Convert the number \(0.00034\) into scientific notation.
\(3.4 \times 10^{-4}\)
\(34 \times 10^{-5}\)
\(3.4 \times 10^{-3}\)
\(34 \times 10^{-4}\)

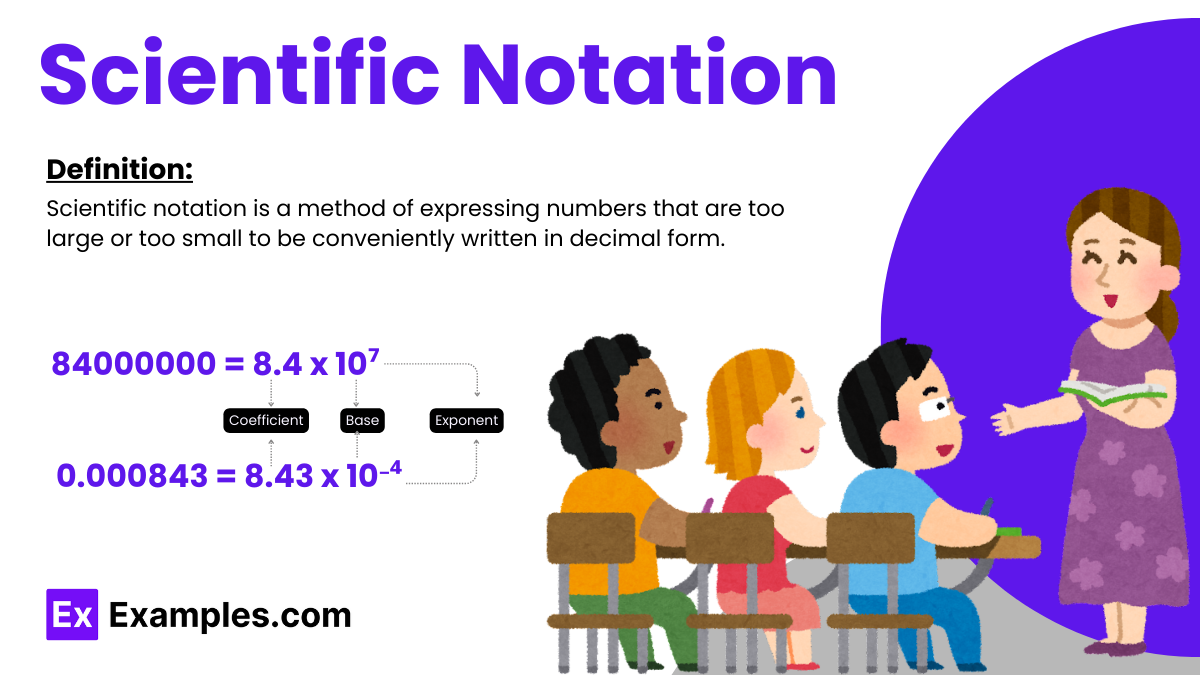
Scientific notation is a method of expressing numbers that are too large or too small to be conveniently written in decimal form. It is often used in science, engineering, and mathematics to make calculations with very large or very small numbers more manageable
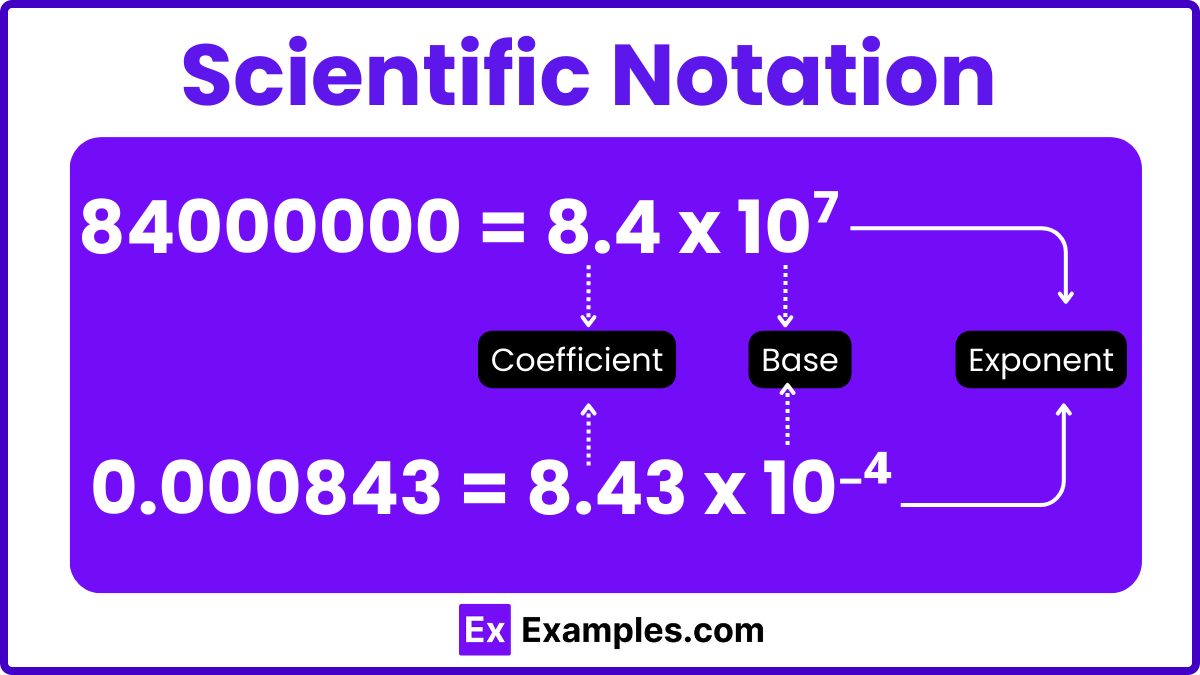
The general representation of scientific notation is:
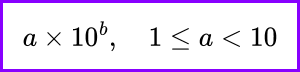
The examples of scientific notation are:
590000000 = 5.9×108
7230000000 = 7.23×109
90500000 = 9.05 x 107
0.000000047 = 4.7 x 10-8
0.0000315 = 3.15 x 10-5
Scientific notation with positive and negative exponents is a versatile way to express a wide range of numbers, from very large to very small. Here’s how these exponents function within the context of scientific notation:
In scientific notation, a positive exponent indicates a number greater than 1. The exponent tells us how many times to multiply the number by ten. For example:
These are typically used to represent large numbers such as distances in astronomy, large amounts of data in bytes, or other significant quantities.
Conversely, a negative exponent signifies a number less than 1. This exponent denotes how many times the number is divided by ten. For instance:
Negative exponents are common when dealing with microscopic scales, such as the sizes of bacteria, wavelengths of light in certain parts of the spectrum, or small time intervals
6.3 is already in a form suitable for scientific notation as 6.3×10⁰ , where the exponent indicates that the decimal point has not moved..
In contexts involving e (Euler’s number), scientific notation uses “e” to denote powers of ten, as in 1.2e3 for 1.2 x 10³
To convert from scientific to standard notation, shift the decimal point in the coefficient right for positive exponents or left for negative exponents by the value of the exponent.
