Find the area of a rectangle with a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters.
30 square meters
35 square meters
40 square meters
45 square meters

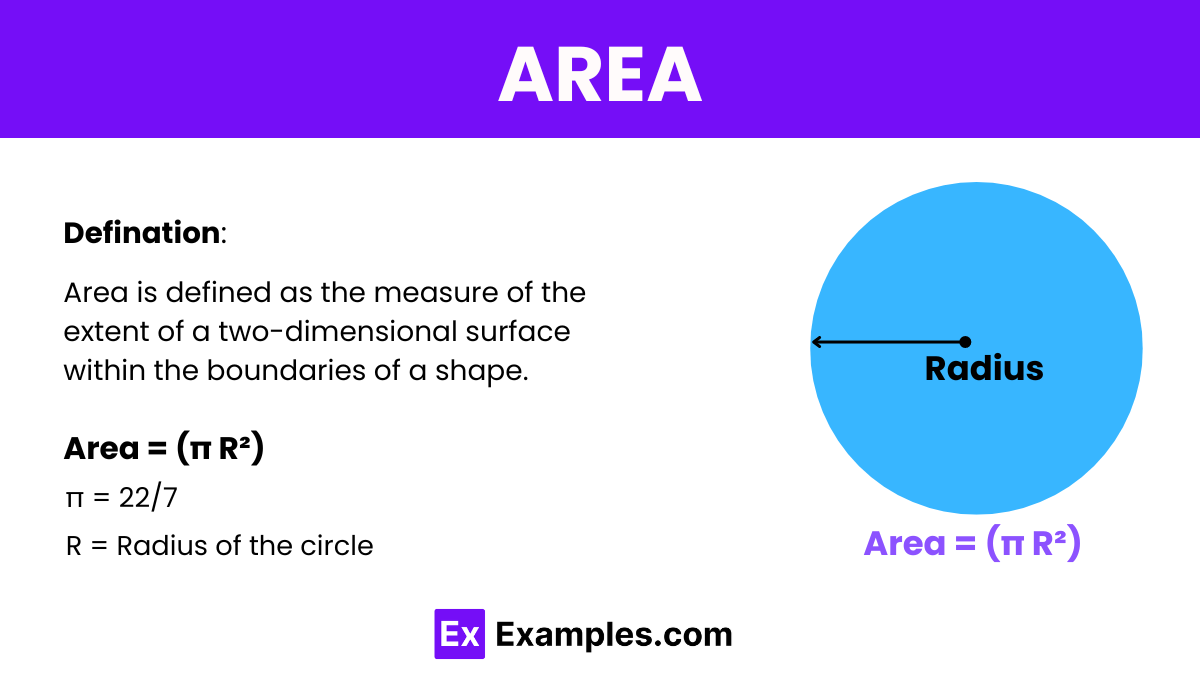
Area is a mathematical concept that describes the size of a two-dimensional surface. It is quantified in square units, reflecting the size of the surface. The calculation methods and formulas for area vary depending on the shape, such as using length times width for rectangles or base times height divided by two for triangles. Area is a fundamental concept used in geometry, science, engineering, and daily life to determine how much space a shape covers.
It is calculated by multiplying the length and width of a shape or by other formulas specific to different shapes, such as circles or triangles. The result is expressed in square units, such as square meters or square feet, indicating the total space enclosed within the boundaries of the shape. Area is a critical measure in various fields, including architecture, land development, and interior design, where understanding the extent of surfaces is essential.

