What is the formula for the area of a rectangle?
A = l + w
A = l × w
A = \frac{l}{w}
A = 2(l + w)

Math formulas are concise mathematical expressions that represent relationships between quantities, properties, or operations. They are used to describe and solve mathematical problems across various fields such as algebra, geometry, calculus, and statistics. Formulas often consist of variables, constants, and mathematical symbols, enabling calculations and predictions in a structured manner. These formulas serve as fundamental tools for understanding and solving mathematical problems efficiently.
Essential mathematical formulas cover arithmetic operation, algebra, geometry, and more. They include equations for basic operations like addition and multiplication, as well as formulas for calculating areas, volumes, and solving equations. These formulas form the foundation of mathematical understanding and problem-solving.
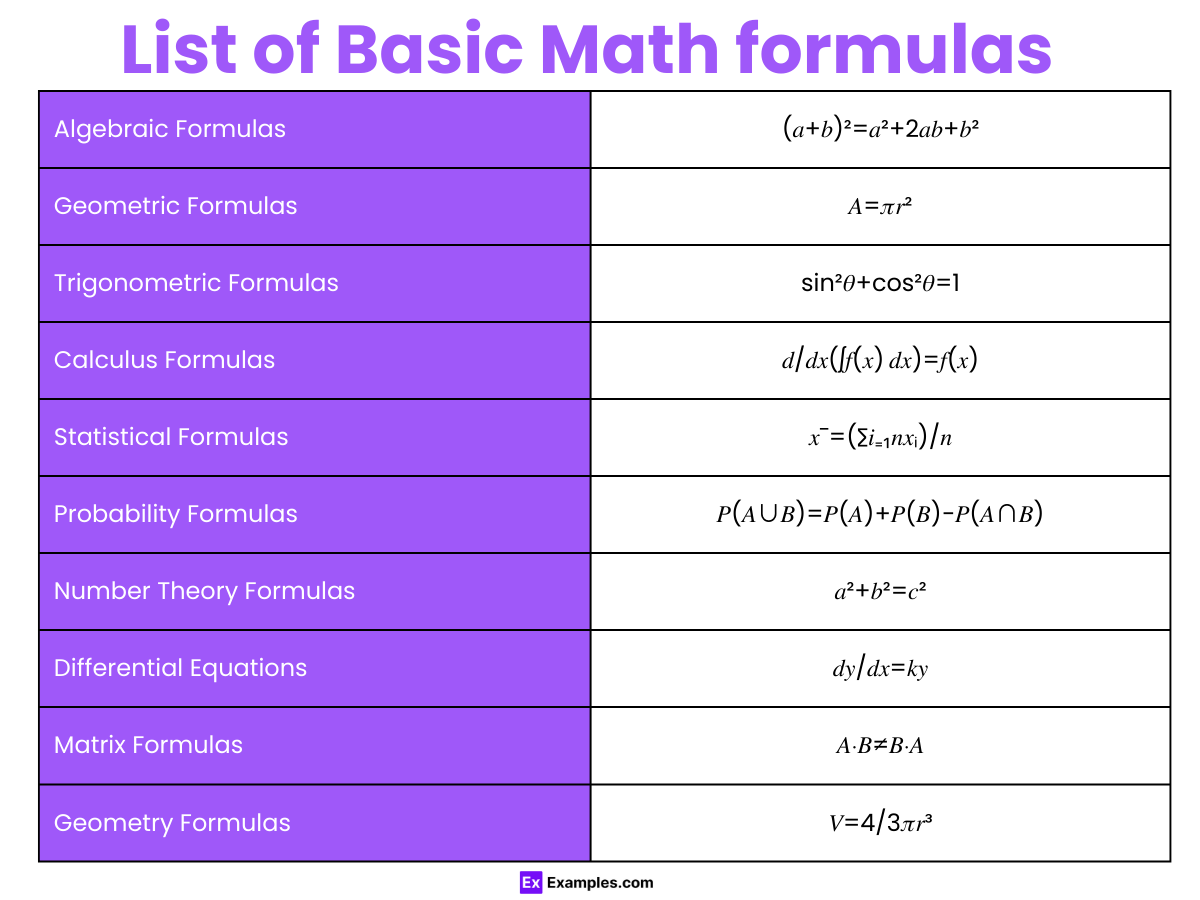
| Algebraic Formulas | (𝑎+𝑏)²=𝑎²+2𝑎𝑏+𝑏² |
| Geometric Formulas | 𝐴=𝜋𝑟² |
| Trigonometric Formulas | sin²𝜃+cos²𝜃=1 |
| Calculus Formulas | 𝑑/𝑑𝑥(∫𝑓(𝑥) 𝑑𝑥)=𝑓(𝑥) |
| Statistical Formulas | 𝑥ˉ=(∑𝑖₌₁𝑛𝑥ᵢ)/𝑛 |
| Probability Formulas | 𝑃(𝐴∪𝐵)=𝑃(𝐴)+𝑃(𝐵)−𝑃(𝐴∩𝐵) |
| Number Theory Formulas | 𝑎²+𝑏²=𝑐² |
| Differential Equations | 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=𝑘𝑦 |
| Matrix Formulas | 𝐴⋅𝐵≠𝐵⋅𝐴 |
| Geometry Formulas | 𝑉=4/3𝜋𝑟³ |
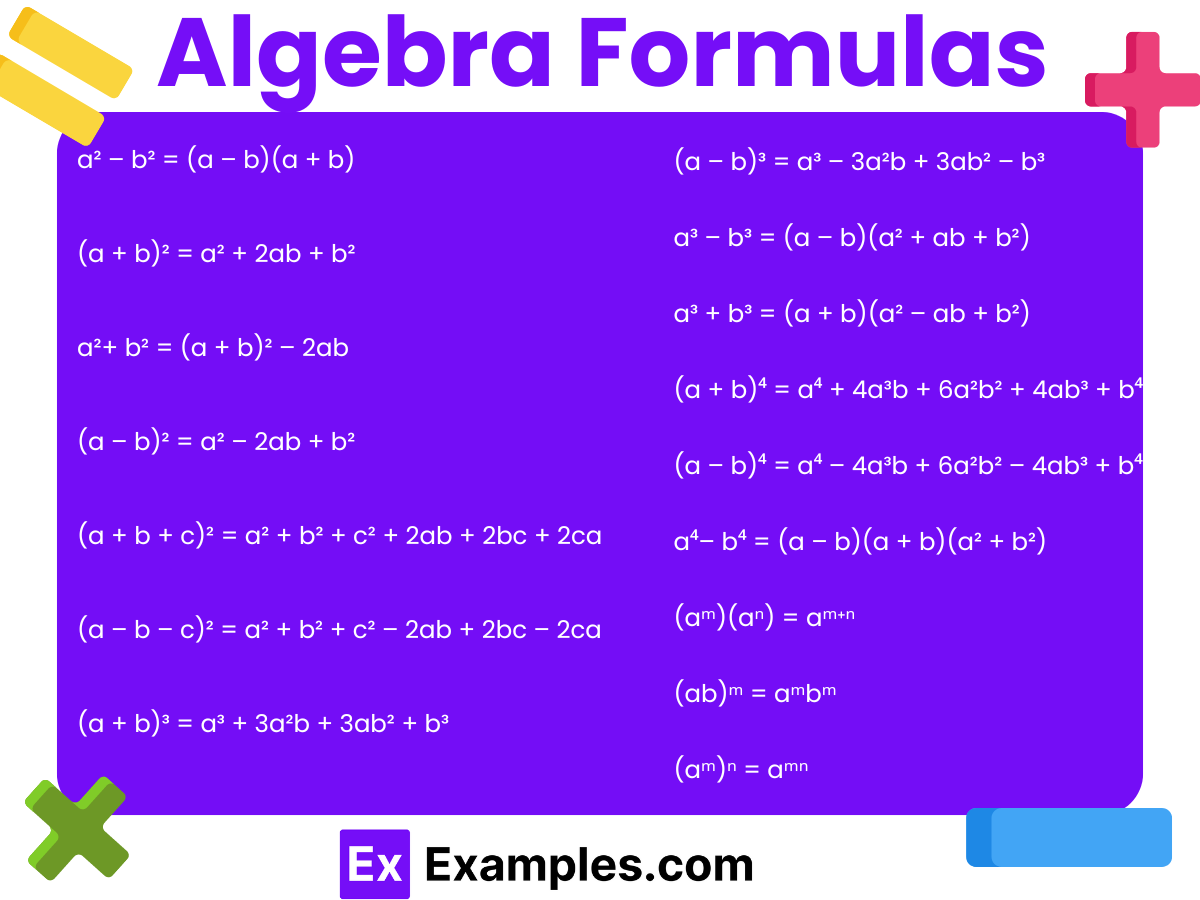
Fundamental rules essential for solving algebraic problems efficiently and accurately. These formulas cover concepts like linear equations, quadratic equations, slopes, distances, and geometric shapes, forming the building blocks for more advanced algebraic manipulations.
