Verbal Communication in Interpersonal Communication – Examples
Dive into the world of Verbal Communication in Interpersonal Communication with this complete guide. It offers practical examples and insightful tips to enhance your verbal skills. Whether it’s in a personal or professional context, understanding the nuances of verbal exchanges is crucial. This guide will walk you through the essentials of verbal interaction, ensuring you communicate your ideas clearly and effectively, fostering stronger connections with those around you.
What is Verbal Communication in Interpersonal Communication?

Verbal communication in interpersonal interactions involves the use of spoken words to convey messages. It’s not just about what is said, but also how it’s said, including tone, pace, and clarity. Understanding the role of verbal cues in interpersonal communication is key to building and maintaining strong relationships.
What is the Best Example of Verbal Communication in Interpersonal Communication?

A prime example of verbal communication in interpersonal interactions is active listening during a conversation. It involves not only hearing the words but also understanding the message and context. This includes acknowledging the speaker’s points, asking clarifying questions, and responding appropriately to ensure effective and meaningful communication.
20 Examples of Verbal Communication in Interpersonal Communication

Verbal communication in interpersonal contexts is pivotal for effective interactions. This comprehensive list of 20 examples highlights diverse scenarios, demonstrating how verbal communication shapes our daily interactions. From expressing emotions to conveying information, these examples underscore the importance and versatility of verbal communication in interpersonal communication. Each example is accompanied by a brief explanation and example sentences, providing practical insights for enhancing communication skills.
- Asking Open-Ended Questions: Encourages detailed responses.
Example: “What are your thoughts on this topic?” - Giving Compliments: Builds positive rapport.
Example: “I really appreciate your hard work on this project.” - Offering Constructive Criticism: Helps improve performance.
Example: “I like your report, but maybe you could add more data analysis.” - Expressing Gratitude: Strengthens relationships.
Example: “Thank you for your support during the project.” - Apologizing When Wrong: Demonstrates humility and respect.
Example: “I apologize for my mistake in the calculations.” - Sharing Personal Experiences: Enhances connection.
Example: “This reminds me of a similar challenge I faced last year.” - Encouraging Others: Motivates and uplifts.
Example: “You’re doing a great job; keep it up!” - Clarifying Misunderstandings: Prevents conflicts.
Example: “Just to clarify, are you suggesting we change the deadline?” - Rephrasing for Understanding: Ensures clarity.
Example: “Let me rephrase that to make sure I’m understood.” - Expressing Sympathy: Shows empathy and support.
Example: “I’m sorry to hear about your loss.” - Giving Directions: Facilitates task completion.
Example: “First, complete the report, then email it to the team.” - Asking for Feedback: Encourages open communication.
Example: “I would appreciate your feedback on my presentation.” - Expressing Agreement: Shows alignment and support.
Example: “I agree with your point about market trends.” - Disagreeing Politely: Maintains respect in differing opinions.
Example: “I see your point, but I have a different perspective.” - Making Small Talk: Builds rapport in casual settings.
Example: “How was your weekend?” - Discussing Plans: Facilitates collaboration.
Example: “Let’s discuss our strategy for the upcoming meeting.” - Expressing Interest: Shows engagement and curiosity.
Example: “That’s interesting, tell me more about it.” - Summarizing Points: Ensures mutual understanding.
Example: “So, to summarize, our main goal is to increase sales by 20%.” - Announcing Decisions: Conveys important information.
Example: “We’ve decided to move forward with the new marketing plan.” - Requesting Assistance: Shows humility and teamwork.
Example: “Could you help me understand this report better?”
