30+ Verse Poem Examples
People can express themselves in many ways by writing their feelings, experiences, and thoughts. Often, one’s writing becomes a passage in a book, personalized journal, narrative essay, or poem. A person can creatively express themselves through the use of a free verse poem, which will relay a person’s thoughts and feelings through similes, metaphors, and other literary devices without the trappings of the verse structure present in different types of poems.
What is a Verse Poem? – Definition
A verse poem is a composition written in metrical or rhymed language that expresses emotions, ideas, or tells a story through a structured form. Verse poetry is characterized by its use of verse lines that follow a particular rhythm or meter and often incorporate rhyme schemes, though not always. This type of poetry can range from short, simple quatrains to complex and lengthy epics. Verse poems stand in contrast to prose poems, which are written in prose form without the formal line breaks or rhythmic patterns typical of verse. The disciplined structure of verse poems allows for a wide range of expressions, from the highly formalized sonnets of Shakespeare to the free verse of modern poets, where traditional patterns are loosened but still present in a structured form.
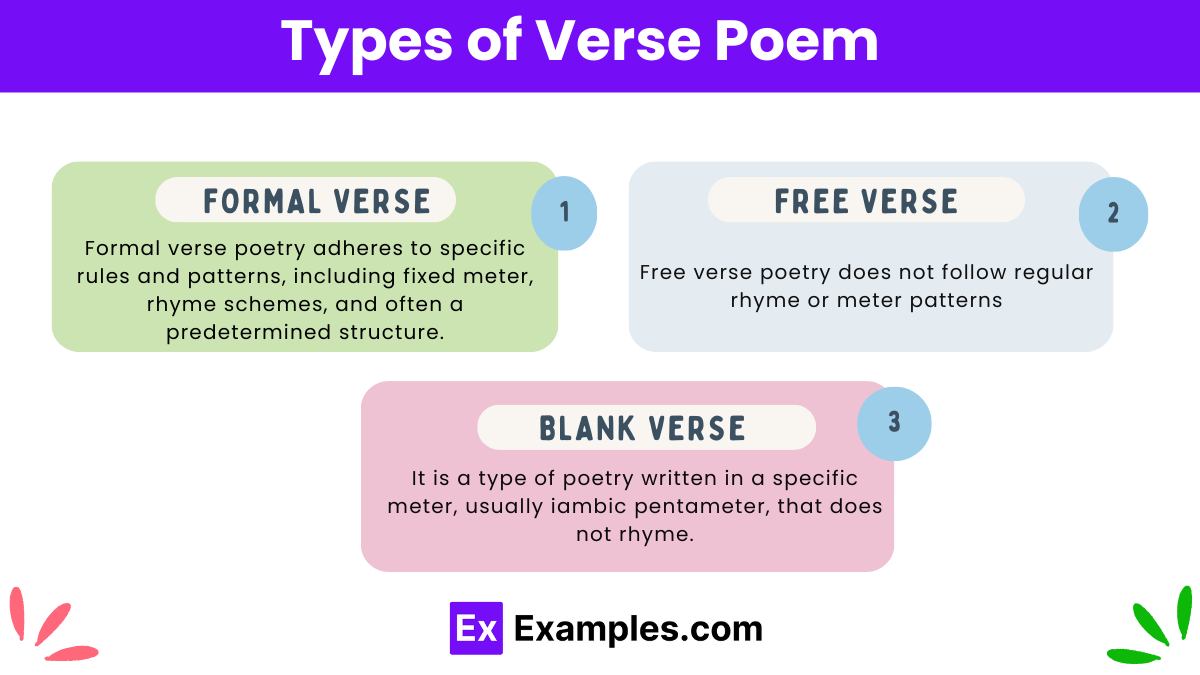
Types of Verse Poem
- Formal Verse: Formal verse poetry adheres to specific rules and patterns, including fixed meter, rhyme schemes, and often a predetermined structure. Examples of formal verse include sonnets, villanelles, haikus, and limericks. These poems follow traditional poetic forms that have been established over centuries.
- Free Verse: Free verse poetry does not follow regular rhyme or meter patterns. Poets writing in free verse have the freedom to craft their poems without adhering to the constraints of traditional structures, allowing for a more spontaneous and personal expression of ideas. This type of verse can vary greatly in line length, rhythm, and layout on the page
- Blank verse: It is a type of poetry written in a specific meter, usually iambic pentameter, that does not rhyme. It is one of the most common and versatile verse forms in English poetry.
Structure of Verse Poem
The structure of a verse poem refers to the organization of its elements, including lines, stanzas, meter, and sometimes rhyme scheme. These components work together to create rhythm, enhance meaning, and contribute to the poem’s overall aesthetic. Here’s a breakdown of the key structural elements in verse poetry:
Lines: The basic building block of a poem. Lines can vary in length and are often used to convey specific ideas or images. The way a line breaks can add emphasis or create a pause in the reading.
Stanzas: Groups of lines separated by spaces. Stanzas can have uniform or varying numbers of lines and serve to organize ideas, themes, or shifts in tone within the poem.
Meter: The rhythmic pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables in a line. Common meters include iambic pentameter (five iambs, or unstressed-stressed syllable pairs, per line), trochaic tetrameter (four trochees, or stressed-unstressed pairs, per line), and others.
Rhyme Scheme: The pattern of rhymes at the end of each line, denoted using letters (e.g., ABAB indicates that the first and third lines rhyme with each other, as do the second and fourth lines). Rhyme schemes can add musicality and structure to a poem.
Blank Verse: Written in iambic pentameter without end rhymes, blank verse is a common structure in English literature, offering a balance between rhythmic discipline and freedom.
Free Verse: Lacks a consistent meter and rhyme scheme, allowing poets to freely shape lines and stanzas. Free verse focuses on the natural rhythms of speech and the visual layout of text on the page.
Formal Poetic Forms: Some verse poems follow specific structures, such as sonnets (14 lines with a specific rhyme scheme), villanelles (19 lines with two repeating rhymes and two refrains), or haikus (three lines with a 5-7-5 syllable count).
Stanza vs. Verse
| Aspect | Stanza | Verse |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | A stanza is a grouped set of lines within a poem, set apart by spaces from other stanzas. | Verse refers to any single line of poetry or any composition written in separate lines of varying lengths, often with rhymed or metered text. |
| 1 | Stanzas structure the poem and organize its ideas, themes, or emotions into coherent units. | Verse serves as the basic building block of a poem, conveying a complete idea or part of the overall theme. |
| 2 | Stanzas can have specific forms, such as quatrains (4 lines), tercets (3 lines), or couplets (2 lines). | Verses can be free (no specific structure) or follow specific meters and rhymes. They can also refer to entire poems or significant sections within longer works of poetry. |
| 3 | Stanzas can follow specific rhyme schemes and rhythmic patterns, varying from one stanza to another. | Verses often maintain a consistent meter or rhythm within each line, contributing to the poem’s overall musicality. |
| 4 | Used to divide poems into sections, sometimes reflecting shifts in tone, topic, or speaker. | Used broadly to describe poetic lines or the poetic form of a work, including both short poems and longer epic poetry. |
30+ Verse Poem Examples
1. Stanza Verse Poem Example

