Maths from Examples.com is your ultimate destination for comprehensive math learning and teaching resources. Designed for all grades, our platform offers a vast collection of examples, meticulously crafted by experts and powered by AI. Our materials are easily editable, printable, and completely free, making it the perfect tool for students and educators alike. Dive into our rich repository to enhance your math skills or enrich your teaching strategies today!
Mathematics is the universal language of logic, patterns, and relationships that governs everything around us—from the tiniest atoms to the vastness of the universe. It is the foundation of science, technology, engineering, and daily life, shaping the way we understand and interact with the world. From simple arithmetic to complex calculus, math enhances problem-solving skills, critical thinking, and innovation. It is the key to unlocking mysteries in nature, finance, artificial intelligence, and beyond. Whether in architecture, medicine, space exploration, or computer algorithms, mathematics remains the backbone of progress, making it one of the most powerful and essential disciplines in human history.
What is Mathematics?
Mathematics is the study of numbers, shapes, patterns, and logical reasoning that helps us make sense of the world. It provides a structured way to analyze and solve problems, using concepts like algebra, geometry, calculus, and statistics. Math is not just about calculations—it is a fundamental tool that drives advancements in science, engineering, economics, and technology. It helps us measure, predict, and optimize everything from daily tasks to groundbreaking discoveries. With its precise and universal nature, mathematics serves as the backbone of innovation, enabling progress in every field of human endeavor.
Math Examples
1. Basic Arithmetic Examples
- Addition: 5 + 7 = 12
- Subtraction: 20 – 8 = 12
- Multiplication: 6 × 4 = 24
- Division: 36 ÷ 6 = 6
2. Algebra Examples
- Solving for x: 2x + 5 = 15 → x = 5
- Quadratic Equation: x² – 4x + 4 = 0 → x = 2
- Finding Slope: Given two points (2,3) and (5,9), slope = (9-3) / (5-2) = 2
3. Geometry Examples
- Perimeter of a Square: If each side is 5 cm, then perimeter = 4 × 5 = 20 cm
- Area of a Circle: If radius = 7 cm, area = π × 7² = 49π cm²
- Pythagorean Theorem: If a = 3, b = 4, then c² = 3² + 4² → c = 5
4. Trigonometry Examples
- Sine Rule: sin(30°) = 1/2
- Cosine Rule: cos(60°) = 1/2
- Tangent Example: tan(45°) = 1
5. Calculus Examples
- Derivative of x²: d/dx (x²) = 2x
- Integral of 2x: ∫2x dx = x² + C
- Limit Example: lim (x→0) (sin x/x) = 1
6. Statistics & Probability Examples
- Mean (Average): For numbers 5, 10, 15 → Mean = (5+10+15)/3 = 10
- Median: For numbers 2, 4, 7, 8, 9 → Median = 7
- Probability of rolling a 6 on a fair die: 1/6
7. Real-Life Math Examples
- Shopping Discounts: A $50 item with a 20% discount costs $50 – (20% of $50) = $40
- Speed Calculation: If a car travels 120 miles in 2 hours, speed = 120 ÷ 2 = 60 mph
- Cooking Measurements: Doubling a recipe that calls for 1.5 cups of sugar → 3 cups
Maths in Real world Examples

Mathematics is deeply embedded in everyday life, helping us make decisions, solve problems, and understand the world around us. Here are some of the best real-world examples of math in action:
1. Finance & Money Management
- Banking & Interest Rates: Calculating interest on savings accounts or loans using formulas like Compound Interest: A = P(1 + r/n)^(nt)
- Budgeting: Managing expenses by adding, subtracting, and estimating costs for groceries, bills, and savings.
- Tax Calculation: Determining income tax percentages and deductions.
2. Shopping & Discounts
- Percentage Discounts: A $100 item with a 25% discount costs $100 – (25% of 100) = $75.
- Buy One Get One (BOGO) Offers: Understanding unit prices to find the best deal.
- Weight & Price Ratio: If 1 kg of apples costs $3, then 2.5 kg costs 2.5 × 3 = $7.50.
3. Cooking & Baking
- Ingredient Proportions: Doubling a recipe that calls for 2 cups of flour means using 2 × 2 = 4 cups.
- Cooking Time: If a dish takes 30 minutes per pound to cook and weighs 4 lbs, total time = 30 × 4 = 120 minutes.
- Measurement Conversions: Converting milliliters to cups or grams to ounces.
4. Travel & Transportation
- Speed Calculation: If a car travels 300 miles in 5 hours, speed = 300 ÷ 5 = 60 mph.
