8+ Outline Examples
A well-written report or speech is most likely the result of an outline. Delivery of a speech or submission of a report is only part of the whole process of making that article. Without a plan, there is no act of doing or action. For example, going into battle without strategy is like running head-on towards a sword. Suicide.
Outline template and speech outline examples in the page show that having an outline to a speech is always helpful and provide guidance to the direction of an article. Scroll down the page to get a better look at other samples.
What is an Outline in Writing?
What Is the Format of a Standard Outline?
A standard outline helps organize ideas and structure information logically. Here’s a common format for a standard outline, often used for essays, research papers, or presentations:
I. Introduction
A. Background information
B. Purpose or thesis statement
II. Main Point 1
A. Subpoint 1
1. Detail or example
2. Detail or example
B. Subpoint 2
1. Detail or example
2. Detail or example
III. Main Point 2
A. Subpoint 1
1. Detail or example
2. Detail or example
B. Subpoint 2
1. Detail or example
2. Detail or example
IV. Main Point 3
A. Subpoint 1
1. Detail or example
2. Detail or example
B. Subpoint 2
1. Detail or example
2. Detail or example
V. Conclusion
A. Summary of main points
B. Restate thesis or main purpose
C. Closing thoughts or call to action
Outline Example for Research
Topic: The Effects of Climate Change on Coral Reefs
I. Introduction
- A. Hook: Start with a compelling statistic or fact about coral reef degradation.
- B. Background Information: Briefly explain what coral reefs are and their ecological importance.
- C. Thesis Statement: Climate change significantly affects coral reefs by causing coral bleaching, ocean acidification, and disrupting marine ecosystems.
II. Coral Bleaching
- A. Definition and Process
- Explain what coral bleaching is.
- B. Causes
- Rising sea temperatures
- C. Consequences
- Loss of vibrant coral colors
III. Ocean Acidification
- A. Definition and Process
- Define ocean acidification.
- B. Effects on Coral Reefs
- Weakening of coral skeletons
- C. Broader Implications
- Impact on marine biodiversity
IV. Disruption of Marine Ecosystems
- A. Changes in Species Composition
- Shifts in dominant species
- B. Impact on Fish Populations
- Decline in fish populations reliant on coral reefs
- C. Ecological Balance
- Altered predator-prey relationships
V. Mitigation and Conservation Efforts
- A. Coral Restoration Projects
- Coral farming and transplantation
- B. Reducing Carbon Footprint
- Global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
- C. Public Awareness and Education
- Campaigns to raise awareness about coral reef conservation
VI. Conclusion
- A. Restate Thesis: Recap the significant effects of climate change on coral reefs.
- B. Summary of Main Points: Briefly summarize the key points discussed.
- C. Call to Action: Emphasize the importance of continued efforts in conservation and climate action to protect coral reefs.
Outline Example for Essay
Topic: The Benefits of Renewable Energy
I. Introduction
- A. Hook: Start with a compelling fact about the rise of renewable energy usage worldwide.
- B. Background Information: Briefly explain what renewable energy is and its importance.
- C. Thesis Statement: Renewable energy offers numerous benefits including environmental protection, economic growth, and energy security.
II. Environmental Protection
- A. Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels
- Mitigation of climate change effects
- B. Decrease in Air Pollution
- Cleaner air quality
- Health benefits from reduced respiratory and cardiovascular diseases
- C. Conservation of Natural Resources
- Sustainable use of resources like wind, solar, and water
- Preservation of ecosystems and biodiversity
III. Economic Growth
- A. Job Creation
- Employment opportunities in renewable energy sectors
- Training and education for green jobs
- B. Energy Independence
- Reduced reliance on imported fossil fuels
- Stabilization of energy prices
- C. Investment Opportunities
- Growth in renewable energy markets
- Attraction of private and public investments
IV. Energy Security
- A. Reliability and Resilience
- Diverse energy sources reducing risk of supply disruption
- Localized energy production enhancing resilience to natural disasters
- B. Technological Advancements
- Innovations in energy storage and grid management
- Improvements in efficiency and cost-effectiveness
- C. Long-term Sustainability
- Unlimited supply of renewable resources
- Future-proof energy solutions for generations to come
V. Conclusion
- A. Restate Thesis: Summarize the key benefits of renewable energy.
- B. Summary of Main Points: Recap the environmental, economic, and energy security advantages discussed.
- C. Call to Action: Encourage the adoption and support of renewable energy initiatives to ensure a sustainable future.
Outline Example for Speech
Topic: The Importance of Healthy Eating
I. Introduction
- A. Hook: Share an engaging statistic or anecdote about the impact of diet on health.
- B. Importance of Topic: Explain why healthy eating is crucial for overall well-being.
- C. Thesis Statement: Healthy eating is essential for maintaining physical health, improving mental well-being, and boosting energy levels.