For 7th graders, scientific notation is a way to write very large or small numbers using a coefficient between 1 and 10 multiplied by a power of ten.
The number 10,000,000,000 is written in scientific notation as 1×10¹⁰
In mathematics, e typically represents Euler’s number, approximately 2.718, which is the base of natural logarithms, used in continuous growth or decay processes.
The three steps are: 1) Move the decimal point in the number to create a new number from 1 up to 10; 2) Count the number of places the decimal moved; 3) Write as a product of the new number and 10 raised to the count.
“10 raised to the power” refers to exponential notation where 10 is multiplied by itself a specified number of times, such as 10³=1000.
Yes, a negative number can be written in scientific notation by placing a minus sign before the coefficient, e.g.,−3.4×10²
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Convert the number \(0.00034\) into scientific notation.
\(3.4 \times 10^{-4}\)
\(34 \times 10^{-5}\)
\(3.4 \times 10^{-3}\)
\(34 \times 10^{-4}\)
Which of the following is equivalent to \(7.2 \times 10^2\)?
72
720
7.2
7200
What is the scientific notation for \(0.0000567\)?
\(5.67 \times 10^{-5}\)
\(5.67 \times 10^{-6}\)
\(56.7 \times 10^{-6}\)
\(567 \times 10^{-7}\)
Which number is represented by \(2.5 \times 10^{-2}\)?
\(0.025\)
\(0.25\)
\(2.5\)
\(25\)
Convert \(8,500\) into scientific notation.
\(8.5 \times 10^3\)
\(85 \times 10^2\)
\(0.85 \times 10^4\)
\(85 \times 10^3\)
Which of the following is equal to 1.2 \times 10^{-3}?
0.0012
0.012
0.00012
0.12
Express \(0.0023\) in scientific notation.
\(2.3 \times 10^{-2}\)
\(23 \times 10^{-4}\)
\(2.3 \times 10^{-3}\)
\(0.23 \times 10^{-2}\)
Which scientific notation represents \(30000\)?
\(3 \times 10^4\)
\(30 \times 10^3\)
\(3 \times 10^3\)
\(0.3 \times 10^5\)
What is \(1.2 \times 10^(-1)\) in standard notation?
\(0.012\)
\(0.12\)
\(1.2\)
\(12\)
Convert \(0.0000009\) to scientific notation.
\(9 \times 10^{-7}\)
\(0.9 \times 10^{-6}\)
\(9 \times 10^{-6}\)
\(90 \times 10^{-8}\)
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