- Fuel Efficiency: If a car runs 25 miles per gallon and the trip is 250 miles, it needs 250 ÷ 25 = 10 gallons of fuel.
- Time Zones: Understanding time differences when traveling internationally.
5. Construction & Architecture
- Measuring Areas & Perimeters: Calculating the area of a room to buy flooring: Length × Width.
- Angles & Geometry: Using the Pythagorean theorem to design stable structures.
- Estimating Materials: If one brick covers 0.5 sq. ft., for a 500 sq. ft. wall, you need 500 ÷ 0.5 = 1000 bricks.
6. Sports & Games
- Statistics & Probabilities: Analyzing player performance, batting averages, and win probabilities in sports.
- Scoring Systems: Understanding points per game and team rankings.
- Angles in Sports: Calculating the best angle for shooting a basketball or kicking a soccer ball.
7. Medicine & Health
- Dosage Calculations: A doctor prescribes 10 mg of medicine per kg of body weight. For a 50 kg patient, dose = 10 × 50 = 500 mg.
- BMI Calculation: BMI = weight (kg) / height² (m²) helps determine healthy body weight.
- Heart Rate & Calories Burned: Fitness trackers use math to estimate exercise efficiency.
8. Weather & Climate Science
- Temperature Conversion: Fahrenheit to Celsius: (°F – 32) × 5/9 = °C.
- Rainfall & Flood Predictions: Using probability and statistics to predict natural disasters.
- Wind Speed & Hurricane Tracking: Mathematical models help track storms.
9. Technology & Computer Science
- Coding & Algorithms: Mathematics forms the basis of AI, cryptography, and data structures.
- Pixel Calculations in Graphics: A 1080p screen has 1920 × 1080 = 2,073,600 pixels.
- Search Engine Algorithms: Google ranks pages using complex mathematical formulas.
10. Space & Astronomy
- Rocket Science: Using calculus to calculate launch trajectories and gravitational pull.
- Distances in Space: The light-year formula helps measure astronomical distances.
- Telescope Magnifications: Understanding ratios to enhance image clarity.
Maths Examples Class 10
1. Real Numbers
- Example: Find the HCF and LCM of 36 and 48 using the prime factorization method.
- 36 = 2² × 3²
- 48 = 2⁴ × 3
- HCF = 2² × 3 = 12
- LCM = 2⁴ × 3² = 144
2. Polynomials
- Example: Find the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial x² – 5x + 6.
- Factorizing: x² – 5x + 6 = (x – 2)(x – 3)
- Zeroes: x = 2, 3
3. Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Example: Solve the system of equations using the substitution method:
- 2x + 3y = 12
- x – y = 3
- From the second equation, x = y + 3
- Substituting in the first: 2(y + 3) + 3y = 12
- 2y + 6 + 3y = 12 → 5y = 6 → y = 2
- x = 5
- Solution: (5,2)
4. Quadratic Equations
- Example: Solve the equation x² – 7x + 10 = 0 using the quadratic formula.
- Quadratic formula: x = (-b ± √(b² – 4ac)) / 2a
- Here, a = 1, b = -7, c = 10
- Discriminant = (-7)² – 4(1)(10) = 49 – 40 = 9
- x = (7 ± √9) / 2
- x = (7 ± 3) / 2 → x = 5 or x = 2
5. Arithmetic Progression (AP)
- Example: Find the 10th term of the AP: 2, 5, 8, 11, …
- Formula: aₙ = a + (n – 1) × d
- a = 2, d = 5 – 2 = 3, n = 10
- a₁₀ = 2 + (10 – 1) × 3 = 2 + 27 = 29
6. Coordinate Geometry
- Example: Find the distance between points A(3,4) and B(7,1).
- Distance formula: d = √[(x₂ – x₁)² + (y₂ – y₁)²]
- d = √[(7 – 3)² + (1 – 4)²] = √[16 + 9] = √25 = 5
7. Trigonometry
- Example: If sin A = 3/5, find cos A.
- Using Pythagoras theorem:
- sin A = opposite/hypotenuse = 3/5
- hypotenuse² = opposite² + adjacent²
- 5² = 3² + adjacent² → adjacent = 4
- cos A = adjacent/hypotenuse = 4/5
8. Circles
- Example: Find the length of the tangent drawn from a point 10 cm away from the center of a circle with radius 6 cm.
- Using Pythagoras theorem, tangent² = hypotenuse² – radius²
- t² = 10² – 6² = 100 – 36 = 64 → t = 8 cm
9. Surface Areas & Volumes
- Example: Find the volume of a cylinder with radius 7 cm and height 10 cm.