II. Maintaining Physical Health
- A. Nutritional Benefits
- Provides essential vitamins and minerals
- Supports immune system function
- B. Disease Prevention
- Reduces risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes
- Helps maintain a healthy weight
- C. Longevity
- Contributes to a longer lifespan
- Improves quality of life in later years
III. Improving Mental Well-being
- A. Mood Regulation
- Impact of nutrients on brain chemistry
- Foods that promote serotonin production
- B. Cognitive Function
- Omega-3 fatty acids and brain health
- Antioxidants and memory improvement
- C. Stress Reduction
- Effects of a balanced diet on stress levels
- Importance of regular meal times and hydration
IV. Boosting Energy Levels
- A. Balanced Diet
- Role of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats
- Importance of portion control
- B. Sustained Energy
- Benefits of complex carbohydrates
- Avoiding energy crashes with balanced meals
- C. Hydration
- Importance of water for energy
- Effects of dehydration on physical and mental performance
V. Conclusion
- A. Restate Thesis: Reiterate the importance of healthy eating for physical health, mental well-being, and energy levels.
- B. Summary of Main Points: Briefly recap the key points discussed.
- C. Call to Action: Encourage the audience to adopt healthier eating habits and make informed food choices.
Resume Outline Example
Creating a well-structured resume is crucial for making a strong impression on potential employers. Here is an example outline for a resume:
I. Contact Information
- Full Name
- Address
- Phone Number
- Email Address
- LinkedIn Profile (optional)
- Professional Website/Portfolio (optional)
II. Objective or Summary Statement
- Objective Statement: A brief statement of your career goals and what you aim to achieve in the desired position.
- Summary Statement: A concise summary of your professional background, key skills, and achievements.
III. Professional Experience
- Job Title
- Company Name, Location (City, State)
- Dates of Employment (Month, Year – Month, Year)
- Key Responsibilities and Achievements:
- Bullet point describing a major responsibility or achievement.
- Bullet point describing another major responsibility or achievement.
- Bullet point describing a quantifiable result or improvement.
IV. Education
- Degree Earned (e.g., Bachelor of Arts in English)
- Institution Name, Location (City, State)
- Graduation Date (Month, Year)
- Relevant Coursework or Honors (optional)
V. Skills
- Technical Skills: List specific technical skills relevant to the job (e.g., software proficiency, programming languages).
- Soft Skills: List key interpersonal skills (e.g., communication, teamwork, leadership).
- Language Skills: List any foreign languages spoken and proficiency level.
VI. Certifications and Licenses
- Certification Name
- Issuing Organization
- Date Earned (Month, Year)
- Relevant Details or Coursework (optional)
VII. Professional Affiliations
- Organization Name
- Role/Title
- Dates of Membership
- Key Contributions or Involvement (optional)
VIII. Volunteer Experience (optional)
- Role/Title
- Organization Name, Location (City, State)
- Dates of Involvement (Month, Year – Month, Year)
- Key Responsibilities and Achievements:
- Bullet point describing a major responsibility or achievement.
- Bullet point describing another major responsibility or achievement.
IX. Awards and Honors (optional)
- Award Name
- Issuing Organization
- Date Received (Month, Year)
- Brief Description of the Award (optional)
X. Publications and Presentations (optional)
- Title of Publication or Presentation
- Venue or Journal Name
- Date of Publication or Presentation (Month, Year)
- Brief Description or Link to the Work (optional)
Paragraph Outline Examples
Creating a paragraph outline helps structure individual paragraphs within a larger piece of writing. Here are some examples of paragraph outlines for different types of paragraphs:
1. Descriptive Paragraph Outline
Topic: A Day at the Beach
I. Topic Sentence
- Introduce the main idea: Describe the atmosphere and experience of a day at the beach.
II. Supporting Details
- Sight: Describe the clear blue sky, the shimmering water, and the golden sand.
- Sound: Mention the sound of waves crashing, children laughing, and seagulls calling.
- Smell: Describe the salty sea air mixed with the scent of sunscreen.
- Touch: Explain the feeling of warm sand underfoot and the cool splash of ocean water.
- Taste: Mention the taste of salty sea air and snacks like ice cream or fresh fruit.
III. Concluding Sentence
- Summarize the sensory details and reiterate the enjoyment of a day at the beach.
2. Narrative Paragraph Outline
Topic: The Day I Learned to Ride a Bike
I. Topic Sentence
- Introduce the main idea: Narrate the experience of learning to ride a bike.
II. Supporting Details
- Setting the Scene: Describe the location, time of day, and initial feelings of excitement and nervousness.
- First Attempts: Explain the initial wobbles, falls, and encouragement from a parent or friend.
- Breakthrough Moment: Describe the moment of balance and realization of riding independently.
- Feelings: Detail the emotions of triumph, freedom, and pride.
- Aftermath: Mention the newfound confidence and desire to ride again.
III. Concluding Sentence
- Reflect on the significance of the experience and its impact on personal growth.
