s” at the end.
Examples:
- Dog
- “The dog barked at the stranger.”
- City
- “The city was bustling with activity.”
- Book
- “She read a fascinating book.”
- Tree
- “A tree fell during the storm.”
- House
- “They bought a house in the suburbs.”
- Car
- “He washed his car every Saturday.”
- Student
- “A student asked a question during the lecture.”
- Pen
- “She wrote with a blue pen.”
- Chair
- “There is a chair in the corner of the room.”
- Idea
- “He had a brilliant idea during the meeting.”
Plural Nouns
Plural nouns refer to more than one person, place, thing, or idea. They are typically formed by adding “s” or “es” to the end of the singular noun, though there are many irregular forms as well.
Examples:
- Dogs
- “The dogs played in the park.”
- Cities
- “The tour included several major cities.”
- Books
- “She borrowed three books from the library.”
- Trees
- “The trees in the forest were tall and dense.”
- Houses
- “The neighborhood has many houses.”
- Cars
- “They saw several cars at the dealership.”
- Students
- “The professor answered questions from several students.”
- Pens
- “He collected different pens from various countries.”
- Chairs
- “We need five chairs for the dining table.”
- Ideas
- “They shared their ideas during the brainstorming session.”
What are the main types of nouns?
The main types of nouns are common nouns, proper nouns, abstract nouns, concrete nouns, collective nouns, countable nouns, uncountable nouns, compound nouns, and possessive nouns.
What is a common noun with an example?
A common noun refers to general items or people. Example: “dog” in “The dog barked.”
What is a proper noun with an example?
A proper noun names specific entities and is capitalized. Example: “London” in “London is a big city.”
What is an abstract noun with an example?
An abstract noun refers to intangible concepts or ideas. Example: “happiness” in “Happiness is important.”
What is a concrete noun with an example?
A concrete noun refers to physical objects. Example: “apple” in “She ate an apple.”
What is a collective noun with an example?
A collective noun represents a group. Example: “team” in “The team won the game.”
What is a countable noun with an example?
A countable noun can be counted. Example: “book” in “She has three books.”
What is an uncountable noun with an example?
An uncountable noun cannot be counted. Example: “water” in “She drank water.”
What is a compound noun with an example?
A compound noun is made of two or more words. Example: “toothpaste” in “He uses toothpaste.”
What is a possessive noun with an example?
A possessive noun shows ownership. Example: “John’s” in “John’s car is new.”
Types of Nouns with 90+ Examples in English, Easy to Learn
Nouns are categorized into various types, each serving a unique function in sentences. Common nouns refer to general items (e.g., city, car). Proper nouns name specific entities (e.g., New York, Toyota). Abstract nouns denote intangible concepts (e.g., love, freedom). Concrete nouns identify physical objects (e.g., book, apple). Collective nouns represent groups (e.g., team, flock). Understanding these types enhances clarity and precision in communication.
What is a Noun?
A noun is a word that identifies a person, place, thing, or idea. There are various types of nouns: common nouns refer to general items (e.g., city), proper nouns name specific entities (e.g., New York), abstract nouns denote concepts (e.g., freedom), concrete nouns identify physical objects (e.g., apple), and collective nouns represent groups (e.g., team).
Different Types of Nouns with Examples
Nouns are words that name people, places, things, or ideas. They can be categorized into several types based on their characteristics and usage. Here are the main types of nouns:
Common Nouns
Common nouns are general names for people, places, things, or ideas. Unlike proper nouns, they are not capitalized unless they begin a sentence. Common nouns refer to general items rather than specific ones.
Examples:
Teacher
“The teacher explained the lesson clearly.”
Car
“She drove her car to work every day.”
Book
“He borrowed a book from the library.”
City
“They moved to a new city last year.”
Dog
“The dog barked at the stranger.”
Chair
“There is a comfortable chair in the living room.”
House
“They bought a house in the suburbs.”
Restaurant
“We had dinner at a new restaurant downtown.”
Laptop
“His laptop is essential for his work.”
Garden
“She planted flowers in her garden.”
Proper Nouns
Proper nouns are specific names given to individual people, places, organizations, or sometimes things. They are always capitalized, regardless of where they appear in a sentence, to distinguish them from common nouns.
Examples:
New York
“New York is known for its skyscrapers and vibrant culture.”
