Complete the square for the expression x²+6x. What is the completed square form?
(x+3)² − 9
(x+3)²
(x+3)² − 6
(x−3)² + 9

Completing the Square is an algebraic method used to solve quadratic equations by transforming them into a perfect square trinomial. It is essential in understanding the relationship between rational and irrational numbers, as the process often reveals the nature of a quadratic equation’s roots. This technique involves manipulating integers, square and square roots to rewrite the equation in a simpler form, which aids in finding exact solutions. In statistics, it’s useful for least squares methods, providing insights into the numerical behavior of data. The method also helps in visualizing quadratic functions, revealing their minimum or maximum values.
Completing the Square is a method used to rewrite a quadratic equation of the form 𝑎𝑥²+𝑏𝑥+𝑐 = 0 into a perfect square form (𝑥−𝑝)² = 𝑞. This transformation makes it easier to solve for the roots of the equation by isolating 𝑥. The process involves adding and subtracting a specific value derived from the coefficient of 𝑥 to create a perfect square trinomial. Once in this form, the equation can be solved by taking the square root on both sides and then isolating 𝑥.
Completing the Square is often used to factorize quadratic equations and identify their roots or zeros, especially when traditional factorization methods fail. A quadratic equation like 𝑎𝑥²+𝑏𝑥+𝑐=0 can sometimes be challenging to factor due to its complexity. In such cases, completing the square offers a viable solution.
If you have a quadratic equation that can’t be easily factorized, completing the square can rearrange it into a more manageable form. This approach involves rewriting 𝑎𝑥²+𝑏𝑥+𝑐 as a perfect square trinomial, making it easier to solve for 𝑥.
Here’s an example with a different quadratic equation:
Step 1:
Factor out the coefficient of 𝑥2x2, which is 33:
3𝑥²+12𝑥+9 = 3(𝑥²+4𝑥+3)
Now, the coefficient of 𝑥² is 1.
Step 2:
Find half of the coefficient of 𝑥x in the factored expression.
Here, the coefficient of 𝑥 is . Half of 4 is 2.
Step 3:
Square this number to find (4/2)² = 4.
Step 4:
Add and subtract 4 after the 𝑥 term inside the parentheses:
3(𝑥²+4𝑥+4−4+3)
Step 5:
Factorize the perfect square trinomial formed by the first three terms:
𝑥²+4𝑥+4 = (𝑥+2)²
So the expression becomes:
3((𝑥+2)²−4+3)
Step 6:
Simplify the constant terms:
−4+3 = −1
So, the final expression is:
3((𝑥+2)²−1) = 3(𝑥+2)²−3
This completes the square for the expression 3𝑥²+12𝑥+9 as:
3(𝑥+2)²−3
To summarize:
The formula for completing the square simplifies the process of converting a quadratic equation into its vertex form. For a quadratic expression 𝑎𝑥²+𝑏𝑥+𝑐, we can rewrite it using the formula 𝑎(𝑥+𝑚)²+𝑛, where 𝑚 and 𝑛n are calculated as 𝑚 = 𝑏/2𝑎 and 𝑛 = 𝑐−𝑏²/4𝑎. This approach allows us to quickly identify the vertex of the parabola represented by the quadratic equation. By substituting the values of 𝑚m and 𝑛n back into the formula, we transform the equation into a format that highlights the parabola’s vertex. For example, given 2𝑥²+8𝑥+5, we find 𝑚 = 2 and 𝑛 = −3, which results in the equivalent form 2(𝑥+2)²−3. This method provides a streamlined way to manipulate quadratic expressions and understand their geometric properties.