3. Expository Paragraph Outline
Topic: The Benefits of Reading Books
I. Topic Sentence
- Introduce the main idea: Explain the benefits of reading books.
II. Supporting Details
- Knowledge Expansion: Discuss how reading books broadens knowledge and understanding of various subjects.
- Cognitive Benefits: Explain how reading improves concentration, critical thinking, and memory.
- Stress Reduction: Describe the calming effect of reading and its ability to reduce stress.
- Empathy and Understanding: Highlight how reading fiction can increase empathy by exposing readers to different perspectives.
- Vocabulary and Language Skills: Mention the improvement in vocabulary and language skills through regular reading.
III. Concluding Sentence
- Summarize the benefits and encourage the reader to incorporate more reading into their routine.
Simple Outline Example
A simple outline helps organize ideas and structure a piece of writing effectively. Here is a straightforward example:
Topic: The Benefits of Exercise
I. Introduction
- A. Hook: Start with an interesting fact or statistic about exercise.
- B. Background Information: Briefly explain what exercise is and its general importance.
- C. Thesis Statement: Exercise provides numerous benefits for physical health, mental well-being, and overall quality of life.
II. Physical Health Benefits
- A. Weight Management
- Helps maintain a healthy weight
- Prevents obesity-related diseases
- B. Cardiovascular Health
- Strengthens the heart
- Reduces the risk of heart disease
- C. Muscle and Bone Strength
- Builds and maintains muscle mass
- Enhances bone density
III. Mental Well-being Benefits
- A. Stress Reduction
- Releases endorphins
- Lowers cortisol levels
- B. Improved Mood
- Reduces symptoms of depression and anxiety
- Enhances overall mood
- C. Better Sleep
- Promotes deeper and more restful sleep
- Helps regulate sleep patterns
IV. Overall Quality of Life
- A. Increased Energy Levels
- Boosts stamina and endurance
- Reduces feelings of fatigue
- B. Enhanced Longevity
- Contributes to a longer lifespan
- Improves quality of life in later years
- C. Social Benefits
- Encourages social interaction through group activities
- Builds a sense of community and support
V. Conclusion
- A. Restate Thesis: Summarize the key benefits of exercise.
- B. Summary of Main Points: Recap the physical, mental, and overall quality of life benefits.
- C. Call to Action: Encourage the audience to incorporate regular exercise into their daily routine for a healthier and happier life.
More Samples & Examples of Outline in PDF
1. Analytical Essay Sample Outline
2. Formal Essay Outline
3. General Protocol Outline
4. Research Protocol Sample Outline
5. Project Plan Outline
6. Business Plan Sample Outline
7. Professional Resume Outline
Uses of an Outline
An outline serves multiple purposes in the writing process, aiding both planning and execution. Here are the key uses:
1. Organizing Ideas
- Clarity: Helps in arranging thoughts logically.
- Structure: Provides a framework for the writing.
2. Guiding the Writing Process
- Roadmap: Acts as a guide during drafting.
- Focus: Keeps the writer on track with the main points.
3. Enhancing Coherence and Flow
- Logical Progression: Ensures ideas flow logically from one to another.
- Connection: Helps in linking paragraphs and sections smoothly.
4. Improving Time Management
- Efficiency: Speeds up the writing process by providing a clear plan.
- Deadlines: Helps in meeting writing deadlines by organizing tasks.
5. Facilitating Revision and Editing
- Overview: Offers a bird’s-eye view for easy identification of weak points.
- Adjustments: Simplifies the process of restructuring and refining ideas.
6. Aiding Collaboration
- Shared Vision: Provides a common framework for group writing projects.
- Coordination: Helps team members stay aligned with the overall plan.
7. Enhancing Persuasiveness
- Strong Argument: Ensures all points support the thesis effectively.
- Balanced Presentation: Allows for the inclusion of counterarguments and their rebuttals.
8. Assisting in Complex Projects
- Detailed Planning: Breaks down large projects into manageable parts.
- Milestones: Helps in setting and achieving intermediate goals.
Guidelines for Writing an Outline

Creating an effective outline involves several key steps to ensure clarity and coherence. Here are the essential guidelines:
1. Understand the Purpose
- Clarify the Goal: Know the purpose of your writing and what you aim to achieve.
- Identify the Audience: Tailor your outline to suit your audience’s needs and expectations.
2. Choose the Outline Type
- Alphanumeric: Uses Roman numerals, letters, and numbers (e.g., I, A, 1).
- Decimal: Uses a numerical system (e.g., 1.0, 1.1, 1.2).
- Subjective: Informal, using bullet points or phrases.
3. Start with a Thesis Statement
- Central Idea: Clearly state the main argument or purpose of your writing.
- Focus: Ensure all points support this central idea.
4. Organize Main Points
- Hierarchy: Arrange points from most to least important.
- Order: Decide on a logical sequence (chronological, spatial, or thematic).
5. Add Supporting Details
- Subpoints: Provide details, examples, and evidence under each main point.
