What is the relationship between the average and mean in mathematics?
They are always different
They are often the same
The average is always greater than the mean
The mean is always greater than the average

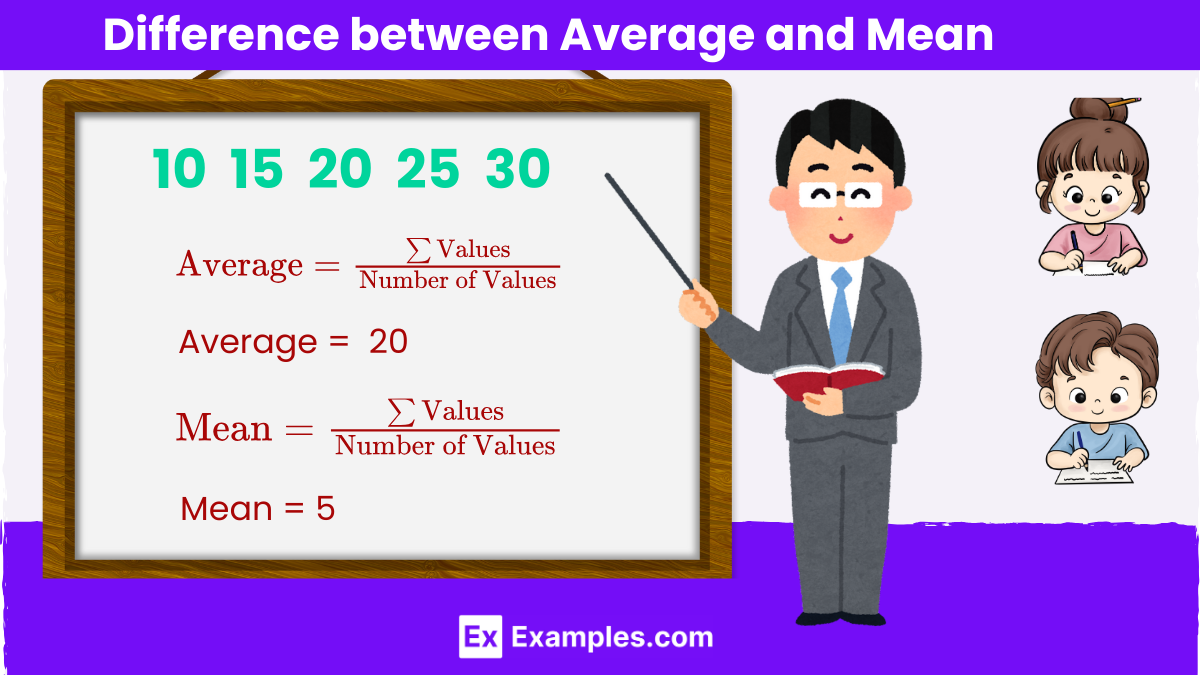
The terms “average” and “mean” are often used interchangeably, but they can have different meanings depending on the context. In mathematics, the “mean” specifically refers to the arithmetic mean, which is the sum of all values divided by the number of values. “Average” is a more general term that can refer to the mean, median, or mode. Understanding the distinction helps in accurately interpreting data and statistical results.What is Average and Mean
Average: A general term for measures of central tendency, including mean, median, and mode, representing the central value in a data set.
Mean: Specifically the arithmetic mean, calculated by summing all values in a data set and dividing by the number of values, representing an average.
An average is a measure of central tendency that summarizes a set of numbers by identifying the central value within that set. It provides a simple way to understand the overall trend or typical value in a data set. The most commonly used type of average is the arithmetic mean.
The formula to calculate the arithmetic mean (average) is:
Average = ∑Values/Number of Values
Where:
Consider the data set: 4, 8, 6, 5, 3.
Using the formula:
Average = 26/5 = 5.2
Thus, the average of the data set 4, 8, 6, 5, 3 is 5.2.
The mean, often referred to as the arithmetic mean, is a measure of central tendency that represents the average value of a data set. It is calculated by summing all the values in the data set and then dividing by the total number of values. The mean provides a useful summary of the overall level of the data.
The formula to calculate the mean is:
Mean = ∑Values/Number of Values
Where:
Consider the data set: 10, 15, 20, 25, 30.
Using the formula:
Mean =100/5 = 20
Thus, the mean of the data set 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 is 20.
The terms “average” and “mean” are often used interchangeably but have distinct meanings in statistics. The “mean” specifically refers to the arithmetic mean, calculated by summing all values in a data set and dividing by the number of values. In contrast, “average” is a broader term that can refer to different measures of central tendency, including the mean, median, and mode. The mean is just one type of average. Thus, while all means are averages, not all averages are means. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurate data analysis and interpretation.