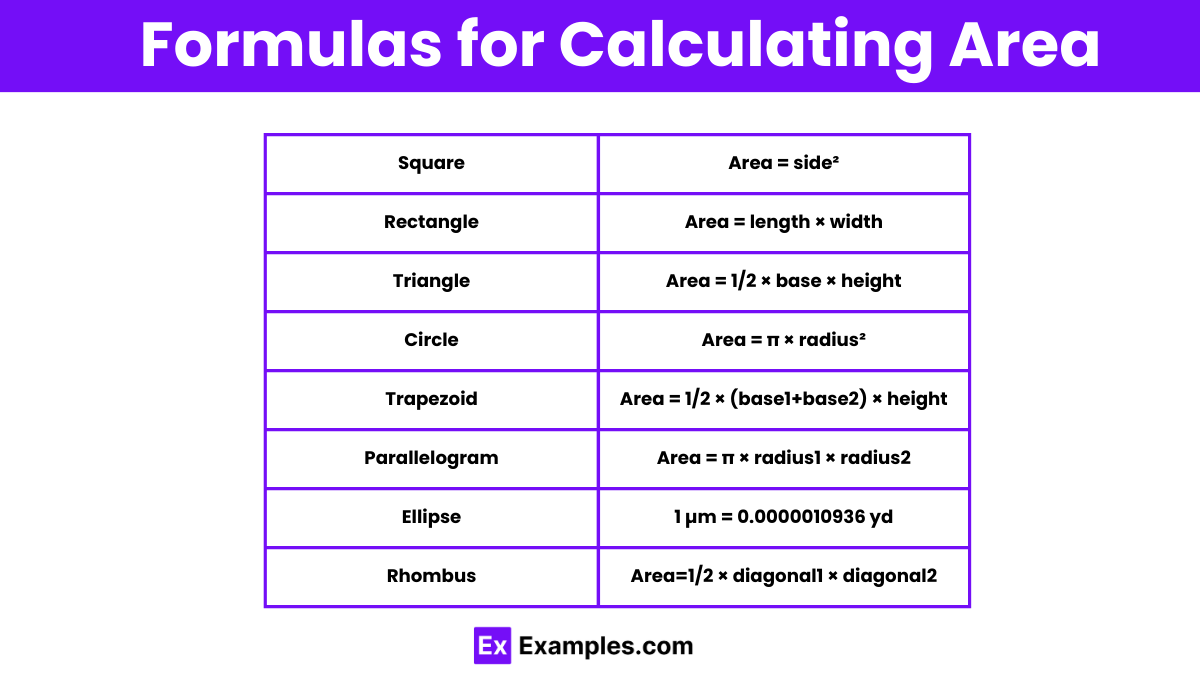
| Shape | Formula |
|---|---|
| Square | Area = side² |
| Rectangle | Area = length × width |
| Triangle | Area = 1/2 × base × height |
| Circle | Area = π × radius² |
| Trapezoid | Area = 1/2 × (base1+base2) × height |
| Parallelogram | Area = base × height |
| Ellipse | Area = π × radius1 × radius2 |
| Rhombus | Area=1/2 × diagonal1 × diagonal2 |
| Aspect | Area | Perimeter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Area is the measure of the space inside a two-dimensional shape. | Perimeter is the total length of the edges or boundary of a shape. |
| Measurement Units | Measured in square units (e.g., square meters, square feet). | Measured in linear units (e.g., meters, feet). |
| Calculation | Involves multiplication or more complex mathematical formulas depending on the shape (e.g., length × width for rectangles, π × radius² for circles). | Involves addition of all the side lengths of a shape. |
| Purpose | Used to determine the amount of material needed to cover a shape, such as flooring or paint. | Used to find the length of material needed to enclose a shape, such as fencing around a yard. |
| Dependency | Area calculation depends on the shape’s dimensions but not on its position or orientation. | Perimeter measurement is independent of the shape’s position but depends solely on the length of its sides. |