- Balance: Ensure each main point has sufficient supporting details.
6. Use Consistent Formatting
- Indentation: Clearly distinguish between main points and subpoints.
- Symbols: Use a consistent system (numbers, letters) to indicate levels.
7. Be Clear and Concise
- Brevity: Use short phrases or sentences to summarize points.
- Clarity: Avoid ambiguity and ensure each point is understandable.
8. Review and Revise
- Coherence: Check that points flow logically and support the thesis.
- Completeness: Ensure all necessary points and details are included.
- Flexibility: Be prepared to adjust the outline as needed.
Why is an outline important?
An outline helps organize thoughts, ensures logical flow, and provides a clear structure, making writing more efficient and coherent.
How do I start creating an outline?
Begin with a thesis statement or main idea, then list the main points and supporting details in a logical order.
What are the different types of outlines?
Common types include alphanumeric, decimal, and full sentence outlines, each varying in detail and format.
Can an outline be revised?
Yes, outlines should be flexible and can be revised as ideas develop and new information is gathered.
What is the difference between a topic and a sentence outline?
A topic outline uses brief phrases, while a sentence outline uses complete sentences to convey more detailed information.
How detailed should an outline be?
The level of detail depends on the complexity of the topic and the needs of the writer, ranging from broad points to specific details.
Should I use a computer or paper for my outline?
Both methods are effective; choose the one that best suits your preference and makes it easier for you to organize your thoughts.
How do I know if my outline is effective?
An effective outline clearly organizes ideas, logically progresses from one point to another, and aligns with the thesis statement.
Can an outline help with time management?
Yes, an outline can streamline the writing process, helping to allocate time efficiently and ensuring all necessary points are covered.
Are there tools or software for creating outlines?
Yes, tools like Microsoft Word, Google Docs, and specialized apps like Scrivener can help create and organize outlines.
8+ Outline Examples
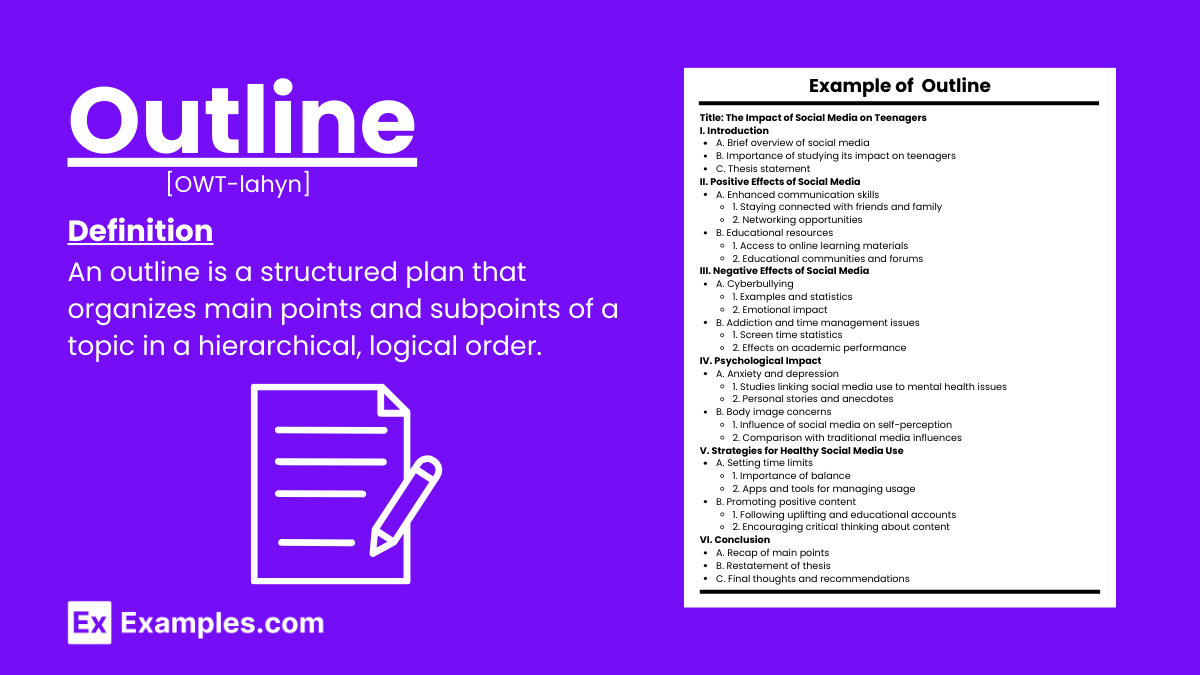
A well-written report or speech is most likely the result of an outline. Delivery of a speech or submission of a report is only part of the whole process of making that article. Without a plan, there is no act of doing or action. For example, going into battle without strategy is like running head-on towards a sword. Suicide.
Outline template and speech outline examples in the page show that having an outline to a speech is always helpful and provide guidance to the direction of an article. Scroll down the page to get a better look at other samples.
