29+ Written Communication Skills Examples
In a world where written words hold immense power, mastering written communication skills is essential. This comprehensive guide dives into the nuances of effective writing, from crafting compelling emails to engaging social media posts. We’ll explore a variety of communication examples to illustrate key principles, ensuring readers gain practical insights. Whether you’re a student, professional, or aspiring writer, these skills are pivotal in conveying your message clearly and persuasively. Join us in exploring the art of written communication, and transform your writing into an impactful tool.
What are Written Communication Skills?

Written communication skills refer to the ability to express ideas, thoughts, and information effectively through writing. It encompasses a range of techniques and styles, from formal reports to casual emails, each tailored to suit the audience and purpose. These skills are crucial in various aspects of life, including education, business, and personal relationships. They involve not just the ability to write clearly and grammatically, but also the capacity to structure thoughts coherently, use appropriate tone, and engage the reader. In today’s digital age, where written communication is ubiquitous, honing these skills is more important than ever.
What is the best Example of Written Communication Skills?

A prime example of written communication skills is a well-crafted business email. It demonstrates clarity, conciseness, and professionalism. The email begins with a polite greeting, clearly states its purpose, uses precise language, and ends with a courteous closing. It’s structured to convey the message effectively while maintaining a tone appropriate for its professional context. This example showcases how effective written communication can be in achieving specific objectives, such as conveying information, requesting action, or maintaining relationships in a professional setting.
30 Written Communication Skills

In the realm of professional and personal interactions, written communication skills play a pivotal role. This comprehensive guide explores thirty distinct skills, each essential for crafting impactful and effective written communications. From clarity and conciseness to empathy and storytelling, these skills cover a wide spectrum, addressing various aspects of writing. Whether you’re drafting a business email, preparing a report, or engaging in creative writing, mastering these skills can significantly enhance the quality and effectiveness of your communication. Each skill is accompanied by a practical example and a brief explanation, providing a clear understanding of how to apply these skills in real-world scenarios. This guide is a valuable resource for anyone looking to refine their written communication abilities, ensuring their messages are not just heard but also resonate with their intended audience.
- Clarity: Essential in written communication skills, clarity ensures your message is straightforward and easily understood. It avoids ambiguity and confusion, making the communication effective.
Example: “Please submit the report by 5 PM on Friday.”
This sentence is direct and leaves no room for misinterpretation, demonstrating clear communication. - Conciseness: Being concise means expressing your message in as few words as necessary. It keeps the reader’s attention and conveys your points efficiently.
Example: “Join our team meeting at 10 AM.”
This succinct sentence conveys the necessary information without unnecessary details. - Formality: Adjusting the level of formality based on the context and audience is a vital written communication skill.
Example: “Dear Mr. Smith, I am writing to inform you…”
This opening is formal, suitable for professional or official communications. - Tone: The tone of your writing should match the intended message and audience, impacting how the reader perceives your words.
Example: “I’m thrilled to announce…”
A positive and enthusiastic tone enhances the message’s impact. - Grammar and Spelling: Proper grammar and spelling are fundamental to written communication, ensuring clarity and professionalism.
Example: “Your assistance in this project has been invaluable.”
Correct grammar and spelling reflect attention to detail and professionalism. - Structure: Organizing your writing logically makes it easier for readers to follow your thoughts and arguments.
Example: “First, we will review the agenda. Next, we discuss…”
This structured approach helps the reader understand the sequence of points. - Persuasiveness: In many cases, particularly in marketing or proposals, being persuasive is a key written communication skill.
Example: “Our product stands out due to its unique features.”
This statement is designed to persuade the reader of the product’s merits. - Empathy: Showing understanding and consideration for the reader’s perspective is crucial, especially in sensitive communications.
Example: “I understand your concerns and would like to address them.”
This shows empathy and a willingness to engage constructively. - Detail-Oriented: Providing the right amount of detail can make your written communication more informative and useful.
Example: “The meeting will cover topics A, B, and C, focusing on…”
Specific details help the reader understand the scope and focus of the meeting. - Engaging: Captivating the reader’s interest, especially in creative writing or marketing, is an essential skill.
Example: “Discover a world of possibilities with our new app.”
This engaging line aims to pique the reader’s curiosity. - Call to Action (CTA): In business writing, a clear CTA guides the reader towards the desired action.
Example: “Sign up now to start your free trial.”