corearts.co.uk
2. Rhyme Verse Poem Example

lexrich5.org
3. Love Verse Poem Example

sciendo.com
4. Short Verse Poem Example

vuir.vu.edu.au
5. Free Verse Poem Example

sjlib.org
6. Friendship Verse Poem Example

scholastic.com
7. Easy Verse Poem Example

hart-ransomcharter.com
8. Summer Verse Poem Example

oundleceprimary.org
9. 3rd Grade Verse Poem Example
digitalcommons.trinity.edu
10. Traditional Verse Poem Example

newpaltz.k12.ny.us
11. Verse Poetry Example

facultyweb.cortland.edu
12. Blank Verse Poem Example
lcps.org
13. Terse Verse Poem Example

killschool.ie
14. Line Verse Poem Example

ucd.ie
15. Family Verse Poem Example

lcps.org
16. School Verse Poem Example

dera.ioe.ac.uk
17. Self Verse Poem Example

digital.scholastic.ca
18. Nature Verse Poem Example

researchguru.net
19. Verse Poem Final Draft Example

artsforlearning.com
20. Verse Poem Study Example

facultyweb.cortland.edu
21. Verse Poem Prompt Example

dvusd.org
22. Verse Poem Exploring Example
jfmueller.faculty.noctrl.edu
23. Verse Arabic Poem Example