Types of Verbal Communication in Interpersonal Communication
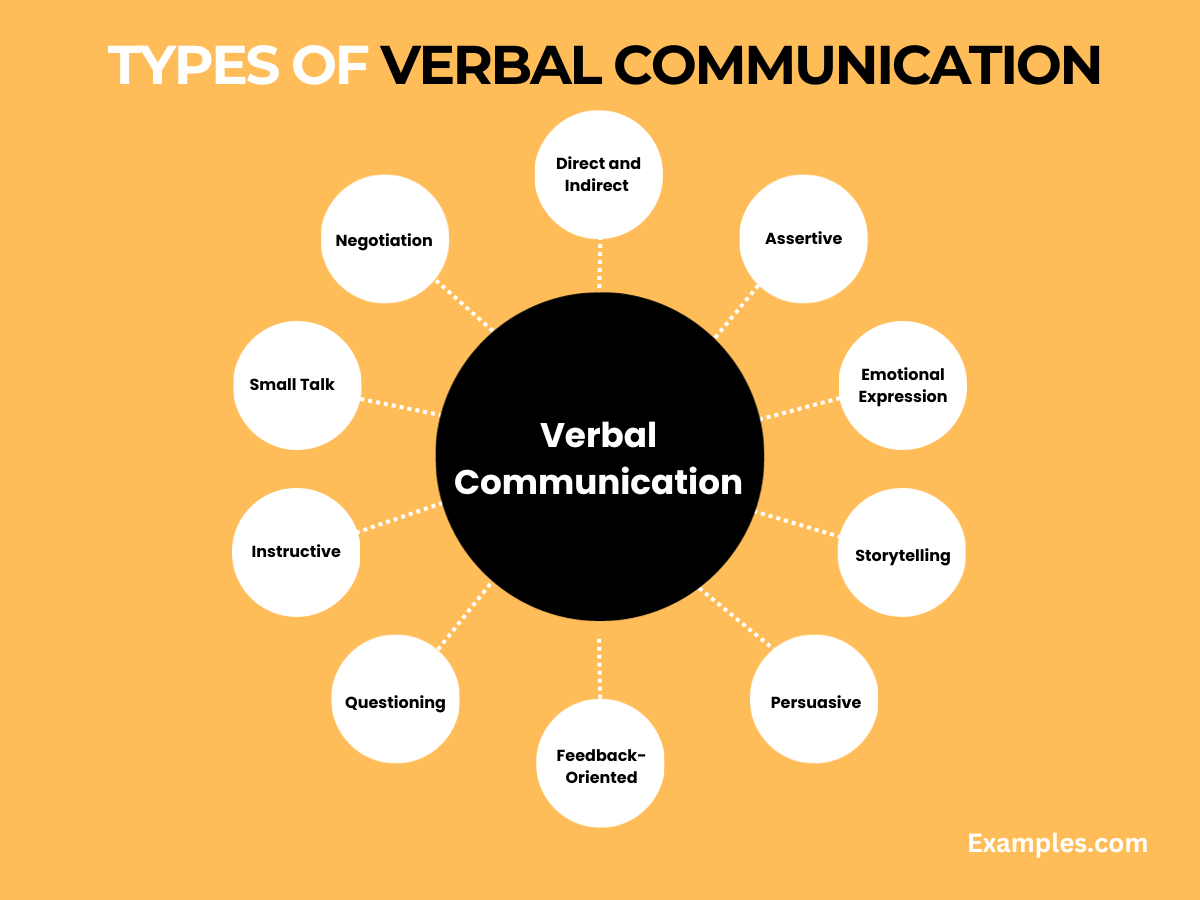
Verbal communication in interpersonal interactions is a multifaceted aspect, encompassing various forms and styles. It plays a pivotal role in conveying thoughts, emotions, and intentions between individuals. Understanding these types can greatly enhance the efficacy of interpersonal exchanges.
- Direct and Indirect Communication: Direct communication is clear and straightforward, leaving little room for misinterpretation. In contrast, indirect communication often relies on hints and suggestions, requiring interpretation beyond the spoken words. Both styles have their place, with directness often appreciated for its clarity and indirect methods valued in cultures where harmony and indirectness are prioritized.
- Assertive Communication: Assertive communication strikes a balance between passivity and aggression. It involves expressing one’s thoughts and feelings confidently and respectfully, without infringing on others’ rights. This style is crucial for healthy and honest dialogues, especially in conflict resolution.
- Emotional Expression: Emotional expression in verbal communication is vital for conveying feelings and building empathy. It ranges from expressing joy and excitement to sharing sadness or frustration, playing a key role in deepening relationships.