This direct CTA encourages immediate action from the reader. - Adaptability: Being able to adjust your writing style for different platforms and purposes is a valuable skill.
Example: “For our social media fans: check out our latest…”
This adapts the message for a specific audience and platform. - Cultural Sensitivity: Being aware of and respecting cultural differences in communication is important for global interactions.
Example: “Happy Diwali to our clients in India!”
This shows cultural awareness and sensitivity in a global business context. - Feedback Incorporation: Using feedback to improve your writing shows adaptability and commitment to growth.
Example: “Based on your suggestions, we have updated our policy.”
This demonstrates responsiveness to feedback. - Storytelling: Effective storytelling can make your writing more relatable and memorable.
Example: “Our founder started in a small garage, dreaming of…”
This storytelling approach makes the content more engaging and personal. - Email Etiquette: Adhering to email etiquette is crucial in professional settings.
Example: “Thank you for your email. Regarding your query…”
This shows respect and professionalism in email communication. - Technical Writing: The ability to explain complex concepts in a clear, concise manner is valuable in many fields.
Example: “The device operates through a simple three-step process.”
This simplifies a technical explanation for better understanding. - Proofreading: Checking your work for errors before sending or publishing is a critical step.
Example: “I have reviewed the document for any inaccuracies.”
Proofreading ensures the final piece is polished and error-free. - Visual Elements: Using visual aids, like charts or graphs, can enhance the understanding of your written text.
Example: “Refer to the attached graph for market trends.”
Visual elements complement and clarify the written content. - Confidentiality: Maintaining confidentiality where required is a key aspect of professional writing.
Example: “This information is confidential and intended for…”
This phrase ensures the reader is aware of the information’s sensitivity. - Transparency: Being open and honest in your communication builds trust.
Example: “We aim to be transparent about our processes.”
Transparency in communication fosters trust and credibility. - Response Time: Timely responses in written communication are often appreciated and show respect for the recipient’s time.
Example: “I will get back to you by tomorrow with more details.”
Setting a clear response time shows respect and efficiency. - Follow-up: Ensuring a follow-up in your communication can keep the conversation going and clarify any doubts.
Example: “Please let me know if you need further clarification.”
Offering a follow-up invites continued dialogue and understanding. - Use of Jargon: Appropriate use of industry-specific jargon can make your writing more relatable to the intended audience.
Example: “Our SEO strategy will focus on organic growth.”
Using relevant jargon demonstrates expertise in the subject. - Citation of Sources: When necessary, citing sources lends credibility to your writing.
Example: “According to a recent study by Harvard…”
Citing sources adds authority and reliability to the information presented. - Use of Analogies: Analogies can make complex concepts easier to understand.
Example: “Navigating the software is like finding your way through a city.”
Analogies help in simplifying and relating complex ideas. - Consistency: Maintaining a consistent style and voice in your writing helps in building a recognizable brand identity.
Example: “As always, our products are crafted with care.”
Consistency in messaging reinforces brand identity and reliability. - Respectful Disagreement: Expressing disagreement in a respectful manner is key in maintaining professionalism.
Example: “I see your point, but I believe another approach may be more effective.”
This phrase shows respect while presenting an alternate viewpoint. - Inclusivity: Using inclusive language ensures that your writing is accessible and respectful to all audiences.
Example: “We welcome clients of all backgrounds and beliefs.”
Inclusive language promotes respect and diversity. - Question-Answer Format: Using a Q&A format can make information more accessible and engaging.
Example: “Q: What are our core values? A: Integrity, innovation, and teamwork.”
This format presents information in an easy-to-digest manner.
Why are Written Communication Skills Important?
Written communication skills are a cornerstone of effective interaction, especially in the modern world where text-based mediums dominate. From emails to reports, the ability to convey thoughts clearly and succinctly is vital. These skills are not only crucial for communication skills at workplace, but they also play a significant role in communication skills for students and professionals alike. Here are ten reasons why these skills are important:
- Clarity of Message: Ensures your point is understood without the need for additional clarification.
- Professionalism: Displays a level of professionalism and competence, essential for communication skills in leadership.
- Record Keeping: Provides a permanent record of your interactions, useful for reference and accountability.
- Efficiency: Saves time and resources, as well-constructed messages require less back-and-forth.
- Global Reach: Enables you to communicate across geographical boundaries, crucial in today’s globalized world.
- Legal and Compliance Requirements: Essential in meeting legal standards and compliance in business and communication skills for legal professionals.