ijresm.com
24. Sample Verse Poem Example

globalacademicgroup.com
25. Verse Narrative Poem Example

blsschool.co.uk
26. Simple Verse Poem Example

edgarscreekps.vic.edu.au
27. Verse Prose Poem Example

vam.ac.uk
28. Verse Poem Brainstorm Example
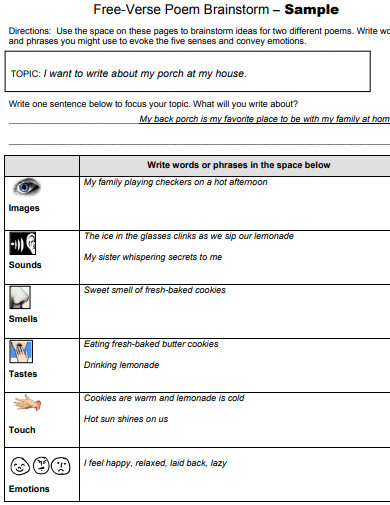
youngaudiences.org
29. Verse Poem Definition Example

scasd.org
30. Characteristics of Verse Poem Example

readwritethink.org
What Is the Common Usage of Verse Poem?
The common usage of verse poetry spans various forms and functions, reflecting the adaptability and expressive range of this literary form. Here are some key points regarding the usage of verse poems:
- Expression of Emotions and Ideas: Verse poetry is widely used to convey deep emotions, philosophical thoughts, personal reflections, and vivid imaginations. Poets utilize verse to explore the complexities of love, grief, joy, and other human experiences.
- Storytelling: Narrative verse poems tell stories, weaving tales of heroes, adventures, tragedies, and triumphs. This form allows for a blend of narrative momentum and poetic expression.
- Cultural and Historical Documentation: Many verse poems serve as records of cultural, historical, and societal moments, capturing the essence of an era, community, or significant event through poetic language.
- Artistic and Aesthetic Expression: Verse poetry is also valued for its aesthetic qualities, including its rhythm, rhyme, and the beauty of its imagery and language. Poets craft verse to create works that are appreciated for their artistry and craftsmanship.
- Educational Tool: Verse poetry is used in educational settings to teach language skills, including vocabulary, syntax, and the power of metaphorical language. Poetry analysis helps students develop critical thinking and interpretive skills.
- Therapeutic Use: Writing and reading verse poetry can have therapeutic benefits, providing a form of emotional expression and exploration that can help individuals process their feelings and experiences.
- Performance: Verse poetry is often designed for performance, whether through readings, spoken word events, or theatrical presentations. The rhythmic and rhymic qualities of verse make it particularly suited to oral performance.
- Ceremonial Functions: Verse poems are frequently used in ceremonies and rituals, such as weddings, funerals, and commemorative events, to honor, celebrate, or remember individuals and occasions.
What is a Free Verse Poem?
A free verse poem uses a free verse structure, which means that the poem will not have any rhyming scheme and word limit per verse in its format. The subject or context of the free verse poem can include multiple complex subjects, themes, and tones, which allows the writer to express themselves creatively through this medium of writing. This type of poem is also known as a freestyle poem that people often use in slam poetry.
How to Write a Free Verse Poem
Unlike most poems, a free verse poem doesn’t have a specific rhyme scheme and structure the writer has to follow. This means that the poem can have multiple verses of different lengths, word combinations, and rhyming schemes. If you need a reference to help write your free verse poem, you may use any of the free verse poem examples available on the links above.
Step 1: Select a Theme or Context for Your Free Verse Poem
Before you will write your free verse poem, you must determine and have a specific theme or context in mind. The chosen theme and context you have chosen will not only determine the words and other literary devices you will use but the theme and context will also decide the overall tone your poem will take. Note that the subject and overall theme of a poem is subjective, which means that each poem has a unique interpretation.
Step 2: Create an Outline for the Free Verse Poem
When you have determined and selected the theme and context of your free verse poem, you can choose to create an outline of the stanzas you will write. This outline format will help structure and pace your free verse poem to ensure that your audience understands and absorbs the correct emotions from your words.
Step 3: Write the Free Verse Poem
You must now write your free verse poem either digitally on writing software or physically on paper. You should take note that a free verse poem does not necessarily have limits and can have phrases or sentences in the stanza that will not make sense. Therefore it is important to keep in mind the various words and sentences you will use in the poetry to make sense of it all.
