100+ Verb Forms V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 Examples
What is V1 V2 V3 V4 V5?
List of 100 verb forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5
| Base Form (V1) | Simple Past (V2) | Past Participle (V3) | ‘-ing’ Form (V4) | Third Person Singular (V5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arise | Arose | Arisen | Arising | Arises |
| Awake | Awoke | Awoken | Awaking | Awakes |
| Be | Was/Were | Been | Being | Is |
| Bear | Bore | Borne/Born | Bearing | Bears |
| Beat | Beat | Beaten | Beating | Beats |
| Become | Became | Become | Becoming | Becomes |
| Begin | Began | Begun | Beginning | Begins |
| Bend | Bent | Bent | Bending | Bends |
| Bet | Bet | Bet | Betting | Bets |
| Bind | Bound | Bound | Binding | Binds |
| Bite | Bit | Bitten | Biting | Bites |
| Bleed | Bled | Bled | Bleeding | Bleeds |
| Blow | Blew | Blown | Blowing | Blows |
| Break | Broke | Broken | Breaking | Breaks |
| Breed | Bred | Bred | Breeding | Breeds |
| Bring | Brought | Brought | Bringing | Brings |
| Build | Built | Built | Building | Builds |
| Burn | Burned/Burnt | Burned/Burnt | Burning | Burns |
| Burst | Burst | Burst | Bursting | Bursts |
| Buy | Bought | Bought | Buying | Buys |
| Cast | Cast | Cast | Casting | Casts |
| Catch | Caught | Caught | Catching | Catches |
| Choose | Chose | Chosen | Choosing | Chooses |
| Cling | Clung | Clung | Clinging | Clings |
| Come | Came | Come | Coming | Comes |
| Cost | Cost | Cost | Costing | Costs |
| Creep | Crept | Crept | Creeping | Creeps |
| Cut | Cut | Cut | Cutting | Cuts |
| Deal | Dealt | Dealt | Dealing | Deals |
| Dig | Dug | Dug | Digging | Digs |
| Do | Did | Done | Doing | Does |
| Draw | Drew | Drawn | Drawing | Draws |
| Dream | Dreamed/Dreamt | Dreamed/Dreamt | Dreaming | Dreams |
| Drink | Drank | Drunk | Drinking | Drinks |
| Drive | Drove | Driven | Driving | Drives |
| Eat | Ate | Eaten | Eating | Eats |
| Fall | Fell | Fallen | Falling | Falls |
| Feed | Fed | Fed | Feeding | Feeds |
| Feel | Felt | Felt | Feeling | Feels |
| Fight | Fought | Fought | Fighting | Fights |
| Find | Found | Found | Finding | Finds |
| Flee | Fled | Fled | Fleeing | Flees |
| Fly | Flew | Flown | Flying | Flies |
| Forget | Forgot | Forgotten | Forgetting | Forgets |
| Forgive | Forgave | Forgiven | Forgiving | Forgives |
| Freeze | Froze | Frozen | Freezing | Freezes |
| Get | Got | Got/Gotten | Getting | Gets |
Uses of v1 v2 v3 v4 v5
V1 (Base Form / Infinitive):
- Used as the base form of the verb.
- Used after modal verbs (can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would) and auxiliary verbs (be, have, do) to form different tenses or moods.
- Used after certain verbs to show purpose or intention (e.g., I want to learn).
V2 (Past Simple):
- Used to express actions or states that occurred in the past and are now finished.
- Typically used with time expressions indicating past time (e.g., yesterday, last week).
V3 (Past Participle):
- Used to form the perfect tenses (present perfect, past perfect, future perfect) and passive voice.
- Used with auxiliary verbs (have, has, had, be, am, is, are, was, were) to show completed actions or states.
V4 (Present Participle):
- Used to form the present continuous (progressive) tense.
- Also used as an adjective (participial phrase) or as part of the gerund.
V5 (Gerund):
- Used as a noun, often as the subject or object of a sentence.
- Used after prepositions (e.g., after, before, by) or as the object of certain verbs.
- Indicates an action or state in a general sense (e.g., Swimming is fun).
Examples of v1 v2 v3 v4 v5
- He wants to learn Spanish.
- She studied French last year.
- They have eaten dinner already.
- The children are playing in the park.
- Swimming helps to stay fit.
- I can read this book in an hour.
- He worked hard yesterday.
- The cake has been baked perfectly.
- We are watching a movie tonight.
- Walking in the morning is refreshing.
- She could sing beautifully when she was younger.
- They visited London last summer.
- The dishes need to be washed after dinner.
- The baby is sleeping peacefully.
- He plays the guitar very well.
- They have gone to the beach.
- Swimming in the pool is enjoyable.
- We are having a party next weekend.
- She taught English for many years.
- Running helps to improve cardiovascular health.
FAQ’s
How do I know which form of the verb to use in a sentence?
