What does the abbreviation "SHour" stand for?
Standard Hour
Solar Hour
Shift Hour
Short Hour


An hour is a unit of time conventionally represents 1^24th of a day and scientifically calculated as 3,600 seconds, depending on the measurement being used. It is a universally accepted measurement that plays a critical role in various aspects of daily life, including scheduling, travel, and the sciences. The hour is a standard time interval used all over the world for civil purposes. The concept of an hour is based on the planet Earth’s rotation on its axis, where two consecutive passages of the sun at its highest point in the sky mark a 24-hour period. The day is divided into 24 hours, each of which provides a framework for planning activities and managing time effectively.
It is scientifically defined as 3,600 seconds and traditionally represents 1^24th of a day. The hour is integral to daily activities, providing a convenient measure for scheduling, timekeeping, and organizing events.
Historically, the concept of the hour has evolved from ancient civilizations, which based their timekeeping on the positions of celestial bodies, to the precise atomic clocks used today. The hour remains a fundamental unit in systems like the International System of Units (SI) and is critical for maintaining the rhythms of human life and society.
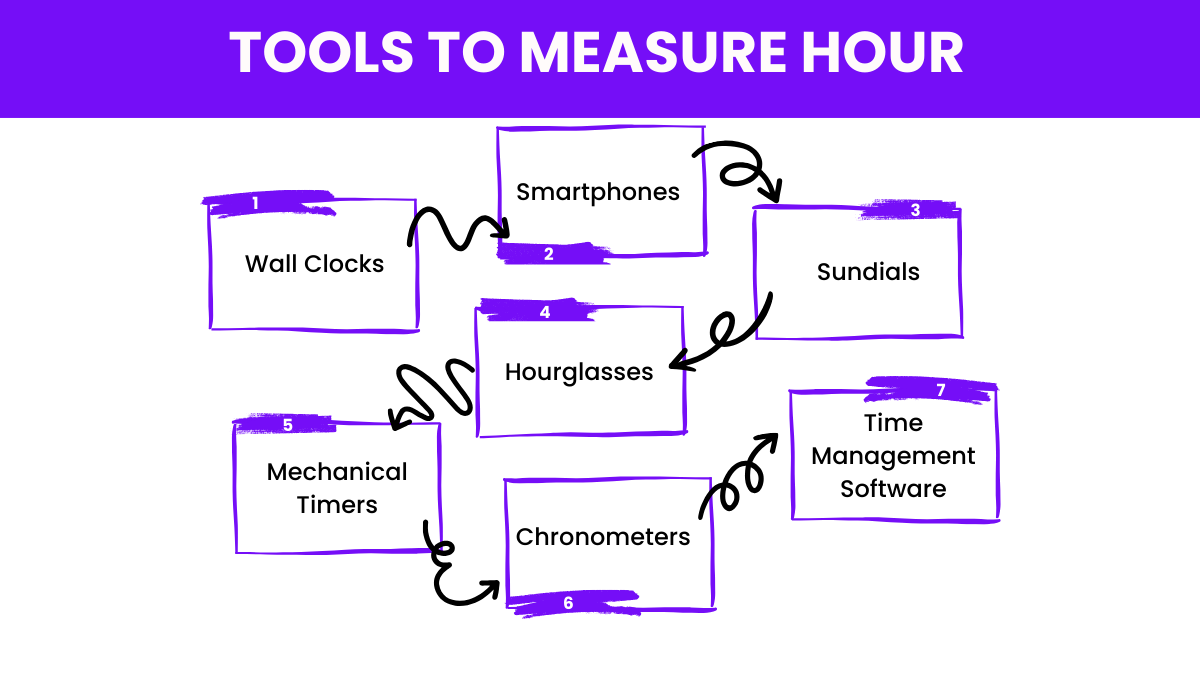
Measuring seconds accurately is essential for various scientific, industrial, and daily activities. Here are some of the primary tools used to measure seconds:
A day consists of 24 hours. This division of the day into 24 equal parts is a timekeeping convention that dates back to ancient civilizations. The choice of 24 as a divisor has historical significance, likely influenced by the Babylonian base-60 (sexagesimal) number system, which facilitated the division of the day and night into 12-hour periods each.
Understanding the 24-Hour Day:
The division of the day into 24 hours allows for precise and uniform timekeeping essential for daily activities, travel, business operations, and global communication. It remains a fundamental aspect of how societies structure their time and manage their schedules.