Given 3𝑥²+12𝑥+7
Given −2𝑥²+4𝑥−1
To complete the square in the expression 𝑎𝑥²+𝑏𝑥+𝑐a, we follow these steps:
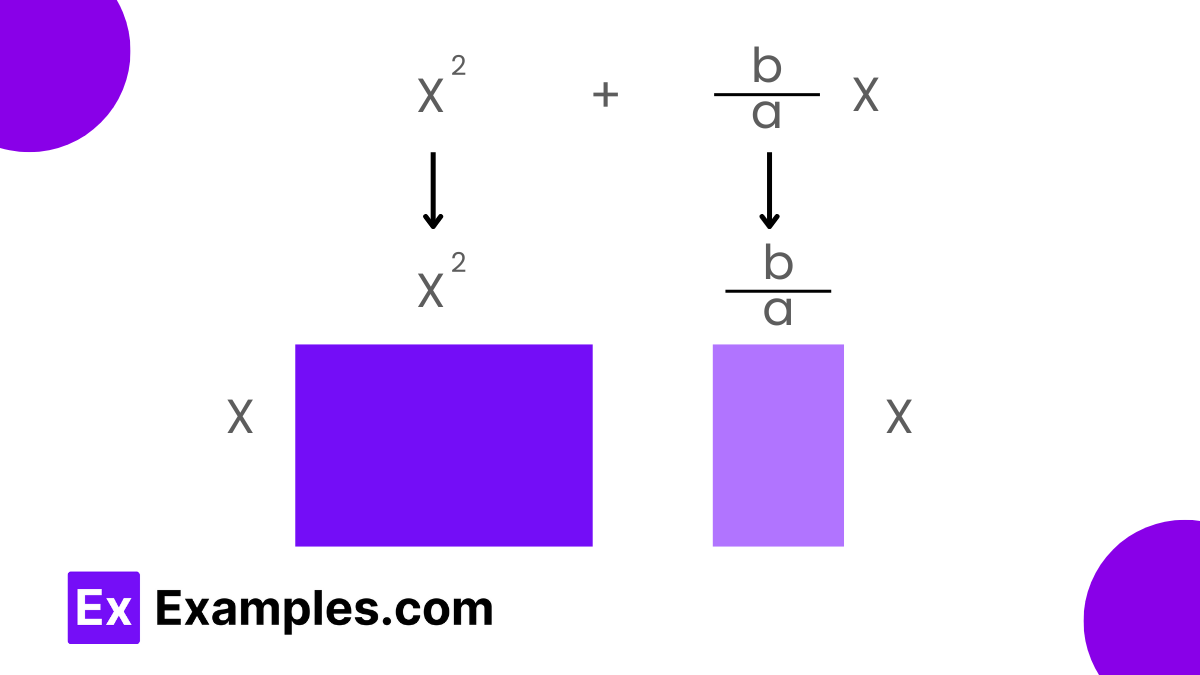
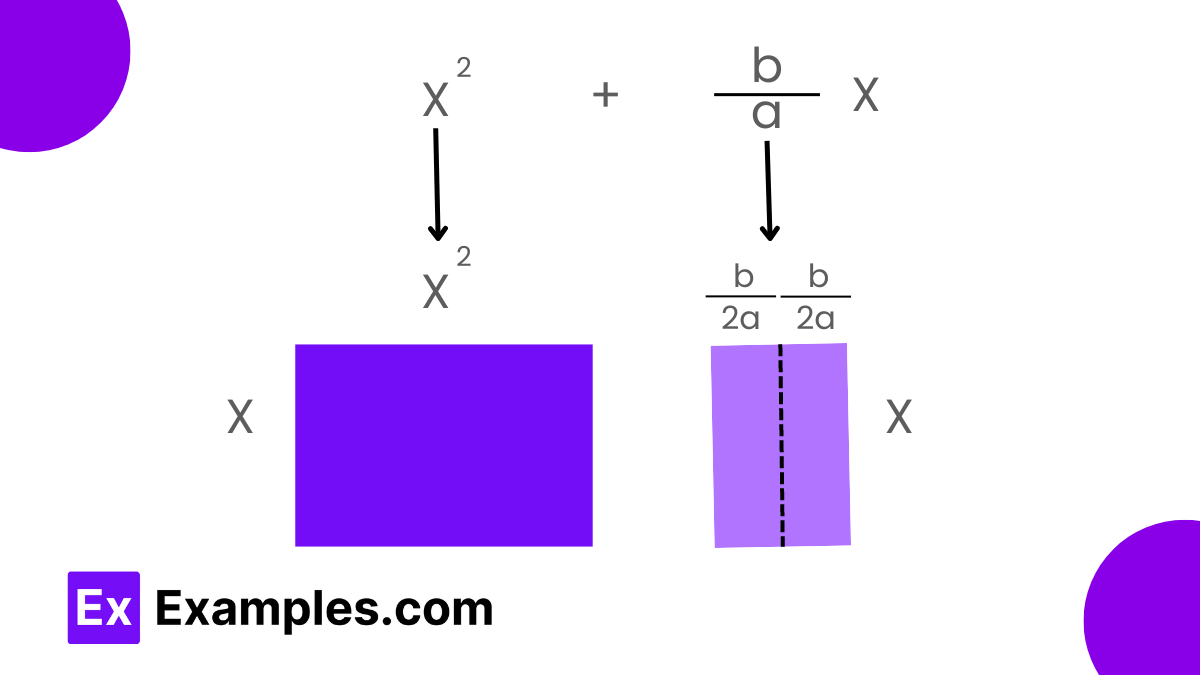
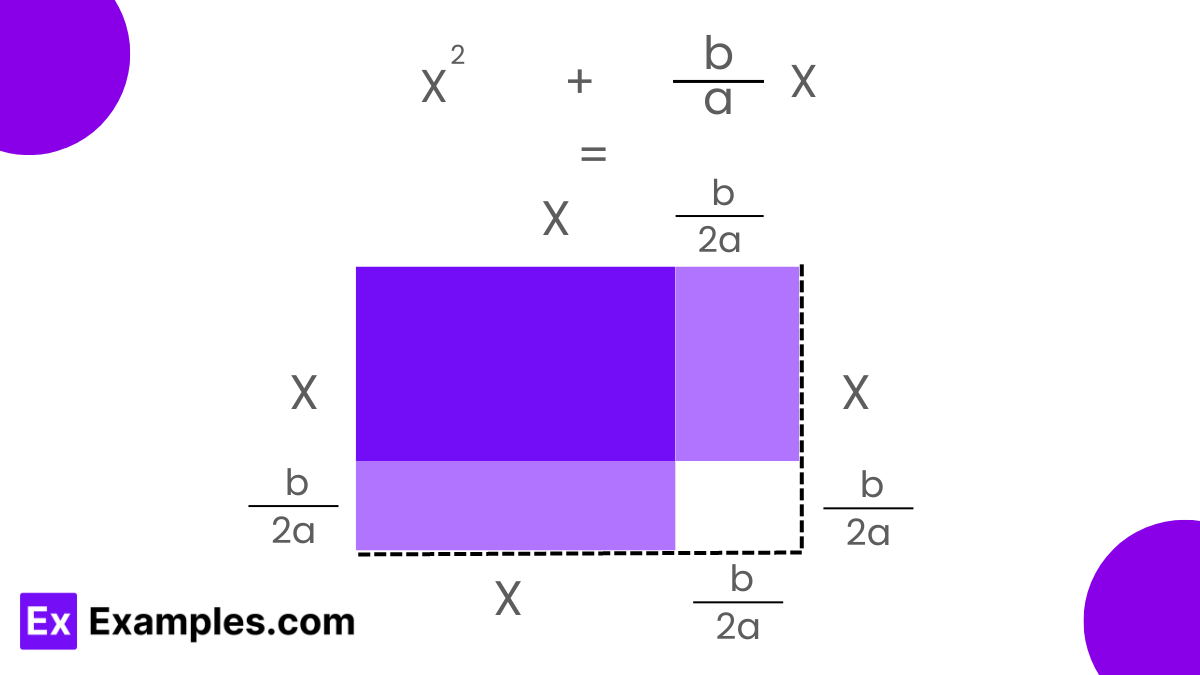
To complete the square for a quadratic expression like 𝑎𝑥²+𝑏𝑥+𝑐, the first step is to factor out 𝑎a to normalize the coefficient of 𝑥² to 1. This transforms the equation into 𝑎[𝑥²+𝑏𝑎𝑥+𝑐𝑎]. Focusing on the first two terms, 𝑥² and (𝑏/𝑎)𝑥, we then calculate half the coefficient of 𝑥, which is 𝑏/2𝑎. Squaring this value yields 𝑏²/4𝑎². We add and subtract this square inside the expression, creating a perfect square trinomial. The equation now looks like 𝑥²+(𝑏/𝑎)𝑥 = (𝑥+𝑏/2𝑎)²−𝑏²4𝑎². By substituting this back into the original equation, we obtain 𝑎𝑥²+𝑏𝑥+𝑐 = 𝑎[(𝑥+𝑏/2𝑎)²−𝑏²4𝑎²]+𝑐. Expanding this and simplifying gives the quadratic equation in completed square form: 𝑎(𝑥+𝑏/2𝑎)²+(𝑐−𝑏²/4𝑎). This transformation provides an easy way to see the vertex of the parabola described by the quadratic equation and simplifies further calculations.
The purpose of completing the square is to rewrite a quadratic expression in a different form, specifically 𝑎(𝑥+𝑚)²+𝑛. This transformation makes it easier to solve quadratic equations and identify the vertex of a parabola.
If the coefficient of 𝑥² isn’t 1, factor out that coefficient from the quadratic and linear terms to normalize it to 1. For example, with 4𝑥²+8𝑥, factor out 4 to get 4(𝑥²+2𝑥).