| Shape Impact | Two shapes with the same perimeter can have different areas. | Two shapes with the same area can have different perimeters. |
| Practical Example | Calculating the amount of carpet needed to cover a room. | Determining the amount of molding required to go around the edges of that room. |
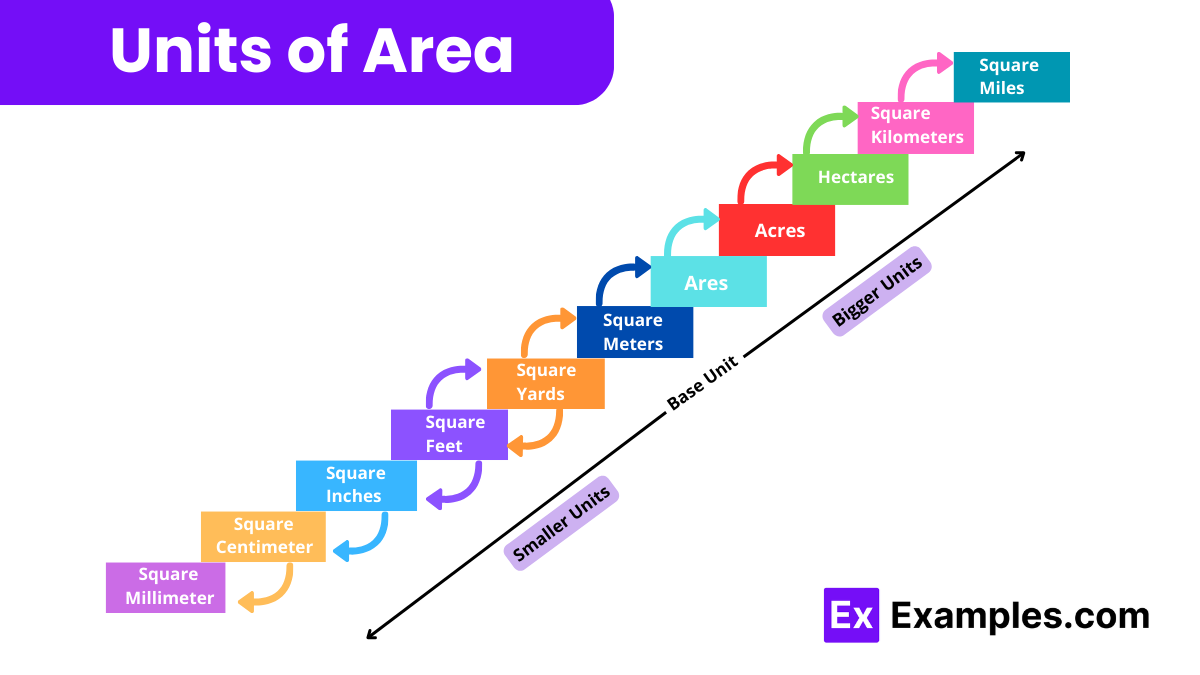
The measurement of area is expressed in units that are derived from the square of a length unit. Here’s a look at the common units used to measure area:
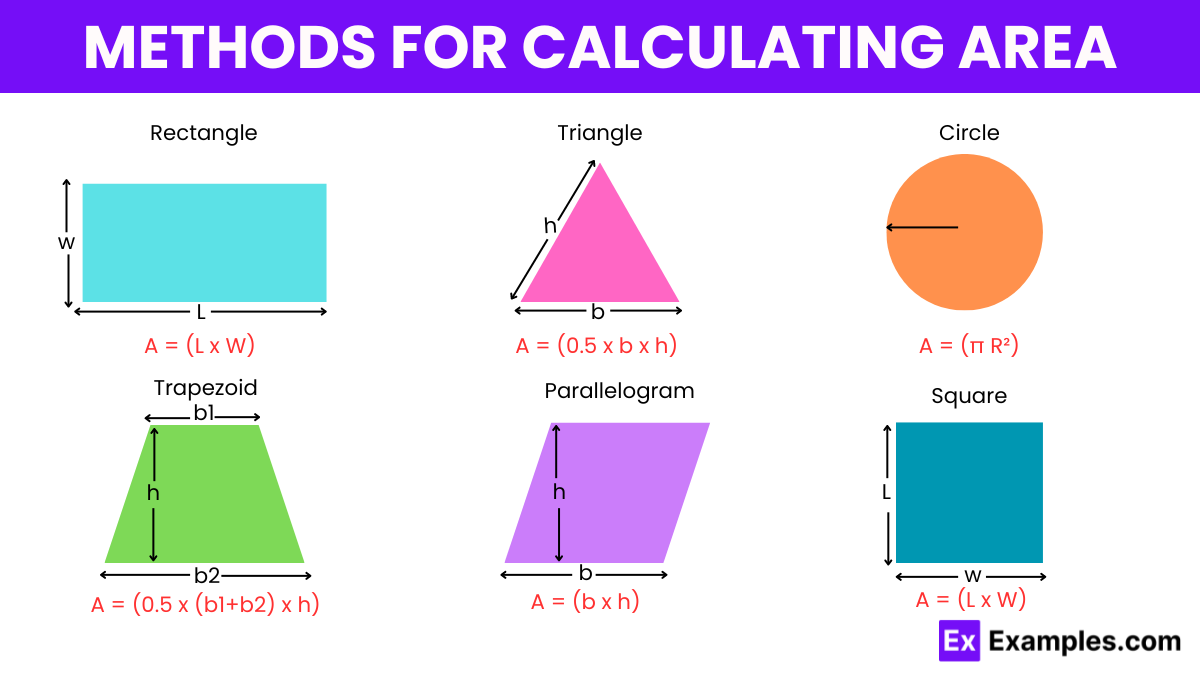
Calculating the area of various shapes requires different methods depending on the geometry of the shape. Here’s an overview of how to calculate the area for some common shapes:
Calculating the area can present various challenges depending on the complexity and accessibility of the shape or region in question. Here are some common challenges:
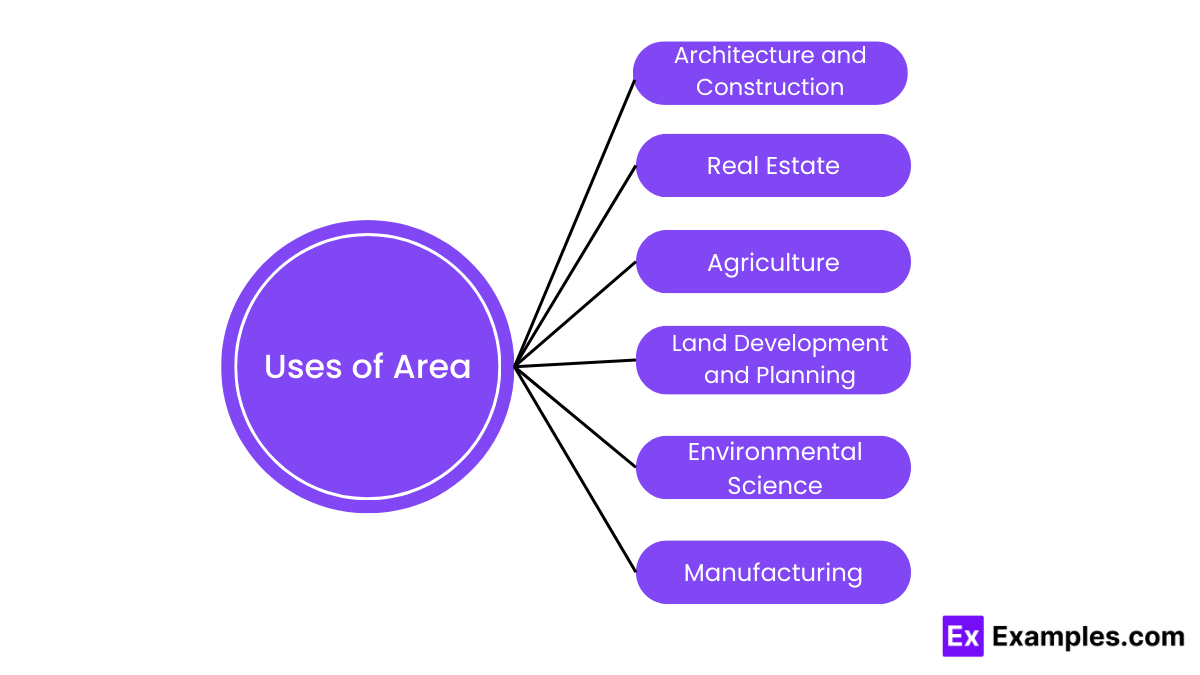
The concept of area is used in numerous fields and applications, reflecting its fundamental importance across various disciplines. Here are some key uses of area:
The area of a shape is the measure of the surface it covers, expressed in square units like square meters or square feet. It quantifies the two-dimensional space enclosed.