- Inclusivity: Allows for communication with individuals who may prefer or require written forms of communication.
- Branding: Reflects your personal or organizational brand, aligning with brand communication strategies.
- Feedback and Improvement: Facilitates the provision and receipt of communication skills feedback.
- Adaptability: Enables adaptation to various formats and styles, catering to diverse audiences.
What Are the Main Types of Written Communication?
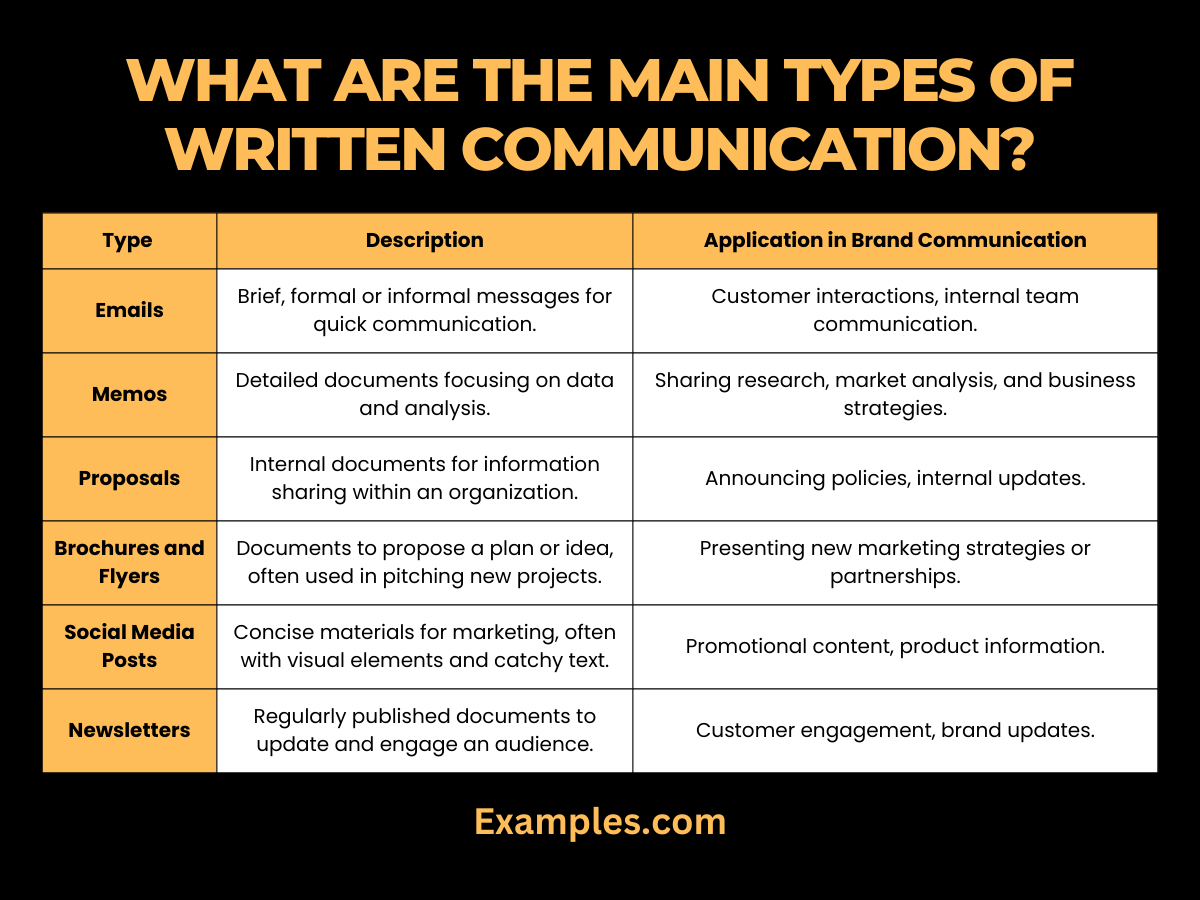
Written communication is a pivotal aspect of brand communication, encompassing various forms and styles. Each type serves a specific purpose and is essential in different contexts. Here’s a table outlining the types of written communication:
| Type | Description | Application in Brand Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Emails | Brief, formal or informal messages for quick communication. | Customer interactions, internal team communication. |
| Reports | Detailed documents focusing on data and analysis. | Sharing research, market analysis, and business strategies. |
| Memos | Internal documents for information sharing within an organization. | Announcing policies, internal updates. |
| Proposals | Documents to propose a plan or idea, often used in pitching new projects. | Presenting new marketing strategies or partnerships. |
| Brochures and Flyers | Concise materials for marketing, often with visual elements and catchy text. | Promotional content, product information. |
| Social Media Posts | Brief and engaging content tailored for different social media platforms. | Brand promotion, customer engagement, Communication Skills for Business. |
| Newsletters | Regularly published documents to update and engage an audience. | Customer engagement, brand updates. |
| Blog Posts | Informative or entertaining articles on a company’s website. | SEO, customer education, brand awareness. |
| Press Releases | Official statements for the media to announce significant news. | Public relations, major announcements. |
| User Manuals/Guides | Instructional content to help users understand and use products or services. | Product support, customer service. |
| Legal Documents | Formal documents for agreements, terms and conditions, etc. | Contracts, legal compliance, company policies. |
| Academic Writing | Research-based writing, often found in journals or academic publications. | Research and development, educational resources. |
Written Communication Strategies
Effective written communication strategies are essential for conveying messages clearly and efficiently. They are particularly important in brand communication and can significantly enhance communication skills for business. Here are five key strategies:
- Understand Your Audience: Tailor your language and style to suit your audience’s needs and expectations.