Practice and familiarity with verb forms through reading, writing, and listening will help you develop an instinct for choosing the correct form based on the tense and context of the sentence.
Are there any exceptions or irregularities to be aware of?
Yes, English has many irregular verbs that don’t follow typical patterns. Learning these irregular verbs and their various forms will improve your proficiency in using verb forms effectively.
Where can I find more resources to study verb forms?
Online grammar guides, textbooks, and language learning websites often provide detailed explanations and exercises to help you practice and master verb forms.
What are some common examples of V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5?
Examples include: (V1) “to eat”, (V2) “ate”, (V3) “eaten”, (V4) “eating”, and (V5) “eating is enjoyable”.
Can one verb have irregular forms for V2 and V3?
Yes, many verbs in English have irregular forms for past simple (V2) and past participle (V3), such as “go” (V1) – “went” (V2) – “gone” (V3).
100+ Verb Forms V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 Examples
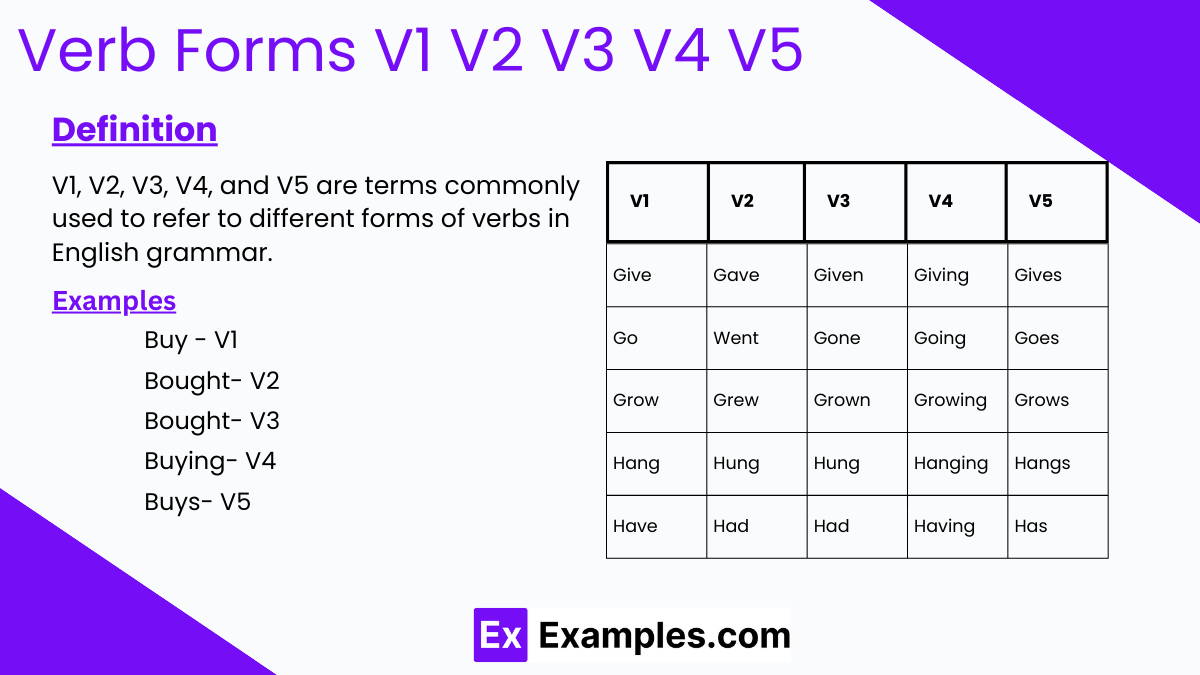
What is V1 V2 V3 V4 V5?
V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5 are terms commonly used to refer to different forms of verbs in English grammar. V1 stands for the base form of the verb, also known as the infinitive form, which is the form of the verb that you would find in the dictionary. V2 represents the past simple tense of the verb, which is used to indicate actions that occurred in the past. V3 refers to the past participle form of the verb, which is used in various tenses such as the present perfect and past perfect. V4 and V5 are less commonly used terms, but they typically refer to the present participle (V4) and the gerund (V5) forms of the verb, which are used to create progressive tenses and function as nouns, respectively.