Geometric formulas essential for calculating properties of shapes, areas, volumes, and angles. These formulas are crucial in geometry, helping solve problems related to triangles, circles, rectangles, and other geometric figures.
We study Geometry formulas under two headings that are,
Key formulas for 2D geometry, including those for calculating area, perimeter, and properties of shapes like triangles, squares, circles, and polygons
| Shape | Formula |
|---|---|
| Square | Area: 𝐴=𝑠² Perimeter: 𝑃=4𝑠P=4s |
| Rectangle | Area: 𝐴=𝑙×𝑤 Perimeter: 𝑃=2𝑙+2w |
| Triangle | Area: 𝐴=1/2×𝑏×ℎ Perimeter: 𝑃=𝑎+𝑏+𝑐 |
| Circle | Area: 𝐴=𝜋𝑟² Circumference: 𝐶=2𝜋𝑟 |
| Parallelogram | Area: 𝐴=𝑏×ℎ Perimeter: 𝑃=2(𝑎+𝑏) |
| Trapezoid | Area: 𝐴=1/2(𝑏₁+𝑏₂)×ℎ Perimeter: 𝑃=𝑎+𝑏₁+𝑐+𝑏₂ |
Essential formulas for 3D geometry, covering calculations for volume, surface area, and characteristics of three-dimensional shapes such as spheres, cubes, cylinders, cones, and prisms.
| Shape | Formula |
|---|---|
| Cube | Volume: V=s³ Surface Area: 𝑆𝐴=6𝑠² |
| Rectangular Prism | Volume: 𝑉=𝑙×𝑤×ℎ Surface Area: 𝑆𝐴=2𝑙𝑤+2𝑙ℎ+2𝑤ℎ |
| Sphere | Volume: 𝑉=4/3𝜋𝑟³ Surface Area: 𝑆𝐴=4𝜋𝑟² |
| Cylinder | Volume: 𝑉=𝜋𝑟²ℎ Lateral Surface Area: 𝐿𝑆𝐴=2𝜋𝑟ℎ Total Surface Area: 𝑇𝑆𝐴=2𝜋𝑟(𝑟+ℎ) |
| Cone | Volume: 𝑉=1/3𝜋𝑟²ℎ Lateral Surface Area: 𝐿𝑆𝐴=𝜋𝑟𝑙 Total Surface Area: 𝑇𝑆𝐴=𝜋𝑟(𝑟+𝑙) |
| Prism | Volume: 𝑉=𝐵ℎ Lateral Surface Area: 𝐿𝑆𝐴=𝑃ℎ Total Surface Area: 𝑇𝑆𝐴=𝑃ℎ+2𝐵 |
| Pyramid | Volume: 𝑉=1/3𝐵ℎ Lateral Surface Area: 𝐿𝑆𝐴=1/2𝑃𝑙 Total Surface Area: 𝑇𝑆𝐴=1/2𝑃𝑙+𝐵 |
Probability can simply be defined as the possibility of the occurrence of an event. It is expressed on a linear scale from 0 to 1. There are three types of probability : theoretical probability , and subjective probability.