Step 4: Edit and Proofread the Poem
When you have finished writing your poem, you must either edit and proofread the poem yourself or have a test reader explore your free verse poem. This will help you determine whether each stanza and passage has no grammatical errors and delivers the intended emotion to the target market or reader.
What is Verse in Poetry?
Verse in poetry refers to any single line of a poem or any composition written in meter. It is the fundamental building block of poetry, characterized by its rhythmic structure, which can vary in pattern and length. Verse contrasts with prose by its formality of structure and its deliberate use of rhythmic and often rhyming elements to enhance or convey meaning. Here are some key points about verse in poetry:
- Meter: Verse is often defined by its meter, the pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables in a line. Common meters include iambic, trochaic, anapestic, and dactylic.
- Form and Structure: Verse can vary greatly in form and structure, including fixed forms like sonnets and haikus, as well as free verse, which eschews traditional patterns for a more open, fluid expression.
- Rhyme: Many verses utilize rhyme schemes, the patterned repetition of similar sounds in multiple lines, to create musicality and resonance.
- Stanzas: Verses are often grouped into stanzas, which can be thought of as the poem’s equivalent of paragraphs. Stanzas provide structure and can vary in length according to the poem’s overall form.
- Expressiveness: Verse allows poets to explore language rhythmically and sonically, creating layers of meaning and emotion beyond the literal words.
- Universality: Verse is a universal form of expression found in nearly every culture around the world, adapting to fit the linguistic and cultural nuances of each.
FAQs
What is the difference between a free verse poem and a haiku?
A free verse poem is a type of poem that has no specific verse or rhyming structure that will dictate the content the poet creates in the poem. A haiku is a type of poem that has its origins in Japan and has a unique and specific verse structure of five-seven-five syllables for the whole poem. The main difference between the free verse poem definition and the haiku definition is the specific verse structure each type of poem has.
What is the difference between a free verse poem and a sonnet?
A free verse poem is a poem that utilizes the free verse structure that will not enforce a specific format to the poet when they will write their poem. A sonnet is a poem that has fourteen lines and a specific variable rhyming scheme on all the lines. The free verse poem has no specific structure and allows the poet to freely style the content of the poem, unlike a sonnet.“]
Can I use a free verse poem to tell a story?
Yes, you can use a free verse poem to tell a story poetically. Just note that a free verse poem is not a storybook or a short story, so it is pivotal to properly pace and describe the story through a poetic lens.
What Is a Short Verse Poem?
A short verse poem is a concise, often impactful piece of poetry that conveys its message or emotion in a limited number of lines. These poems focus on vivid imagery, sharp emotions, or a singular idea, making every word count for maximum effect.
What Is a One Verse Poem Called?
A one verse poem, consisting of a single stanza or a standalone set of lines, is often referred to as a monostich. Monostich poems are succinct, capturing an essence, emotion, or imagery in a very brief form, emphasizing the power of brevity in poetry.
Is a Verse a Poem?
Yes, a verse can be a poem, especially when it stands alone as a complete, self-contained piece. The term “verse” refers to any single line of poetry or any composition written in lines, including entire poems. In broader terms, verse signifies poetic writing.
What Is a Verse in a Poem for Kids?
For kids, a verse in a poem is like a building block that makes up the poem. It’s a line or group of lines where words come together to form a part of the story, describe a scene, or share a feeling. Poems can have one or many verses, each adding to the poem’s rhythm and meaning.
A free verse poem is a specific type of poem that allows the poet to freely create a poem without the requirement of a specific structure, rhythm, and rhyme scheme. To create a good free verse poem it is important for the person to first know the themes and context they will cater to the poem and know how to properly utilize literary elements.