Area is measured by calculating the space within the boundaries of a shape using specific formulas or tools, depending on the shape’s geometry and size.
Among basic shapes, the circle has the most area relative to its perimeter, making it the most efficient shape for enclosing space.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Find the area of a rectangle with a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters.
30 square meters
35 square meters
40 square meters
45 square meters
Find the area of a square with side length 15 cm.
200 cm²
215 cm²
225cm²
230 cm²
What is the area of a triangle with a base of 10 cm and a height of 12 cm?
60 cm²
80 cm²
90 cm²
120 cm²
Calculate the area of a circle with a radius of 7 cm. (Use π≈3.14)
140 cm²
144cm²
150 cm²
154 cm²
Find the area of a parallelogram with base 8 cm and height 6 cm.
48 cm²
54 cm²
60 cm²
66 cm²
What is the area of a rectangle with length 14 m and width 9 m?
120 m²
125 m²
126 m²
130 m²
Calculate the area of a triangle with a base of 14 m and height of 10 m.
60 m²
70 m²
80 m²
90 m²
Find the area of a square with a side length of 9 cm.
80 cm²
81 cm²
82 cm²
83 cm²
Find the area of a rectangle with length 22 m and width 18 m.
392 m²
396 m²
400 m²
404 m²
Calculate the area of a triangle with a base of 20 cm and height of 15 cm.
120 cm²
130 cm²
140 cm²
150 cm²
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