P(A) = n(A)/n(S)
Where,
P(A) is the Probability of an Event.
n(A) is the Number of Favourable Outcomes
n(S) is the Total Number of Events
| Formula Type | Formula |
|---|---|
| Probability of an Event | 𝑃(𝐸)=Number of favorable outcomes / Total number of outcomes |
| Probability of the Complement of an Event | 𝑃(𝐸′)=1−𝑃(𝐸) |
| Conditional Probability | 𝑃(𝐴∣𝐵)=𝑃(𝐴∩𝐵)/𝑃(𝐵) |
| Addition Rule | 𝑃(𝐴∪𝐵)=𝑃(𝐴)+𝑃(𝐵)−𝑃(𝐴∩𝐵) |
| Multiplication Rule (Independent Events) | 𝑃(𝐴∩𝐵)=𝑃(𝐴)×𝑃(𝐵) |
| Multiplication Rule (Dependent Events) | 𝑃(𝐴∩𝐵)=𝑃(𝐴)×𝑃(𝐵∣𝐴) |
| Bayes’ Theorem | 𝑃(𝐴∣𝐵)={𝑃(𝐵∣𝐴)×𝑃(𝐴)}/𝑃(𝐵) |
Basic Trigonometric Formulas of Addition
| Formula Type | Formula |
|---|---|
| Sine of Sum | sin(𝑎+𝑏)=sin𝑎 cos𝑏+cos𝑎 sin𝑏 |
| Cosine of Sum | cos(𝑎+𝑏)=cos𝑎 cos𝑏−sin𝑎 sin𝑏 |
| Tangent of Sum | tan(𝑎+𝑏)=(tan𝑎+tan𝑏)/1−tan𝑎tan𝑏 |
| Formula Type | Formula |
|---|---|
| Sine of Difference | sin(𝑎−𝑏)=sin𝑎 cos𝑏−cos𝑎 sin𝑏sin |
| Cosine of Difference | cos(𝑎−𝑏)=cos𝑎 cos𝑏+sin𝑎 sin𝑏 |
| Tangent of Difference | tan(𝑎−𝑏)=tan𝑎−tan𝑏1+tan𝑎 tan𝑏 |
| Formula Type | Formula |
|---|---|
| Double Angle for Sine | sin2𝜃=2sin𝜃cos𝜃sin2θ=2sinθcosθ |
| Double Angle for Cosine | cos2𝜃=cos2𝜃−sin2𝜃cos2θ=cos2θ−sin2θ |
| Double Angle for Tangent | tan2𝜃=2tan𝜃1−tan2𝜃tan2θ=1−tan2θ2tanθ |
Trigonometric Formulas for Division
| Formula Type | Formula |
|---|---|
| Sine Division | sin𝑎/sin𝑏 |
| Cosine Division | cos𝑎/cos𝑏 |
| Tangent Division | tan𝑎/tan𝑏=(sin𝑎/cos𝑎)/(sin𝑏/cos𝑏)=(sin𝑎 cos𝑏) / (cos𝑎 sin𝑏) |
| Cosecant Division | csc𝑎/csc𝑏=sin𝑏/sin𝑎 |
| Secant Division | sec𝑎/sec𝑏=cos𝑏/cos𝑎 |
| Cotangent Division | cot𝑎/cot𝑏=(sin𝑏 cos𝑎) / (sin𝑎 cos𝑏 ) |
| Formula Type | Formula |
|---|---|
| Sine (sin) | sin𝜃=opposite / hypotenuse |
| Cosine (cos) | cos𝜃=adjacent / hypotenuset |
| Tangent (tan) | tan𝜃=opposite / adjacent |
| Cosecant (csc) | csc𝜃=1/sin𝜃 |
| Secant (sec) | sec𝜃=1/cos𝜃 |
| Cotangent (cot) | cot𝜃=1/tan𝜃 |
| Pythagorean Identity | sin²𝜃+²𝜃=1 |
| Sine of Sum | sin(𝑎+𝑏)=sin𝑎 cos𝑏+cos𝑎 sin𝑏 |
| Cosine of Sum | cos(𝑎+𝑏)=cos𝑎 cos𝑏−sin𝑎 sin𝑏 |
| Tangent of Sum | tan(𝑎+𝑏)=(tan𝑎+tan𝑏)/ (1−tan𝑎 tan𝑏) |
| Sine of Difference | sin(𝑎−𝑏)=sin𝑎 cos𝑏−cos𝑎 sin𝑏 |
| Cosine of Difference | cos(𝑎−𝑏)=cos𝑎 cos𝑏+sin𝑎 sin𝑏 |
| Tangent of Difference | tan(𝑎−𝑏)= (tan𝑎−tan𝑏) / (1+tan𝑎 tan𝑏) |
| Double Angle for Sine | sin2𝜃=2sin𝜃 cos𝜃 |
| Double Angle for Cosine | cos2𝜃=cos²𝜃−sin²𝜃c |
| Double Angle for Tangent | tan2𝜃=2tan𝜃1−tan2𝜃t |
| Half-Angle for Sine | sin𝜃/2=±√ 1−cos𝜃/2 |
| Half-Angle for Cosine | cos𝜃/2=±√ 1+cos𝜃/2 |
| Half-Angle for Tangent | tan𝜃/2=±√ 1−cos𝜃 / 1+cos𝜃 |
A fraction represents a numerical value expressed as the quotient of two integers. The top number, called the numerator, indicates how many parts of the whole are being considered, while the bottom number, the denominator, denotes the total number of equal parts that make up the whole.