Adding and subtracting the square helps create a perfect square trinomial. This trinomial can then be rewritten as a squared binomial, which is essential to putting the quadratic equation into the desired completed square form.
Completing the square is a method that can be used to derive the quadratic formula. It transforms the quadratic equation into a form where taking the square root directly reveals the values of 𝑥.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Complete the square for the expression x²+6x. What is the completed square form?
(x+3)² − 9
(x+3)²
(x+3)² − 6
(x−3)² + 9
What is the completed square form of x²−8?
(x+4)² − 16
(x−4)²
(x−4)² − 8
(x−4)²−16
Complete the square for x² + 10x + 9. What is the completed square form?
(x+5)² − 16
(x+5)²−6
(x+5)²+6
(x+5)²−9
What is the completed square form of x² − 2x + 1?
(x−1)²
(x−1)²−1
(x+1)²
(x+1)²−1
Complete the square for x² + 4x − 5. What is the completed square form?
(x+2)²−9
(x+2)²+1
(x+2)²−7
(x+2)²−1
What is the completed square form of x² − 6x + 8?
(x−3)²+2
(x−3)² + 1
(x−3)² − 2
(x−3)²−1
Complete the square for x² + 2x + 3. What is the completed square form?
(x+1)²+1
(x+1)²+2
(x+1)²+3
(x+1)²−1
What is the completed square form of x² − 4x − 5?
(x−2)²−7
(x−2)²+1
(x−2)²−9
(x−2)²−6
What is the completed square form of x² + 8x + 16?
(x+4)²
(x+4)²−16
(x+4)²−8
(x+4)²+16
Complete the square for x² + 6x + 10. What is the completed square form?
(x+3)²−1
(x+3)² + 1
(x+3)²+4
(x+3)²+2
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