What is an Outline in Writing?
An outline in writing is a structured plan that organizes main ideas and supporting details before drafting a text. It helps writers logically arrange their thoughts, ensuring clarity and coherence. Outlines can be formal, with numbered headings and subheadings, or informal, using bullet points. They serve as a roadmap for the writing process, aiding in the development of a clear and effective composition.
What Is the Format of a Standard Outline?
A standard outline helps organize ideas and structure information logically. Here’s a common format for a standard outline, often used for essays, research papers, or presentations:
I. Introduction
A. Background information
B. Purpose or thesis statement
II. Main Point 1
A. Subpoint 1
1. Detail or example
2. Detail or example
B. Subpoint 2
1. Detail or example
2. Detail or example
III. Main Point 2
A. Subpoint 1
1. Detail or example
2. Detail or example
B. Subpoint 2
1. Detail or example
2. Detail or example
IV. Main Point 3
A. Subpoint 1
1. Detail or example
2. Detail or example
B. Subpoint 2
1. Detail or example
2. Detail or example
V. Conclusion
A. Summary of main points
B. Restate thesis or main purpose
C. Closing thoughts or call to action
Outline Example for Research
Topic: The Effects of Climate Change on Coral Reefs
I. Introduction
A. Hook: Start with a compelling statistic or fact about coral reef degradation.
B. Background Information: Briefly explain what coral reefs are and their ecological importance.
C. Thesis Statement: Climate change significantly affects coral reefs by causing coral bleaching, ocean acidification, and disrupting marine ecosystems.
II. Coral Bleaching
A. Definition and Process
Explain what coral bleaching is.
B. Causes
Rising sea temperatures
C. Consequences
Loss of vibrant coral colors
III. Ocean Acidification
A. Definition and Process
Define ocean acidification.
B. Effects on Coral Reefs
Weakening of coral skeletons
C. Broader Implications
Impact on marine biodiversity
IV. Disruption of Marine Ecosystems
A. Changes in Species Composition
Shifts in dominant species
B. Impact on Fish Populations
Decline in fish populations reliant on coral reefs
C. Ecological Balance
Altered predator-prey relationships
V. Mitigation and Conservation Efforts
A. Coral Restoration Projects
Coral farming and transplantation
B. Reducing Carbon Footprint
Global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
C. Public Awareness and Education
Campaigns to raise awareness about coral reef conservation
VI. Conclusion
A. Restate Thesis: Recap the significant effects of climate change on coral reefs.
B. Summary of Main Points: Briefly summarize the key points discussed.
C. Call to Action: Emphasize the importance of continued efforts in conservation and climate action to protect coral reefs.
Outline Example for Essay
Topic: The Benefits of Renewable Energy
I. Introduction
A. Hook: Start with a compelling fact about the rise of renewable energy usage worldwide.
B. Background Information: Briefly explain what renewable energy is and its importance.
C. Thesis Statement: Renewable energy offers numerous benefits including environmental protection, economic growth, and energy security.
II. Environmental Protection
A. Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels
Mitigation of climate change effects
B. Decrease in Air Pollution
Cleaner air quality
Health benefits from reduced respiratory and cardiovascular diseases
C. Conservation of Natural Resources
Sustainable use of resources like wind, solar, and water
Preservation of ecosystems and biodiversity
III. Economic Growth
A. Job Creation
Employment opportunities in renewable energy sectors
Training and education for green jobs
B. Energy Independence
Reduced reliance on imported fossil fuels
Stabilization of energy prices
C. Investment Opportunities
Growth in renewable energy markets
Attraction of private and public investments
IV. Energy Security
A. Reliability and Resilience
Diverse energy sources reducing risk of supply disruption
Localized energy production enhancing resilience to natural disasters
B. Technological Advancements
Innovations in energy storage and grid management
Improvements in efficiency and cost-effectiveness
C. Long-term Sustainability
Unlimited supply of renewable resources
Future-proof energy solutions for generations to come
V. Conclusion
A. Restate Thesis: Summarize the key benefits of renewable energy.
B. Summary of Main Points: Recap the environmental, economic, and energy security advantages discussed.
C. Call to Action: Encourage the adoption and support of renewable energy initiatives to ensure a sustainable future.
Outline Example for Speech
Topic: The Importance of Healthy Eating
I. Introduction
A. Hook: Share an engaging statistic or anecdote about the impact of diet on health.
B. Importance of Topic: Explain why healthy eating is crucial for overall well-being.
C. Thesis Statement: Healthy eating is essential for maintaining physical health, improving mental well-being, and boosting energy levels.