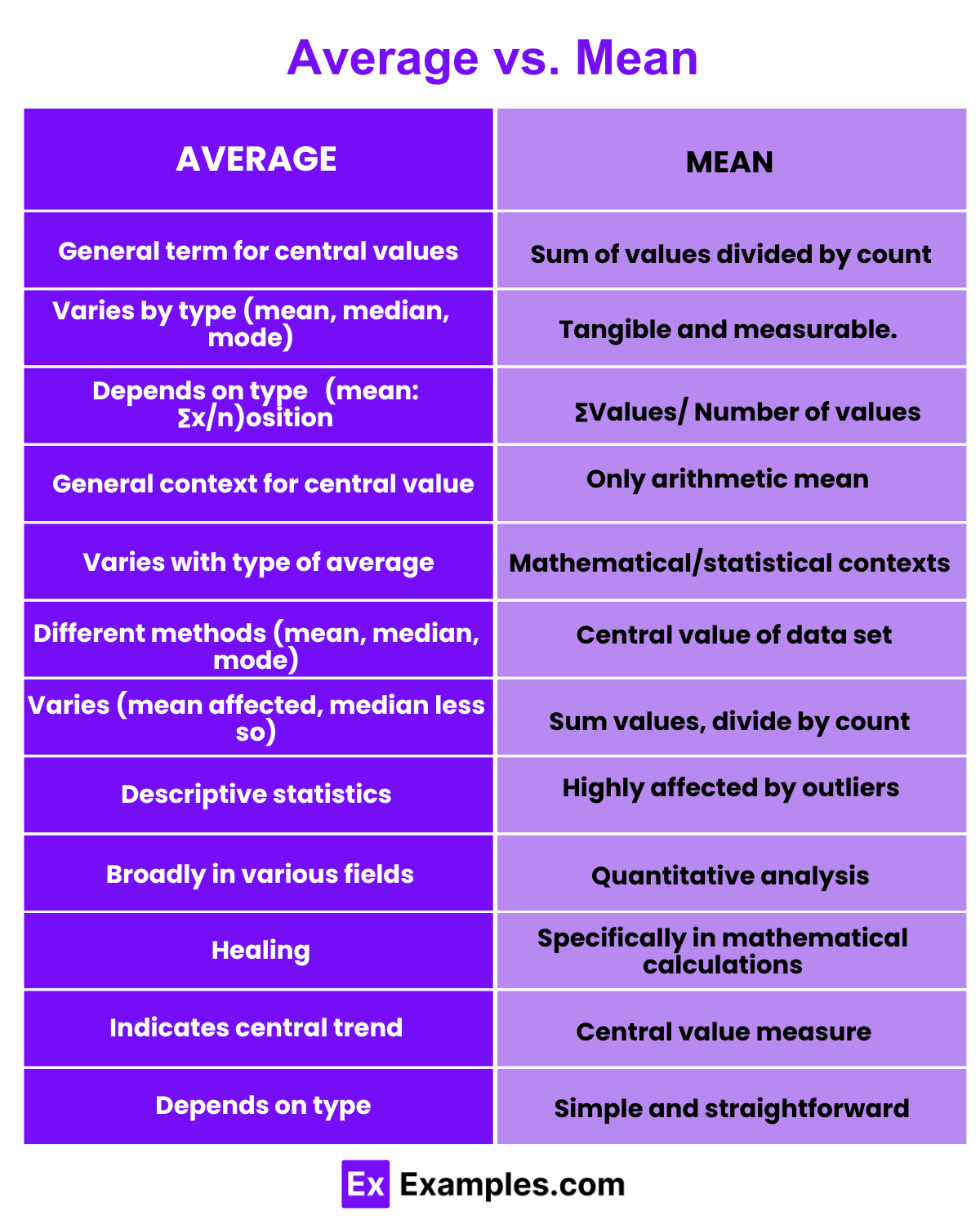
| Aspect | Average | Mean |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A general term for measures of central tendency, including mean, median, and mode. | Specifically refers to the arithmetic mean, a type of average. |
| Calculation | Can be calculated in various ways depending on the type (mean, median, mode). | Calculated by summing all values and dividing by the number of values. |
| Formula | Varies (mean: ∑Values/Number of Values; median: middle value; mode: most frequent value). | Mean=∑Values/Number of Values |
| Usage | Broad term used in general contexts to indicate a central value. | Specific term used in mathematical and statistical contexts. |
| Types | Includes mean, median, mode, and other statistical averages. | Only the arithmetic mean is referred to as the mean. |
| Interpretation | May vary depending on the type of average used. | Represents the central value of a data set. |
Add all the values together and divide by the number of values.
The main types of averages are mean, median, and mode.
The geometric mean is the nth root of the product of n values, useful for multiplicative data.
Multiply all the values together and take the nth root of the product, where n is the number of values.
The harmonic mean is the reciprocal of the average of the reciprocals of the values, useful for rates and ratios.
The weighted mean accounts for different weights assigned to each value in a data set.
The mean is the average of all values, while the median is the middle value when data is ordered.
Use the mean for data without extreme outliers and for additive data.
Use the median for skewed data or data with outliers.
The mode is the most frequently occurring value in a data set.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the relationship between the average and mean in mathematics?
They are always different
They are often the same
The average is always greater than the mean
The mean is always greater than the average
Which of the following is a correct definition of the arithmetic mean?
The middle value in a data set
The most frequently occurring value
The sum of all values divided by the number of values
The difference between the largest and smallest values
In which situation would the mean and the average be considered different?
When calculating the mode
When calculating the median
When working with different types of means (e.g., geometric mean)
When calculating the range
How is the mean of a data set generally calculated?
By subtracting the smallest value from the largest
By adding the values and dividing by the total number of values
By finding the value that appears most frequently
By arranging the data in ascending order and finding the middle value
What is one reason why the mean might not be a good measure of central tendency in a skewed distribution?
The mean is always the same as the median
The mean is always greater than the mode
The mean ignores the number of values
The mean can be affected by extreme values
If a data set has the values 5, 7, 7, 8, and 10, what is the arithmetic mean?
7.4
8
7
6.5
In a set of data, if the mean is 20 and the sum of all data points is 200, how many data points are there?
10
15
20
25
What does the term "average" typically refer to in everyday language?
The arithmetic mean
The median
The mode
The range
If the mean of five numbers is 12, what is the total sum of these numbers?
48
60
72
81
What is the mean of the numbers 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10?
4
5
6
7
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

