What are the factors of 4?
1, 2, 4
1, 3, 4
1, 2, 3
1, 2, 5
The number 4 has several factors that are essential to understanding its properties. The factors of 4 are 1, 2, and 4. Its prime factorization is 2 × 2 or 22. The positive pair factors of 4 are (1, 4) and (2, 2), while the negative pair factors are (-1, -4) and (-2, -2). The sum of all positive factors of 4 is 1 + 2 + 4 = 7. Knowing these factors helps in various mathematical calculations and problem-solving scenarios. This information is crucial for students and enthusiasts looking to deepen their understanding of basic number theory.
The factors of 4 are 1, 2, and 4, which means these are the numbers that can divide 4 without leaving a remainder. The prime factorization of 4 is 2×2 or 22, indicating that 4 is composed of the prime number 2 multiplied by itself. The positive pair factors of 4 are (1, 4) and (2, 2), while the negative pair factors are (-1, -4) and (-2, -2). Adding the positive factors together gives a sum of 7 (1 + 2 + 4). Understanding these factors is essential for various mathematical applications, including problem-solving and number theory.
The factor pairs of 4 are combinations of two numbers that, when multiplied together, equal 4. These pairs include both positive and negative numbers.
The positive factor pairs of 4 are:
The negative factor pairs of 4 are:
These pairs show all the possible combinations of numbers that can be multiplied to result in 4.
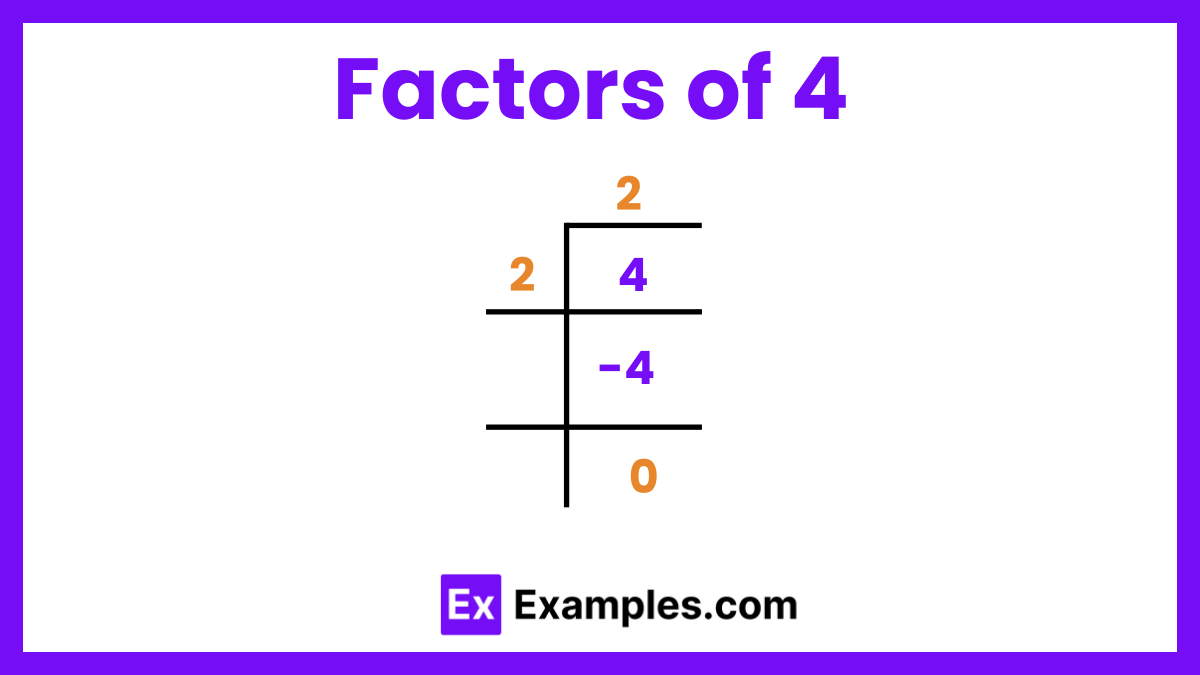
Calculating the prime factors of a number involves finding all the prime numbers that multiply together to result in the original number. Here’s how you can calculate the prime factors of 4:
A prime factor is a prime number that can divide a given number without leaving a remainder. A prime number is a number greater than 1 that has no divisors other than 1 and itself.
The smallest prime number is 2. Divide 4 by 2: 4÷2=2 Since 2 is a prime number and divides 4 without leaving a remainder, 2 is a prime factor of 4.
Now take the quotient from Step 2 and divide it again by 2: 2÷2=1 Once again, 2 divides without leaving a remainder, so 2 is again a prime factor.
The process ends when the quotient is 1. The prime factors of 4 are all the prime numbers you used in the division steps, which in this case is 2, repeated twice. Thus, the prime factors of 4 are 2×2 or 22.
Here are some tips and tricks that can help you quickly find factors of numbers, especially when dealing with larger numbers or teaching this concept:
2 is considered a factor of 4 twice because it can multiply by itself to yield 4 (2 × 2 = 4). In factorization, each occurrence of a factor in such a pairing is counted, so 2 is both a factor and its own pair.
No, 0 cannot be a factor of any number because multiplying 0 by any number always results in 0, which would not give the original number unless the original number is also 0.
No, 4 is not a prime number because it has more than two factors (1, 2, and 4). A prime number has exactly two distinct factors: 1 and itself.
Common multiples of 4 include 8, 12, 16, 20, and so on. These are numbers that can be evenly divided by 4.
Yes, negative numbers can also be factors. The negative factors of 4 are -1, -2, and -4, because multiplying any pair of these negative factors results in 4 (e.g., -1 x -4 = 4).
The sum of the factors of 4 is 1 + 2 + 4, which equals 7. Factors are the numbers that divide the original number exactly without leaving a remainder. In this case, adding the factors 1, 2, and 4 results in a total of 7.
Yes, 2 is a factor of 4. This is because when you divide 4 by 2, the result is 2, which is a whole number. Factors are numbers that divide another number evenly, and 2 divides 4 without leaving any remainder.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What are the factors of 4?
1, 2, 4
1, 3, 4
1, 2, 3
1, 2, 5
Which of the following numbers is a factor of 4?
2
3
6
8
If you multiply a number by 4 and the result is 16, what could the number be?
2
3
4
5
What is the smallest factor of 4?
1
2
3
4
How many factors does the number 4 have?
1
2
3
4
Which pair of numbers, when multiplied, equals 4?
2 and 3
1 and 4
3 and 5
2 and 2
What is the greatest factor of 4?
1
2
3
4
Which of the following is not a factor of 4?
1
2
3
4
If you divide 4 by its smallest factor, what is the result?
1
2
3
4
What is the sum of all factors of 4?
5
6
7
8
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

