What is the total number of minutes in 3 hours?
120
180
240
300

In our daily lives, the concept of time is pivotal. It dictates our schedules, appointments, and deadlines. Among the units used to measure time, minutes play a fundamental role. This article delves into the definition, importance, and usage of minutes in time.
Minutes are a unit of time equivalent to 1/60th of an hour or 60 seconds. This measurement originates from the ancient Babylonians, who used a sexagesimal (base-60) numbering system for astronomical calculations. The division of an hour into 60 minutes is a legacy of this ancient system.

Digital clocks display time in a direct and straightforward manner, typically in the format of hours: minutes. Here’s how to read minutes on a digital clock:
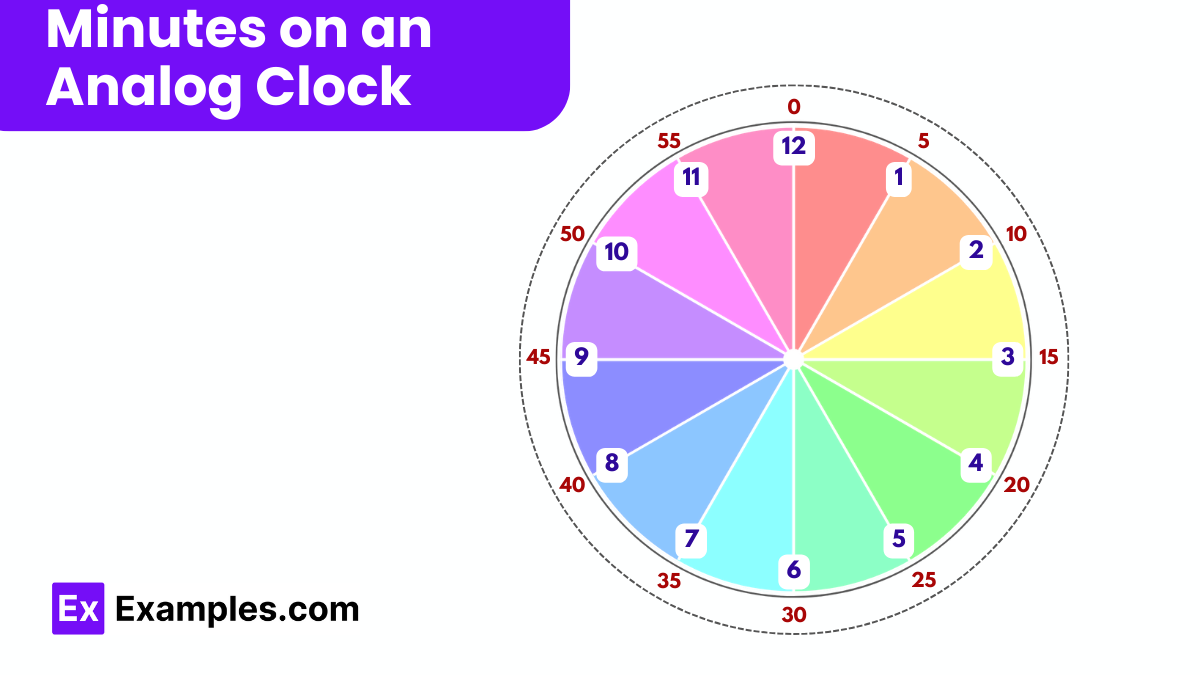
An analog clock presents a bit more complexity, with its face displaying hours, minutes, and sometimes seconds via moving hands.
Reading minutes accurately is crucial for time management, planning daily activities, and understanding schedules. While the basic concept of minutes as units of time remains the same, there are various methods to read and interpret these units across different contexts. This article explores the different ways of reading minutes, ranging from digital and analog clocks to more specialized contexts.
Different languages and cultures have unique expressions for telling time, especially regarding minutes. These can range from simple translations to completely different systems of time-telling that may divide the hour into different segments.
| From | To | Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| Seconds | Minutes | 1 second = 1/60 minute |
| Hours | Minutes | 1 hour = 60 minutes |
| Days | Minutes | 1 day = 1,440 minutes |
| Weeks | Minutes | 1 week = 10,080 minutes |
| Months | Minutes | 1 month ≈ 43,800 minutes (approx.) |
| Years | Minutes | 1 year ≈ 525,600 minutes (approx.) |
| Feature | Minute Hand | Hour Hand |
|---|---|---|
| Length | Typically longer than the hour hand | Shorter than the minute hand |
| Movement | Moves continuously around the clock | Moves slowly and can be either continuous or jump in fixed intervals |
| Speed | Moves faster, completing one full circle every hour | Moves slower, completing one full circle every 12 hours |
| Indication | Indicates the current minute of the hour | Indicates the current hour |
| Markings | Points to specific minute markings, with each marking representing a single minute | Points closer to the numbers on the clock face, indicating hours |
| Numerical Representation | Each complete revolution represents 60 minutes | Each complete revolution represents 12 hours (or half a day) |
| Visual Distinction | Often thinner but longer, making it distinct from the hour hand | Often shorter but thicker or wider, to distinguish it from the minute hand |
Minutes, as a fundamental unit of time, play a crucial role in various aspects of daily life, society, and even the broader cosmos. Understanding their importance helps underscore the value of time management and the precision in scheduling that modern life demands.
Minutes form the backbone of timekeeping systems worldwide, serving as a critical bridge between the smaller unit of seconds and the larger unit of hours. This division facilitates a global standard for communication, coordination, and planning across different time zones and cultures.
In both personal and professional settings, minutes are vital for creating detailed schedules. They allow for the precise allocation of time to tasks, meetings, and breaks, optimizing productivity and ensuring that activities can be coordinated with others smoothly and efficiently.
Minutes are essential in the planning and execution of transportation schedules. Trains, planes, buses, and even space flights rely on minute-by-minute scheduling to maintain order, safety, and efficiency, affecting millions of commutes and shipments daily.
In scientific experiments and technological processes, minutes often serve as a critical unit of measurement. They are used to time reactions, track astronomical events, and synchronize data collection, where even a slight deviation can impact results significantly.
Minutes have also held historical significance, marking the passage of time in historical documents, events, and discoveries. They help in understanding historical timelines and the sequencing of events in precise detail.
Minutes, as a crucial unit of time measurement, have a wide array of applications across different fields and daily activities. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how minutes are used, emphasizing their versatility and importance:
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the total number of minutes in 3 hours?
120
180
240
300
If a meeting starts at 2:15 PM and lasts for 45 minutes, what time does it end?
3:00 PM
3:15 PM
2:45 PM
2:30 PM
How many minutes are there in a quarter of an hour?
10
15
20
25
If an event lasts for 120 minutes, how many hours does it last?
1 hour
2 hour
3 hour
4 hour
A movie starts at 5:45 PM and runs for 1 hour and 20 minutes. What is the end time?
7:05 PM
7:15 PM
7:25 PM
7:30 PM
How many minutes are there in 4.5 hours?
240
270
300
330
If you need to study for 90 minutes and you start at 6:30 PM, what time will you finish?
7:30 PM
8:20 PM
8:00 PM
9:00 PM
What is the number of minutes in 2.75 hours?
150
165
170
175
If a train travels for 150 minutes, how many hours and minutes is that?
2 hours 30 minutes
3 hours
2 hours 15 minutes
2 hours 45 minutes
What is the equivalent of 2 hours and 10 minutes in minutes?
120
130
110
100
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