- Formula: V = πr²h
- V = (22/7) × 7² × 10 = 1540 cm³
10. Probability
- Example: A bag contains 5 red, 3 blue, and 2 green balls. What is the probability of drawing a red ball?
- Total balls = 5 + 3 + 2 = 10
- P(Red) = Favorable Outcomes / Total Outcomes = 5/10 = 1/2
Math Examples for Inequality
Inequalities are mathematical expressions that compare two values using inequality symbols:
- Greater than (>)
- Less than (<)
- Greater than or equal to (≥)
- Less than or equal to (≤)
- Not equal to (≠)
Here are different types of inequality examples:
1. Basic Inequality Examples
- 5 > 3 (Five is greater than three)
- 7 < 10 (Seven is less than ten)
- x + 4 > 10 (x must be greater than 6)
- 2y ≤ 12 (y must be less than or equal to 6)
2. Solving Linear Inequalities
Example 1: Solving an Inequality
Solve 2x – 5 < 7
- Step 1: Add 5 to both sides → 2x < 12
- Step 2: Divide by 2 → x < 6
Example 2: Inequality with a Negative Coefficient
Solve -3x + 4 ≥ 10
- Step 1: Subtract 4 from both sides → -3x ≥ 6
- Step 2: Divide by -3 (flip the inequality sign) → x ≤ -2
3. Compound Inequality Examples
Example 3: Solving a Compound Inequality
Solve 3 ≤ 2x + 1 < 7
- Step 1: Subtract 1 from all sides → 2 ≤ 2x < 6
- Step 2: Divide by 2 → 1 ≤ x < 3
4. Quadratic Inequality Example
Example 4: Solving a Quadratic Inequality
Solve x² – 4x – 5 > 0
- Factor: (x – 5)(x + 1) > 0
- Find critical points: x = 5, x = -1
- Test intervals:
- If x < -1, choose x = -2 → (-2 – 5)(-2 + 1) = (-7)(-1) > 0 ✅
- If -1 < x < 5, choose x = 0 → (0 – 5)(0 + 1) = (-5)(1) < 0 ❌
- If x > 5, choose x = 6 → (6 – 5)(6 + 1) = (1)(7) > 0 ✅
- Solution: x < -1 or x > 5
5. Absolute Value Inequality Examples
Example 5: Solving an Absolute Value Inequality
Solve |x – 3| ≤ 5
- Step 1: Remove absolute value and write two inequalities:
- Step 2: Add 3 to all sides:
6. Real-Life Inequality Examples
- Speed Limits: If a speed limit is ≤ 60 mph, a car traveling at 55 mph follows the rule, but 65 mph does not.
- Budgeting: If you have ≤ $500 to spend, a $450 purchase is allowed, but a $600 purchase is not.
- Temperature Control: If an air conditioner is set to maintain ≥ 18°C, it won’t let the room go below 18°C.
Math Examples of Deductive Reasoning
Deductive reasoning is a logical process where a general statement or rule is applied to specific cases to reach a guaranteed conclusion. In mathematics, it is commonly used in proofs, problem-solving, and logical reasoning.
1. Basic Example of Deductive Reasoning
Example:
- Premise 1: All even numbers are divisible by 2.
- Premise 2: 24 is an even number.
- Conclusion: Therefore, 24 is divisible by 2.
This follows the rule that all even numbers are divisible by 2, and since 24 is even, the conclusion must be true.
2. Deductive Reasoning in Algebra
Example: Solving an equation using logical steps
Solve for x in the equation 2x + 6 = 14
- Premise 1: If two expressions are equal, performing the same operation on both sides preserves equality.
- Step 1: Subtract 6 from both sides → 2x = 8
- Step 2: Divide by 2 → x = 4
- Conclusion: Therefore, x = 4 is the correct solution.
3. Deductive Reasoning in Geometry
Example: Triangle Angle Sum Theorem
- Premise 1: The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180°.
- Premise 2: A triangle has angles 50° and 60°.
- Conclusion: The third angle is 180° – (50° + 60°) = 70°.
This follows the Triangle Sum Theorem, leading to a guaranteed conclusion.
4. Deductive Reasoning in Number Theory
Example: Prime Number Property
- Premise 1: A prime number has exactly two factors: 1 and itself.
- Premise 2: 17 is only divisible by 1 and 17.
- Conclusion: Therefore, 17 is a prime number.
Since 17 satisfies the definition of a prime number, the conclusion is logically valid.
5. Deductive Reasoning in Probability
Example: Probability of Rolling a Die
- Premise 1: A standard die has six sides numbered 1 to 6.
- Premise 2: The probability of rolling an even number (2, 4, or 6) is calculated as (favorable outcomes / total outcomes).