- Storytelling: Storytelling is a powerful verbal tool that captures attention and conveys messages in a memorable way. It’s used in both personal and professional contexts to share experiences, teach lessons, or entertain.
- Persuasive Communication: Persuasive communication is aimed at influencing the listener’s thoughts or actions. It involves presenting arguments and information in a way that appeals to logic, emotions, or values.
- Feedback-Oriented Communication: This involves giving and receiving feedback constructively. Effective feedback in verbal communication helps in personal and professional growth.
- Questioning: Asking questions is fundamental in verbal communication. It encourages dialogue, clarifies understanding, and stimulates deeper thinking.
- Instructive Communication: Often used in educational or professional settings, this type involves giving directions, guidelines, or explanations to help the listener understand a task or concept.
- Small Talk: Engaging in light, casual conversation is a form of verbal communication that helps build rapport and ease into more substantial topics.
- Negotiation: This type involves discussing to reach an agreement or compromise, essential in both personal and professional contexts.
Importance of Verbal Communication in Interpersonal Communication
Verbal communication is a cornerstone in building interpersonal relationships. It enables individuals to convey their thoughts, feelings, and intentions clearly and effectively. The significance of verbal communication in interpersonal dynamics cannot be overstated, as it facilitates understanding, fosters trust, and builds connections. Here are 10 detailed points highlighting its importance:
- Expression of Thoughts and Feelings: Verbal communication allows individuals to express their ideas, emotions, and opinions. This expression is crucial for sharing information and building empathy.
- Facilitates Understanding: Clear verbal communication helps in accurately conveying messages, ensuring that the receiver understands the speaker’s intent.
- Builds Relationships: Through sharing thoughts and experiences, verbal communication fosters deeper connections between people.
- Conflict Resolution: Effective verbal communication is key in resolving misunderstandings and conflicts by clarifying issues and finding common ground.
- Informs Decision Making: In group settings, verbal communication provides the necessary information for informed decision-making.
- Cultural Exchange: It allows for the sharing of cultural values and norms, enhancing cross-cultural understanding.
- Educational Tool: In educational settings, verbal communication is essential for teaching and learning.
- Professional Success: Strong verbal communication skills are crucial for career advancement and professional relationships.
- Persuasion and Influence: Persuasive verbal communication can influence others’ thoughts and actions, playing a vital role in leadership and negotiation.
- Emotional Support: Verbal expressions of support and understanding are fundamental in providing emotional comfort to others.
What is the Role of Verbal Communication in Interpersonal Communication
Verbal communication plays several pivotal roles in interpersonal interactions. It is not just about exchanging information; it’s about understanding the emotion and intentions behind the information. The role of verbal communication in interpersonal communication can be explained through these 10 points:
- Transmitting Information: The primary function of verbal communication is to transmit thoughts, ideas, and facts.
- Building Trust: Honest and open verbal communication can help build trust between individuals.
- Reflecting Personality: How a person communicates verbally can reveal much about their personality and character.
- Facilitating Emotional Expression: Verbal communication is a powerful tool for expressing emotions and feelings.
- Negotiating and Persuading: In negotiations, the choice of words and tone can significantly influence outcomes.
- Encouraging Feedback: Verbal communication encourages feedback, allowing for a two-way exchange of ideas and thoughts.
- Enhancing Learning: It plays a crucial role in educational environments, facilitating learning and comprehension.
- Social Interaction: Verbal communication is fundamental to social interactions, helping to form social bonds and networks.
- Professional Development: In the workplace, verbal communication skills are essential for teamwork, leadership, and customer relations.
- Cultural Reflection: It reflects cultural practices and norms, playing a key role in cultural identity and exchange.
In conclusion, verbal communication in interpersonal contexts is a multifaceted and dynamic process, integral to the fabric of our daily interactions. Whether in personal conversations, professional settings, or digital platforms, the way we express ourselves verbally can significantly impact our relationships and the effectiveness of our communication. This guide has highlighted various aspects of verbal communication, offering valuable insights for enhancing our skills and understanding the subtleties involved in effective verbal exchanges.