- Be Clear and Concise: Avoid unnecessary jargon and keep your messages straightforward.
- Organize Your Content: Structure your writing logically, making it easy for the reader to follow.
- Use Appropriate Tone: The tone should reflect the context and purpose of your communication.
- Review and Edit: Always proofread your writing to eliminate errors and improve clarity.
How to Improve Your Written Communication Skills
Improving your written communication skills is essential for success in many areas, including communication skills in relationships and communication skills in nursing. Here are ten tips to enhance these skills:
- Read Regularly: Reading a variety of texts can improve vocabulary and understanding of different writing styles.
- Practice Writing: Regular practice helps you develop your own style and improves fluency.
- Seek Feedback: Getting communication skills feedback can provide insights into areas for improvement.
- Attend Workshops: Participating in writing workshops can provide practical tips and techniques.
- Use Technology: Leverage tools like grammar checkers to help refine your writing.
- Study Good Examples: Analyze well-written documents to understand effective communication techniques.
- Understand the Purpose: Be clear about what you want to achieve with your writing.
- Be Audience-Centric: Adapt your writing style to suit your audience’s preferences and comprehension level.
- Edit Ruthlessly: Be prepared to cut unnecessary content to enhance clarity and conciseness.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of the latest trends and norms in professional writing.
Tips for Written Communication Skills
Here are ten additional tips to further refine your written communication skills, which are crucial in areas like communication skills for young adults and communication skills training:
- Use Simple Language: Avoid complex words where simpler ones will suffice.
- Be Specific: Avoid vagueness to ensure the recipient understands your message clearly.
- Use Active Voice: Active voice makes your writing more direct and engaging.
- Be Mindful of Non-Verbal Cues: In written communication, elements like tone and structure can convey non-verbal cues.
- Adapt to Cultural Differences: Be aware of and respect cultural differences in communication styles.
- Use Visuals When Appropriate: Diagrams and charts can sometimes convey information more effectively than words.
- Plan Before You Write: Organize your thoughts and plan the structure of your communication.
- Use Bullet Points and Headings: These help to break down information and make it more digestible.
- Keep the Audience Engaged: Use questions or prompts to engage the reader.
- Constantly Update Your Skills: Stay informed about new communication tools and techniques.
In summary, understanding the diverse types of written communication is crucial for effective brand communication. Whether it’s engaging through social media posts, formalizing agreements with legal documents, or educating customers via user manuals, each form plays a significant role in conveying a brand’s message. Mastery of these formats ensures clear, consistent, and impactful communication with various stakeholders, enhancing overall brand presence and reputation.
Moreover, the various forms of written communication, including emails, reports, memos, and social media posts, each serve specific purposes in brand communication. Mastering these different types enhances your ability to communicate effectively with a wide range of stakeholders, thereby strengthening your brand’s presence and reputation. To further refine your written communication skills, consider regularly reading diverse texts, practicing writing, and seeking feedback. Also, attending workshops and using technology like grammar checkers can provide additional support in honing these skills.
For more insights on effective communication strategies, the Harvard Business Review offers valuable resources on communication skills in the workplace. Visit Harvard Business Review – Communication for detailed articles and case studies.