- Conclusion: P(even number) = 3/6 = 1/2 = 50%
Since the calculation follows probability rules, the conclusion is certain.
6. Real-Life Deductive Reasoning in Math
- Traffic Signals: If a red light means stop, and the light is red, then you must stop.
- Shopping Discounts: If a 20% discount applies to all products and a product costs $100, then the discounted price is $100 – 20% = $80.
- Time Calculation: If a train takes 2 hours to cover 100 miles, then in 4 hours, it will cover 200 miles.
Math Examples of Functions
1. Basic Function Examples
Example 1: Linear Function
A linear function follows the form f(x) = mx + b.
- Function:
- Example Calculation:
- If x=1, then
- If x=4, then
Example 2: Quadratic Function
A quadratic function follows the form f(x) = ax² + bx + c.
- Function:
- Example Calculation:
- If x=2, then
- If x=5, then
2. Real-Life Function Examples
Example 3: Temperature Conversion Function
The formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
C(F) = 5/9(F−32)
- If F = 50, then C(50) = (5/9)(50 – 32) = (5/9)(18) = 10°C
Example 4: Distance-Time Function
The relationship between distance, speed, and time is:
- If a car moves at 60 mph, the function is d(t) = 60t
- If t = 2 hours, then d(2) = 60 × 2 = 120 miles
3. Exponential Function Example
Example 5: Population Growth
Exponential functions follow the form f(x) = a × r^x.
- Function:
(Population grows by 5% per year)
- If t = 3 years, then
P(3)=1000×1.053=1157.63
4. Trigonometric Function Example
Example 7: Sine Function
The height of a Ferris wheel over time follows:
- If t = 5 seconds, then
Since sin(π/2) = 1,
Types of Mathematics
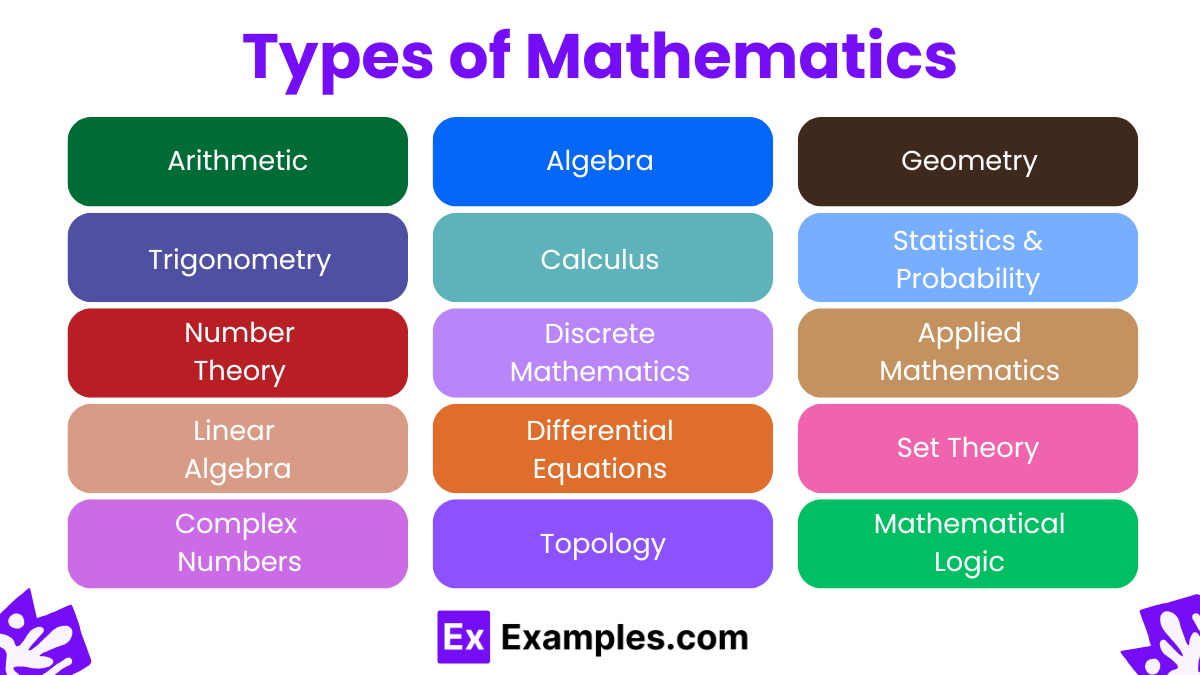
1. Arithmetic
The study of basic mathematical operations on numbers.
Applications: Used in everyday life for calculations, shopping, banking, and budgeting.