Albert Einstein
“Albert Einstein developed the theory of relativity.”
Amazon
“Amazon is one of the largest online retailers in the world.”
Christmas
“Christmas is celebrated on December 25th each year.”
Shakespeare
“Shakespeare wrote many famous plays, including ‘Hamlet’ and ‘Macbeth.'”
Mount Everest
“Mount Everest is the highest mountain in the world.”
Google
“Google is the most widely used search engine.”
Paris
“Paris is known as the City of Light and is famous for the Eiffel Tower.”
Coca-Cola
“Coca-Cola is a popular soft drink brand.”
Harvard University
“Harvard University is one of the most prestigious universities in the world.”
Concrete Nouns
Concrete nouns are nouns that refer to physical objects, substances, or entities that can be perceived by the senses. They are tangible and have a physical form that can be seen, touched, smelled, heard, or tasted.
Examples:
Apple
“She ate a red apple for breakfast.”
Car
“He washed his car every Saturday.”
Book
“The book on the shelf is very interesting.”
Dog
“The dog barked at the mailman.”
Chair
“She sat on a wooden chair by the window.”
House
“They live in a beautiful house by the beach.”
Tree
“The tree in the backyard provides a lot of shade.”
Laptop
“He uses his laptop for both work and entertainment.”
Table
“The table in the dining room is made of oak.”
Pen
“She wrote the letter with a blue pen.”
Abstract Nouns
Abstract nouns refer to intangible concepts, ideas, or feelings that cannot be perceived with the five senses. They represent things that do not have a physical form and cannot be seen, touched, heard, smelled, or tasted.
Examples:
Love
“Her love for her family is unconditional.”
Freedom
“Freedom of speech is a fundamental right.”
Happiness
“Happiness is often found in simple things.”
Courage
“He showed great courage during the rescue mission.”
Knowledge
“Knowledge is power.”
Wisdom
“Wisdom comes with experience and age.”
Friendship
“Their friendship has lasted over two decades.”
Justice
“Justice must be served in this case.”
Peace
“The country has been in a state of peace for many years.”
Honesty
“Honesty is one of the most important values.”
Collective Nouns
Collective nouns are words that represent a group of people, animals, or things as a single entity. Even though the noun is singular, it encompasses multiple members within the group.
Examples:
Team
“The soccer team won the championship.”
Flock
“A flock of birds flew over the field.”
Class
“The class took a field trip to the museum.”
Herd
“A herd of elephants roamed the savannah.”
Committee
“The planning committee organized the event.”
Family
“Her family gathers for a reunion every year.”
Audience
“The audience clapped loudly after the performance.”
Bunch
“She bought a bunch of bananas from the market.”
Choir
“The choir sang beautifully during the concert.”
Pack
“A pack of wolves was spotted near the forest.”
Countable Nouns
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted as individual units. They have both singular and plural forms, and you can use numbers or quantifiers with them.
Examples:
Cat
Singular: “A cat sat on the windowsill.”
Plural: “Several cats were playing in the yard.”
Book
Singular: “She borrowed a book from the library.”
Plural: “He has many books on his shelf.”
Chair
Singular: “There is a chair in the corner.”
Plural: “We need five chairs for the dining table.”
House
Singular: “They bought a new house.”
Plural: “The neighborhood has many houses.”
Apple
Singular: “He ate an apple for lunch.”
Plural: “She bought a dozen apples.”
Car
Singular: “He owns a new car.”
Plural: “They saw several cars at the dealership.”
Pen
Singular: “She wrote with a blue pen.”
Plural: “He collected different pens from various countries.”
Student
Singular: “A student asked a question during the lecture.”
Plural: “The professor answered questions from several students.”
Tree
Singular: “A tree fell during the storm.”
Plural: “The park is full of tall trees.”
Idea
Singular: “She had an interesting idea for the project.”
Plural: “They shared their ideas during the brainstorming session.”
Uncountable Nouns
Uncountable nouns (also known as mass nouns) refer to substances, concepts, or items that cannot be counted as individual units. They do not have a plural form and are often used with quantifiers like “some,” “much,” “a lot of,” or “a little.”
Examples:
Water
“She drank a glass of water.”
Information
“He provided valuable information during the meeting.”
Rice
“They served rice with every meal.”
Advice
“She gave me good advice about my career.”