A percentage represents a ratio or a numerical value expressed as a part of 100. It is commonly denoted by the “%” symbol.
Percentage = (Given Value/Total Value) × 100
Using math formulas efficiently requires understanding and practice. Here are some tips to help you make the most of them:
The best formula to learn math is one that’s fundamental and widely applicable, such as the Pythagorean theorem, which relates to geometry and has real-world applications in areas like engineering and architecture.
A simple and intuitive formula for kids is the area formula for squares and rectangles (Area = length × width). It’s easy to understand and apply, making it a foundational concept in early math education.
The most famous formula in math is arguably Euler’s identity: 𝑒𝑖𝜋+1=0. It elegantly combines five fundamental mathematical constants (e, π, i, 1, and 0) in a single equation, demonstrating the beauty and interconnectedness of mathematics.
One of the most used formulas in math is the quadratic formula: 𝑥=−𝑏±𝑏²−4𝑎𝑐²𝑎 . It’s vital for solving quadratic equations and has applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and economics.
The golden rule of algebra is to maintain equality by performing the same operation on both sides of an equation. This ensures that the equation remains balanced and valid, allowing for accurate mathematical manipulation and problem-solving.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the formula for the area of a rectangle?
A = l + w
A = l × w
A = \frac{l}{w}
A = 2(l + w)
What is the formula for the circumference of a circle?
C = \pi r^2
C = 2 \pi r
C = \pi d
C = 2r
What is the quadratic formula?
x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}
x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 + 4ac}}{2a}
x = \frac{b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}
x = \frac{b \pm \sqrt{b^2 + 4ac}}{2a}
What is the formula for the volume of a cylinder?
V = πr²h
V = πrh
V = 2πr²h
V = 2πrh
What is the formula for the slope of a line?
m = \frac{y_2 + y_1}{x_2 - x_1}
m = \frac{y_2 - y_1}{x_2 - x_1}
m = \frac{y_2 - y_1}{x_2 + x_1}
m = \frac{y_2 + y_1}{x_2 + x_1}
What is the formula for the area of a triangle?
A = \frac{1}{2} b + h
A = b \times h
A = \frac{1}{2} b \times h
A = \frac{1}{2} (b + h)
What is the formula for the Pythagorean theorem?
a² + b² = c
a² − b² = c²
a² + b² = c²
a + b = c²
What is the formula for the area of a circle?
A = 2πr
A = πr
A = 2πr²
A = πr²
What is the formula for the distance between two points (x₁,y₁) and (x₂,y₂)?
d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}
d = \sqrt{(x_2 + x_1)^2 + (y_2 + y_1)^2}
d = (x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2
d = (x_2 + x_1)^2 + (y_2 + y_1)^2
What is the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle?
P = 2(l+w)
P = l × w
P = l + w
P = 2l × 2w
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