Examples:
- Addition: 8 + 2 = 10
- Subtraction: 15 – 5 = 10
- Multiplication: 7 × 6 = 42
- Division: 20 ÷ 4 = 5
2. Algebra
The study of mathematical symbols, expressions, and equations.
Applications: Used in engineering, physics, computer science, and economics.
Examples:
- Solve for x: 2x + 3 = 11 → x = 4
- Quadratic equation: x² – 5x + 6 = 0 → (x – 2)(x – 3) = 0 → x = 2, 3
3. Geometry
The study of shapes, sizes, and properties of space.
Applications: Used in architecture, engineering, art, and construction.
Examples:
- Area of a rectangle: A = length × width
- Pythagorean theorem: c² = a² + b²
4. Trigonometry
The study of relationships between angles and sides of triangles.
Applications: Used in physics, surveying, astronomy, and navigation.
Examples:
- sin 30° = 1/2, cos 60° = 1/2
- tan θ = opposite/adjacent
5. Calculus
The study of change and motion using derivatives and integrals.
Applications: Used in physics, engineering, economics, and artificial intelligence.
Examples:
- Derivative: d/dx (x²) = 2x
- Integral: ∫ 2x dx = x² + C
6. Statistics & Probability
The study of data collection, analysis, and prediction.
Applications: Used in business, economics, medicine, and research.
Examples:
- Mean (Average) of 3, 6, 9: (3+6+9)/3 = 6
- Probability of rolling a 6 on a die: 1/6
7. Number Theory
The study of properties of integers and their relationships.
Applications: Used in cryptography, coding theory, and computer science.
Examples:
- Prime numbers: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11…
- Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) of 18 and 24 = 6
8. Discrete Mathematics
The study of countable, distinct mathematical structures.
Applications: Used in computer science, algorithms, and artificial intelligence.
Examples:
- Binary numbers: 1011 (11 in decimal)
- Graph theory: Shortest path in a network
9. Applied Mathematics
The application of mathematical concepts to solve real-world problems.
Applications: Used in finance, physics, biology, and social sciences.
Examples:
- Mathematical modeling in engineering
- Financial formulas for interest calculations
10. Linear Algebra
The study of vectors, matrices, and linear equations.
Applications: Used in physics, computer graphics, and machine learning.
Examples:
- Solving system of equations using matrices
- Matrix multiplication
11. Differential Equations
The study of equations involving derivatives.
Applications: Used in physics, biology, economics, and engineering.
Examples:
- dy/dx = 3x² → y = x³ + C
- Newton’s law of cooling equations
12. Set Theory
The study of collections of objects and their relationships.
Applications: Used in logic, databases, and probability.
Examples:
- Union of sets: A = {1,2}, B = {2,3} → A ∪ B = {1,2,3}
- Intersection of sets: A ∩ B = {2}
13. Complex Numbers
The study of numbers that include imaginary numbers.
Applications: Used in electrical engineering and quantum physics.
Examples:
- i² = -1
- (3 + 2i) + (4 – i) = 7 + i
14. Topology
The study of properties of space that are preserved under transformations.
Applications: Used in physics, robotics, and material science.
Examples:
- Möbius strip and continuous deformations
15. Mathematical Logic
The study of formal systems, reasoning, and proofs.
Applications: Used in artificial intelligence, philosophy, and computing.
Examples:
- Logical statements: If P → Q, and P is true, then Q must be true.
16. Game Theory
The study of mathematical models of strategic interactions.
Applications: Used in economics, business, and decision-making.
Examples:
- Prisoner’s dilemma strategy analysis
How to Study Math
1. Understand the Concepts
- Focus on logic, not memorization.
- Break problems into simpler parts.
- Use real-life examples.
2. Practice Regularly
- Solve problems daily.
- Start with easy, then move to harder ones.
- Focus on weak areas.
3. Learn from Mistakes
- Review incorrect answers.
- Redo problems without solutions.
- Keep a mistake notebook.
4. Use Visual Aids
- Draw graphs, diagrams, and charts.
- Use color coding.
- Watch math videos.
5. Break Problems into Steps
- Write every step.
- Follow a structured approach.
- Double-check calculations.
6. Master Formulas and Theorems
- Understand their derivation.
- Create flashcards.
- Use mnemonics for recall.
7. Apply Math to Real Life
- Use math in shopping, travel, and finance.
- Relate concepts to daily activities.
8. Use Online Resources
- Try apps, websites, and video tutorials.
- Join online math communities.
9. Work on Past Papers
- Solve previous exams and tests.
- Identify recurring question patterns.
10. Stay Consistent & Confident
- Study math daily.
- Believe in your problem-solving ability.