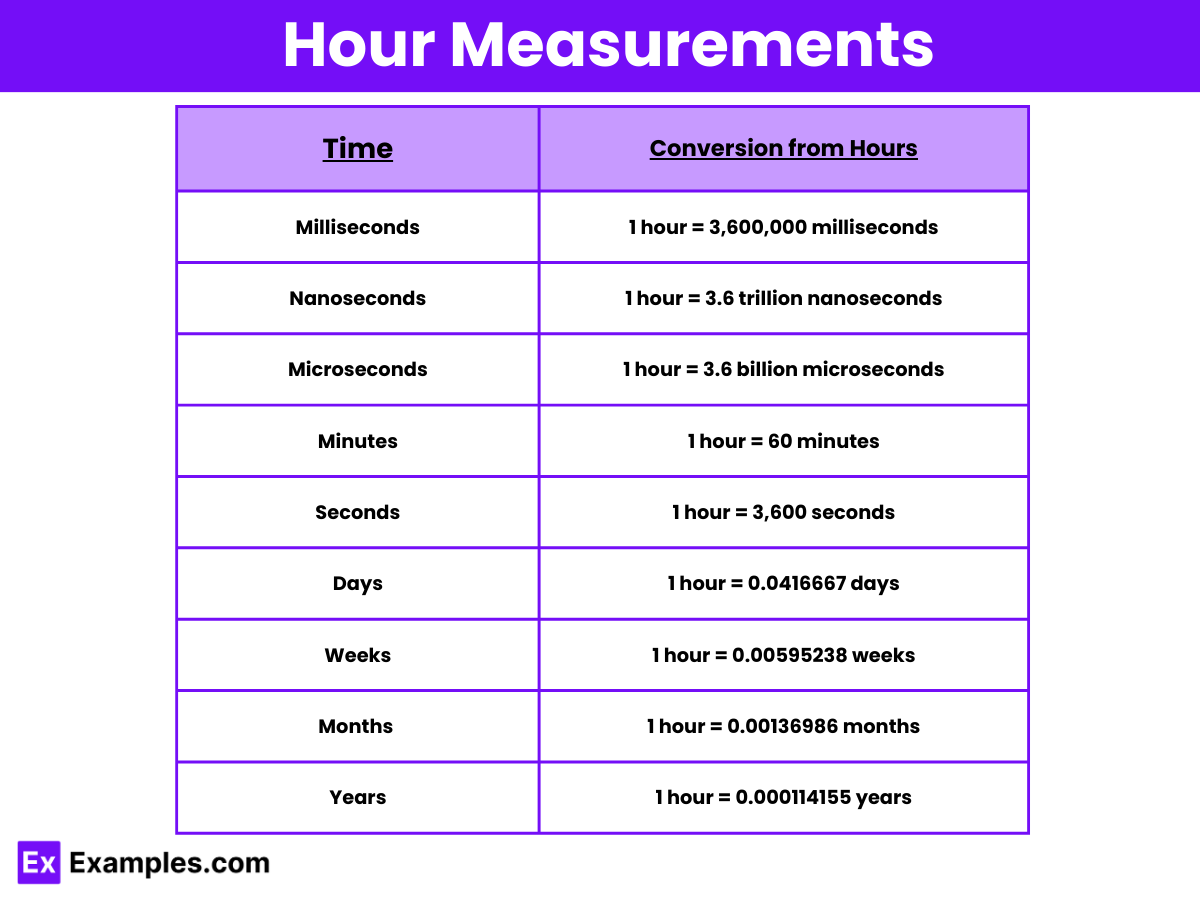
Here’s a table that provides various conversions from one hour to other common units of time:
| Time Unit | Conversion from Hours |
|---|---|
| Minutes | 1 hour = 60 minutes |
| Seconds | 1 hour = 3,600 seconds |
| Milliseconds | 1 hour = 3,600,000 milliseconds |
| Microseconds | 1 hour = 3.6 billion microseconds |
| Nanoseconds | 1 hour = 3.6 trillion nanoseconds |
| Days | 1 hour = 0.0416667 days |
| Weeks | 1 hour = 0.00595238 weeks |
| Months (average) | 1 hour = 0.00136986 months |
| Years | 1 hour = 0.000114155 years |
This table helps in understanding how one hour can be represented in various other units of time, providing a clear and precise conversion metric.
Understanding how to convert hours to other units of time is crucial for planning, scheduling, and coordinating events across different time zones. Whether you’re managing your daily activities, working on projects, or engaging in scientific measurements, accurate time conversion ensures effective time management. Here’s a straightforward guide to converting hours to and from other common units of time:

The hour is a crucial unit of time used globally for a variety of purposes. Here are some key uses of an hour:
One hour in time is a unit of measurement equal to 60 minutes or 3,600 seconds. It is commonly used for scheduling daily activities and events.
Three hours is a duration of time equal to 180 minutes or 10,800 seconds. It’s commonly used for meetings, movies, or deep-focus work sessions.
To solve for 1 hour, you would typically convert it to other units of time, such as 60 minutes, 3,600 seconds, or 0.0416667 days, depending on the context needed.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What does the abbreviation "SHour" stand for?
Standard Hour
Solar Hour
Shift Hour
Short Hour
What is the time span of 0.75 SHour in minutes?
45 minutes
30 minutes
60 minutes
90 minutes
Convert 4 SHours into minutes.
240 minutes
300 minutes
180 minutes
200 minutes
If you worked 3.5 SHours, how many minutes did you work?
180 minutes
210 minutes
150 minutes
120 minutes
How many SHours are there in a 30-minute break?
0.5 SHour
1 SHour
0.25 SHour
0.75 SHour
In a work schedule, how would you represent a 15-minute break within a 4 SHour shift?
As 15 minutes
As 1 SHour
As 0.25 SHour
As 15 SHours
If a task takes 2 SHours to complete, how many minutes does it take?
90 minutes
120 minutes
60 minutes
180 minutes
How would you convert 5 SHours into minutes?
Multiply by 60
Divide by 60
Multiply by 100
Divide by 100
What is the typical duration of a SHour in a 24-hour period?
1 SHour
2 SHour
3 SHour
4 SHour
If you work a 12-hour shift, how many SHours have you worked?
12 SHours
10 SHours
8 SHours
6 SHours
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