List of 100 verb forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5
Base Form (V1) | Simple Past (V2) | Past Participle (V3) | ‘-ing’ Form (V4) | Third Person Singular (V5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Arise | Arose | Arisen | Arising | Arises |
Awake | Awoke | Awoken | Awaking | Awakes |
Be | Was/Were | Been | Being | Is |
Bear | Bore | Borne/Born | Bearing | Bears |
Beat | Beat | Beaten | Beating | Beats |
Become | Became | Become | Becoming | Becomes |
Begin | Began | Begun | Beginning | Begins |
Bend | Bent | Bent | Bending | Bends |
Bet | Bet | Bet | Betting | Bets |
Bind | Bound | Bound | Binding | Binds |
Bite | Bit | Bitten | Biting | Bites |
Bleed | Bled | Bled | Bleeding | Bleeds |
Blow | Blew | Blown | Blowing | Blows |
Break | Broke | Broken | Breaking | Breaks |
Breed | Bred | Bred | Breeding | Breeds |
Bring | Brought | Brought | Bringing | Brings |
Build | Built | Built | Building | Builds |
Burn | Burned/Burnt | Burned/Burnt | Burning | Burns |
Burst | Burst | Burst | Bursting | Bursts |
Buy | Bought | Bought | Buying | Buys |
Cast | Cast | Cast | Casting | Casts |
Catch | Caught | Caught | Catching | Catches |
Choose | Chose | Chosen | Choosing | Chooses |
Cling | Clung | Clung | Clinging | Clings |
Come | Came | Come | Coming | Comes |
Cost | Cost | Cost | Costing | Costs |
Creep | Crept | Crept | Creeping | Creeps |
Cut | Cut | Cut | Cutting | Cuts |
Deal | Dealt | Dealt | Dealing | Deals |
Dig | Dug | Dug | Digging | Digs |
Do | Did | Done | Doing | Does |
Draw | Drew | Drawn | Drawing | Draws |
Dream | Dreamed/Dreamt | Dreamed/Dreamt | Dreaming | Dreams |
Drink | Drank | Drunk | Drinking | Drinks |
Drive | Drove | Driven | Driving | Drives |
Eat | Ate | Eaten | Eating | Eats |
Fall | Fell | Fallen | Falling | Falls |
Feed | Fed | Fed | Feeding | Feeds |
Feel | Felt | Felt | Feeling | Feels |
Fight | Fought | Fought | Fighting | Fights |
Find | Found | Found | Finding | Finds |
Flee | Fled | Fled | Fleeing | Flees |
Fly | Flew | Flown | Flying | Flies |
Forget | Forgot | Forgotten | Forgetting | Forgets |
Forgive | Forgave | Forgiven | Forgiving | Forgives |
Freeze | Froze | Frozen | Freezing | Freezes |
Get | Got | Got/Gotten | Getting | Gets |
Uses of v1 v2 v3 v4 v5
V1 (Base Form / Infinitive):
Used as the base form of the verb.
Used after modal verbs (can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would) and auxiliary verbs (be, have, do) to form different tenses or moods.
Used after certain verbs to show purpose or intention (e.g., I want to learn).
V2 (Past Simple):
Used to express actions or states that occurred in the past and are now finished.
Typically used with time expressions indicating past time (e.g., yesterday, last week).
V3 (Past Participle):
Used to form the perfect tenses (present perfect, past perfect, future perfect) and passive voice.
Used with auxiliary verbs (have, has, had, be, am, is, are, was, were) to show completed actions or states.
V4 (Present Participle):
Used to form the present continuous (progressive) tense.
Also used as an adjective (participial phrase) or as part of the gerund.
V5 (Gerund):
Used as a noun, often as the subject or object of a sentence.
Used after prepositions (e.g., after, before, by) or as the object of certain verbs.
Indicates an action or state in a general sense (e.g., Swimming is fun).
Examples of v1 v2 v3 v4 v5
He wants to learn Spanish.
She studied French last year.
They have eaten dinner already.
The children are playing in the park.
Swimming helps to stay fit.
I can read this book in an hour.
He worked hard yesterday.
The cake has been baked perfectly.
We are watching a movie tonight.
Walking in the morning is refreshing.
She could sing beautifully when she was younger.
They visited London last summer.
The dishes need to be washed after dinner.
The baby is sleeping peacefully.
He plays the guitar very well.
They have gone to the beach.
Swimming in the pool is enjoyable.
We are having a party next weekend.
She taught English for many years.
Running helps to improve cardiovascular health.
FAQ’s
How do I know which form of the verb to use in a sentence?
Practice and familiarity with verb forms through reading, writing, and listening will help you develop an instinct for choosing the correct form based on the tense and context of the sentence.
Are there any exceptions or irregularities to be aware of?
Yes, English has many irregular verbs that don’t follow typical patterns. Learning these irregular verbs and their various forms will improve your proficiency in using verb forms effectively.
Where can I find more resources to study verb forms?
Online grammar guides, textbooks, and language learning websites often provide detailed explanations and exercises to help you practice and master verb forms.
What are some common examples of V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5?
Examples include: (V1) “to eat”, (V2) “ate”, (V3) “eaten”, (V4) “eating”, and (V5) “eating is enjoyable”.
Can one verb have irregular forms for V2 and V3?
Yes, many verbs in English have irregular forms for past simple (V2) and past participle (V3), such as “go” (V1) – “went” (V2) – “gone” (V3).