II. Maintaining Physical Health
A. Nutritional Benefits
Provides essential vitamins and minerals
Supports immune system function
B. Disease Prevention
Reduces risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes
Helps maintain a healthy weight
C. Longevity
Contributes to a longer lifespan
Improves quality of life in later years
III. Improving Mental Well-being
A. Mood Regulation
Impact of nutrients on brain chemistry
Foods that promote serotonin production
B. Cognitive Function
Omega-3 fatty acids and brain health
Antioxidants and memory improvement
C. Stress Reduction
Effects of a balanced diet on stress levels
Importance of regular meal times and hydration
IV. Boosting Energy Levels
A. Balanced Diet
Role of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats
Importance of portion control
B. Sustained Energy
Benefits of complex carbohydrates
Avoiding energy crashes with balanced meals
C. Hydration
Importance of water for energy
Effects of dehydration on physical and mental performance
V. Conclusion
A. Restate Thesis: Reiterate the importance of healthy eating for physical health, mental well-being, and energy levels.
B. Summary of Main Points: Briefly recap the key points discussed.
C. Call to Action: Encourage the audience to adopt healthier eating habits and make informed food choices.
Resume Outline Example
Creating a well-structured resume is crucial for making a strong impression on potential employers. Here is an example outline for a resume:
I. Contact Information
Full Name
Address
Phone Number
Email Address
LinkedIn Profile (optional)
Professional Website/Portfolio (optional)
II. Objective or Summary Statement
Objective Statement: A brief statement of your career goals and what you aim to achieve in the desired position.
Summary Statement: A concise summary of your professional background, key skills, and achievements.
III. Professional Experience
Job Title
Company Name, Location (City, State)
Dates of Employment (Month, Year – Month, Year)
Key Responsibilities and Achievements:
Bullet point describing a major responsibility or achievement.
Bullet point describing another major responsibility or achievement.
Bullet point describing a quantifiable result or improvement.
IV. Education
Degree Earned (e.g., Bachelor of Arts in English)
Institution Name, Location (City, State)
Graduation Date (Month, Year)
Relevant Coursework or Honors (optional)
V. Skills
Technical Skills: List specific technical skills relevant to the job (e.g., software proficiency, programming languages).
Soft Skills: List key interpersonal skills (e.g., communication, teamwork, leadership).
Language Skills: List any foreign languages spoken and proficiency level.
VI. Certifications and Licenses
Certification Name
Issuing Organization
Date Earned (Month, Year)
Relevant Details or Coursework (optional)
VII. Professional Affiliations
Organization Name
Role/Title
Dates of Membership
Key Contributions or Involvement (optional)
VIII. Volunteer Experience (optional)
Role/Title
Organization Name, Location (City, State)
Dates of Involvement (Month, Year – Month, Year)
Key Responsibilities and Achievements:
Bullet point describing a major responsibility or achievement.
Bullet point describing another major responsibility or achievement.
IX. Awards and Honors (optional)
Award Name
Issuing Organization
Date Received (Month, Year)
Brief Description of the Award (optional)
X. Publications and Presentations (optional)
Title of Publication or Presentation
Venue or Journal Name
Date of Publication or Presentation (Month, Year)
Brief Description or Link to the Work (optional)
Paragraph Outline Examples
Creating a paragraph outline helps structure individual paragraphs within a larger piece of writing. Here are some examples of paragraph outlines for different types of paragraphs:
1. Descriptive Paragraph Outline
Topic: A Day at the Beach
I. Topic Sentence
Introduce the main idea: Describe the atmosphere and experience of a day at the beach.
II. Supporting Details
Sight: Describe the clear blue sky, the shimmering water, and the golden sand.
Sound: Mention the sound of waves crashing, children laughing, and seagulls calling.
Smell: Describe the salty sea air mixed with the scent of sunscreen.
Touch: Explain the feeling of warm sand underfoot and the cool splash of ocean water.
Taste: Mention the taste of salty sea air and snacks like ice cream or fresh fruit.
III. Concluding Sentence
Summarize the sensory details and reiterate the enjoyment of a day at the beach.
2. Narrative Paragraph Outline
Topic: The Day I Learned to Ride a Bike
I. Topic Sentence
Introduce the main idea: Narrate the experience of learning to ride a bike.
II. Supporting Details
Setting the Scene: Describe the location, time of day, and initial feelings of excitement and nervousness.
First Attempts: Explain the initial wobbles, falls, and encouragement from a parent or friend.
Breakthrough Moment: Describe the moment of balance and realization of riding independently.
Feelings: Detail the emotions of triumph, freedom, and pride.
Aftermath: Mention the newfound confidence and desire to ride again.
III. Concluding Sentence
Reflect on the significance of the experience and its impact on personal growth.
3. Expository Paragraph Outline
Topic: The Benefits of Reading Books
I. Topic Sentence
Introduce the main idea: Explain the benefits of reading books.
II. Supporting Details
Knowledge Expansion: Discuss how reading books broadens knowledge and understanding of various subjects.
Cognitive Benefits: Explain how reading improves concentration, critical thinking, and memory.
Stress Reduction: Describe the calming effect of reading and its ability to reduce stress.
Empathy and Understanding: Highlight how reading fiction can increase empathy by exposing readers to different perspectives.