Furniture
“The furniture in the living room is modern and stylish.”
Money
“He saved a lot of money for his vacation.”
Knowledge
“Knowledge is power.”
Milk
“She poured some milk into her cereal.”
Music
“They enjoyed listening to classical music.”
Sand
“The beach was covered in fine, white sand.”
Compound Nouns
Compound nouns are nouns made up of two or more words that function as a single unit to name a person, place, thing, or idea. These words can be written as one word, hyphenated, or as separate words.
Examples:
Toothpaste
“She squeezed toothpaste onto her brush.”
Mother-in-law
“Her mother-in-law is visiting for the holidays.”
Basketball
“They played basketball at the gym.”
Coffee table
“There are magazines on the coffee table.”
Sunflower
“The garden is full of blooming sunflowers.”
Ice cream
“He loves to eat ice cream in the summer.”
Bedroom
“She cleaned her bedroom over the weekend.”
Firefighter
“The firefighter bravely entered the burning building.”
Notebook
“He wrote his notes in a new notebook.”
Haircut
“She got a stylish haircut at the salon.”
Possessive Nouns
Possessive nouns show ownership or possession of something. They typically involve adding an apostrophe and an “s” to a noun, though the placement of the apostrophe can vary depending on whether the noun is singular or plural.
Examples:
Child’s
“The child’s toy was left on the floor.”
Teacher’s
“The teacher’s desk was neatly organized.”
Dogs’
“The dogs’ owner took them for a walk.”
Men’s
“The men’s restroom is down the hall.”
Alice’s
“Alice’s book was on the table.”
Students’
“The students’ homework was graded by the teacher.”
Boss’s
“The boss’s office is at the end of the hallway.”
Cats’
“The cats’ food bowls were lined up in the kitchen.”
Doctor’s
“The doctor’s appointment was scheduled for next week.”
Parents’
“The parents’ meeting will be held in the school auditorium.”
Singular Nouns
Singular nouns refer to one person, place, thing, or idea. They are used to indicate a single entity and typically do not have an “s” at the end.
Examples:
Dog
“The dog barked at the stranger.”
City
“The city was bustling with activity.”
Book
“She read a fascinating book.”
Tree
“A tree fell during the storm.”
House
“They bought a house in the suburbs.”
Car
“He washed his car every Saturday.”
Student
“A student asked a question during the lecture.”
Pen
“She wrote with a blue pen.”
Chair
“There is a chair in the corner of the room.”
Idea
“He had a brilliant idea during the meeting.”
Plural Nouns
Plural nouns refer to more than one person, place, thing, or idea. They are typically formed by adding “s” or “es” to the end of the singular noun, though there are many irregular forms as well.
Examples:
Dogs
“The dogs played in the park.”
Cities
“The tour included several major cities.”
Books
“She borrowed three books from the library.”
Trees
“The trees in the forest were tall and dense.”
Houses
“The neighborhood has many houses.”
Cars
“They saw several cars at the dealership.”
Students
“The professor answered questions from several students.”
Pens
“He collected different pens from various countries.”
Chairs
“We need five chairs for the dining table.”
Ideas
“They shared their ideas during the brainstorming session.”
What are the main types of nouns?
The main types of nouns are common nouns, proper nouns, abstract nouns, concrete nouns, collective nouns, countable nouns, uncountable nouns, compound nouns, and possessive nouns.
What is a common noun with an example?
A common noun refers to general items or people. Example: “dog” in “The dog barked.”
What is a proper noun with an example?
A proper noun names specific entities and is capitalized. Example: “London” in “London is a big city.”
What is an abstract noun with an example?
An abstract noun refers to intangible concepts or ideas. Example: “happiness” in “Happiness is important.”
What is a concrete noun with an example?
A concrete noun refers to physical objects. Example: “apple” in “She ate an apple.”
What is a collective noun with an example?
A collective noun represents a group. Example: “team” in “The team won the game.”
What is a countable noun with an example?
A countable noun can be counted. Example: “book” in “She has three books.”
What is an uncountable noun with an example?
An uncountable noun cannot be counted. Example: “water” in “She drank water.”
What is a compound noun with an example?
A compound noun is made of two or more words. Example: “toothpaste” in “He uses toothpaste.”
What is a possessive noun with an example?
A possessive noun shows ownership. Example: “John’s” in “John’s car is new.”