Vocabulary and Language Skills: Mention the improvement in vocabulary and language skills through regular reading.
III. Concluding Sentence
Summarize the benefits and encourage the reader to incorporate more reading into their routine.
Simple Outline Example
A simple outline helps organize ideas and structure a piece of writing effectively. Here is a straightforward example:
Topic: The Benefits of Exercise
I. Introduction
A. Hook: Start with an interesting fact or statistic about exercise.
B. Background Information: Briefly explain what exercise is and its general importance.
C. Thesis Statement: Exercise provides numerous benefits for physical health, mental well-being, and overall quality of life.
II. Physical Health Benefits
A. Weight Management
Helps maintain a healthy weight
Prevents obesity-related diseases
B. Cardiovascular Health
Strengthens the heart
Reduces the risk of heart disease
C. Muscle and Bone Strength
Builds and maintains muscle mass
Enhances bone density
III. Mental Well-being Benefits
A. Stress Reduction
Releases endorphins
Lowers cortisol levels
B. Improved Mood
Reduces symptoms of depression and anxiety
Enhances overall mood
C. Better Sleep
Promotes deeper and more restful sleep
Helps regulate sleep patterns
IV. Overall Quality of Life
A. Increased Energy Levels
Boosts stamina and endurance
Reduces feelings of fatigue
B. Enhanced Longevity
Contributes to a longer lifespan
Improves quality of life in later years
C. Social Benefits
Encourages social interaction through group activities
Builds a sense of community and support
V. Conclusion
A. Restate Thesis: Summarize the key benefits of exercise.
B. Summary of Main Points: Recap the physical, mental, and overall quality of life benefits.
C. Call to Action: Encourage the audience to incorporate regular exercise into their daily routine for a healthier and happier life.
More Samples & Examples of Outline in PDF
1. Analytical Essay Sample Outline

teacherweb.com
2. Formal Essay Outline

users.bloomfield.edu
3. General Protocol Outline

research.wustl.edu
4. Research Protocol Sample Outline
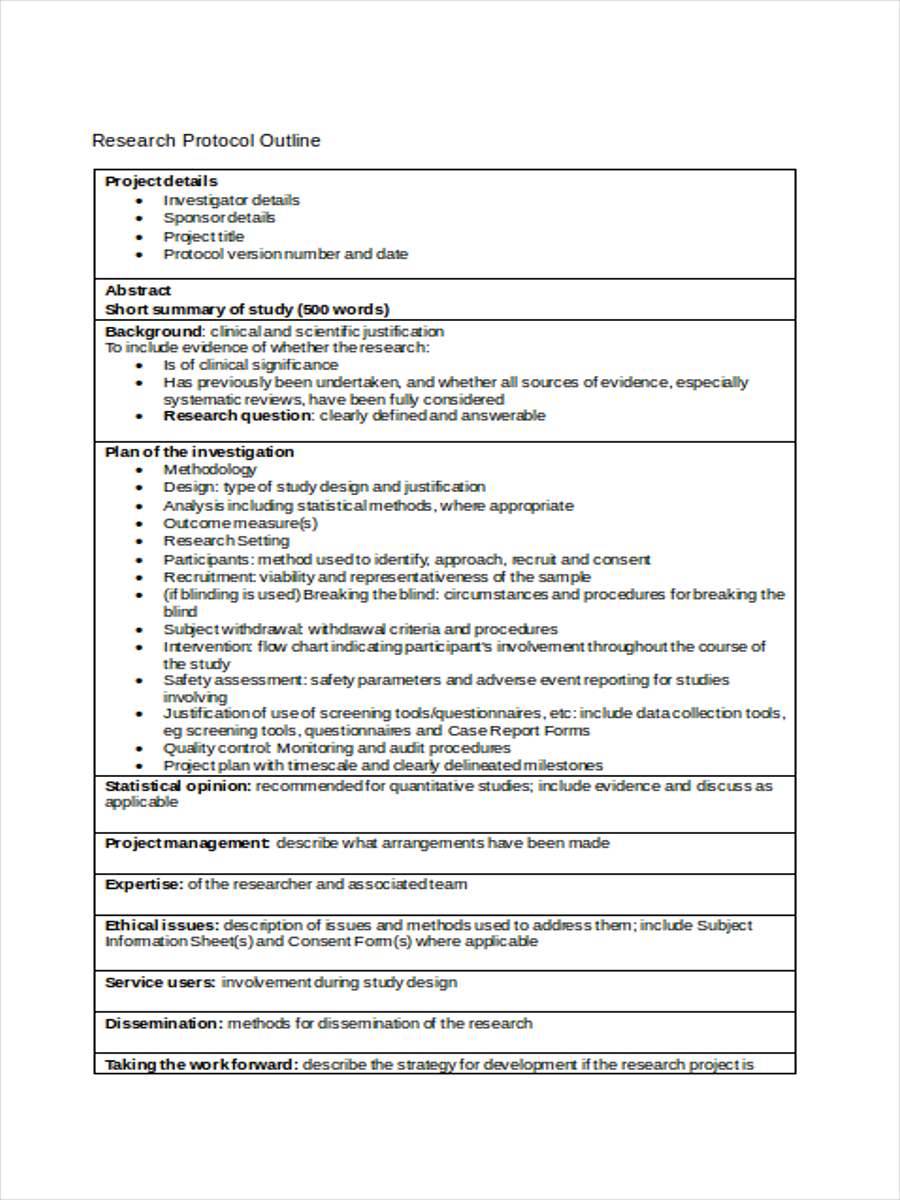
southwestyorkshire.nhs.uk
5. Project Plan Outline

cpe.vt.edu
6. Business Plan Sample Outline

centralpt.com
7. Professional Resume Outline

wcu.edu
Uses of an Outline
An outline serves multiple purposes in the writing process, aiding both planning and execution. Here are the key uses:
1. Organizing Ideas
Clarity: Helps in arranging thoughts logically.
Structure: Provides a framework for the writing.
2. Guiding the Writing Process
Roadmap: Acts as a guide during drafting.
Focus: Keeps the writer on track with the main points.
3. Enhancing Coherence and Flow
Logical Progression: Ensures ideas flow logically from one to another.
Connection: Helps in linking paragraphs and sections smoothly.
4. Improving Time Management
Efficiency: Speeds up the writing process by providing a clear plan.
Deadlines: Helps in meeting writing deadlines by organizing tasks.
5. Facilitating Revision and Editing
Overview: Offers a bird’s-eye view for easy identification of weak points.
Adjustments: Simplifies the process of restructuring and refining ideas.
6. Aiding Collaboration
Shared Vision: Provides a common framework for group writing projects.
Coordination: Helps team members stay aligned with the overall plan.
7. Enhancing Persuasiveness
Strong Argument: Ensures all points support the thesis effectively.
Balanced Presentation: Allows for the inclusion of counterarguments and their rebuttals.
8. Assisting in Complex Projects
Detailed Planning: Breaks down large projects into manageable parts.
Milestones: Helps in setting and achieving intermediate goals.
Guidelines for Writing an Outline
Creating an effective outline involves several key steps to ensure clarity and coherence. Here are the essential guidelines:
1. Understand the Purpose
Clarify the Goal: Know the purpose of your writing and what you aim to achieve.
Identify the Audience: Tailor your outline to suit your audience’s needs and expectations.
2. Choose the Outline Type
Alphanumeric: Uses Roman numerals, letters, and numbers (e.g., I, A, 1).
Decimal: Uses a numerical system (e.g., 1.0, 1.1, 1.2).
Subjective: Informal, using bullet points or phrases.
3. Start with a Thesis Statement
Central Idea: Clearly state the main argument or purpose of your writing.
Focus: Ensure all points support this central idea.
4. Organize Main Points
Hierarchy: Arrange points from most to least important.
Order: Decide on a logical sequence (chronological, spatial, or thematic).
5. Add Supporting Details
Subpoints: Provide details, examples, and evidence under each main point.
Balance: Ensure each main point has sufficient supporting details.
6. Use Consistent Formatting
Indentation: Clearly distinguish between main points and subpoints.
Symbols: Use a consistent system (numbers, letters) to indicate levels.
7. Be Clear and Concise
Brevity: Use short phrases or sentences to summarize points.
Clarity: Avoid ambiguity and ensure each point is understandable.
8. Review and Revise
Coherence: Check that points flow logically and support the thesis.
Completeness: Ensure all necessary points and details are included.
Flexibility: Be prepared to adjust the outline as needed.
Why is an outline important?
An outline helps organize thoughts, ensures logical flow, and provides a clear structure, making writing more efficient and coherent.
How do I start creating an outline?
Begin with a thesis statement or main idea, then list the main points and supporting details in a logical order.
What are the different types of outlines?
Common types include alphanumeric, decimal, and full sentence outlines, each varying in detail and format.
Can an outline be revised?
Yes, outlines should be flexible and can be revised as ideas develop and new information is gathered.
What is the difference between a topic and a sentence outline?
A topic outline uses brief phrases, while a sentence outline uses complete sentences to convey more detailed information.
How detailed should an outline be?
The level of detail depends on the complexity of the topic and the needs of the writer, ranging from broad points to specific details.
Should I use a computer or paper for my outline?
Both methods are effective; choose the one that best suits your preference and makes it easier for you to organize your thoughts.
How do I know if my outline is effective?
An effective outline clearly organizes ideas, logically progresses from one point to another, and aligns with the thesis statement.
Can an outline help with time management?
Yes, an outline can streamline the writing process, helping to allocate time efficiently and ensuring all necessary points are covered.
Are there tools or software for creating outlines?
Yes, tools like Microsoft Word, Google Docs, and specialized apps like Scrivener can help create and organize outlines.


